三菱PLC 串口通信开发心得经验
三菱PLC 串口通信开发心得
备注:
记得两年前刚开始从事软件开发工作时,第一份任务就是开发一个程序能够实现与三菱PLC 串口通信。所谓通信,其实质主要是对PLC 的D寄存器(dword)读写操作。但是因为日本为了保护其产品,并不开发串口通信协议。在不开发通信协议的情况,如果想实现通信,首先需要做的便是通过数据分析,破解其通信协议。
这里就不讲解如何破解了,主要是介绍下当时博主开发程序的背景。
写这篇博客的主要目的是为了分享过去自己的开发经验,因为自己在开发的过程中曾经接受过很多开源软件的帮助,也算是将开源精神延续下去吧
现在这是转入正题。
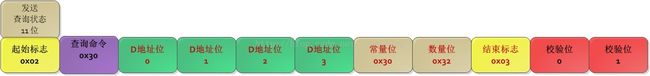
涉及字节流数据通信,必然要涉及通信协议。鉴于当时的开发需求,博主仅对D 寄存器的读写协议分析过。其他寄存器理论上是相似,有兴趣的同学可以自行分析数据进行测试。
D 寄存器的通信协议相对比较简单
主要可以分为:
1 问候应答协议
2 状态查询协议
3 状态配置协议
4 数据反馈协议
在PLC 通信过程中主要的三个难点在于 寄存器的加密解密, 数据信息加密和解密, 以及字符的校验。
寄存器地址 加密过程:
void PLC_dataparse::Encrypt_toPLCaddress( BYTE *parray , const UINT paddress )
{
int encode_address = 0x1000 + paddress * 2;
BYTE encrypt_key = encode_address & 0xf;
parray[3] = (encrypt_key<10) ? (encrypt_key + 0x30) : (encrypt_key + 0x41 - 0xa);
encrypt_key = (encode_address >> 4) & 0xf;
parray[2] = (encrypt_key<10) ? (encrypt_key + 0x30) : (encrypt_key + 0x41 - 0xa);
encrypt_key = (encode_address >> 8) & 0xf;
parray[1] = (encrypt_key<10) ? (encrypt_key + 0x30) : (encrypt_key + 0x41 - 0xa);
encrypt_key = (encode_address >> 12) & 0xf;
parray[0] = (encrypt_key<10) ? (encrypt_key + 0x30) : (encrypt_key + 0x41 - 0xa);
}
数据信息的加密过程:
void PLC_dataparse::Encrypt_toPLCcontent( BYTE * parray , const UINT pcontent )
{
BYTE encrypt_key = pcontent & 0xf;
parray[1] = (encrypt_key<10) ? (encrypt_key + 0x30) : (encrypt_key + 0x41 - 0xa);
encrypt_key = (pcontent >> 4) & 0xf;
parray[0] = (encrypt_key<10) ? (encrypt_key + 0x30) : (encrypt_key + 0x41 - 0xa);
encrypt_key = (pcontent >> 8) & 0xf;
parray[3] = (encrypt_key<10) ? (encrypt_key + 0x30) : (encrypt_key + 0x41 - 0xa);
encrypt_key = (pcontent >> 12) & 0xf;
parray[2] = (encrypt_key<10) ? (encrypt_key + 0x30) : (encrypt_key + 0x41 - 0xa);
}
添加校验码:
void PLC_dataparse::Add_checkcode( BYTE * pdest , BYTE * psrc , const UINT plenth )
{
int sumtemp = 0;
for ( unsigned int i = 0; i< plenth; i++)
{
sumtemp += (*(psrc + i));
}
BYTE encrypt_key = sumtemp & 0xf; // get low 4 bit
pdest[1] = (encrypt_key<10) ? (encrypt_key + 0x30) : (encrypt_key + 0x41 - 0xa);
encrypt_key = (sumtemp >> 4) & 0xf; // get high 4 bit
pdest[0] = (encrypt_key<10) ? (encrypt_key + 0x30) : (encrypt_key + 0x41 - 0xa);
}
提取数据信息:
double PLC_dataparse::Get_content( BYTE *parray , UINT plenth )
{
BYTE dl_data[4];
BYTE pre_data[4];
double pow_numb;
for (int j = 0; j<4; j++) //剔除杂码
{
pre_data[j] = parray[j + 1];
}
//
dl_data[1] = (pre_data[0]<0x40) ? (pre_data[0] - 0x30) : (pre_data[0] - 0x41 + 0x0a);
dl_data[0] = (pre_data[1]<0x40) ? (pre_data[1] - 0x30) : (pre_data[1] - 0x41 + 0x0a);
dl_data[3] = (pre_data[2]<0x40) ? (pre_data[2] - 0x30) : (pre_data[2] - 0x41 + 0x0a);
dl_data[2] = (pre_data[3]<0x40) ? (pre_data[3] - 0x30) : (pre_data[3] - 0x41 + 0x0a);
for (int i = 0; i<4; i++)
{
dl_data[i] = dl_data[i] & 0xf;
}
pow_numb = dl_data[3] * pow(16.0, 3.0) + dl_data[2] * pow(16.0, 2.0) + dl_data[1] * 16 + dl_data[0];
return pow_numb;
}
校验接受数据校验码:
int PLC_dataparse::Check_checkcode( BYTE *parray , UINT plenth )
{
int error_code = PLC_SUCCESS;
const int legal_lenth = 8; //the define legal lenth
if (plenth != legal_lenth)
{
error_code = PLC_CRCERROR;
return error_code;
}
//
//check code
else
{
BYTE *pbyte = new BYTE[2];
// split out head mark , tail check out
Add_checkcode(&pbyte[0], &parray[1], plenth - 3); //calculate the check code
for (int j = 0; j<2; j++)
{
if (pbyte[j] != parray[plenth - 2 + j])
{
error_code = PLC_CRCERROR;
break;
}
}
// release the pointer and it's stack
delete pbyte;
pbyte = NULL;
return error_code;
}
}
上述代码是使用PLC 窗口通信的最大的难点。 一旦掌握几大难点,基本PLC 的串口通信就
另附上一份当时自己开发的 三菱PLC D寄存器调试程序。
备注: 该调试工具 仅支持xp 系统
欢迎关注我的github: https://github.com/lionm117
一起学习,共同成长
测试程序下载链接:http://download.csdn.net/detail/hesiyuan4/8304407
动态链接库下载链接: http://download.csdn.net/detail/hesiyuan4/8394939
源码库下载链接: http://download.csdn.net/detail/hesiyuan4/8394961