- SpringBlade dict-biz/list 接口 SQL 注入漏洞
文章永久免费只为良心
oracle数据库
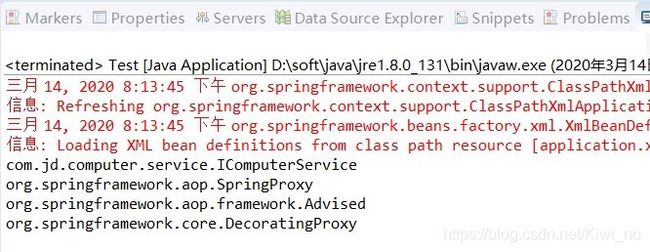
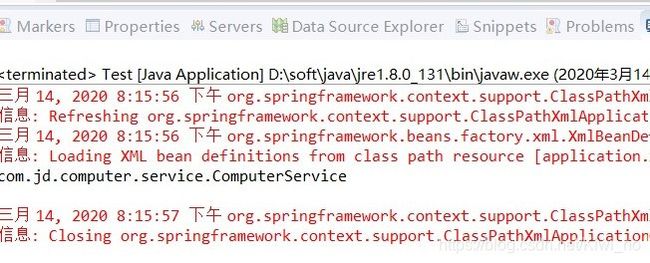
SpringBladedict-biz/list接口SQL注入漏洞POC:构造请求包查看返回包你的网址/api/blade-system/dict-biz/list?updatexml(1,concat(0x7e,md5(1),0x7e),1)=1漏洞概述在SpringBlade框架中,如果dict-biz/list接口的后台处理逻辑没有正确地对用户输入进行过滤或参数化查询(PreparedSta
- spring如何整合druid连接池?
惜.己
springspringjunit数据库javaidea后端xml
目录spring整合druid连接池1.新建maven项目2.新建mavenModule3.导入相关依赖4.配置log4j2.xml5.配置druid.xml1)xml中如何引入properties2)下面是配置文件6.准备jdbc.propertiesJDBC配置项解释7.配置druid8.测试spring整合druid连接池1.新建maven项目打开IDE(比如IntelliJIDEA,Ecl
- SpringCloudAlibaba—Sentinel(限流)
菜鸟爪哇
前言:自己在学习过程的记录,借鉴别人文章,记录自己实现的步骤。借鉴文章:https://blog.csdn.net/u014494148/article/details/105484410Sentinel介绍Sentinel诞生于阿里巴巴,其主要目标是流量控制和服务熔断。Sentinel是通过限制并发线程的数量(即信号隔离)来减少不稳定资源的影响,而不是使用线程池,省去了线程切换的性能开销。当资源
- springboot+vue项目实战一-创建SpringBoot简单项目
苹果酱0567
面试题汇总与解析springboot后端java中间件开发语言
这段时间抽空给女朋友搭建一个个人博客,想着记录一下建站的过程,就当做笔记吧。虽然复制zjblog只要一个小时就可以搞定一个网站,或者用cms系统,三四个小时就可以做出一个前后台都有的网站,而且想做成啥样也都行。但是就是要从新做,自己做的意义不一样,更何况,俺就是专门干这个的,嘿嘿嘿要做一个网站,而且从零开始,首先呢就是技术选型了,经过一番思量决定选择-SpringBoot做后端,前端使用Vue做一
- Spring MVC 全面指南:从入门到精通的详细解析
一杯梅子酱
技术栈学习springmvcjava
引言:SpringMVC,作为Spring框架的一个重要模块,为构建Web应用提供了强大的功能和灵活性。无论是初学者还是有一定经验的开发者,掌握SpringMVC都将显著提升你的Web开发技能。本文旨在为初学者提供一个全面且易于理解的学习路径,通过详细的知识点分析和实际案例,帮助你快速上手SpringMVC,让学习过程既深刻又高效。一、SpringMVC简介1.1什么是SpringMVC?Spri
- Spring Boot中实现跨域请求
BABA8891
springboot后端java
在SpringBoot中实现跨域请求(CORS,Cross-OriginResourceSharing)可以通过多种方式,以下是几种常见的方法:1.使用@CrossOrigin注解在SpringBoot中,你可以在控制器或者具体的请求处理方法上使用@CrossOrigin注解来允许跨域请求。在控制器上应用:importorg.springframework.web.bind.annotation.
- 博客网站制作教程
2401_85194651
javamaven
首先就是技术框架:后端:Java+SpringBoot数据库:MySQL前端:Vue.js数据库连接:JPA(JavaPersistenceAPI)1.项目结构blog-app/├──backend/│├──src/main/java/com/example/blogapp/││├──BlogApplication.java││├──config/│││└──DatabaseConfig.java
- RabbitMQ生产者重复机制与确认机制
java炒饭小能手
java-rabbitmqrabbitmqjava
重复机制生产者发送消息时,出现了网络故障,导致与MQ的连接中断。为了解决这个问题,SpringAMQP提供的消息发送时的重试机制。即:当RabbitTemplate与MQ连接超时后,多次重试。需要修该发送端模块的application.yaml文件,添加下面的内容:spring:rabbitmq:connection-timeout:1s#设置MQ的连接超时时间template:retry:ena
- 【Java】已解决:org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.lookup.DataSourceLookupFailureException
屿小夏
java开发语言
文章目录一、分析问题背景问题背景描述出现问题的场景二、可能出错的原因三、错误代码示例四、正确代码示例五、注意事项已解决:org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.lookup.DataSourceLookupFailureException在使用Spring框架进行开发时,数据源的配置和使用是非常关键的一环。然而,有时候我们可能会遇到org.springframewo
- SpringBoot和SpringMVC是什么关系?SpringBoot替代SpringMVC了吗?
瑞金彭于晏
springboot后端javaMVCspring数据库
SpringBoot和SpringMVC都是SpringFramework生态系统中的一部分,但它们各自扮演着不同的角色和提供不同的功能集。理解它们之间的关系,首先需要了解SpringFramework本身。SpringFrameworkSpringFramework是一个全面的、开源的应用程序开发框架,它提供了广泛的功能来支持企业应用开发的几乎所有方面。SpringFramework的核心特性之
- spring mvc @RequestBody String类型参数
zoyation
spring-mvcspringmvc
通过如下配置:text/html;charset=UTF-8application/json;charset=UTF-8在springmvc的Controller层使用@RequestBody接收Content-Type为application/json的数据时,默认支持Map方式和对象方式参数@RequestMapping(value="/{code}/saveUser",method=Requ
- Java -jar 如何在后台运行项目
vincent_hahaha
撸了今年阿里、头条和美团的面试,我有一个重要发现.......>>>说到运行jar包通常我们都会以下面的方式运行:java-jarspringboot-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar这样运行的话会有一个问题,就是我们一关闭当前窗口就会停止运行项目,要想解决这个问题,就需要在后台运行。nohupjava-jarbabyshark-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar >log.file 2>&
- spring security中几大组件的作用和执行顺序
阿信在这里
javaspring
springsecurity中几大组件的作用和执行顺序在SpringSecurity中,AuthenticationProvider、GroupPermissionEvaluator、PermissionEvaluator、AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter、DefaultMethodSecurityExpressionHandler和ManageSecu
- 探索Zebra4J:构建高效企业级Web应用的微服务框架
叶准鑫Natalie
探索Zebra4J:构建高效企业级Web应用的微服务框架ZebraZebra4J/Zebra4Js基于SpringBoot的JavaWeb/Nodejs框架项目地址:https://gitcode.com/gh_mirrors/zebra/Zebra项目介绍在当今快速发展的技术环境中,构建高效、可扩展的企业级Web应用是每个开发团队的追求。Zebra4J作为一款基于SpringBoot的全新微服务
- 基于JavaWeb开发的Java+SpringMvc+vue+element实现上海汽车博物馆平台
网顺技术团队
成品程序项目javavue.js汽车课程设计springboot
基于JavaWeb开发的Java+SpringMvc+vue+element实现上海汽车博物馆平台作者主页网顺技术团队欢迎点赞收藏⭐留言文末获取源码联系方式查看下方微信号获取联系方式承接各种定制系统精彩系列推荐精彩专栏推荐订阅不然下次找不到哟Java毕设项目精品实战案例《1000套》感兴趣的可以先收藏起来,还有大家在毕设选题,项目以及论文编写等相关问题都可以给我留言咨询,希望帮助更多的人文章目录基
- 分布式锁和spring事务管理
暴躁的鱼
锁及事务分布式springjava
最近开发一个小程序遇到一个需求需要实现分布式事务管理业务需求用户在使用小程序的过程中可以查看景点,对景点地区或者城市标记是否想去,那么需要统计一个地点被标记的人数,以及记录某个用户对某个地点是否标记为想去,用两个表存储数据,一个地点表记录改地点被标记的次数,一个用户意向表记录某个用户对某个地点是否标记为想去。由于可能有多个用户同时标记一个地点,每个用户在前端点击想去按钮之后,后台接收到请求,从数据
- Java面试笔记记录6
今天背八股了吗
java面试笔记
1.Spring是什么?特性?有哪些模块?Spring是一个轻量级、非入侵式的控制反转Ioc和面向切面AOP的框架。特性:1.Ioc和DISpring的核心就是一个大的工厂容器,可以维护所有对象的创建和依赖关系,Spring工厂用于生成Bean,并且管理Bean的生命周期,实现高内聚低耦合的设计理念。2.AOP编程Spring提供面向切面编程,可以方便实现对程序进行权限拦截、运行监控等切面功能。3
- Sentinel
眼泪落在琴弦
springcloudjavajava
Sentinel(服务熔断降级限流)1.引入spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinel2.下载sentinel服务器3.配置application地址信息4.在控制台调整参数【默认所以流控设置保存在内存中,重启失效】5.想实时监控需每个微服务导入actuator,并配置application暴露所有端口6.自定义sentinel流控返回数据7.配置sentinel类
- Spring @Async 深度解读:默认线程池执行器的配置与优化
小码快撩
springjava前端
在Spring中,@Async注解用于异步执行方法。默认情况下,@Async注解的任务是由一个线程池执行的。然而,这个默认的线程池是如何初始化的呢?本文将深入探讨这一过程,帮助你理解Spring异步任务背后的线程池执行器的初始化原理。1.@Async的基本使用首先,让我们快速回顾一下@Async的基本用法。@Async通常用于标注在需要异步执行的方法上,比如:@Servicepublicclass
- Sentinel实时监控不展示问题
朱杰jjj
sentinelsentinel
问题官方插件Endpoint支持,可以实时统计出SpringBoot的健康状况和请求的调用信息在使用Endpoint特性之前需要在Maven中添加spring-boot-starter-actuator依赖,并在配置中允许Endpoints的访问。SpringBoot1.x中添加配置management.security.enabled=false。暴露的endpoint路径为/sentinelS
- 36. MyBatis如何支持多数据库操作?如何配置不同的数据源?
这孩子叫逆
Mybatis笔记mybatis数据库
在许多企业级应用中,可能需要访问多个数据库。MyBatis可以通过配置多个数据源和动态切换数据源来支持多数据库操作。下面介绍如何在MyBatis中配置和使用多个数据源。1.多数据源的基本配置1.1配置多个数据源要支持多个数据源,首先需要在Spring或SpringBoot中配置不同的数据源。假设我们要连接两个数据库db1和db2,可以通过以下步骤进行配置。SpringBoot示例:applicat
- SpringBoot整合ES搜索引擎 实现网站热搜词及热度计算
码踏云端
springbootElasticsearchspringbootelasticsearch后端热搜词热度计算java
博主简介:历代文学网(PC端可以访问:https://literature.sinhy.com/#/literature?__c=1000,移动端可微信小程序搜索“历代文学”)总架构师,15年工作经验,精通Java编程,高并发设计,Springboot和微服务,熟悉Linux,ESXI虚拟化以及云原生Docker和K8s,热衷于探索科技的边界,并将理论知识转化为实际应用。保持对新技术的好奇心,乐于
- Spring Security静态资源过滤(11)
小黑屋说YYDS
spring
在一个实际项目中,并非所有的请求都需要经过SpringSecurity过滤器,有一些特殊的请求,例如静态资源等,一般来说并不需要经过SpringSecurity过滤器链,用户如果访问这些静态资源,直接返回对应的资源即可。回顾关于WebSecurity的讲解,提到它里边维护了一个ignoredRequests变量,该变量,记录的就是所有需要被忽略的请求,这些被忽略的请求将不再经过SpringSecu
- Spring Security定义多个过滤器链(10)
小黑屋说YYDS
spring
在SpringSecurity中可以同时存在多个过滤器链,一个WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter的实例就可以配置一条过滤器链。我们来看如下一个案例:@ConfigurationpublicclassSecurityConfig{@BeanUserDetailsServiceus(){InMemoryUserDetailsManagerusers=newInMemoryUser
- java 技术 架构 相关文档
圣心
java架构开发语言
在Java中,有许多不同的技术和架构,这里我将列举一些常见的Java技术和架构,并提供一些相关的文档资源。SpringFrameworkSpring是一个开源的Java/JavaEE全功能框架,以Apache许可证形式发布,提供了一种实现企业级应用的方法。官方文档:SpringFrameworkSpringBootSpringBoot是Spring的一个子项目,旨在简化创建生产级的Spring应用
- SpringSecurity初学总结
weixin_66442229
spring
springSecurity安全框架基于Java的安全框架主要有:SpringSecurity和Shiro介绍基础概念安全框架是对用户访问权限的控制,保证应用的安全性。其主要的工作是用户认证和用户授权|鉴权主要应用于Spring的企业应用系统,提供声明式的安全访问控制解决方案。它提供了一组可以在Spring应用上下文中配置的Bean能很好的结合Spring的DI依赖注入和AOP面向切面编程功能应用
- java获取applicationcontext,SpringBoot获取ApplicationContext的3种方式
花儿街参考
ApplicationContext是什么?简单来说就是Spring中的容器,可以用来获取容器中的各种bean组件,注册监听事件,加载资源文件等功能。ApplicationContext获取的几种方式1直接使用Autowired注入@ComponentpublicclassBook1{@AutowiredprivateApplicationContextapplicationContext;pub
- SpringBoot 设置传入参数非必要
loveLifeLoveCoding
springbootspringbootjavaspring
查看RequestParam源码packageorg.springframework.web.bind.annotation;importjava.lang.annotation.Documented;importjava.lang.annotation.ElementType;importjava.lang.annotation.Retention;importjava.lang.annotat
- SpringBoot 获取 ApplicationContext
loveLifeLoveCoding
springbootspringbootjavaspring
1.概念ApplicationContext是什么?简单来说就是Spring中的容器,可以用来获取容器中的各种bean组件,注册监听事件,加载资源文件等功能2.获取ApplicationContext的方式2.1.创建工具类通过此工具类,可以方便的获取bean组件,获取配置信息等importorg.springframework.beans.BeansException;importorg.spr
- java打印标签(机型TOSHIBA条码打印机B-EX4T)
嘘
JAVAjava
java打印标签实现方式标签效果代码获取更多相关资料实现rfid写入功能实现方式打印机设置网络ipjava获取socket连接,调用TPCL指令标签效果代码packageorg.jeecg.modules.invinfo.util;importorg.jeecg.modules.invinfo.vo.BatKcInventoryDetailVo;importorg.springframework.
- java的(PO,VO,TO,BO,DAO,POJO)
Cb123456
VOTOBOPOJODAO
转:
http://www.cnblogs.com/yxnchinahlj/archive/2012/02/24/2366110.html
-------------------------------------------------------------------
O/R Mapping 是 Object Relational Mapping(对象关系映
- spring ioc原理(看完后大家可以自己写一个spring)
aijuans
spring
最近,买了本Spring入门书:spring In Action 。大致浏览了下感觉还不错。就是入门了点。Manning的书还是不错的,我虽然不像哪些只看Manning书的人那样专注于Manning,但怀着崇敬 的心情和激情通览了一遍。又一次接受了IOC 、DI、AOP等Spring核心概念。 先就IOC和DI谈一点我的看法。IO
- MyEclipse 2014中Customize Persperctive设置无效的解决方法
Kai_Ge
MyEclipse2014
高高兴兴下载个MyEclipse2014,发现工具条上多了个手机开发的按钮,心生不爽就想弄掉他!
结果发现Customize Persperctive失效!!
有说更新下就好了,可是国内Myeclipse访问不了,何谈更新...
so~这里提供了更新后的一下jar包,给大家使用!
1、将9个jar复制到myeclipse安装目录\plugins中
2、删除和这9个jar同包名但是版本号较
- SpringMvc上传
120153216
springMVC
@RequestMapping(value = WebUrlConstant.UPLOADFILE)
@ResponseBody
public Map<String, Object> uploadFile(HttpServletRequest request,HttpServletResponse httpresponse) {
try {
//
- Javascript----HTML DOM 事件
何必如此
JavaScripthtmlWeb
HTML DOM 事件允许Javascript在HTML文档元素中注册不同事件处理程序。
事件通常与函数结合使用,函数不会在事件发生前被执行!
注:DOM: 指明使用的 DOM 属性级别。
1.鼠标事件
属性
- 动态绑定和删除onclick事件
357029540
JavaScriptjquery
因为对JQUERY和JS的动态绑定事件的不熟悉,今天花了好久的时间才把动态绑定和删除onclick事件搞定!现在分享下我的过程。
在我的查询页面,我将我的onclick事件绑定到了tr标签上同时传入当前行(this值)参数,这样可以在点击行上的任意地方时可以选中checkbox,但是在我的某一列上也有一个onclick事件是用于下载附件的,当
- HttpClient|HttpClient请求详解
7454103
apache应用服务器网络协议网络应用Security
HttpClient 是 Apache Jakarta Common 下的子项目,可以用来提供高效的、最新的、功能丰富的支持 HTTP 协议的客户端编程工具包,并且它支持 HTTP 协议最新的版本和建议。本文首先介绍 HTTPClient,然后根据作者实际工作经验给出了一些常见问题的解决方法。HTTP 协议可能是现在 Internet 上使用得最多、最重要的协议了,越来越多的 Java 应用程序需
- 递归 逐层统计树形结构数据
darkranger
数据结构
将集合递归获取树形结构:
/**
*
* 递归获取数据
* @param alist:所有分类
* @param subjname:对应统计的项目名称
* @param pk:对应项目主键
* @param reportList: 最后统计的结果集
* @param count:项目级别
*/
public void getReportVO(Arr
- 访问WEB-INF下使用frameset标签页面出错的原因
aijuans
struts2
<frameset rows="61,*,24" cols="*" framespacing="0" frameborder="no" border="0">
- MAVEN常用命令
avords
Maven库:
http://repo2.maven.org/maven2/
Maven依赖查询:
http://mvnrepository.com/
Maven常用命令: 1. 创建Maven的普通java项目: mvn archetype:create -DgroupId=packageName
- PHP如果自带一个小型的web服务器就好了
houxinyou
apache应用服务器WebPHP脚本
最近单位用PHP做网站,感觉PHP挺好的,不过有一些地方不太习惯,比如,环境搭建。PHP本身就是一个网站后台脚本,但用PHP做程序时还要下载apache,配置起来也不太很方便,虽然有好多配置好的apache+php+mysq的环境,但用起来总是心里不太舒服,因为我要的只是一个开发环境,如果是真实的运行环境,下个apahe也无所谓,但只是一个开发环境,总有一种杀鸡用牛刀的感觉。如果php自己的程序中
- NoSQL数据库之Redis数据库管理(list类型)
bijian1013
redis数据库NoSQL
3.list类型及操作
List是一个链表结构,主要功能是push、pop、获取一个范围的所有值等等,操作key理解为链表的名字。Redis的list类型其实就是一个每个子元素都是string类型的双向链表。我们可以通过push、pop操作从链表的头部或者尾部添加删除元素,这样list既可以作为栈,又可以作为队列。
&nbs
- 谁在用Hadoop?
bingyingao
hadoop数据挖掘公司应用场景
Hadoop技术的应用已经十分广泛了,而我是最近才开始对它有所了解,它在大数据领域的出色表现也让我产生了兴趣。浏览了他的官网,其中有一个页面专门介绍目前世界上有哪些公司在用Hadoop,这些公司涵盖各行各业,不乏一些大公司如alibaba,ebay,amazon,google,facebook,adobe等,主要用于日志分析、数据挖掘、机器学习、构建索引、业务报表等场景,这更加激发了学习它的热情。
- 【Spark七十六】Spark计算结果存到MySQL
bit1129
mysql
package spark.examples.db
import java.sql.{PreparedStatement, Connection, DriverManager}
import com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
import org.apache.spark.{SparkContext, SparkConf}
object SparkMySQLInteg
- Scala: JVM上的函数编程
bookjovi
scalaerlanghaskell
说Scala是JVM上的函数编程一点也不为过,Scala把面向对象和函数型编程这两种主流编程范式结合了起来,对于熟悉各种编程范式的人而言Scala并没有带来太多革新的编程思想,scala主要的有点在于Java庞大的package优势,这样也就弥补了JVM平台上函数型编程的缺失,MS家.net上已经有了F#,JVM怎么能不跟上呢?
对本人而言
- jar打成exe
bro_feng
java jar exe
今天要把jar包打成exe,jsmooth和exe4j都用了。
遇见几个问题。记录一下。
两个软件都很好使,网上都有图片教程,都挺不错。
首先肯定是要用自己的jre的,不然不能通用,其次别忘了把需要的lib放到classPath中。
困扰我很久的一个问题是,我自己打包成功后,在一个同事的没有装jdk的电脑上运行,就是不行,报错jvm.dll为无效的windows映像,如截图
最后发现
- 读《研磨设计模式》-代码笔记-策略模式-Strategy
bylijinnan
java设计模式
声明: 本文只为方便我个人查阅和理解,详细的分析以及源代码请移步 原作者的博客http://chjavach.iteye.com/
/*
策略模式定义了一系列的算法,并将每一个算法封装起来,而且使它们还可以相互替换。策略模式让算法独立于使用它的客户而独立变化
简单理解:
1、将不同的策略提炼出一个共同接口。这是容易的,因为不同的策略,只是算法不同,需要传递的参数
- cmd命令值cvfM命令
chenyu19891124
cmd
cmd命令还真是强大啊。今天发现jar -cvfM aa.rar @aaalist 就这行命令可以根据aaalist取出相应的文件
例如:
在d:\workspace\prpall\test.java 有这样一个文件,现在想要将这个文件打成一个包。运行如下命令即可比如在d:\wor
- OpenJWeb(1.8) Java Web应用快速开发平台
comsci
java框架Web项目管理企业应用
OpenJWeb(1.8) Java Web应用快速开发平台的作者是我们技术联盟的成员,他最近推出了新版本的快速应用开发平台 OpenJWeb(1.8),我帮他做做宣传
OpenJWeb快速开发平台以快速开发为核心,整合先进的java 开源框架,本着自主开发+应用集成相结合的原则,旨在为政府、企事业单位、软件公司等平台用户提供一个架构透
- Python 报错:IndentationError: unexpected indent
daizj
pythontab空格缩进
IndentationError: unexpected indent 是缩进的问题,也有可能是tab和空格混用啦
Python开发者有意让违反了缩进规则的程序不能通过编译,以此来强制程序员养成良好的编程习惯。并且在Python语言里,缩进而非花括号或者某种关键字,被用于表示语句块的开始和退出。增加缩进表示语句块的开
- HttpClient 超时设置
dongwei_6688
httpclient
HttpClient中的超时设置包含两个部分:
1. 建立连接超时,是指在httpclient客户端和服务器端建立连接过程中允许的最大等待时间
2. 读取数据超时,是指在建立连接后,等待读取服务器端的响应数据时允许的最大等待时间
在HttpClient 4.x中如下设置:
HttpClient httpclient = new DefaultHttpC
- 小鱼与波浪
dcj3sjt126com
一条小鱼游出水面看蓝天,偶然间遇到了波浪。 小鱼便与波浪在海面上游戏,随着波浪上下起伏、汹涌前进。 小鱼在波浪里兴奋得大叫:“你每天都过着这么刺激的生活吗?简直太棒了。” 波浪说:“岂只每天过这样的生活,几乎每一刻都这么刺激!还有更刺激的,要有潮汐变化,或者狂风暴雨,那才是兴奋得心脏都会跳出来。” 小鱼说:“真希望我也能变成一个波浪,每天随着风雨、潮汐流动,不知道有多么好!” 很快,小鱼
- Error Code: 1175 You are using safe update mode and you tried to update a table
dcj3sjt126com
mysql
快速高效用:SET SQL_SAFE_UPDATES = 0;下面的就不要看了!
今日用MySQL Workbench进行数据库的管理更新时,执行一个更新的语句碰到以下错误提示:
Error Code: 1175
You are using safe update mode and you tried to update a table without a WHERE that
- 枚举类型详细介绍及方法定义
gaomysion
enumjavaee
转发
http://developer.51cto.com/art/201107/275031.htm
枚举其实就是一种类型,跟int, char 这种差不多,就是定义变量时限制输入的,你只能够赋enum里面规定的值。建议大家可以看看,这两篇文章,《java枚举类型入门》和《C++的中的结构体和枚举》,供大家参考。
枚举类型是JDK5.0的新特征。Sun引进了一个全新的关键字enum
- Merge Sorted Array
hcx2013
array
Given two sorted integer arrays nums1 and nums2, merge nums2 into nums1 as one sorted array.
Note:You may assume that nums1 has enough space (size that is
- Expression Language 3.0新特性
jinnianshilongnian
el 3.0
Expression Language 3.0表达式语言规范最终版从2013-4-29发布到现在已经非常久的时间了;目前如Tomcat 8、Jetty 9、GlasshFish 4已经支持EL 3.0。新特性包括:如字符串拼接操作符、赋值、分号操作符、对象方法调用、Lambda表达式、静态字段/方法调用、构造器调用、Java8集合操作。目前Glassfish 4/Jetty实现最好,对大多数新特性
- 超越算法来看待个性化推荐
liyonghui160com
超越算法来看待个性化推荐
一提到个性化推荐,大家一般会想到协同过滤、文本相似等推荐算法,或是更高阶的模型推荐算法,百度的张栋说过,推荐40%取决于UI、30%取决于数据、20%取决于背景知识,虽然本人不是很认同这种比例,但推荐系统中,推荐算法起的作用起的作用是非常有限的。
就像任何
- 写给Javascript初学者的小小建议
pda158
JavaScript
一般初学JavaScript的时候最头痛的就是浏览器兼容问题。在Firefox下面好好的代码放到IE就不能显示了,又或者是在IE能正常显示的代码在firefox又报错了。 如果你正初学JavaScript并有着一样的处境的话建议你:初学JavaScript的时候无视DOM和BOM的兼容性,将更多的时间花在 了解语言本身(ECMAScript)。只在特定浏览器编写代码(Chrome/Fi
- Java 枚举
ShihLei
javaenum枚举
注:文章内容大量借鉴使用网上的资料,可惜没有记录参考地址,只能再传对作者说声抱歉并表示感谢!
一 基础 1)语法
枚举类型只能有私有构造器(这样做可以保证客户代码没有办法新建一个enum的实例)
枚举实例必须最先定义
2)特性
&nb
- Java SE 6 HotSpot虚拟机的垃圾回收机制
uuhorse
javaHotSpotGC垃圾回收VM
官方资料,关于Java SE 6 HotSpot虚拟机的garbage Collection,非常全,英文。
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/gc-tuning-6-140523.html
Java SE 6 HotSpot[tm] Virtual Machine Garbage Collection Tuning
&