HDLbits答案更新系列14(3.2.5 Finite State Machines 3.2.5.14 One-hot FSM等)
目录
前言
3.2.5 Finite State Machines
3.2.5.14 One-hot FSM(Fsm onehot)
3.2.5.15 PS/2 packet parser(Fsm ps2)
3.2.5.16 PS/2 packet parser and datapath(Fsm ps2data)
结语
HDLbits网站链接
前言
今天继续更新几道题目。
3.2.5 Finite State Machines
3.2.5.14 One-hot FSM(Fsm onehot)
module top_module(
input in,
input [9:0] state,
output [9:0] next_state,
output out1,
output out2);
parameter S0 = 4'd0, S1 = 4'd1, S2 = 4'd2, S3 = 4'd3, S4 = 4'd4;
parameter S5 = 4'd5, S6 = 4'd6, S7 = 4'd7, S8 = 4'd8, S9 = 4'd9;
assign next_state[S0] = ~in & (state[S0] | state[S1] | state[S2] | state[S3] | state[S4] | state[S7] | state[S8] | state[S9]);
assign next_state[S1] = in & (state[S0] | state[S8] | state[S9]);
assign next_state[S2] = in & state[S1];
assign next_state[S3] = in & state[S2];
assign next_state[S4] = in & state[S3];
assign next_state[S5] = in & state[S4];
assign next_state[S6] = in & state[S5];
assign next_state[S7] = in & (state[S6] | state[S7]);
assign next_state[S8] = ~in & state[S5];
assign next_state[S9] = ~in & state[S6];
assign out1 = state[S8] | state[S9];
assign out2 = state[S7] | state[S9];
endmodule
这道题目大家直接按照题目来就可以了,这里的one-hot编码和我们平时在状态机中使用的其实是一样的,大家姑且为了一个success就好了,博主直接全部用组合逻辑写出来了。
3.2.5.15 PS/2 packet parser(Fsm ps2)
module top_module(
input clk,
input [7:0] in,
input reset, // Synchronous reset
output done); //
parameter S1 = 3'd0, S2 = 3'd1, S3 = 3'd2, DONE = 3'd3;
reg [2:0] current_state;
reg [2:0] next_state;
always@(posedge clk)begin
if(reset)begin
current_state <= S1;
end
else begin
current_state <= next_state;
end
end
always@(*)begin
case(current_state)
S1:begin
next_state = in[3] ? S2 : S1;
end
S2:begin
next_state = S3;
end
S3:begin
next_state = DONE;
end
DONE:begin
next_state = in[3] ? S2 : S1;
end
default:begin
next_state = S1;
end
endcase
end
assign done = (current_state == DONE);
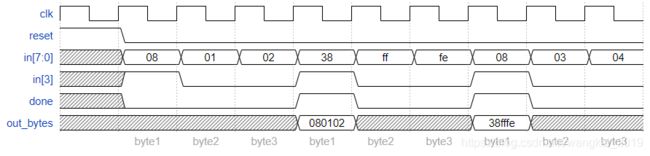
endmodule首先,这道题目中作者表明in的第3位为1时,状态机启动,其他两位可能为1或0,注意,这里不允许重叠检测,根据作者给出的时序图,大家应该就可以写出状态机了。
3.2.5.16 PS/2 packet parser and datapath(Fsm ps2data)
module top_module(
input clk,
input [7:0] in,
input reset, // Synchronous reset
output [23:0] out_bytes,
output done); //
parameter S1 = 3'd0, S2 = 3'd1, S3 = 3'd2, DONE = 3'd3;
reg [2:0] current_state;
reg [2:0] next_state;
reg [23:0] out_bytes_reg;
always@(posedge clk)begin
if(reset)begin
current_state <= S1;
end
else begin
current_state <= next_state;
end
end
always@(*)begin
case(current_state)
S1:begin
next_state = in[3] ? S2 : S1;
// out_bytes_reg[23:16] = in;
end
S2:begin
next_state = S3;
// out_bytes_reg[15:8] = in;
end
S3:begin
next_state = DONE;
// out_bytes_reg[7:0] = in;
end
DONE:begin
next_state = in[3] ? S2 : S1;
// out_bytes_reg[23:16] = in;
end
default:begin
next_state = S1;
end
endcase
end
always@(posedge clk)begin
if(next_state == S2)begin
if(current_state == S1)begin
out_bytes_reg[23:16] <= in;
end
else if(current_state == DONE)begin
out_bytes_reg[23:16] <= in;
end
end
end
always@(posedge clk)begin
if(next_state == S3)begin
out_bytes_reg[15:8] = in;
end
end
always@(posedge clk)begin
if(next_state == DONE)begin
out_bytes_reg[7:0] = in;
end
end
assign done = (current_state == DONE);
assign out_bytes = done ? out_bytes_reg : 23'd0;
endmodule这道题目相比上一道多了数据位输出,当done信号为1时,输出24bit的数据,这24bit的数据高8位,中8位,低8位分别从in[3]为1开始计起,依次输出。done信号为0的时候不关心数据信号。这里有一个难点就是高8位的输出,大家注意,这里高8位,博主使用了两层判断,因为在next_state为S2的时候,current_state可能为S1或者DONE,希望大家体会一下。
结语
今天更新三道题目吧,明天继续更新。还是那句话:如果有代码或者语言描述错误的地方,希望大家指出来,我会尽快改正。
HDLbits网站链接
https://hdlbits.01xz.net/wiki/Main_Page