shell脚本中的语句
###语句########
学习目标:
for 语句
while语句
if语句
case语句
expect语句
exit,break,continue
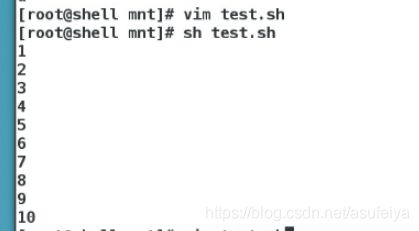
{1…10}
seq 1 10
都是1-10





eg:
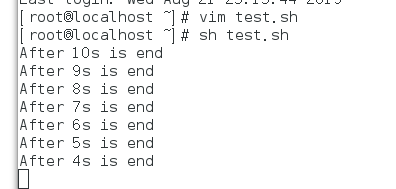
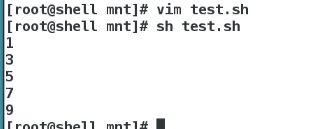
10秒倒计时:
#!/bin/bash
for SEC in {10..1}
do
echo -n "After ${SEC}s is end " ##-n表示不换行输出
echo -ne "\r" ##后面的信息把前面的刷掉
sleep 1 ##1秒执行一次
done
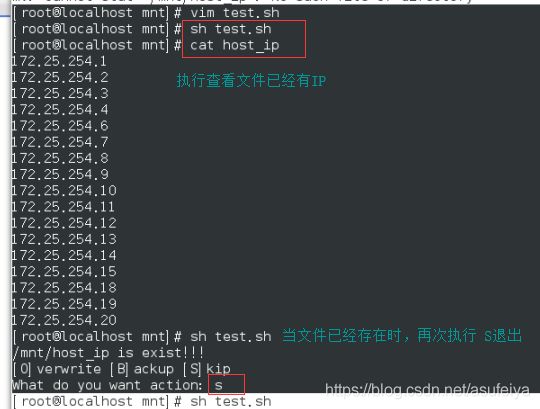
eg:20台主机 1-20中开着的主机 找出来导入host_ip
>>不会覆盖之前的数据
#!/bin/bash
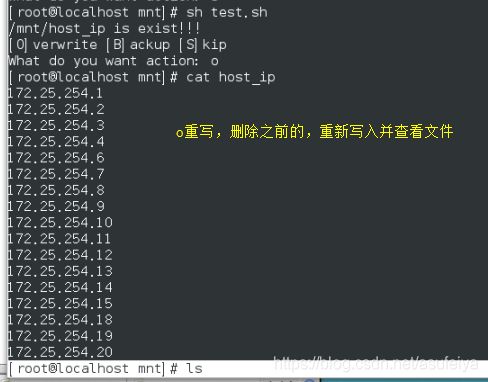
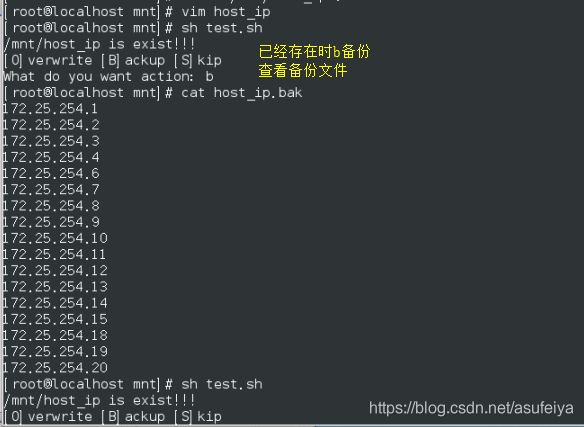
[ -e "/mnt/host_ip" ]&&{
echo /mnt/host_ip is exist!!!
echo "[O]verwrite [B]ackup [S]kip"
read -p "What do you want action: " WORD
ACTION=`echo $WORD|tr 'a-z' 'A-Z'`
[ "$ACTION" = "O" ]&&{
rm -fr /mnt/host_ip
}
[ "$ACTION" = "B" ]&&{
mv /mnt/host_ip /mnt/host_ip.bak
}
[ "$ACTION" = "S" ]&&{
exit 0
}
}
for ip in {1..20}
do
ping -c1 -w1 172.25.254.$ip &>/dev/null &&{
echo 172.25.254.$ip >> /mnt/host_ip
}
done

######while##############
相当于&& 只不过可以循环
until 相当于||
while语句
while条件
do
done



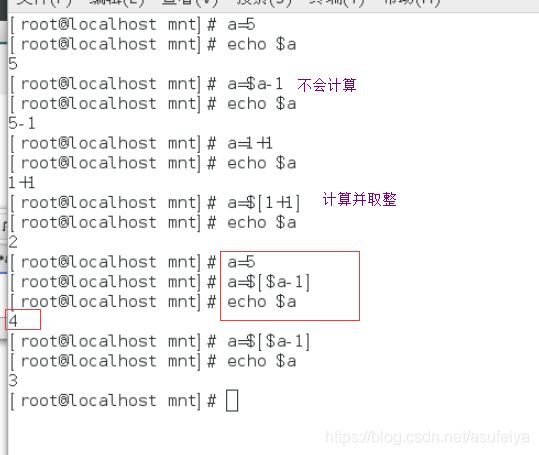
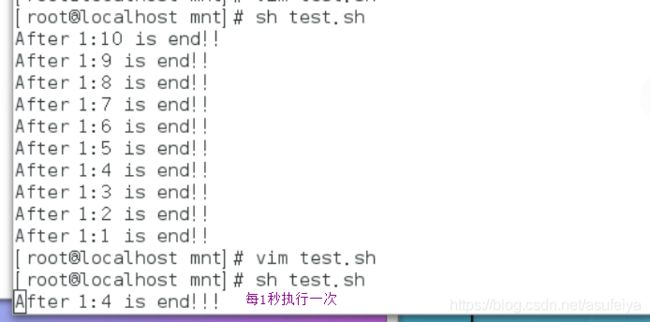
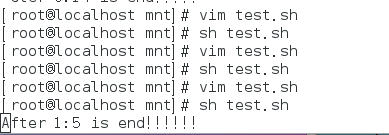
eg:每隔1秒自减
1分10秒倒计时
1:00 --- 0:59
SEC=10
MIN=2
for ((SEC=10;SEC>=0;SEC--))
do
while [ "$SEC" = "0" -a "$MIN" = "0" ]
do
exit 0
done
while [ "$SEC" = "0" ]
do
echo -ne "After $MIN:$SEC is end!!!!!!"
echo -ne "\r"
sleep 1 ##如果不执行这个不会出现 $MIN:0
SEC=59 ##如果不加这个在SEC执行到0的时候会卡住,需要重新赋值。
((MIN--))
done
echo -ne "After $MIN:$SEC is end!!"
echo -ne "\r"
sleep 1
done
######### if语句
if 效率低
从上往下执行
if
then
elif
then
。。。
else
fi ##语句结束
简单的示例:‘
【1】只有if,then,fi
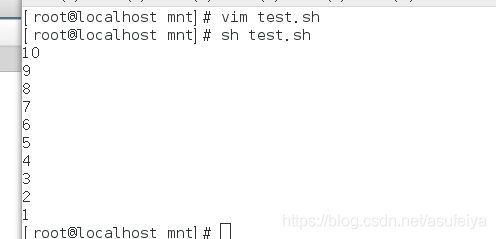
vim test.sh
if [ -z "$1" ]
then
echo -e "\033[31mPlease input filename following $0!!!\033[0m"
exit 1
fi
【2】只有if,then,elif,fi
vim test.sh
#!/bin/bash
if [ -z "$1" ]
then
echo -e "\033[31mPlease input filename following $0!!!\033[0m"
exit 1
elif [ -e "$1" ]
then
echo "$1 is exist"
exit 0
fi
sh test.sh
sh test.sh westos
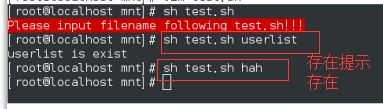
【3】加入else
vim test.sh
if [ -z "$1" ]
then
echo -e "\033[31mPlease input filename following $0!!!\033[0m"
exit 1
elif [ -e "$1" ]
then
echo "$1 is exist"
exit 0
else ##除了以上情况外,输入以下内容
echo "$1 is directory"
fi
sh test.sh
sh test.sh westos
sh test.sh hello

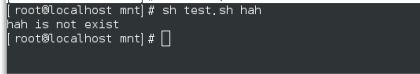

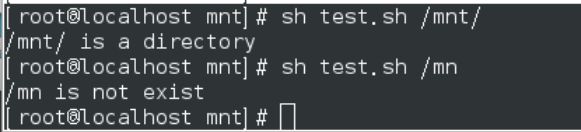
继续提示Please input filename:exit(大小写都退出) 不用tr 因为下面还要判断这个真实文件

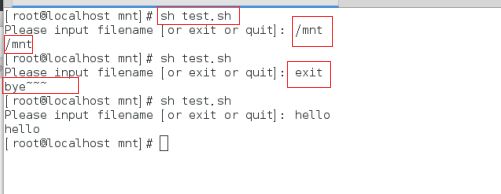

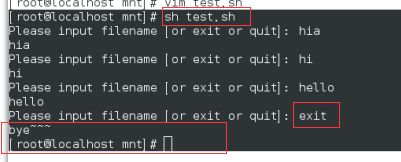
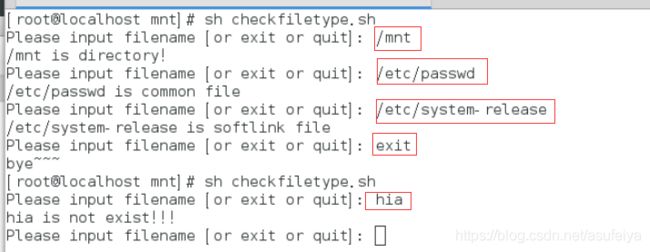
练习1:
判断
[root@localhost mnt]# checkfiletype.sh \
> Please input filename: /mnt \
> /mnt is directory \
> /mnt is not exist \
> Please input filename: exit \
> bye
步骤:
vim checkfiletype.sh
#!/bin/bash
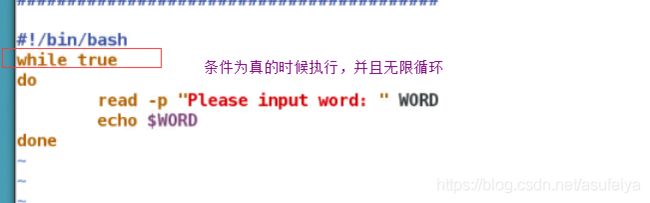
while true
do
read -p "Please input filename [or exit or quit]: " NAME
if [ "$NAME" = "EXIT " -o "$NAME" = "exit" ]
then
echo bye~~~
exit 0
elif [ -L "$NAME" ]
then
echo "$NAME is softlink file"
elif [ -d "$NAME" ]
then
echo "$NAME is directory!"
elif [ -f "$NAME" ]
then
echo "$NAME is common file"
else
echo "$NAME is not exist!!!"
fi
done
sh checkfiletype.sh
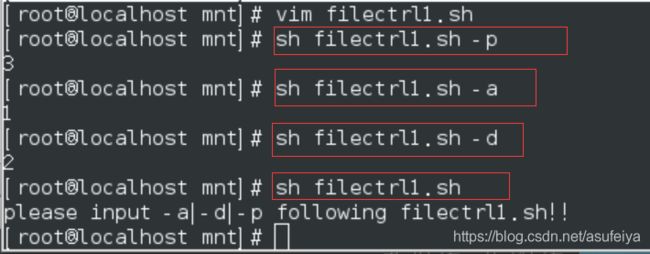
练习2:
当执行filectrl -a file ##创建文件
-d 删掉
-p 备份到/mnt目录下
什么都不是,则报错
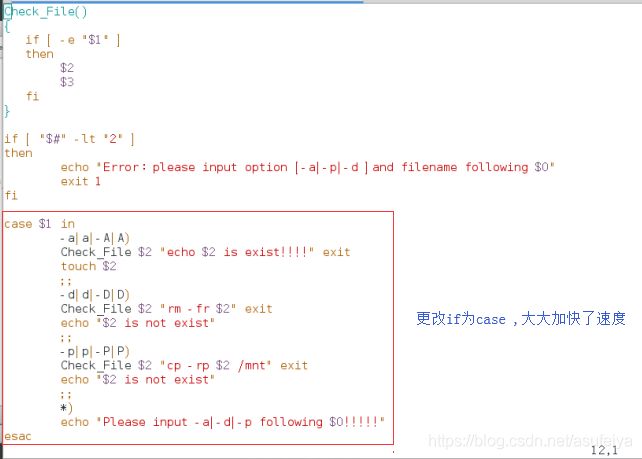
#!/bin/bash
Check_File() 【1】
{
if [ -e "$1" ]
then
$2 ##相当于"echo $2 is exist !"
$3 ##相当于exit
fi
}
if [ "$#" -lt "2" ]
then
echo -e "\033[31mError:Please input option [-a|-d|-p] and following filename $0:\033[0m"
exit 1
fi
if [ "$1" = "-a" ]
then
Check_File $2 "echo $2 is exist !" exit
touch $2
elif [ "$1" = "-d" ]
then
Check_File $2 "rm -fr $2" exit
echo "$2 is not exist"
elif [ "$1" = "-p" ]
then
Check_File $2 "cp -rp $2 /mnt" exit
echo "$2 is not exist"
else
echo "Please input option [-a|-d|-p] following $0!!"
fi
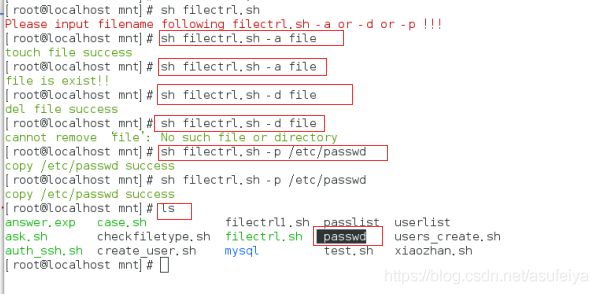
测试:
sh /mnt/filectrl.sh -a file
sh /mnt/filectrl.sh -d file
sh /mnt/filectrl.sh -p /etc/passwd
ls /mnt

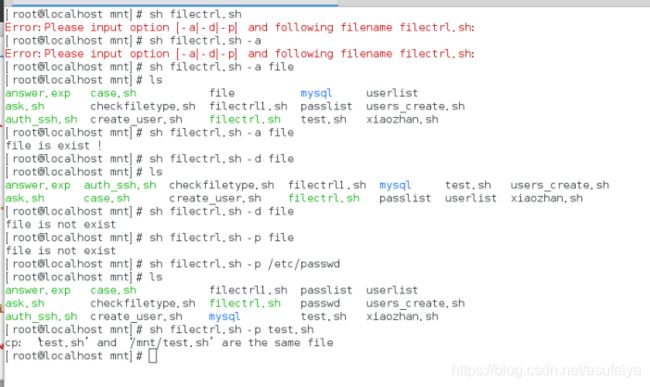

############### case ,点名机制,速度快,做整体对比,进行匹配
case ##代替if,比较方便
esca
易懂的示例:
vim case.sh
#!/bin/bash
case $1 in
westos)
echo linux
;;
linux)
echo redhat
;;
redhat)
echo westos
;;
*) ###输入其他,显示错误
echo Error
esac
sh case.sh westos
sh case.sh linux
sh case.sh redhat
sh case.sh haha