利用http协议实现一个简单的web服务器
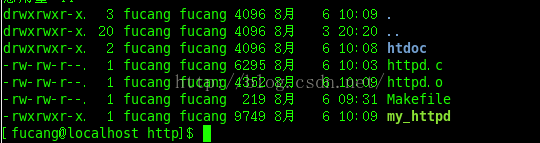
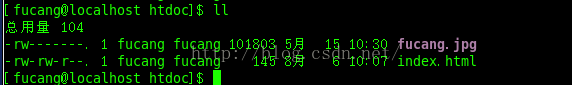
目录文件:
htdoc:
html文件:
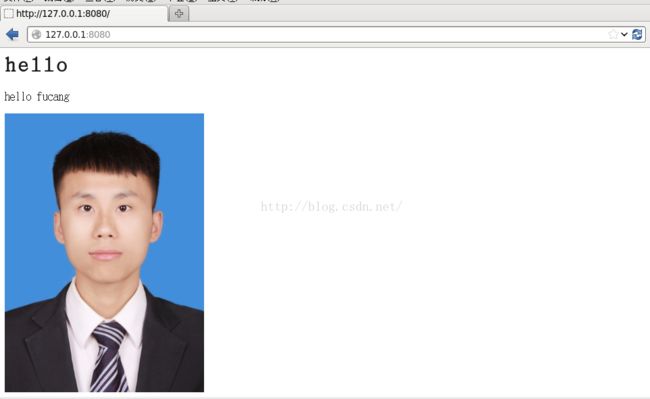
hello
hello fucang

Makefile:
BIN=my_httpd
SRC=httpd.c
OBJ=$(SRC:.c=.o)
CC=gcc
LDFLAGS=-lpthread
$(BIN):$(OBJ)
$(CC) -o $@ $^ $(LDFLAGS)
%.o:%.c
$(CC) -c $<
.PHONY:clean
clean:
rm -f $(OBJ) $(BIN)
.PHONY:debug
debug:
@echo $(SRC)
@echo $(OBJ)
/*************************************************************************
> File Name: httpd.c
> Author: fucang_zxx
> Mail: [email protected]
> Created Time: Wed 03 Aug 2016 08:29:42 PM CST
************************************************************************/
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define _SIZE_ 1024
static void echo_errno(int sock)
{
//
}
int statup(char *_ip, int _port)
{
int sock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if(sock < 0)
{
perror("socket");
exit(3);
}
int opt = 1;
//消除2倍的MSL时间
setsockopt(sock, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR, &opt, sizeof(opt));
struct sockaddr_in local;
local.sin_family = AF_INET;
local.sin_port = htons(_port);
local.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(_ip);
if(bind(sock, (struct sockaddr*)&local, sizeof(local)) < 0)
{
perror("bind");
exit(4);
}
if(listen(sock, 5) < 0)
{
perror("listen");
exit(5);
}
return sock;
}
static int get_line(int sock, char buf[], int len)
{
if( buf == NULL || len < 0)
{
return -1;
}
char c = '\0';//注意要初始化
int n = 0;
int i = 0;
while( (i < len - 1) && (c != '\n') )//读到空行为止
{
n = recv(sock, &c, 1, 0); //从客户端接收消息
if(n > 0)//读取成功
{
//将\r \n \r\n全转化为\n
if(c == '\r')
{
n = recv(sock, &c, 1, MSG_PEEK); //向前看一个字符,但实际没有读过去
if(n > 0 && c == '\n')
{
recv(sock, &c, 1, 0);//确认是\n,读过去
}
c = '\n';
}
buf[i++] = c;
}
else
{
c = '\n'; //读取失败,直接结束
}
}
buf[i] = '\0';
// printf("get_line buf = %s\n", buf);
return i;
}
static void clear_header(int sock)
{
int ret = 1;
char buf[_SIZE_];
do
{
ret = get_line(sock, buf, sizeof(buf));
}while((ret > 0) && (strcmp(buf, "\n") != 0));
}
void echo_www(int sock, const char* path, int size)
{
// printf("echo HTMLFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF\n");
int fd = open(path, O_RDONLY);
if(fd < 0)
{
echo_errno(sock);
return;
}
// printf("sever path : %s\n", path); path = htdoc/1.jpg
char buf[_SIZE_];
sprintf(buf, "HTTP/1.0 200 OK\r\n\r\n");
send(sock, buf, strlen(buf), 0);
if(sendfile(sock, fd, NULL, size) < 0)
{
echo_errno(sock);
close(fd);
return;
}
close(fd);
}
void* accept_request(void *arg)
{
int sock = (int)arg;
char buf[_SIZE_];
char method[_SIZE_]; //存放方法名即GET or POST
char url[_SIZE_]; //存放路径
char path[_SIZE_];
memset(buf, '\0', sizeof(buf));
memset(method, '\0', sizeof(method));
memset(url, '\0', sizeof(url));
memset(path, '\0', sizeof(path));
int cgi = 0;
int ret = -1;
char *query_string = NULL; //保存数据参数
#ifdef _DEBUG_
do
{
//http的请求报时按行存储
ret = get_line(sock, buf, sizeof(buf));//获取消息报的一行
printf("%s", buf);
fflush(stdout);
}while((ret > 0) && strcmp(buf, "\n") != 0); //读取到空行
#endif /*_DEBUG*/
ret = get_line(sock, buf, sizeof(buf)); //获取请求行
// printf("buf = %s\n", buf);
if(ret < 0)
{
echo_errno(sock);
return (void*)1;
}
//GET / HTTP/1.1
int i = 0; //method index
int j = 0; //buf index
//请求行包括 方法 url http/1.1(0)
//
//获取方法 GET POST
while( (i < sizeof(method) - 1) && (j < sizeof(buf)) && (!isspace(buf[j])))
{
method[i] = buf[j];
++i;
++j;
}
method[i] = '\0';
//strcasecmp比较时不考虑大小写,
if(strcasecmp(method, "GET") != 0 && strcasecmp(method, "POST") != 0)
{
echo_errno(sock);
return (void*)2;
}
// printf("method = %s\n", method);
//如果以GET方式传输,所带参数附加在CGI程式的URL后直接传给server,并可从server端的
//QUERY_STRING这个环境变量中获取
//如果以POST方式传输,则参数会被打包在数据报中传送给server,并可从CONTENT_LENGTH这
//个环境变量中读取
//理论上讲,GET是从服务器上请求数据,POST是发送数据到服务器
//GET方法是把数据参数队列(query string)加到一个URL上,GET方法通常会限制字符的大小
//POST方法可以没有时间限制的传送数据到服务器,用户在浏览器端是看不到这一过程的,
//所以POST方法比较适合用于发送一个保密的或者比较大量的数据到服务器
if(strcasecmp(method, "POST") == 0)
{
cgi = 1;
}
//跳过空格
while(isspace(buf[j]))
{
++j;
}
//获取url
i = 0;
while( (i < sizeof(url) - 1) && (j < sizeof(buf)) && (!isspace(buf[j])))
{
url[i] = buf[j];
++i;
++j;
}
if(strcasecmp(method, "GET") == 0)
{
query_string = url;
//路径和数据参数以 ?分隔
while(*query_string != '\0' && *query_string != '?')
{
++query_string;
}
if(*query_string == '?')
{
cgi = 1;
*query_string++ = '\0';
}
}
// / /aa/bb/cc
sprintf(path, "htdoc%s", url);
if(path[strlen(path) -1] == '/')
{
strcat(path, "index.html");
}
// printf("method : %s\n", method);
// printf("path: %s\n", path);
// printf("query_string: %s\n", query_string);
struct stat st;
if(stat(path, &st) < 0)
{
echo_errno(sock);
return (void*)3;
}
else
{
if(S_ISDIR(st.st_mode))
{
strcpy(path, "htdoc/index.html");
}
else if((st.st_mode & S_IXUSR) || \
(st.st_mode & S_IXGRP) || \
(st.st_mode & S_IXOTH))
{
cgi = 1;
}
else
{
}
if(cgi)
{
// exec_cgi(sock, path, method, query_string);
}
else
{
clear_header(sock);
echo_www(sock, path,st.st_size);
}
}
close(sock);
return (void*)0;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
if(argc != 3)
{
printf("Usage#: %s [ip] [port]\n", argv[0]);
exit(1);
}
int listen_sock = statup(argv[1], atoi(argv[2]));
struct sockaddr_in peer;
socklen_t len = sizeof(peer);
int done = 0;
while(!done)
{
int new_sock = accept(listen_sock, (struct sockaddr*)&peer, &len);
if(new_sock < 0)
{
perror("accept");
exit(2);
}
printf("debug : client socket: %s:%d\n", inet_ntoa(peer.sin_addr), ntohs(peer.sin_port));
pthread_t tid;
pthread_create(&tid, NULL, accept_request, (void*)new_sock);
pthread_detach(tid);
}
return 0;
} 运行截图: