PCIe学习笔记之MSI/MSI-x中断及代码分析
本文基于linux 5.7.0, 平台是arm64
1. MSI/MSI-X概述
PCIe有三种中断,分别为INTx中断,MSI中断,MSI-X中断,其中INTx是可选的,MSI/MSI-X是必须实现的。
1.1 什么是MSI中断?
MSI, message signal interrupt, 是PCI设备通过写一个特定消息到特定地址,从而触发一个CPU中断。特定消息指的是PCIe总线中的Memory Write TLP, 特定地址一般存放在MSI capability中。
和传统的INTx中断相比,MSI中断有以下几个优点:
(1) 基于引脚的传统中断会被多个设备所共享,中断共享时,如果触发了中断,linux需要一一调用对应的中断处理函数,这样会有性能上的损失,而MSI不存在共享的问题。
(2) 设备向内存写入数据,然后发起引脚中断, 有可能会出现CPU收到中断时,数据还没有达到内存。 而使用MSI中断时,产生中断的写不能越过数据的写,驱动可以确信所有的数据已经达到内存。
(3) 多功能的PCI设备,每一个功能最多只有一个中断引脚,当具体的事件产生时,驱动需要查询设备才能知道是哪一个事件产生,这样会降低中断的处理速度。而一个设备可以支持32个MSI中断,每个中断可以对应特定的功能。
1.2 什么是MSI-X中断?
MSI-x是MSI的扩展和增强。MSI有它自身的局限性,MSI最多支持32个中断,且要求中断向量连续, 而MSI-x没有这个限制,且支持的中断数量更多。此外,MSI-X的中断向量信息并不直接存储在capability中,而是在一块特殊Memory中.
MSI和MSI-X的规格对比:
| MSI | MSI-X | |
|---|---|---|
| 中断向量数 | 32 | 2048 |
| 中断号约束 | 必须连续 | 可以随意分配 |
| MSI信息存放 | capability寄存器 | MSI-X Table(BAR空间) |
总之,PCIe设备在提交MSI中断请求时,都是向MSI/MSI-X Capability结构中的Message Address的地址写Message Data数据,从而组成一个存储器写TLP,向处理器提交中断请求。
在arm64中,MSI/MSI-X对应的是LPI中断, 在之前的文章【ARM GICv3 ITS介绍及代码分析】有介绍过,外设通过写GITS_TRANSLATER寄存器,可以发起LPI中断, 所以相应的,如果在没有使能SMMU时,MSI的message address指的就是ITS_TRANSLATER的地址。
2. MSI/MSI-X capability
2.1 MSI capability
MSI Capability的ID为5, 共有四种组成方式,分别是32和64位的Message结构,32位和64位带中断Masking的结构。
以带bit mask的capability register为例:

Capability ID :记录msi capability的ID号,固定为0x5.
next pointer: 指向下一个新的Capability寄存器的地址.
Message Control Register: 存放当前PCIe设备使用MSI机制进行中断请求的状态和控制信息

MSI enable控制MSI是否使能,Multiple Message Capable表示设备能够支持的中断向量数量, Multi Message enable表示实际使用的中断向量数量, 64bit Address Capable表示使用32bit格式还是64bit格式。
Message Address Register: 当MSI enable时,保存中断控制器种接收MSI消息的地址。
Message Data Register: 当MSI enable时,保存MSI报文的数据。
Mask Bits: 可选,Mask Bits字段由32位组成,其中每一位对应一种MSI中断请求。
Pending Bits: 可选,需要与Mask bits配合使用, 可以防止中断丢失。当Mask bits为1的时候,设备发送的MSI中断请求并不会发出,会将pending bits置为1,当mask bits变为0时,MSI会成功发出,pending位会被清除。
2.2 MSI-X capability
MSI-x的capability寄存器结构和MSI有一些差异:

Capability ID:记载MSI-X Capability结构的ID号,其值为0x11
Message Control: 存放当前PCIe设备使用MSI-x机制进行中断请求的状态和控制信息
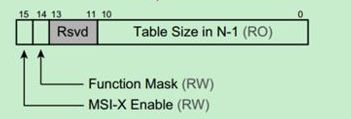
MSI-x enable,控制MSI-x的中断使能 ;
Function Mask,是中断请求的全局Mask位,如果该位为1,该设备所有的中断请求都将被屏蔽;如果该位为0,则由Per Vector Mask位,决定是否屏蔽相应的中断请求。Per Vector Mask位在MSI-X Table中定义;
Table Size, 存放MSI-X table的大小
Table BIR:BAR Indicator Register。该字段存放MSI-X Table所在的位置,PCIe总线规范规定MSI-X Table存放在设备的BAR空间中。该字段表示设备使用BAR0 ~ 5寄存器中的哪个空间存放MSI-X table。
Table Offset: 存放MSI-X Table在相应BAR空间中的偏移。
PBA(Pending Bit Array) BIR: 存放Pending Table在PCIe设备的哪个BAR空间中。在通常情况下,Pending Table和MSI-X Table存放在PCIe设备的同一个BAR空间中。
PBA Offset: 该字段存放Pending Table在相应BAR空间中的偏移。
通过Table BIR和Table offset知道了MSI-Xtable在哪一个bar中以及在bar中的偏移,就可以找到对应的MSI-X table。
查找过程如下:

查找到的MSI-X table结构:

MSI-X Table由多个Entry组成,其中每个Entry与一个中断请求对应。
除了msg data和msg addr外,还有一个vector control的参数,表示PCIe设备是否能够使用该Entry提交中断请求, 类似MSI的mask位。
3. 确认设备的MSI/MSI-X capability
lspci -v可以查看设备支持的capability, 如果有MSI或者MSI-x或者message signal interrupt的描述,并且这些描述后面都有一个enable的flag, “+”表示enable,"-"表示disable。
[root@localhost linux]# lspci -s 00:16.0 -v
00:16.0 PCI bridge: VMware PCI Express Root Port (rev 01) (prog-if 00 [Normal decode])
Flags: bus master, fast devsel, latency 0, IRQ 32
Bus: primary=00, secondary=0b, subordinate=0b, sec-latency=0
I/O behind bridge: 00005000-00005fff
Memory behind bridge: fd300000-fd3fffff
Prefetchable memory behind bridge: 00000000e7900000-00000000e79fffff
Capabilities: [40] Subsystem: VMware PCI Express Root Port
Capabilities: [48] Power Management version 3
Capabilities: [50] Express Root Port (Slot+), MSI 00
Capabilities: [8c] MSI: Enable+ Count=1/1 Maskable+ 64bit+
Kernel driver in use: pcieport
Kernel modules: shpchp
4. 设备怎么使用MSI/MSI-x中断?
传统中断在系统初始化扫描PCI bus tree时就已自动为设备分配好中断号, 但是如果设备需要使用MSI,驱动需要进行一些额外的配置。
当前linux内核提供pci_alloc_irq_vectors来进行MSI/MSI-X capablity的初始化配置以及中断号分配。
int pci_alloc_irq_vectors(struct pci_dev *dev, unsigned int min_vecs,
unsigned int max_vecs, unsigned int flags);
函数的返回值为该PCI设备分配的中断向量个数。
min_vecs是设备对中断向量数目的最小要求,如果小于该值,会返回错误。
max_vecs是期望分配的中断向量最大个数。
flags用于区分设备和驱动能够使用的中断类型,一般有4种:
#define PCI_IRQ_LEGACY (1 << 0) /* Allow legacy interrupts */
#define PCI_IRQ_MSI (1 << 1) /* Allow MSI interrupts */
#define PCI_IRQ_MSIX (1 << 2) /* Allow MSI-X interrupts */
#define PCI_IRQ_ALL_TYPES (PCI_IRQ_LEGACY | PCI_IRQ_MSI | PCI_IRQ_MSIX)
PCI_IRQ_ALL_TYPES可以用来请求任何可能类型的中断。
此外还可以额外的设置PCI_IRQ_AFFINITY, 用于将中断分布在可用的cpu上。
使用示例:
i = pci_alloc_irq_vectors(dev->pdev, min_msix, msi_count, PCI_IRQ_MSIX | PCI_IRQ_AFFINITY);
与之对应的是释放中断资源的函数pci_free_irq_vectors(), 需要在设备remove时调用:
void pci_free_irq_vectors(struct pci_dev *dev);
此外,linux还提供了pci_irq_vector()用于获取IRQ number.
int pci_irq_vector(struct pci_dev *dev, unsigned int nr);
5. 设备的MSI/MSI-x中断是怎样处理的?
5.1 MSI的中断分配pci_alloc_irq_vectors()
深入理解下pci_alloc_irq_vectors()
pci_alloc_irq_vectors() --> pci_alloc_irq_vectors_affinity()
int pci_alloc_irq_vectors_affinity(struct pci_dev *dev, unsigned int min_vecs,
unsigned int max_vecs, unsigned int flags,
struct irq_affinity *affd)
{
struct irq_affinity msi_default_affd = {0};
int msix_vecs = -ENOSPC;
int msi_vecs = -ENOSPC;
if (flags & PCI_IRQ_AFFINITY) {
if (!affd)
affd = &msi_default_affd;
} else {
if (WARN_ON(affd))
affd = NULL;
}
if (flags & PCI_IRQ_MSIX) {
msix_vecs = __pci_enable_msix_range(dev, NULL, min_vecs,
max_vecs, affd, flags); ------(1)
if (msix_vecs > 0)
return msix_vecs;
}
if (flags & PCI_IRQ_MSI) {
msi_vecs = __pci_enable_msi_range(dev, min_vecs, max_vecs,
affd); ----- (2)
if (msi_vecs > 0)
return msi_vecs;
}
/* use legacy IRQ if allowed */
if (flags & PCI_IRQ_LEGACY) {
if (min_vecs == 1 && dev->irq) {
/*
* Invoke the affinity spreading logic to ensure that
* the device driver can adjust queue configuration
* for the single interrupt case.
*/
if (affd)
irq_create_affinity_masks(1, affd);
pci_intx(dev, 1); ------ (3)
return 1;
}
}
if (msix_vecs == -ENOSPC)
return -ENOSPC;
return msi_vecs;
}
(1) 先确认申请的是否为MSI-X中断
__pci_enable_msix_range()
+-> __pci_enable_msix()
+-> msix_capability_init()
+-> pci_msi_setup_msi_irqs()
msix_capability_init会对msi capability进行一些配置。
关键函数pci_msi_setup_msi_irqs, 会创建msi irq number:
static int pci_msi_setup_msi_irqs(struct pci_dev *dev, int nvec, int type)
{
struct irq_domain *domain;
domain = dev_get_msi_domain(&dev->dev);
if (domain && irq_domain_is_hierarchy(domain))
return msi_domain_alloc_irqs(domain, &dev->dev, nvec);
return arch_setup_msi_irqs(dev, nvec, type);
}
这里的irq_domain获取的是pcie device结构体中定义的dev->msi_domain.
这里的msi_domain是在哪里定义的呢?
在drivers/irqchip/irq-gic-v3-its-pci-msi.c中, kernel启动时会:
its_pci_msi_init()
+-> its_pci_msi_init()
+-> its_pci_msi_init_one()
+-> pci_msi_create_irq_domain(handle, &its_pci_msi_domain_info,parent)
pci_msi_create_irq_domain中会去创建pci_msi irq_domain, 传递的参数分别是its_pci_msi_domain_info以及设置parent为its irq_domain.
所以现在逻辑就比较清晰:
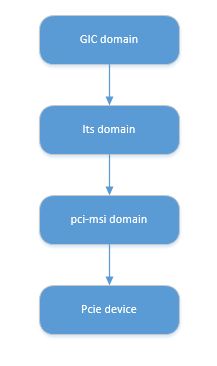
gic中断控制器初始化时会去add gic irq_domain, gic irq_domain是its irq_domain的parent节点,its irq_domain中的host data对应的pci_msi irq_domain.
gic irq_domain --> irq_domain_ops(gic_irq_domain_ops)
^ --> .alloc(gic_irq_domain_alloc)
|
its irq_domain --> irq_domain_ops(its_domain_ops)
^ --> .alloc(its_irq_domain_alloc)
| --> ...
| --> host_data(struct msi_domain_info)
| --> msi_domain_ops(its_msi_domain_ops)
| --> .msi_prepare(its_msi_prepare)
| --> irq_chip, chip_data, handler...
| --> void *data(struct its_node)
pci_msi irq_domain对应的ops:
static const struct irq_domain_ops msi_domain_ops = {
.alloc = msi_domain_alloc,
.free = msi_domain_free,
.activate = msi_domain_activate,
.deactivate = msi_domain_deactivate,
};
回到上面的pci_msi_setup_msi_irqs()函数,获取了pci_msi irq_domain后, 调用msi_domain_alloc_irqs()函数分配IRQ number.
msi_domain_alloc_irqs()
// 对应的是its_pci_msi_ops中的its_pci_msi_prepare
+-> msi_domain_prepare_irqs()
// 分配IRQ number
+-> __irq_domain_alloc_irqs()
msi_domain_prepare_irqs()对应的是its_msi_prepare函数,会去创建一个its_device.
__irq_domain_alloc_irqs()会去分配虚拟中断号,从allocated_irq位图中取第一个空闲的bit位作为虚拟中断号。
至此, msi-x的中断分配已经完成,且msi-x的配置也已经完成。
(2) 如果不是MSI-X中断, 再确认申请的是否为MSI中断, 流程与MSI-x类似。
(3) 如果不是MSI/MSI-X中断, 再确认申请的是否为传统intx中断
5.2 MSI的中断注册
kernel/irq/manage.c
request_irq()
+-> __setup_irq()
+-> irq_activate()
+-> msi_domain_activate()
// msi_domain_info中定义的irq_chip_write_msi_msg
+-> irq_chip_write_msi_msg()
// irq_chip对应的是pci_msi_create_irq_domain中关联的its_msi_irq_chip
+-> data->chip->irq_write_msi_msg(data, msg);
+-> pci_msi_domain_write_msg()
从这个流程可以看出,MSI是通过irq_write_msi_msg往一个地址发一个消息来激活一个中断。
参考资料
PCIe扫盲——中断机制介绍(MSI-X)
PCIe体系结构导读
MSI/MSI-X Capability结构
GIC ITS 学习笔记(一)
Documentation/PCI/MSI-HOWTO.txt