HashMap - 哈希表
文章目录
- TreeMap分析
- HashMap
- hash
- Long和Double的哈希值
- 字符串的哈希值
- 关于31的探讨
- 扰动计算
- 自定义对象作为key
- Hash Collision
- JDK1.8的哈希冲突解决方案
- put
- containsKey
- containsValue
- 扩容
TreeMap分析
内部通过红黑树实现节点存储Entity映射
◼ 时间复杂度(平均)
添加、删除、搜索:O(logn)
◼ 特点
Key 必须具备可比较性
元素的分布是有顺序的
◼ 在实际应用中,很多时候的需求
Map 中存储的元素不需要讲究顺序
Map 中的 Key 不需要具备可比较性
◼ 不考虑顺序、不考虑 Key 的可比较性,Map 有更好的实现方案,平均时间复杂度可以达到 O(1)
那就是采取哈希表来实现 Map
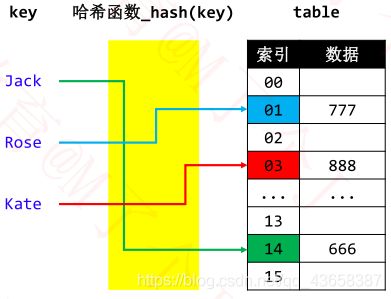
HashMap
通过哈希表实现Map
◼ 添加、搜索、删除的流程都是类似的
-
利用哈希函数生成 key 对应的 index【O(1)】
-
根据 index 操作定位数组元素【O(1)】
◼ 哈希表是【空间换时间】的典型应用
◼ 哈希函数,也叫做散列函数
◼ 哈希表内部的数组元素,很多地方也叫 Bucket(桶),整个数组叫 Buckets 或者 Bucket Array
hash
-
先生成 key 的哈希值(必须是整数)
-
再让 key 的哈希值跟数组的大小进行相关运算,生成一个索引值
◼ 良好的哈希函数
让哈希值更加均匀分布 → 减少哈希冲突次数 → 提升哈希表的性能
✓ 尽量让每个 key 的哈希值是唯一的
✓ 尽量让 key 的所有信息参与运算
◼ 为了提高效率,可以使用 & 位运算取代 % 运算**【前提:将数组的长度设计为 2 的幂( 2n )】**
| 1100 1010 | 1011 1100 |
|---|---|
| & 1111 | & 1111 |
| 1010 | 1100 |
Long和Double的哈希值
◼ >>> 和 ^ 的作用是?
高32bit 和 低32bit 混合计算出 32bit 的哈希值
充分利用所有信息计算出哈希值
| value | 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1011 0110 0011 1001 0110 1111 1100 1010 |
|---|---|
| value >>> 32 | 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 |
| value ^ (value >>> 32) | 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 0100 1001 1100 0110 1001 0000 0011 0101 |
字符串的哈希值
首先类比5489的计算
◼ 整数 5489 是如何计算出来的?
5 ∗ 103 + 4 ∗ 102 + 8 ∗ 101 + 9 ∗ 100
◼ 字符串是由若干个字符组成的
比如字符串 jack,由 j、a、c、k 四个字符组成(字符的本质就是一个整数)
因此,jack 的哈希值可以表示为 j ∗ n3 + a ∗ n2 + c ∗ n1 + k ∗ n0 ,等价于 [ ( j ∗ n + a ) ∗ n + c ] ∗ n + k 在JDK中,乘数 n 为 31,为什么使用 31?
✓ 31 是一个奇素数,JVM会将 31 * i 优化成 (i << 5) – i
关于31的探讨
◼ 31 * i = (2^5 – 1) * i = i * 2^5 – i = (i << 5) – i
◼ 31不仅仅是符合2^n – 1,它是个奇素数(既是奇数,又是素数,也就是质数)
素数和其他数相乘的结果比其他方式更容易产成唯一性,减少哈希冲突
最终选择31是经过观测分布结果后的选择
如果哈希值太大,整型溢出怎么办?
✓ 不用作任何处理(相当于只保留)
扰动计算
无论key是哪种类型,重新计算hash值
h = key.hashCode();
(h ^ (h >>> 16)) & (table.length - 1); // 其实在对hash值进行高低位混合计算
自定义对象作为key
◼ 自定义对象作为 key,最好同时重写 hashCode 、equals 方法
equals :用以判断 2 个 key 是否为同一个 key
✓ 自反性:对于任何非 null 的 x,x.equals(x)必须返回true
✓ 对称性:对于任何非 null 的 x、y,如果 y.equals(x) 返回 true,x.equals(y) 必须返回 true
✓ 传递性:对于任何非 null 的 x、y、z,如果 x.equals(y)、y.equals(z) 返回 true,那么x.equals(z)必须返回 true
✓ 一致性:对于任何非 null 的 x、y,只要 equals 的比较操作在对象中所用的信息没有被修改,多次调用x.equals(y) 就会一致地返回 true,或者一致地返回 false
✓ 对于任何非 null 的 x,x.equals(null) 必须返回 false
hashCode :必须保证 equals 为 true 的 2 个 key 的哈希值一样
反过来 hashCode 相等的 key,不一定 equals 为 true
◼ 不重写 hashCode 方法只重写 equals 会有什么后果?
✓ 可能会导致 2 个 equals 为 true 的 key 同时存在哈希表中
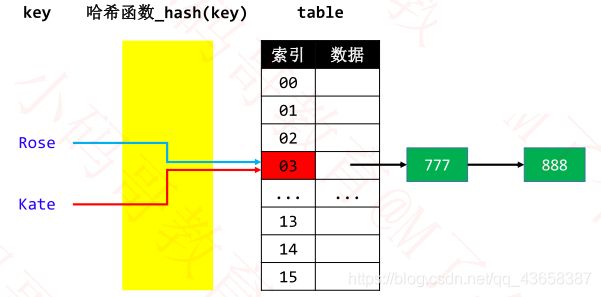
Hash Collision
2 个不同的 key,经过哈希函数计算出相同的结果
key1 ≠ key2 ,hash(key1) = hash(key2)
◼ 解决哈希冲突的常见方法
- 开放定址法(Open Addressing)
✓ 按照一定规则向其他地址探测,直到遇到空桶 - 再哈希法(Re-Hashing)
✓ 设计多个哈希函数 - 链地址法(Separate Chaining)
✓ 比如通过链表将同一index的元素串起来
JDK1.8的哈希冲突解决方案
◼ 默认使用单向链表将元素串起来
◼ 在添加元素时,可能会由单向链表转为红黑树来存储元素
比如当哈希表容量 ≥ 64 且 单向链表的节点数量大于 8 时
◼ 当红黑树节点数量少到一定程度时,又会转为单向链表
◼ JDK1.8中的哈希表是使用链表+红黑树解决哈希冲突
◼ 思考:这里为什么使用单链表?
每次都是从头节点开始遍历
- 当确定到同一索引处,通过比较equals,确定是否为同一entity
- 所以一定要从头开始逐个比较
- 更新
单向链表比双向链表少一个指针,可以节省内存空间
put
先不考虑扩容
-
当计算得到的索引的bucket为空时
说明红黑树为空,直接添加
-
当bucket非空时
-
如果之前加入过相同key,覆盖
-
没有加入过,添加
-
先实现根据key查找对应节点
// 由key计算出索引,再到相应bucket查找
private Node<K, V> node(K key) {
Node<K, V> root = table[index(key)];
return root == null ? null : node(root, key);
}
实现查找key最简单的方式:
-
最简单的查找结点实现
直接比较是否equals,不equals再去去扫描,并且只要找不到,就默认添加到红黑树的右子节点
-
优化一
为了减少递归查找调用,每次从红黑树的根节点开始比较时
通过比较存在相同的key【cmp = 0】,覆盖,之后退出循环
当最终不存在这个key时【cmp != 0】,递归比较当前结点和它的所有子节点,如果没有找到,那么默认继续和右子节点比较
对于之后的节点,如果扫描过,记录下来和都已经比较过,即当前节点和其子树都不存在key,那么默认
do {
K k2 = node.key;
if (Objects.equals(k1, k2)) {
cmp = 0;
} else if (searched) { // 下面就是既not equals 就不具备可比较性,那就扫描查找存不存在 // 已经扫描了
cmp = 1
} else { // searched == false; 还没有扫描,然后再根据内存地址大小决定左右
if ((node.left != null && (result = node(node.left, k1)) != null) // 在左边找到
|| (node.right != null && (result = node(node.right, k1)) != null)) { // 在右边找到
// 已经存在这个key
node = result;
cmp = 0;
} else { // 不存在这个key
searched = true; // 当扫描到当前节点时,找不到
cmp = 1
}
}
if (cmp > 0) {
node = node.right;
} else if (cmp < 0) {
node = node.left;
} else { // 相等,覆盖
V oldValue = node.value;
node.key = key;
node.value = value;
node.hash = h1;
return oldValue;
}
} while (node != null);
public V put(K key, V value) {
int index = index(key);
// 取出index位置的红黑树根节点
Node<K, V> root = table[index];
if (root == null) {
root = new Node<>(key, value, null);
table[index] = root;
size++;
afterPut(root);
return null;
}
// 添加新的节点到红黑树上面
Node<K, V> parent = root;
Node<K, V> node = root;
int cmp = 0;
K k1 = key;
int h1 = k1 == null ? 0 : k1.hashCode();
Node<K, V> result = null;
boolean searched = false; // 是否已经搜索过这个key
do {
parent = node;
K k2 = node.key;
int h2 = node.hash;
if (h1 > h2) {
cmp = 1;
} else if (h1 < h2) {
cmp = -1;
} else if (Objects.equals(k1, k2)) {
cmp = 0;
} else if (k1 != null && k2 != null
&& k1.getClass() == k2.getClass()
&& k1 instanceof Comparable
&& (cmp = ((Comparable) k1).compareTo(k2)) != 0) { // 如果只是大小相等,cmp==0,是不能确定equals所以要扫描
} else if (searched) { // 下面就是既not equals 就不具备可比较性,那就扫描查找存不存在 // 已经扫描了
cmp = System.identityHashCode(k1) - System.identityHashCode(k2);
} else { // searched == false; 还没有扫描,然后再根据内存地址大小决定左右
if ((node.left != null && (result = node(node.left, k1)) != null) // 在左边找到
|| (node.right != null && (result = node(node.right, k1)) != null)) { // 在右边找到
// 已经存在这个key
node = result;
cmp = 0;
} else { // 不存在这个key
searched = true; // 当扫描到当前节点时,找不到
cmp = System.identityHashCode(k1) - System.identityHashCode(k2);
}
}
if (cmp > 0) {
node = node.right;
} else if (cmp < 0) {
node = node.left;
} else { // 相等,覆盖
V oldValue = node.value;
node.key = key;
node.value = value;
node.hash = h1;
return oldValue;
}
} while (node != null);
// 看看插入到父节点的哪个位置
Node<K, V> newNode = new Node<>(key, value, parent);
if (cmp > 0) {
parent.right = newNode;
} else {
parent.left = newNode;
}
size++;
// 新添加节点之后的处理
afterPut(newNode);
return null;
}
-
优化二
先比较hash,并增加规则
再比较equals,not equals再比较
无可比较性,再扫描
并且随机向红黑树左右子树添加
do {
parent = node;
K k2 = node.key;
int h2 = node.hash;
if (h1 > h2) {
cmp = 1;
} else if (h1 < h2) {
cmp = -1;
} else if (Objects.equals(k1, k2)) {
cmp = 0;
} else if (k1 != null && k2 != null
&& k1.getClass() == k2.getClass()
&& k1 instanceof Comparable
&& (cmp = ((Comparable) k1).compareTo(k2)) != 0) { // 如果只是大小相等,cmp==0,是不能确定equals所以要扫描
} else if (searched) { // 下面就是既not equals 就不具备可比较性,那就扫描查找存不存在 // 已经扫描了
cmp = System.identityHashCode(k1) - System.identityHashCode(k2);
} else { // searched == false; 还没有扫描,然后再根据内存地址大小决定左右
if ((node.left != null && (result = node(node.left, k1)) != null) // 在左边找到
|| (node.right != null && (result = node(node.right, k1)) != null)) { // 在右边找到
// 已经存在这个key
node = result;
cmp = 0;
} else { // 不存在这个key
searched = true; // 当扫描到当前节点时,找不到
cmp = System.identityHashCode(k1) - System.identityHashCode(k2);
}
}
if (cmp > 0) {
node = node.right;
} else if (cmp < 0) {
node = node.left;
} else { // 相等,覆盖
V oldValue = node.value;
node.key = key;
node.value = value;
node.hash = h1;
return oldValue;
}
} while (node != null);
containsKey
红黑树中都是存放的node
所以根据key查找node实现containsKey
优化
-
添加时先比较hash值,大的放右边
所以,查找时也先从右边找
-
再比较是否equals
-
再通过比较性,判断向左子树还是右子树继续查找
【比较性】大小相等,cmp==0,不代表找到key,只有equals才可以确定
private Node<K, V> node(K key) {
Node<K, V> root = table[index(key)];
return root == null ? null : node(root, key);
}
// 在node所在的根结点的红黑树中找
private Node<K, V> node(Node<K, V> node, K k1) {
int h1 = hash(k1);
// 存储查找结果
Node<K, V> result = null;
int cmp = 0;
while (node != null) {
K k2 = node.key;
int h2 = node.hash;
// 添加时先比较hash值,大的放右边
// 所以,查找时也先从右边找
if (h1 > h2) {
node = node.right;
} else if (h1 < h2) {
node = node.left;
} else if (Objects.equals(k1, k2)) { // hashcode相等
return node; // equals相等,找到
} else if (k1 != null && k2 != null
&& k1.getClass() == k2.getClass()
&& k1 instanceof Comparable
&& (cmp = ((Comparable) k1).compareTo(k2)) != 0) {
node = cmp > 0 ? node.right : node.left;
} else if (node.right != null && (result = node(node.right, k1)) != null) { // 不具备可比较性,向右子树查找
return result; // 在右子树找到key
} else { // 右边扫描找不到,只能往左边找
node = node.left;
}
// } else if (node.left != null && (result = node(node.left, k1)) != null) {
// return result; // 把left传参,等价于把left赋值node循环
// } else {
// return null;
// }
}
return null;
}
containsValue
value可以是任意的,所以只能遍历扫描
这里采用了层序查找
public boolean containsValue(V value) {
if (size == 0) return false;
Queue<Node<K, V>> queue = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < table.length; i++) { // bucket
if (table[i] == null) continue;
queue.offer(table[i]);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) { // RBTree
Node<K, V> node = queue.poll();
if (Objects.equals(value, node.value)) return true;
if (node.left != null) {
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.offer(node.right);
}
}
}
return false;
}
扩容
◼ 装填因子(Load Factor):节点总数量 / 哈希表桶数组长度,也叫做负载因子
◼ 在JDK1.8的HashMap中,如果装填因子超过0.75,就扩容为原来的2倍
当扩容为原来容量的2倍时,节点的索引有2种情况
- 保持不变
- index = index+旧容量
一开始容量为2^2
1010
& 11
----
10
1110
& 11
----
10
扩容为2^3
1010
&111
----
010
1110
&111
----
110
Reference:小码哥MJ