Spring之AOP
什么是AOP?
AOP:aspect object programming 面向切面编程
- 作用:使得关注点代码和业务代码分离
- AOP概述:对于许多功能都依赖的代码进行抽取成为切面,然后在运行时往业务方法上动态植入切面代码
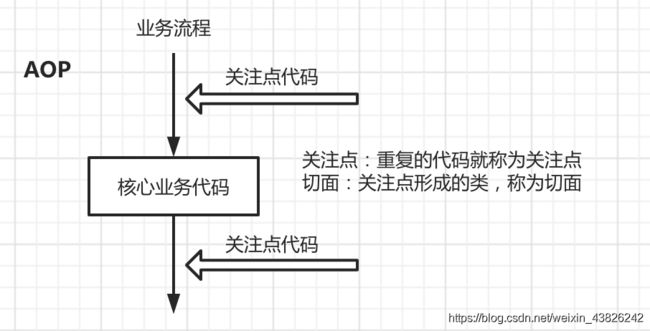
- 切入点:被关注的某类的某方法(即需要使用AOP的方法)
- 切入点表达式:用来指定切入点
使用Spring开发AOP
准备工作
- 引入相关jar包
- 引入aop命名空间
applicationContext.xml:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd ">
beans>
注解方式实现AOP
需要关心如下内容:切面类,切入点,切入表达式
首先在配置文件中开启AOP注解方式
<context:component-scan base-package="pojo"/>
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
接下来创建切面类MyAspect(即我们想要提取出的操作):
/**
* 我的切面类
*/
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAspect {
@Before("execution(* pojo.*.*(..))")
public void begin(){
System.out.println("开始执行");
}
@After("execution(* pojo.*.*(..))")
public void close(){
System.out.println("结束执行");
}
}
使用@Aspect注解来标识这是一个切面类,使用@Before和@After注解来指定该方法作用的关注点时机,注解中的字符串属性是切点表达式,指定了该切面的关注点对象是pojo包下的所有类的所有方法
在pojo包下创建一个UserDao类,其下有save方法:
@Component
public class UserDao {
public void save(){
System.out.println("保存用户...");
}
}
接下来在xml配置文件中配置UserDao这个bean:
<bean id="userDao" class="pojo.UserDao"/>
然后在测试类Main中获取UserDao类并且调用save方法,观察结果:
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ac =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
UserDao userDao = (UserDao) ac.getBean("userDao");
userDao.save();
输出结果如下:
开始执行
保存用户...
结束执行
可以看到关注点方法已经在切入点方法前后分别执行了
这里联想上一篇文章可以得到:因为UserDao没有实现接口,所以使用的代理方式为CGLib动态代理,我们可以输出获取到的userDao对象的class看一下:
class pojo.UserDao$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$2f4b0e96
注解方式实现AOP的API
@Aspect
@Pointcut("切入点表达式")
@Before("切入点表达式")
@After("切入点表达式")
@AfterReturning("切入点表达式")
@AfterThrowing("切入点表达式")
@Around("切入点表达式")
下面是一个切面类实例:
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAspect {
/**
* Pointcut指定切入点表达式,以此来方便后面所有切点表达式的书写
*/
@Pointcut("execution(* pojo.*.*(..))")
public void myPoint(){
}
/**
* 在方法执行前切入
*/
@Before("myPoint()")
public void before(){
System.out.println("before");
}
/**
* 在方法执行后切入
* 无论是否出现异常都会执行
*/
@After("myPoint()")
public void after(){
System.out.println("after");
}
/**
* 调用目标方法结束后执行
* 出现异常不执行
*/
@AfterReturning("myPoint()")
public void afterReturning(){
System.out.println("afterReturning");
}
/**
* 目标方法异常时执行
*/
@AfterThrowing("myPoint()")
public void afterThrowing(){
System.out.println("afterThrowing");
}
/**
* 环绕目标方式执行
* 如果around定义了并且before/after也同时定义了
* around 就会只执行一次
*/
@Around("myPoint()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint point) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("around前...");
Object proceed = point.proceed();
System.out.println("around后...");
return proceed;
}
}
接下来对这个切面类进行测试,正常输出结果如下:
around前...
before
保存用户...
around后...
after
afterReturning
需要注意的是上面的关注点方法调用顺序
如果在调用业务代码的过程中报错,错误输出如下:
around前...
before
保存用户...
after
afterThrowing
可以看到报错了之后,around环绕方法直接中断执行,然后进入after方法,最后会执行afterThrowing方法,而afterReturning切点方法不执行
XML方式实现AOP
其实就是把切面类的书写转换到了xml文件书写,在xml文件中创建切面bean,并且定义切入点,下面是一个xml方式切面配置的例子:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd ">
<bean id="userDao" class="pojo.UserDao"/>
<bean id="myAspect" class="pojo.MyAspect"/>
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="myPoint" expression="execution(* pojo.UserDao.*(..))"/>
<aop:aspect ref="myAspect">
<aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="myPoint"/>
<aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="myPoint"/>
<aop:after-returning method="afterReturning" pointcut-ref="myPoint"/>
<aop:after-throwing method="afterThrowing" pointcut-ref="myPoint"/>
<aop:around method="around" pointcut-ref="myPoint"/>
aop:aspect>
aop:config>
beans>
aop:aspect和aop:advisor
那么在xml配置方式的时候我们在aop:config标签下面发现了这两种标签:
<aop:aspect>
<aop:advisor>
在面向切面编程时,我们会使用< aop:aspect>
在进行事务管理时,我们会使用< aop:advisor>
< aop:aspect>定义切面时,只需要定义一般的bean就行,
而定义< aop:advisor>中引用的通知时,通知必须实现Advice接口。
上面呢我们已经见识到了使用普通的aop:aspect标签来配置切面,这次想要使用aop:advisor,需要另外创建一个新的切面类MyNewAspect
这个类有一个要求:需要实现Advice接口:
@Component("myNewAspect")
public class MyNewAspect implements
MethodBeforeAdvice,
AfterReturningAdvice {
@Override
public void before(Method method, Object[] objects, Object o) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("before");
}
@Override
public void afterReturning(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects, Object o1) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("afterReturning");
}
}
因为经常用于事务管理,所以下面这是一个使用事务的例子:
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="*" timeout="120" propagation="REQUIRED" rollback-for="Exception" />
tx:attributes>
tx:advice>
<aop:config proxy-target-class="true">
<aop:pointcut id="txPointCut" expression="..."/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="txPointCut" />
aop:config>
切点表达式
execution(modifyType returnType declareType Package.Class.Method(params) throwsType)
通配符:
- *号表示任意
- "…"表示可变参数
有一些部分一般省略不写,常用如下:
@Before("execution(* Package.Class.Method(..))")
