[java][44]软件测试-JUnit实践篇
java小白的学习记录......
本文将建立一个计算器类(含加法、减法),通过JUnit进行单元测试。
创建Calculator.java,放在junit包
package junit;
public class Calculator {
/**
* 加法
* @param a
* @param b
* @return Double对象
*/
public Double add(double a,double b)
{
return(Double.valueOf(a+b));
}
/**
* 减法
* @param a
* @param b
* @return
*/
public Double subtract(double a,double b)
{
return(Double.valueOf(a-b));
}
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Calculator calculator = new Calculator();
System.out.println(calculator.add(10, 1));
}
}下面将对Calculator类 进行JUnit单元测试
所有测试用例都将放在junit.test包
1. 导入JUnit包:在项目上右键,点击build path->add libraries -> 选择JUnit4
2. 直接测试add()和substract()方法,只是证明了方法可以运行
右击Calculator.java -> new -> JUnit Test Case -> 自动生成类名CalculatorTest
1)CalculatorTest.java
package junit.test;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
public class CalculatorTest
{
Calculator calc;
@Before
public void init()
{
calc = new Calculator();
System.out.println("init");
}
@Test
public void testAdd()
{
calc.add(10, 11);
}
@Test
public void testSubtract()
{
calc.subtract(100, 10);
}
@After
public void exit()
{
calc = null; //清理对象
System.out.println("exit");
}
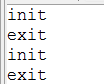
}2)为什么输出2次init,exit呢?
原因:每个Test()方法都会执行 init() -> Test() -> exit()
而本程序有2个Test()方法
4. assert断言,判断结果是否与预想一致
常用assertEquals和assertTrue,将3.的代码改为:
package junit.test;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
import junit.Calculator;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
public class CalculatorTest
{
Calculator calc;
@Before
public void init()
{
calc = new Calculator();
System.out.println("init");
}
@Test
public void testAddPositive()
{
assertEquals(Double.valueOf(21),calc.add(10, 11));
assertTrue(21 == calc.add(10, 11));
}
@Test
public void testAddNegative()
{
assertEquals(Double.valueOf(-21),calc.add(-10, -11));
assertTrue(-21 == calc.add(-10, -11));
}
@Test
public void testSubtract()
{
assertTrue(calc.subtract(100, 10)==90 );
}
@After
public void exit()
{
calc = null; //清理对象
System.out.println("exit");
}
}5. 用testSuite测试多个用例
1)首先,创建CalculatorTest2.java,其Test()方法为空,只是为了方便TestSuite的说明
package junit.test;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
public class CalculatorTest2
{
@Before
public void setUp() throws Exception
{
}
@After
public void tearDown() throws Exception
{
}
@Test
public void test()
{
}
}2)solution 1:通过代码手动添加
右键junit.test -> new -> Other... -> 搜索框输入Test并选择TestSuite
package junit.test;
import junit.framework.JUnit4TestAdapter;
import junit.framework.Test;
import junit.framework.TestSuite;
public class CalculatorTestSuite
{
public static Test suite()
{
TestSuite suite = new TestSuite("Test for junit.test");
// $JUnit-BEGIN$
suite.addTest(new JUnit4TestAdapter(CalculatorTest.class));//添加代码行1
suite.addTest(new JUnit4TestAdapter(CalculatorTest2.class));//添加代码行2
// $JUnit-END$
return suite;
}
}结果:
可见,供测试了4个方法
3)solution 2:通过注解
同上,新建名为CalculatorTestSuite的Test Suite
package junit.test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.junit.runners.Suite;
import junit.framework.Test;
import junit.framework.TestSuite;
@RunWith(Suite.class)
//如需测试多个类时,只需要把相关的测试类加入到"{}"即可
@Suite.SuiteClasses({CalculatorTest.class,CalculatorTest2.class,CalculatorTestSuite.class})
public class CalculatorTests
{
}结果:
测试了8个方法
![[java][44]软件测试-JUnit实践篇_第1张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/3c00eec39f394c978f6f5da1a64a744f.png)
![[java][44]软件测试-JUnit实践篇_第2张图片](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/5328c4983e5748cdad751551d8d96e44.png)