Zookeeper源码解析之监听机制
Zookeeper源码解析之监听机制
ZooKeeper 允许客户端向服务端注册一个 Watcher 监听,当服务器的一些特定事件触发了这个 Watcher,那么就会向指定客户端发送一个事件通知来实现分布式的通知功能。
ZooKeeper 的 Watcher 机制主要包括客户端线程、客户端 WatchManager 和 ZooKeeper 服务器三部分。
ZooKeeper Watcher 存储
ZooKeeper 的 Watcher 不管在客户端还是在 ZooKeeper 服务器中都有存储,首先我们看一下Watcher对象
public interface Watcher {
interface Event {
@InterfaceAudience.Public
enum KeeperState {
@Deprecated
Unknown(-1),
Disconnected(0),
@Deprecated
NoSyncConnected(1),
SyncConnected(3),
AuthFailed(4),
ConnectedReadOnly(5),
SaslAuthenticated(6),
Expired(-112),
Closed(7);
private final int intValue; // Integer representation of value
KeeperState(int intValue) {
this.intValue = intValue;
}
//……
}
@InterfaceAudience.Public
enum EventType {
None(-1),
NodeCreated(1),
NodeDeleted(2),
NodeDataChanged(3),
NodeChildrenChanged(4),
DataWatchRemoved(5),
ChildWatchRemoved(6),
PersistentWatchRemoved (7);
// Integer representation of value
private final int intValue;
//……
}
}
enum WatcherType {
Children(1),
Data(2),
Any(3);
// Integer representation of value
private final int intValue;
WatcherType(int intValue) {
this.intValue = intValue;
}
//……
}
void process(WatchedEvent event);//执行watcher 监听实现,用户自定义事件在服务端是发送事件,客户端收到事件通知后执行用户自定义处理
}
从Watcher中我们可以知道监听的三个主要信息,ZooKeeper的状态,事件类型和监听类型。在服务器端注册通过客户端的不同连接分为NIOServerCnxn和NettyServerCnxn两个Watcher实现类,客户端注册时保存用户自定义的监听实现类。
不论在客户端还是在服务端,Watch都是通过监听管理器来管理和使用的,下面我们先看一下服务端的管理器的一些主要方法。
服务端的管理器 IWatchManager
在 Zookeeper 服务端中同时存在两个IWatchManager管理器——WatchManager和WatchManagerOptimized,WatchManagerOptimized已经优化过的,WatchManager未经优化的,优化主要体现在对Watch的不同存储上。他们同时都是实现IWatchManager,下面我们先看IWatchManager主要提供了哪些服务:
public interface IWatchManager {
//添加watcher
boolean addWatch(String path, Watcher watcher);
//添加watcher,watch的模式:watcherMode——是否持久化,是否递归
default boolean addWatch(String path, Watcher watcher, WatcherMode watcherMode) {
if (watcherMode == WatcherMode.DEFAULT_WATCHER_MODE) {//WatchManagerOptimized使用默认实现,不支持持久化和递归
return addWatch(path, watcher);
}
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
//检查path路径下是否存在Watch
boolean containsWatcher(String path, Watcher watcher);
//移除path路径下是否存在Watch
boolean removeWatcher(String path, Watcher watcher);
//当连接关闭时移除事件
void removeWatcher(Watcher watcher);
//只触发path路径下具体EventType的Watch
WatcherOrBitSet triggerWatch(String path, EventType type);
//只触发path路径下具体EventType的Watch,但是忽略suppress中存在的事件,WatcherOrBitSet通过位记录是否以触发改事件
WatcherOrBitSet triggerWatch(String path, EventType type, WatcherOrBitSet suppress);
//……
}
下面我们先看一下WatchManager的实现,WatchManager的Watcher存储和实现:
public class WatchManager implements IWatchManager {
private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(WatchManager.class);
private final Map<String, Set<Watcher>> watchTable = new HashMap<>();//使用map存储path下的多个Watcher
//通过Watcher类型寻找该类型Watcher 的path节点
private final Map<Watcher, Set<String>> watch2Paths = new HashMap<>();
private final WatcherModeManager watcherModeManager = new WatcherModeManager();
private boolean isDeadWatcher(Watcher watcher) {
return watcher instanceof ServerCnxn && ((ServerCnxn) watcher).isStale();
}
@Override
public boolean addWatch(String path, Watcher watcher) {
return addWatch(path, watcher, WatcherMode.DEFAULT_WATCHER_MODE);
}
@Override
public synchronized boolean addWatch(String path, Watcher watcher, WatcherMode watcherMode) {
if (isDeadWatcher(watcher)) {//判断是否已失效
LOG.debug("Ignoring addWatch with closed cnxn");
return false;
}
Set<Watcher> list = watchTable.get(path);//通过znode的path路径获取该znode下的所有注册Watcher
if (list == null) {//如果未注册过初始化容器
list = new HashSet<>(4);
watchTable.put(path, list);
}
list.add(watcher);//加入新的Watcher
Set<String> paths = watch2Paths.get(watcher);//获取Watcher下的path并加入刚添加的znode的path
if (paths == null) {
paths = new HashSet<>();
watch2Paths.put(watcher, paths);
}
watcherModeManager.setWatcherMode(watcher, path, watcherMode);
return paths.add(path);
}
@Override
public synchronized void removeWatcher(Watcher watcher) {
Set<String> paths = watch2Paths.remove(watcher);
if (paths == null) {
return;
}
for (String p : paths) {
Set<Watcher> list = watchTable.get(p);
if (list != null) {
list.remove(watcher);
if (list.isEmpty()) {
watchTable.remove(p);
}
}
watcherModeManager.removeWatcher(watcher, p);
}
}
@Override
public WatcherOrBitSet triggerWatch(String path, EventType type) {
return triggerWatch(path, type, null);
}
//触发Watcher
@Override
public WatcherOrBitSet triggerWatch(String path, EventType type, WatcherOrBitSet supress) {
WatchedEvent e = new WatchedEvent(type, KeeperState.SyncConnected, path);//创建Watcher事件
Set<Watcher> watchers = new HashSet<>();
PathParentIterator pathParentIterator = getPathParentIterator(path);//path路径目录遍历器
synchronized (this) {
for (String localPath : pathParentIterator.asIterable()) {//返回目录遍历,保证技能触发当前znode上的事件,也能触发所有znode树上的父节点的触发
Set<Watcher> thisWatchers = watchTable.get(localPath);
if (thisWatchers == null || thisWatchers.isEmpty()) {
continue;
}
Iterator<Watcher> iterator = thisWatchers.iterator();//获取当前路径下所有的Watcher
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Watcher watcher = iterator.next();
WatcherMode watcherMode = watcherModeManager.getWatcherMode(watcher, localPath);//获取Watcher的模式
if (watcherMode.isRecursive()) {//如果是Watcher是递归的
if (type != EventType.NodeChildrenChanged) {
watchers.add(watcher);//只添加,不移除改事件,下次可以接着触发
}
} else if (!pathParentIterator.atParentPath()) {
watchers.add(watcher);
if (!watcherMode.isPersistent()) {//非持久化模式下从直接移除
iterator.remove();
Set<String> paths = watch2Paths.get(watcher);//同时从watch2Paths中移除
if (paths != null) {
paths.remove(localPath);
}
}
}
}
if (thisWatchers.isEmpty()) {//如果当前path下没有可执行的Wacher,则从watchTable中移除记录
watchTable.remove(localPath);
}
}
}
if (watchers.isEmpty()) {
if (LOG.isTraceEnabled()) {
ZooTrace.logTraceMessage(LOG, ZooTrace.EVENT_DELIVERY_TRACE_MASK, "No watchers for " + path);
}
return null;
}
for (Watcher w : watchers) {
if (supress != null && supress.contains(w)) {
continue;
}
w.process(e);//顺序同步调用所有的事件
}
switch (type) {//统计
case NodeCreated:
ServerMetrics.getMetrics().NODE_CREATED_WATCHER.add(watchers.size());
break;
case NodeDeleted:
ServerMetrics.getMetrics().NODE_DELETED_WATCHER.add(watchers.size());
break;
case NodeDataChanged:
ServerMetrics.getMetrics().NODE_CHANGED_WATCHER.add(watchers.size());
break;
case NodeChildrenChanged:
ServerMetrics.getMetrics().NODE_CHILDREN_WATCHER.add(watchers.size());
break;
default:
// Other types not logged.
break;
}
return new WatcherOrBitSet(watchers);//WatcherOrBitSet 记录以触发的Watcher
}
}
我们看到代码中WatcherOrBitSet记录已经触发的Watcher,它是通过位实现的,他有两种实现,一种是通过Set记录所有的Watcher,一种是通过BitSet是实现
public class WatcherOrBitSet {
private Set<Watcher> watchers;
private BitHashSet watcherBits;
public WatcherOrBitSet(final Set<Watcher> watchers) {
this.watchers = watchers;
}
public WatcherOrBitSet(final BitHashSet watcherBits) {
this.watcherBits = watcherBits;
}
public boolean contains(Watcher watcher) {
if (watchers == null) {
return false;
}
return watchers.contains(watcher);
}
public boolean contains(int watcherBit) {
if (watcherBits == null) {
return false;
}
return watcherBits.contains(watcherBit);
}
public int size() {
if (watchers != null) {
return watchers.size();
}
if (watcherBits != null) {
return watcherBits.size();
}
return 0;
}
}
public class BitHashSet implements Iterable<Integer> {//包装BitSet
private final BitSet elementBits = new BitSet();
private final Set<Integer> cache = new HashSet<Integer>();
private final int cacheSize;
private int elementCount = 0;
public BitHashSet() {
this(Integer.getInteger("zookeeper.bitHashCacheSize", 10));
}
public BitHashSet(int cacheSize) {
this.cacheSize = cacheSize;
}
public synchronized boolean add(Integer elementBit) {
if (elementBit == null || elementBits.get(elementBit)) {
return false;
}
if (cache.size() < cacheSize) {
cache.add(elementBit);
}
elementBits.set(elementBit);
elementCount++;
return true;
}
public synchronized int remove(Set<Integer> bitSet, BitSet bits) {
cache.removeAll(bitSet);
elementBits.andNot(bits);//通过非实现移除
int elementCountBefore = elementCount;
elementCount = elementBits.cardinality();
return elementCountBefore - elementCount;
}
public synchronized boolean remove(Integer elementBit) {
if (elementBit == null || !elementBits.get(elementBit)) {
return false;
}
cache.remove(elementBit);
elementBits.clear(elementBit);
elementCount--;
return true;
}
public synchronized boolean contains(Integer elementBit) {
if (elementBit == null) {
return false;
}
return elementBits.get(elementBit);
}
}
下面我们看看优化后的WatchManagerOptimized有什么不同
public class WatchManagerOptimized implements IWatchManager, IDeadWatcherListener {
private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(WatchManagerOptimized.class);
//通过BitHashSet来存储多个Watcher,空间复杂变小,时间复杂度降低
private final ConcurrentHashMap<String, BitHashSet> pathWatches = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, BitHashSet>();
//BitMap
private final BitMap<Watcher> watcherBitIdMap = new BitMap<Watcher>();
private final WatcherCleaner watcherCleaner;
private final ReentrantReadWriteLock addRemovePathRWLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
public WatchManagerOptimized() {
watcherCleaner = new WatcherCleaner(this);
watcherCleaner.start();
}
@Override
public boolean addWatch(String path, Watcher watcher) {
boolean result = false;
addRemovePathRWLock.readLock().lock();
try {
if (isDeadWatcher(watcher)) {
LOG.debug("Ignoring addWatch with closed cnxn");
} else {
Integer bit = watcherBitIdMap.add(watcher);//生成并记录Watcher的位数值
BitHashSet watchers = pathWatches.get(path);//获取path保存的Watcher——BitHashSet
if (watchers == null) {
watchers = new BitHashSet();//不存在则初始化
if (existingWatchers != null) {
watchers = existingWatchers;
}
}
result = watchers.add(bit);//加入Watcher
}
} finally {
addRemovePathRWLock.readLock().unlock();
}
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean removeWatcher(String path, Watcher watcher) {
addRemovePathRWLock.writeLock().lock();
try {
BitHashSet list = pathWatches.get(path);//获取path保存的Watcher——BitHashSet
if (list == null || !list.remove(watcherBitIdMap.getBit(watcher))) {//通过watcher的Bit位移除watcher
return false;
}
if (list.isEmpty()) {
pathWatches.remove(path);
}
return true;
} finally {
addRemovePathRWLock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
@Override
public void processDeadWatchers(Set<Integer> deadWatchers) {
BitSet bits = new BitSet();
for (int dw : deadWatchers) {
bits.set(dw);
}
for (BitHashSet watchers : pathWatches.values()) {
watchers.remove(deadWatchers, bits);
}
for (Integer wbit : deadWatchers) {
watcherBitIdMap.remove(wbit);
}
}
@Override
public WatcherOrBitSet triggerWatch(String path, EventType type) {
return triggerWatch(path, type, null);
}
@Override
public WatcherOrBitSet triggerWatch(String path, EventType type, WatcherOrBitSet suppress) {
WatchedEvent e = new WatchedEvent(type, KeeperState.SyncConnected, path);
BitHashSet watchers = remove(path);//获取并移除path下的BitHashSet
if (watchers == null) {
return null;
}
int triggeredWatches = 0;
synchronized (watchers) {
for (Integer wBit : watchers) {
if (suppress != null && suppress.contains(wBit)) {//过滤已经触发过的
continue;
}
Watcher w = watcherBitIdMap.get(wBit);//通过BitHashSet中记录bit位获取Watcher
if (w == null || isDeadWatcher(w)) {
continue;
}
w.process(e);//顺序同步调用所有的事件
triggeredWatches++;
}
}
updateMetrics(type, triggeredWatches);
return new WatcherOrBitSet(watchers);
}
private BitHashSet remove(String path) {
addRemovePathRWLock.writeLock().lock();
try {
return pathWatches.remove(path);
} finally {
addRemovePathRWLock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
//……
}
public class BitMap<T> {//包装BitSet为map使用
private final Map<T, Integer> value2Bit = new HashMap<T, Integer>();//位-对象
private final Map<Integer, T> bit2Value = new HashMap<Integer, T>();//对象-位
private final BitSet freedBitSet = new BitSet();
private Integer nextBit = Integer.valueOf(0);
private final ReentrantReadWriteLock rwLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
public Integer add(T value) {
Integer bit = getBit(value);
if (bit != null) {
return bit;
}
rwLock.writeLock().lock();
try {
bit = value2Bit.get(value);
if (bit != null) {
return bit;
}
bit = freedBitSet.nextSetBit(0);//寻找下一个可用位
if (bit > -1) {
freedBitSet.clear(bit);
} else {
bit = nextBit++;
}
value2Bit.put(value, bit);//记录位-对象
bit2Value.put(bit, value);//记录对象-位
return bit;
} finally {
rwLock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
}
客户端的管理器 ClientWatchManager
下边我们看一下客户端中如何存储,客户端中管理类服务接口ClientWatchManager提过的服务比较简单,我们看一下
public interface ClientWatchManager {
//实现
Set<Watcher> materialize(Watcher.Event.KeeperState state, Watcher.Event.EventType type, String path);
}
static class ZKWatchManager implements ClientWatchManager {
//保存不同类型的Watcher
private final Map<String, Set<Watcher>> dataWatches = new HashMap<String, Set<Watcher>>();
private final Map<String, Set<Watcher>> existWatches = new HashMap<String, Set<Watcher>>();
private final Map<String, Set<Watcher>> childWatches = new HashMap<String, Set<Watcher>>();
private final Map<String, Set<Watcher>> persistentWatches = new HashMap<String, Set<Watcher>>();
private final Map<String, Set<Watcher>> persistentRecursiveWatches = new HashMap<String, Set<Watcher>>();
private boolean disableAutoWatchReset;
ZKWatchManager(boolean disableAutoWatchReset) {
this.disableAutoWatchReset = disableAutoWatchReset;
}
protected volatile Watcher defaultWatcher;
public Set<Watcher> materialize(
Watcher.Event.KeeperState state,
Watcher.Event.EventType type,
String clientPath
) {
final Set<Watcher> result = new HashSet<>();
switch (type) {
//根据不同的type把事件添加到不过的Watcher Map中,比较简单
case None:
if (defaultWatcher != null) {
result.add(defaultWatcher);
}
boolean clear = disableAutoWatchReset && state != Watcher.Event.KeeperState.SyncConnected;
synchronized (dataWatches) {
for (Set<Watcher> ws : dataWatches.values()) {
result.addAll(ws);
}
if (clear) {
dataWatches.clear();
}
}
synchronized (existWatches) {
for (Set<Watcher> ws : existWatches.values()) {
result.addAll(ws);
}
if (clear) {
existWatches.clear();
}
}
synchronized (childWatches) {
for (Set<Watcher> ws : childWatches.values()) {
result.addAll(ws);
}
if (clear) {
childWatches.clear();
}
}
synchronized (persistentWatches) {
for (Set<Watcher> ws: persistentWatches.values()) {
result.addAll(ws);
}
}
synchronized (persistentRecursiveWatches) {
for (Set<Watcher> ws: persistentRecursiveWatches.values()) {
result.addAll(ws);
}
}
return result;
case NodeDataChanged:
case NodeCreated:
synchronized (dataWatches) {
addTo(dataWatches.remove(clientPath), result);
}
synchronized (existWatches) {
addTo(existWatches.remove(clientPath), result);
}
addPersistentWatches(clientPath, result);
break;
case NodeChildrenChanged:
synchronized (childWatches) {
addTo(childWatches.remove(clientPath), result);
}
addPersistentWatches(clientPath, result);
break;
case NodeDeleted:
synchronized (dataWatches) {
addTo(dataWatches.remove(clientPath), result);
}
synchronized (existWatches) {
Set<Watcher> list = existWatches.remove(clientPath);
if (list != null) {
addTo(list, result);
LOG.warn("We are triggering an exists watch for delete! Shouldn't happen!");
}
}
synchronized (childWatches) {
addTo(childWatches.remove(clientPath), result);
}
addPersistentWatches(clientPath, result);
break;
default:
String errorMsg = String.format(
"Unhandled watch event type %s with state %s on path %s",
type,
state,
clientPath);
LOG.error(errorMsg);
throw new RuntimeException(errorMsg);
}
return result;
}
}
监听的注册和触发回调
这样我们就大概了解了Wacther在服务端和客户端的存储,下边了解一下监听是如果通过客户端注册并在服务端触发的,下边是大概的流程:
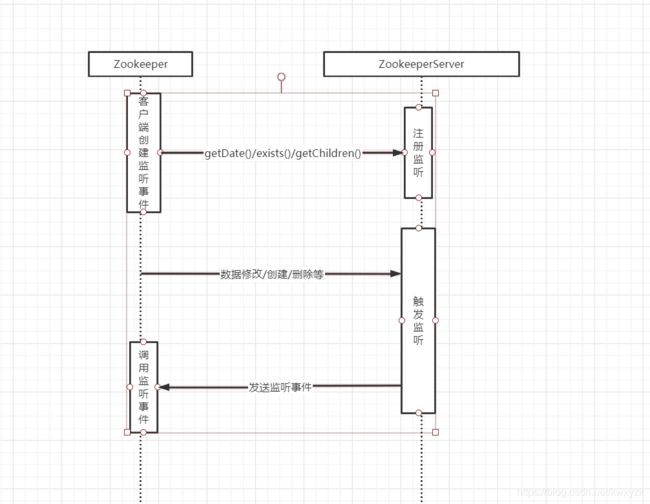
客户端注册 Watcher
在创建一个 ZooKeeper 客户端对象实例时,可以向构造方法中传入一个默认的 Watcher,在注册 Watcher 时,可以使用默认的 Watcher,会一直被保存在客户端 ZKWatchManager 的 defaultWatcher 中。
public ZooKeeper(String connectString, int sessionTimeout, Watcher watcher) throws IOException {
this(connectString, sessionTimeout, watcher, false);
}
ZooKeeper 客户端也可以通过 getData()、exists() 和 getChildren() 三个接口来向 ZooKeeper 服务器注册 Watcher,无论哪种方式,注册 Watcher 的工作原理都是一致的。
public byte[] getData(final String path, Watcher watcher, Stat stat) throws KeeperException, InterruptedException {
final String clientPath = path;
PathUtils.validatePath(clientPath);//路径校验
WatchRegistration wcb = null;
if (watcher != null) {
wcb = new DataWatchRegistration(watcher, clientPath);//包装 Watcher
}
final String serverPath = prependChroot(clientPath); //添加服务配置根路径
RequestHeader h = new RequestHeader();
h.setType(ZooDefs.OpCode.getData);
GetDataRequest request = new GetDataRequest();
request.setPath(serverPath);
request.setWatch(watcher != null);
GetDataResponse response = new GetDataResponse();
ReplyHeader r = cnxn.submitRequest(h, request, response, wcb); //提交请求
if (r.getErr() != 0) {
throw KeeperException.create(KeeperException.Code.get(r.getErr()), clientPath);
}
if (stat != null) {
DataTree.copyStat(response.getStat(), stat);
}
return response.getData();
}
客户端使用 cnxn.submitRequest(h, request, response, wcb) 方法向服务器提交请求时携带这个Watcher,同时等待请求的返回。请求发送完成后会由客户端 SendThread 线程的 readResponse 方法负责接收来自服务端的响应,readResponse 方法的最后会调用finishPacket 方法,它会从 Packet 中取出对应的 Watcher 并注册到 ZKWatchManager 中去
class SendThread extends ZooKeeperThread {
private long lastPingSentNs;
private final ClientCnxnSocket clientCnxnSocket;
private Random r = new Random();
private boolean isFirstConnect = true;
void readResponse(ByteBuffer incomingBuffer) throws IOException {
//……
finishPacket(packet);
//……
}
protected void finishPacket(Packet p) {
int err = p.replyHeader.getErr();
if (p.watchRegistration != null) {
p.watchRegistration.register(err);//注册监听
}
//……
if (p.cb == null) {
synchronized (p) {
p.finished = true;
p.notifyAll();
}
} else {
p.finished = true;
eventThread.queuePacket(p);//请求放入eventThread列队
}
}
}
watchRegistration.register方法就是把 WatchRegistration 子类里面的 Watcher 实例放到 ZKWatchManager 的 dataWatches 中存储起来。
//注册监听
public abstract class WatchRegistration {
private Watcher watcher;
private String clientPath;
public WatchRegistration(Watcher watcher, String clientPath) {
this.watcher = watcher;
this.clientPath = clientPath;
}
protected abstract Map<String, Set<Watcher>> getWatches(int rc);
public void register(int rc) {
if (shouldAddWatch(rc)) {
Map<String, Set<Watcher>> watches = getWatches(rc);//通过子类的实现取得ZKWatchManager 中的 dataWatches
synchronized (watches) {
Set<Watcher> watchers = watches.get(clientPath);
if (watchers == null) {
watchers = new HashSet<Watcher>();
watches.put(clientPath, watchers);
}
watchers.add(watcher);
}
}
}
protected boolean shouldAddWatch(int rc) {
return rc == 0;
}
}
当使用ZooKeeper 使用 getData()、exists() 和 getChildren() 三个接口来向 ZooKeeper 服务器注册 Watcher 的时候,首先将此消息传递给服务端,传递成功后,服务端会通知客户端,然后客户端将该路径和Watcher对应关系存储起来备用。
###服务端处理
服务端收到客户端的 Watcher 注册请求后,将 Watcher 根据请求包装成NettyServerCnxn或NIOServerCnxn注册到服务 IWatchManager 管理器中,在Zookeeper服务端处理请求的最后一个请求处理器为FinalRequestProcessor,我们通过入口看一下如何注册客户端请求的监听
public void processRequest(Request request) {
//……
switch (request.type) {
case OpCode.getData: {
lastOp = "GETD";
GetDataRequest getDataRequest = new GetDataRequest();
ByteBufferInputStream.byteBuffer2Record(request.request, getDataRequest);
path = getDataRequest.getPath();
rsp = handleGetDataRequest(getDataRequest, cnxn, request.authInfo);//处理请求
requestPathMetricsCollector.registerRequest(request.type, path);
break;
}
}
//……
}
private Record handleGetDataRequest(Record request, ServerCnxn cnxn, List<Id> authInfo) throws KeeperException, IOException {
GetDataRequest getDataRequest = (GetDataRequest) request;
String path = getDataRequest.getPath();
DataNode n = zks.getZKDatabase().getNode(path);
if (n == null) {
throw new KeeperException.NoNodeException();
}
zks.checkACL(cnxn, zks.getZKDatabase().aclForNode(n), ZooDefs.Perms.READ, authInfo, path, null);
Stat stat = new Stat();
//ZKDatabase获取数据并添加Watcher
byte[] b = zks.getZKDatabase().getData(path, stat, getDataRequest.getWatch() ? cnxn : null);
return new GetDataResponse(b, stat);
}
public byte[] getData(String path, Stat stat, Watcher watcher) throws KeeperException.NoNodeException {
DataNode n = nodes.get(path);
byte[] data = null;
if (n == null) {
throw new KeeperException.NoNodeException();
}
synchronized (n) {
n.copyStat(stat);
if (watcher != null) {
dataWatches.addWatch(path, watcher);//IWatchManager添加Watcher
}
data = n.data;
}
updateReadStat(path, data == null ? 0 : data.length);
return data;
}
上边就是我们在注册请求时的添加过程,服务端注册IWatchManager.Watcher()我们在讲监听管理器就说过了,这里不再多说,下边我们看一下请求怎么触发监听,我们直接看DataTree中
public Stat setData(String path, byte[] data, int version, long zxid, long time) throws KeeperException.NoNodeException {
Stat s = new Stat();
DataNode n = nodes.get(path);
if (n == null) {
throw new KeeperException.NoNodeException();
}
byte[] lastdata = null;
synchronized (n) {
lastdata = n.data;
nodes.preChange(path, n);
n.data = data;
n.stat.setMtime(time);
n.stat.setMzxid(zxid);
n.stat.setVersion(version);
n.copyStat(s);
nodes.postChange(path, n);
}
String lastPrefix = getMaxPrefixWithQuota(path);
long dataBytes = data == null ? 0 : data.length;
if (lastPrefix != null) {
this.updateCountBytes(lastPrefix, dataBytes - (lastdata == null ? 0 : lastdata.length), 0);
}
nodeDataSize.addAndGet(getNodeSize(path, data) - getNodeSize(path, lastdata));
updateWriteStat(path, dataBytes);
dataWatches.triggerWatch(path, EventType.NodeDataChanged);//通过IWatchManager触发监听
return s;
}
在服务端Watcher主要包装成网络请求的 NettyServerCnxn 或者 NIOServerCnxn,根据客户端请求的连接包装成其中一个,我们看看NettyServerCnxn中process的实现
public void process(WatchedEvent event) {
ReplyHeader h = new ReplyHeader(ClientCnxn.NOTIFICATION_XID, -1L, 0);
if (LOG.isTraceEnabled()) {
ZooTrace.logTraceMessage(
LOG,
ZooTrace.EVENT_DELIVERY_TRACE_MASK,
"Deliver event " + event + " to 0x" + Long.toHexString(this.sessionId) + " through " + this);
}
WatcherEvent e = event.getWrapper();//包装WatcherEvent
try {
sendResponse(h, e, "notification");//发送到客户端
} catch (IOException e1) {
LOG.debug("Problem sending to {}", getRemoteSocketAddress(), e1);
close();
}
}
@Override
public void sendResponse(ReplyHeader h, Record r, String tag,
String cacheKey, Stat stat, int opCode) throws IOException {
if (closingChannel || !channel.isOpen()) {
return;
}
sendBuffer(serialize(h, r, tag, cacheKey, stat, opCode));//发送数据
decrOutstandingAndCheckThrottle(h);
}
这样,客户端注册的监听就通过事件发送回客户端进行处理。
客户端处理回调 Watcher
Zookeeper 客服端SendThread不仅接受返送请求的返回,同时也是一个ReadThread,接受服务端发送的请求,服务端发送的触发事件也是通过这里传入的
class SendThread extends ZooKeeperThread {
void readResponse(ByteBuffer incomingBuffer) throws IOException {
ByteBufferInputStream bbis = new ByteBufferInputStream(incomingBuffer);
BinaryInputArchive bbia = BinaryInputArchive.getArchive(bbis);
ReplyHeader replyHdr = new ReplyHeader();
replyHdr.deserialize(bbia, "header");
switch (replyHdr.getXid()) {
case NOTIFICATION_XID:
WatcherEvent event = new WatcherEvent();
event.deserialize(bbia, "response");//反序列化请求
// 转化server path 为 client path
if (chrootPath != null) {
String serverPath = event.getPath();
if (serverPath.compareTo(chrootPath) == 0) {
event.setPath("/");
} else if (serverPath.length() > chrootPath.length()) {
event.setPath(serverPath.substring(chrootPath.length()));
} else {
LOG.warn("Got server path {} which is too short for chroot path {}.",
event.getPath(), chrootPath);
}
}
WatchedEvent we = new WatchedEvent(event);
LOG.debug("Got {} for session id 0x{}", we, Long.toHexString(sessionId));
eventThread.queueEvent(we);//通过EventThread处理WatchedEvent
return;
default:
break;
}
}
}
EventThread 专门处理事件,将WatchedEvent放入处理队列中,然后统一处理WatchedEvent
class EventThread extends ZooKeeperThread {
public void queueEvent(WatchedEvent event) {//接受请求
queueEvent(event, null);
}
private void queueEvent(WatchedEvent event, Set<Watcher> materializedWatchers) {
if (event.getType() == EventType.None && sessionState == event.getState()) {
return;
}
sessionState = event.getState();
final Set<Watcher> watchers;
if (materializedWatchers == null) {
// materialize 这里取出移并除ZKWatchManager中注册的事件,保证事件只调用一次
watchers = watcher.materialize(event.getState(), event.getType(), event.getPath());
} else {
watchers = new HashSet<Watcher>();
watchers.addAll(materializedWatchers);
}
// event 来生成一个 WatcherSetEventPair 类型的pari,这个pari只是把 event 加了一个壳,然后附加上了这个节点上所有的 Watcher
WatcherSetEventPair pair = new WatcherSetEventPair(watchers, event);
// 放入处理等待队列
waitingEvents.add(pair);
}
public void run() {
try {
isRunning = true;
while (true) {
Object event = waitingEvents.take();//从等待队列中弹出
if (event == eventOfDeath) {
wasKilled = true;
} else {
processEvent(event);
}
if (wasKilled) {
synchronized (waitingEvents) {
if (waitingEvents.isEmpty()) {
isRunning = false;
break;
}
}
}
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
LOG.error("Event thread exiting due to interruption", e);
}
}
private void processEvent(Object event) {
try {
if (event instanceof WatcherSetEventPair) {
// each watcher will process the event
WatcherSetEventPair pair = (WatcherSetEventPair) event;
for (Watcher watcher : pair.watchers) {
try {
watcher.process(pair.event);//监听执行
} catch (Throwable t) {
LOG.error("Error while calling watcher.", t);
}
}
} else
{//……}
}
}
这样整个流程客户端注册-》服务端注册-》服务端触发回调-》客服端处理监听 就结束
下边时注册方式对事件的可监控性
| 注册方式 | NodeCreated | NodeChildrenChanged | NodeDeleted | NodeDataChanged |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| getData | 可监控 | 可监控 | 可监控 | |
| getChildren | 可监控 | 可监控 | ||
| exists | 可监控 | 可监控 | 可监控 |