There are lots of tutorials about promise in the internet.
Recently I am studying the frontend code of SAP Cloud for Customer and I come across a real example of how promise is used there.
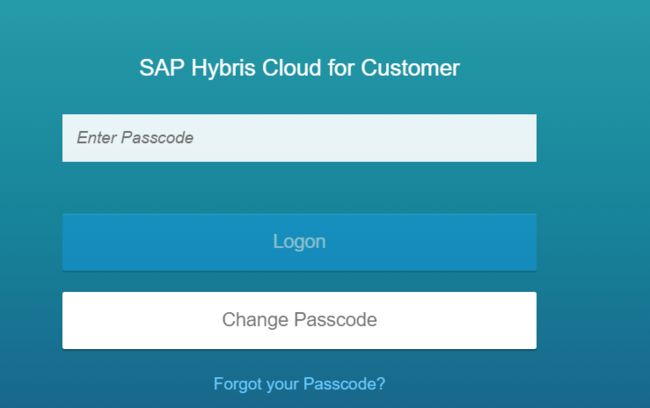
Below is the Passcode logon view.
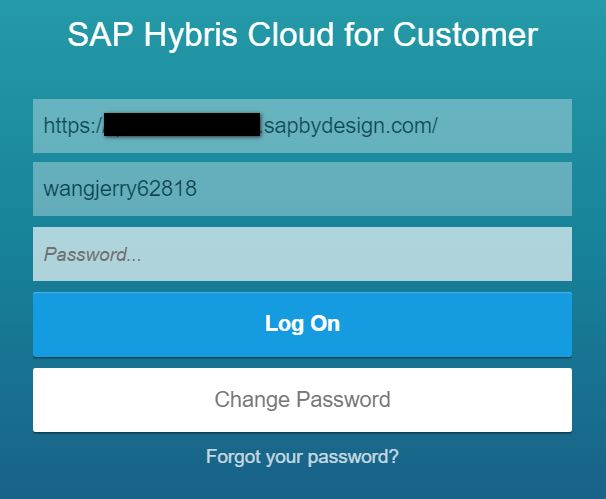
Once Passcode is entered, suppose I have already entered the system url and frontend user name in the past, they will be directly retrieved from browser storage.
Currently I use Chrome to access C4C and Web SQL is used as browser storage, where the system url and logon user name could be found from Chrome development tool.
The corresponding database initialization and table read is done by code below in file AppStatusService.js.
The series of callback functions are chained by promise API “then()” which are expected to be executed sequentially:
(1) _createTable() could only be executed after database initialization is done.
(2) _getApplicationStatus could NOT be executed unless the database table which stores Application status is available – this is ensured by _createTable.
(3) After application status is read from database table, _createDefaultEntries could be called to render the default value in Passcode logon view.
All above three steps are organized by promise to achieve the asynchronous execution mode.
In order for me to understand how the above code works, I write a simplified version for illustration:
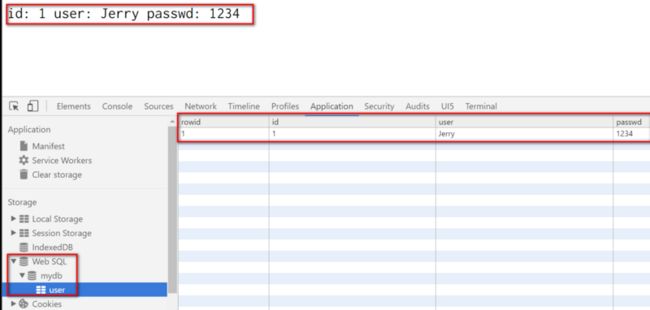
Open the html page with Chrome, and you can find that a database with name mydb and a table user is created with one record inserted.
In order to achieve the simulation that each step of webSQL is a time-consuming operation, I wrap the real logic into setTimeout with a certain time delay.
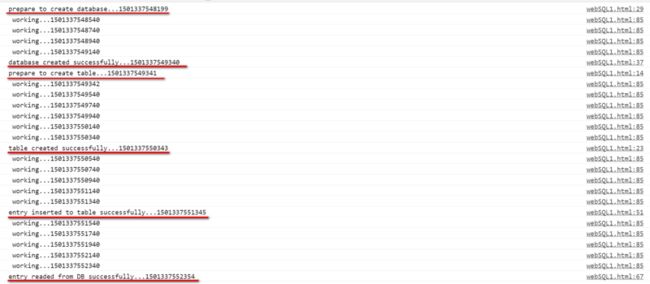
I scheduled function work to simulate the main work to do and the database related job are done in an asynchronous way organized within function module setupDB() by promise API.
The console output proves that the database operations are really executed asynchronously in exactly the same order as they are scheduled via then API of promise.
Note
Not all browsers support WebSQL and the specification of WebSQL is no longer in active maintenance.
Even in C4C frontend framework code we can see more and more usage on IndexedDB instead:
See the comparison on these two techniques from this link Migrating your WebSQL DB to IndexedDB.
要获取更多Jerry的原创文章,请关注公众号"汪子熙":![]()