Spring Boot统一异常处理以及参数校验
Spring Boot统一异常处理以及参数校验
参数自动校验
一般情况我们前端向后端传递参数都是2种方式 JSON或者表单提交
因此本文分别讲述JSON提交参数校验和表单提交参数校验在Spring Boot中是如何操作,以及校验失败如何统一转交给异常处理类去处理的。
Api设计如下:
表单方式: http://localhost:8080/get-args-valid?username=xxx&password=xxx
JSON方式: http://localhost:8080/post-args-valid
{
"username":"123",
"password":"123"
}
采用JSON方式提交,所以设置content-type如下:
Content-Type: application/json
新建一个Spring Boot项目
Api如下设计:
/**
* @author: hujiansong
* @email: [email protected]
* @since: 2019/1/29 16:53
*/
@RestController
public class ValidController {
@GetMapping("/get-args-valid")
public String getArgsValid(String username, String password) {
return null;
}
@PostMapping("/post-args-valid")
public String postArgsValid(@RequestBody User user) {
return null;
}
@Data
class User {
String username;
String password;
}
}
先讲JSON方式如何进行参数校验
JSON方式:
@RestController
public class ValidController {
@PostMapping("/post-args-valid")
public String postArgsValid(@Valid<1> @RequestBody User user) {
return null;
}
@Data
static class User {
@NotNull(message = "用户名不能为空")<2>
String username;
@NotNull(message = "密码不能为空")
String password;
}
}
注意: 这里内部类
User需要加上static,否则json传过来无法解析
<1>: @Valid表示这个实体参数交给Spring去校验
<2>: @NotNull校验规则
如上2步操作就可以完成参数校验:
可以看到如何password不传递,spring 已经帮我们做了参数校验,再来看看表单方式
表单方式:
@RestController
@Validated<1>
public class ValidController {
@GetMapping("/get-args-valid")
public String getArgsValid(@NotNull(message = "用户名不能空")<2> String username, @NotNull(message = "密码不能为空") String password) {
return null;
}
}
同样也是2步搞定
<1>: @Validated,交给Spring去校验
<2>: @NotNull校验规则
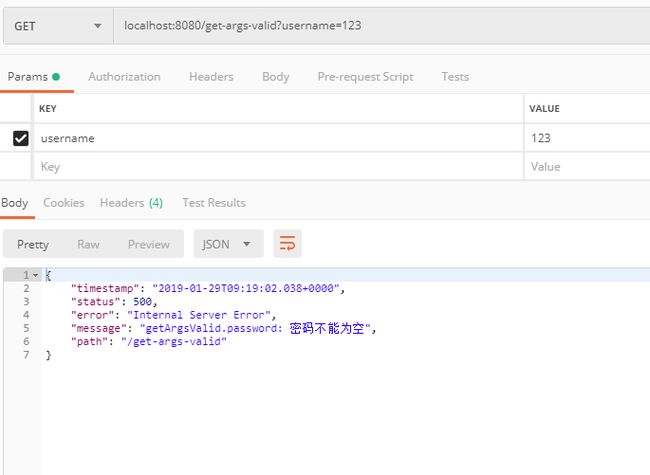
看看如果password不传递会返回什么:
可见,Spring已经替我们做了参数校验
Spring 还包含了很多校验规则如下:
| 注解 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| @Null | 被注释的元素必须为 null |
| @NotNull | 被注释的元素必须不为 null |
| @AssertTrue | 被注释的元素必须为 true |
| @AssertFalse | 被注释的元素必须为 false |
| @Min(value) | 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须大于等于指定的最小值 |
| @Max(value) | 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须小于等于指定的最大值 |
| @DecimalMin | 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须大于等于指定的最小值 |
| @DecimalMax | 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须小于等于指定的最大值 |
| @Size(max=, min=) | 被注释的元素的大小必须在指定的范围内 |
| @Digits | 被注释的元素必须是一个数字,其值必须在可接受的范围内 |
| @Past | 被注释的元素必须是一个过去的日期 |
| @Future | 被注释的元素必须是一个将来的日期 |
| @Pattern(regex=) | 被注释的元素必须符合指定的正则表达式 |
异常统一处理
上面介绍了如何让Spring校验我们的参数,那么可以看到JSON方式校验返回的结果一大串,不是十分优雅。那么利用统一异常处理则可优雅返回参数校验结果。
JSON方式:校验失败后,会抛出一个 MethodArgumentNotValidException
表单方式:校验失败,会抛出一个ConstraintViolationException
因此只需要在统一异常处理类里面处理这2个异常即可。
ExceptionHanlder
表单方式:
@RestControllerAdvice
public class ExceptionHandler {
@org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler(ConstraintViolationException.class)
public Map<String, Object> methodArgNotValidException(ConstraintViolationException cve, HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest) {
Set<ConstraintViolation<?>> cves = cve.getConstraintViolations();
StringBuffer errorMsg = new StringBuffer();
cves.forEach(ex -> errorMsg.append(ex.getMessage()));
Map<String, Object> respMap = new HashMap<>(4);
respMap.put("code", -1);
respMap.put("msg", errorMsg);
return respMap;
}
}
重新调用:
JSON方式:
@RestControllerAdvice
public class ExceptionHandler {
@org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler({MethodArgumentNotValidException.class})
public Map<String, Object> methodDtoNotValidException(Exception ex, HttpServletRequest request) {
MethodArgumentNotValidException c = (MethodArgumentNotValidException) ex;
List<ObjectError> errors = c.getBindingResult().getAllErrors();
StringBuffer errorMsg = new StringBuffer();
errors.stream().forEach(x -> {
errorMsg.append(x.getDefaultMessage()).append(";");
});
Map<String, Object> respMap = new HashMap<>(4);
respMap.put("code", -1);
respMap.put("msg", errorMsg);
return respMap;
}
}
同样调用,这次username为空试试看:
完整的代码