卷积神经网络手写体识别
- CNN
- 背景
- 卷积
- LeNet网络结构
- C1
- S2
- C3
- S4
- C5
- F6
- 输出
- 数据集
- 代码及运行结果
- 测试
CNN
1995年, Yann LeCun 与Yoshua Bengio 提出了convolutional neural networks框架, 并用于手写体数字识别。
背景
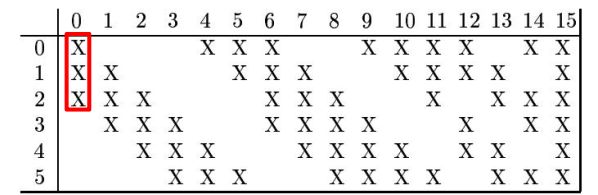
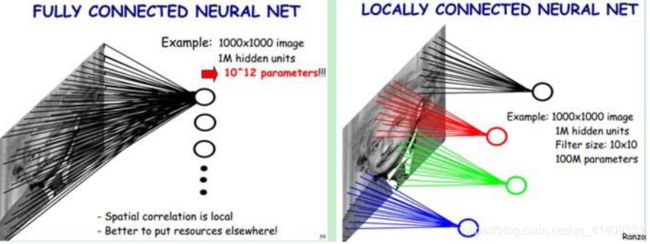
在BP网络用于图像处理中, 如果要对输入图像分类, 可设计多层网络结构。如果采用全连接结构, 存在参数爆炸问题。 如对10001000的图像进行卷积, 大约需要1000100010001000个参数。利用局部卷积替换全连接结构, 可将参数降低至100010001010≈100M。
如果进一步采用权值共享的策略, 即同一特征图卷积核、Bias相同, 将卷积参数将至1010。 为尽可能地保存信息, 可设计多个卷积特征图, 将参数将至10K。
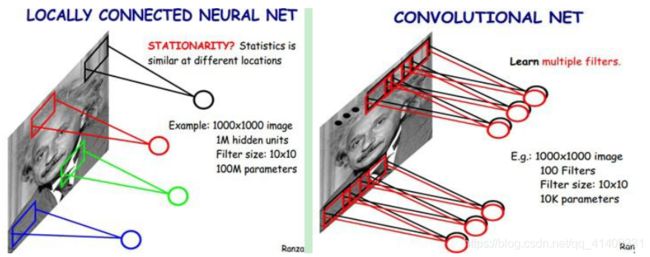
卷积
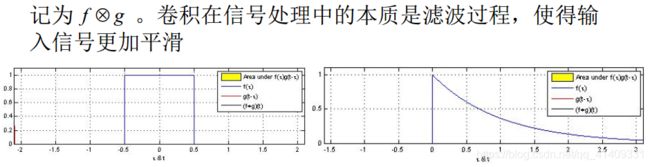
函数卷积
函数f(x)与g(x)卷积的定义(一维) 为:
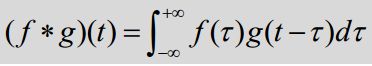
图像卷积
在图像处理中, 卷积也被称为滤波, 一般是由卷积核(滤波器) w与在图像中f(x, y)的卷积结果为: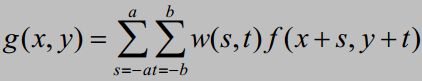
![]()
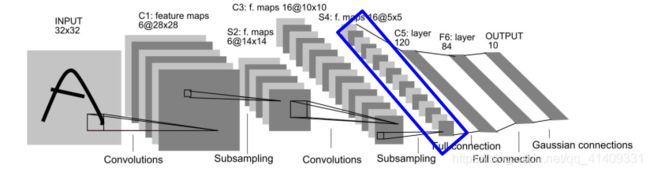
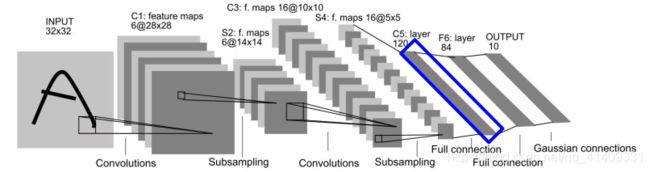
LeNet网络结构
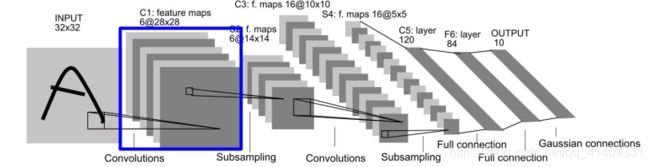
输入层为3232图像, 一般限定字符最大范围为2020(居中)
C*: 卷基层
S*: 采样层(Pooling层)
F*: 全连接层
C1
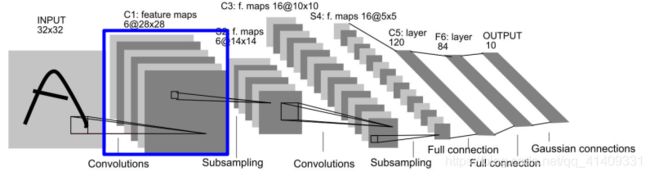
输入层为3232图像, 卷积核大小为55
C1: 卷积层为6副28*28的特征图。 C1层具有如下特点:
- 拓扑结构: 输入层相邻节点卷积后仍然相邻
- 稀疏连接: 每个像素仅与输入层的相邻结点相连
- 权值共享: 同一副特征图共享相同的卷积核
C1层神经元连接数量为2828(55+1)6=122304, 由于采用了权值共享,
因此待学习参数为(55+1)6=156。
如果采用全连接策略, 总参数量可达(3232+1)(28*28)*6
S2
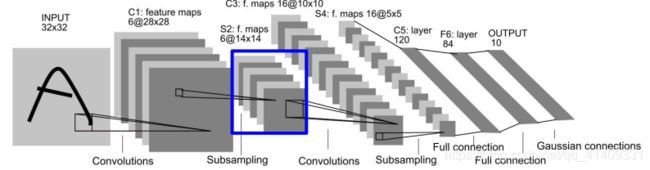
S2: Pooling层将2828的特征图将采样为1414的图像:
- 采用2*2非重叠采样。
- S2层每个单元的4个输入相加, 乘以一个可训练参数, 再加上一个可
训练偏置。 - 结果通过sigmoid函数计算。
S2层神经元连接数量为1414(2*2+1)6=5880, 待学习参数为62=12。
C3
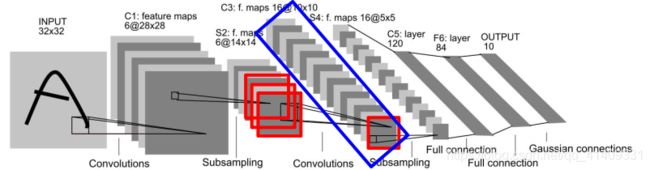
C3: 将6副2828的特征图卷积为16副1010的图像, 卷积核为5*5:
S4
- 降采样过程与S2层一致
- S4层神经元连接数量为55(2*2+1)16=2000, 待学习参数为162=32
C5
- F6中每个神经元与S4所有神经元相连。
- C5层神经元连接数量为120*(16*25+1) = 48120, 全部为待学习参数。
F6
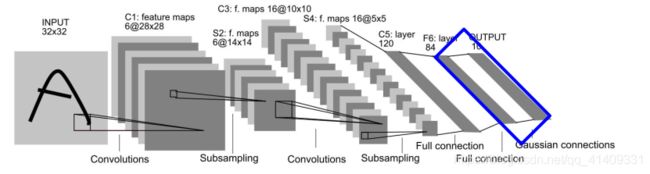
F6: 构建84个神经元, 每个神经元与C5的120个神经元全连接:
- F6层神经元连接数量为84*(120+1)=10164, 全部为待学习参数。
输出
输出层: 为10个神经元, 每个神经元的激活值表示对应字符的相应强度,
最大值则为对应的识别结果。
数据集
0-9共十个数字每个数字训练集在6000张图片左右。
训练图片中倾斜,扭曲,粗细不一致,甚至旋转,如
倾斜
![]()
扭曲
![]()
粗细不一致
![]()
![]()
旋转(数字7)
![]()
代码及运行结果
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import filedialog
from PIL import Image, ImageTk
from tkinter import filedialog
import time
def creat_windows():
win = tk.Tk() # 创建窗口
sw = win.winfo_screenwidth()
sh = win.winfo_screenheight()
ww, wh = 400, 450
x, y = (sw-ww)/2, (sh-wh)/2
win.geometry("%dx%d+%d+%d"%(ww, wh, x, y-40)) # 居中放置窗口
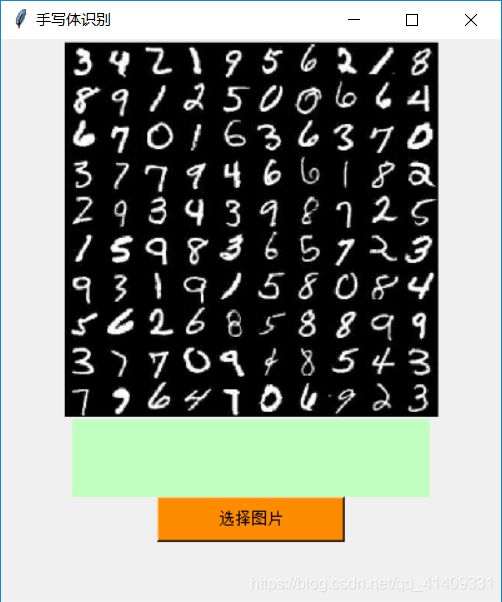
win.title('手写体识别') # 窗口命名
bg1_open = Image.open("timg.jpg").resize((300, 300))
bg1 = ImageTk.PhotoImage(bg1_open)
canvas = tk.Label(win, image=bg1)
canvas.pack()
var = tk.StringVar() # 创建变量文字
var.set('')
tk.Label(win, textvariable=var, bg='#C1FFC1', font=('宋体', 21), width=20, height=2).pack()
tk.Button(win, text='选择图片', width=20, height=2, bg='#FF8C00', command=lambda:main(var, canvas), font=('圆体', 10)).pack()
win.mainloop()
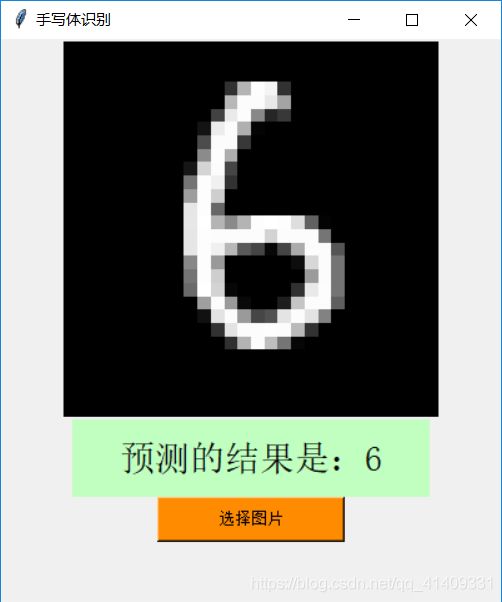
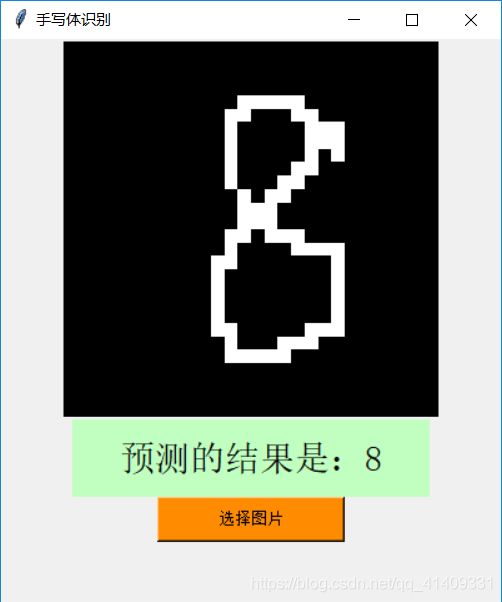
def main(var, canvas):
file_path = filedialog.askopenfilename()
bg1_open = Image.open(file_path).resize((28, 28))
pic = np.array(bg1_open).reshape(784,)
bg1_resize = bg1_open.resize((300, 300))
bg1 = ImageTk.PhotoImage(bg1_resize)
canvas.configure(image=bg1)
canvas.image = bg1
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
saver = tf.train.import_meta_graph('save/model.meta') # 载入模型结构
saver.restore(sess, 'save/model') # 载入模型参数
graph = tf.get_default_graph() # 加载计算图
x = graph.get_tensor_by_name("x-input:0") # 从模型中读取占位符变量
keep_prob = graph.get_tensor_by_name("keep_prob:0")
y_conv = graph.get_tensor_by_name("y-pred:0") # 关键的一句 从模型中读取占位符变量
prediction = tf.argmax(y_conv, 1)
predint = prediction.eval(feed_dict={x: [pic], keep_prob: 1.0}, session=sess) # feed_dict输入数据给placeholder占位符
answer = str(predint[0])
var.set("预测的结果是:" + answer)
if __name__ == "__main__":
creat_windows()
#coding:utf8
import os
import cv2
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
def getTrain():
train=[[],[]] # 指定训练集的格式,一维为输入数据,一维为其标签
# 读取所有训练图像,作为训练集
train_root="mnist_train"
labels = os.listdir(train_root)
for label in labels:
imgpaths = os.listdir(os.path.join(train_root,label))
for imgname in imgpaths:
img = cv2.imread(os.path.join(train_root,label,imgname),0)
array = np.array(img).flatten() # 将二维图像平铺为一维图像
array=MaxMinNormalization(array)
train[0].append(array)
label_ = [0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0]
label_[int(label)] = 1
train[1].append(label_)
train = shuff(train)
return train
def getTest():
test=[[],[]] # 指定训练集的格式,一维为输入数据,一维为其标签
# 读取所有训练图像,作为训练集
test_root="mnist_test"
labels = os.listdir(test_root)
for label in labels:
imgpaths = os.listdir(os.path.join(test_root,label))
for imgname in imgpaths:
img = cv2.imread(os.path.join(test_root,label,imgname),0)
array = np.array(img).flatten() # 将二维图像平铺为一维图像
array=MaxMinNormalization(array)
test[0].append(array)
label_ = [0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0]
label_[int(label)] = 1
test[1].append(label_)
test = shuff(test)
return test[0],test[1]
def shuff(data):
temp=[]
for i in range(len(data[0])):
temp.append([data[0][i],data[1][i]])
import random
random.shuffle(temp)
data=[[],[]]
for tt in temp:
data[0].append(tt[0])
data[1].append(tt[1])
return data
count = 0
def getBatchNum(batch_size,maxNum):
global count
if count ==0:
count=count+batch_size
return 0,min(batch_size,maxNum)
else:
temp = count
count=count+batch_size
if min(count,maxNum)==maxNum:
count=0
return getBatchNum(batch_size,maxNum)
return temp,min(count,maxNum)
def MaxMinNormalization(x):
x = (x - np.min(x)) / (np.max(x) - np.min(x))
return x
# 1、权重初始化,偏置初始化
# 为了创建这个模型,我们需要创建大量的权重和偏置项
# 为了不在建立模型的时候反复操作,定义两个函数用于初始化
def weight_variable(shape):
initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape,stddev=0.1)#正太分布的标准差设为0.1
return tf.Variable(initial)
def bias_variable(shape):
initial = tf.constant(0.1,shape=shape)
return tf.Variable(initial)
# 2、卷积层和池化层也是接下来要重复使用的,因此也为它们定义创建函数
# tf.nn.conv2d是Tensorflow中的二维卷积函数,参数x是输入,w是卷积的参数
# strides代表卷积模块移动的步长,都是1代表会不遗漏地划过图片的每一个点,padding代表边界的处理方式
# padding = 'SAME',表示padding后卷积的图与原图尺寸一致,激活函数relu()
# tf.nn.max_pool是Tensorflow中的最大池化函数,这里使用2 * 2 的最大池化,即将2 * 2 的像素降为1 * 1的像素
# 最大池化会保留原像素块中灰度值最高的那一个像素,即保留最显著的特征,因为希望整体缩小图片尺寸
# ksize:池化窗口的大小,取一个四维向量,一般是[1,height,width,1]
# 因为我们不想再batch和channel上做池化,一般也是[1,stride,stride,1]
def conv2d(x, w):
return tf.nn.conv2d(x, w, strides=[1,1,1,1],padding='SAME') # 保证输出和输入是同样大小
def max_pool_2x2(x):
return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1,2,2,1], strides=[1,2,2,1],padding='SAME')
iterNum = 1000
batch_size=1024
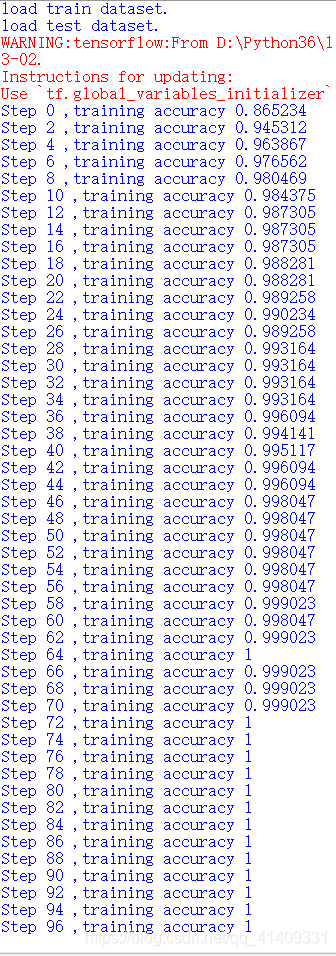
print("load train dataset.")
train=getTrain()
print("load test dataset.")
test0,test1=getTest()
# 3、参数
# 这里的x,y_并不是特定的值,它们只是一个占位符,可以在TensorFlow运行某一计算时根据该占位符输入具体的值
# 输入图片x是一个2维的浮点数张量,这里分配给它的shape为[None, 784],784是一张展平的MNIST图片的维度
# None 表示其值的大小不定,在这里作为第1个维度值,用以指代batch的大小,means x 的数量不定
# 输出类别y_也是一个2维张量,其中每一行为一个10维的one_hot向量,用于代表某一MNIST图片的类别
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None,784], name="x-input")
y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,10]) # 10列
# 4、第一层卷积,它由一个卷积接一个max pooling完成
# 张量形状[5,5,1,32]代表卷积核尺寸为5 * 5,1个颜色通道,32个通道数目
w_conv1 = weight_variable([5,5,1,32])
b_conv1 = bias_variable([32]) # 每个输出通道都有一个对应的偏置量
# 我们把x变成一个4d 向量其第2、第3维对应图片的宽、高,最后一维代表图片的颜色通道数(灰度图的通道数为1,如果是RGB彩色图,则为3)
x_image = tf.reshape(x,[-1,28,28,1])
# 因为只有一个颜色通道,故最终尺寸为[-1,28,28,1],前面的-1代表样本数量不固定,最后的1代表颜色通道数量
h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x_image, w_conv1) + b_conv1) # 使用conv2d函数进行卷积操作,非线性处理
h_pool1 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv1) # 对卷积的输出结果进行池化操作
# 5、第二个和第一个一样,是为了构建一个更深的网络,把几个类似的堆叠起来
# 第二层中,每个5 * 5 的卷积核会得到64个特征
w_conv2 = weight_variable([5,5,32,64])
b_conv2 = bias_variable([64])
h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool1, w_conv2) + b_conv2)# 输入的是第一层池化的结果
h_pool2 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv2)
# 6、密集连接层
# 图片尺寸减小到7 * 7,加入一个有1024个神经元的全连接层,
# 把池化层输出的张量reshape(此函数可以重新调整矩阵的行、列、维数)成一些向量,加上偏置,然后对其使用Relu激活函数
w_fc1 = weight_variable([7 * 7 * 64, 1024])
b_fc1 = bias_variable([1024])
h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool2, [-1,7 * 7 * 64])
h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat, w_fc1) + b_fc1)
# 7、使用dropout,防止过度拟合
# dropout是在神经网络里面使用的方法,以此来防止过拟合
# 用一个placeholder来代表一个神经元的输出
# tf.nn.dropout操作除了可以屏蔽神经元的输出外,
# 还会自动处理神经元输出值的scale,所以用dropout的时候可以不用考虑scale
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, name="keep_prob")# placeholder是占位符
h_fc1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(h_fc1, keep_prob)
# 8、输出层,最后添加一个softmax层
w_fc2 = weight_variable([1024,10])
b_fc2 = bias_variable([10])
y_conv = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(h_fc1_drop, w_fc2) + b_fc2, name="y-pred")
# 9、训练和评估模型
# 损失函数是目标类别和预测类别之间的交叉熵
# 参数keep_prob控制dropout比例,然后每100次迭代输出一次日志
cross_entropy = tf.reduce_sum(-tf.reduce_sum(y_ * tf.log(y_conv),reduction_indices=[1]))
train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(1e-4).minimize(cross_entropy)
# 预测结果与真实值的一致性,这里产生的是一个bool型的向量
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_conv, 1), tf.argmax(y_, 1))
# 将bool型转换成float型,然后求平均值,即正确的比例
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
# 初始化所有变量,在2017年3月2号以后,用 tf.global_variables_initializer()替代tf.initialize_all_variables()
sess.run(tf.initialize_all_variables())
# 保存最后一个模型
saver = tf.train.Saver(max_to_keep=1)
for i in range(iterNum):
for j in range(int(len(train[1])/batch_size)):
imagesNum=getBatchNum(batch_size,len(train[1]))
batch = [train[0][imagesNum[0]:imagesNum[1]],train[1][imagesNum[0]:imagesNum[1]]]
train_step.run(feed_dict={x: batch[0], y_: batch[1], keep_prob: 0.5})
if i % 2 == 0:
train_accuracy = accuracy.eval(feed_dict={x: batch[0], y_: batch[1],keep_prob: 1.0})
print("Step %d ,training accuracy %g" % (i, train_accuracy))
print("test accuracy %f " % accuracy.eval(feed_dict={x: test0, y_:test1, keep_prob: 1.0}))
# 保存模型于文件夹
saver.save(sess,"save/model")