1、system context的初始化过程
1.1 SystemServer.createSystemContext()
private void createSystemContext() {
ActivityThread activityThread = ActivityThread.systemMain();
mSystemContext = activityThread.getSystemContext();
mSystemContext.setTheme(android.R.style.Theme_DeviceDefault_Light_DarkActionBar);
}
ActivityThread管理着一个应用进程的主线程,用来调度和执行运行在该进程中的Activities,Broadcasrs以及其他的相关操作。在android中,每个应用都运行在一个独立的进程中,在这个进程中至少含有一个主线程,这个主线程由ActivityThread来管理,ActivityThread本身运行在主线程中。
1.2 ActivityThread.systemMain()
public static ActivityThread systemMain() {
// The system process on low-memory devices do not get to use hardware
// accelerated drawing, since this can add too much overhead to the
// process.
if (!ActivityManager.isHighEndGfx()) {// 对于低内存的设备,直接关闭硬件加速功能
HardwareRenderer.disable(true);
} else {
HardwareRenderer.enableForegroundTrimming();
}
// 创建ActivityThread 实例
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
thread.attach(true);
return thread;
}
这个方法主要作用:硬件加速的开关,ActivityThread的初始化。
1.3 ActivityThread.attach()
private void attach(boolean system) {
sCurrentActivityThread = this;
mSystemThread = system;
if (!system) {// 非系统应用
ViewRootImpl.addFirstDrawHandler(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
ensureJitEnabled();
}
});
// DDMS中显示的进程名字
android.ddm.DdmHandleAppName.setAppName("",
UserHandle.myUserId());
RuntimeInit.setApplicationObject(mAppThread.asBinder());
// 得到ActivityManagerService对象
final IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault();
try {// mAppThread是一个ApplicationThread
mgr.attachApplication(mAppThread);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
// Ignore
}
// Watch for getting close to heap limit.
// DC回收机制:当应用消耗的内存大于总内存的75%的时候,就要开始进行资源的回收了
BinderInternal.addGcWatcher(new Runnable() {
@Override public void run() {
if (!mSomeActivitiesChanged) {
return;
}
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
long dalvikMax = runtime.maxMemory();
long dalvikUsed = runtime.totalMemory() - runtime.freeMemory();
if (dalvikUsed > ((3*dalvikMax)/4)) {
if (DEBUG_MEMORY_TRIM) Slog.d(TAG, "Dalvik max=" + (dalvikMax/1024)
+ " total=" + (runtime.totalMemory()/1024)
+ " used=" + (dalvikUsed/1024));
mSomeActivitiesChanged = false;
try {
mgr.releaseSomeActivities(mAppThread);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
}
}
});
} else {//系统应用
// Don't set application object here -- if the system crashes,
// we can't display an alert, we just want to die die die.
// 显示在DDMS中的进程名
android.ddm.DdmHandleAppName.setAppName("system_process",
UserHandle.myUserId());
try {
// 初始化Instrumentation
mInstrumentation = new Instrumentation();
// 生成一个Context,是一个ContextImpl
ContextImpl context = ContextImpl.createAppContext(
this, getSystemContext().mPackageInfo);
// Application初始化
mInitialApplication = context.mPackageInfo.makeApplication(true, null);
// 执行Application.onCreate()
mInitialApplication.onCreate();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to instantiate Application():" + e.toString(), e);
}
}
// add dropbox logging to libcore
DropBox.setReporter(new DropBoxReporter());
// 应用对内存的管理
ViewRootImpl.addConfigCallback(new ComponentCallbacks2() {
@Override
public void onConfigurationChanged(Configuration newConfig) {
synchronized (mResourcesManager) {
// We need to apply this change to the resources
// immediately, because upon returning the view
// hierarchy will be informed about it.
if (mResourcesManager.applyConfigurationToResourcesLocked(newConfig, null)) {
// This actually changed the resources! Tell
// everyone about it.
if (mPendingConfiguration == null ||
mPendingConfiguration.isOtherSeqNewer(newConfig)) {
mPendingConfiguration = newConfig;
sendMessage(H.CONFIGURATION_CHANGED, newConfig);
}
}
}
}
@Override
public void onLowMemory() {
}
@Override
public void onTrimMemory(int level) {
}
});
}
因为systemMain传过来的参数为true,因而这里的attach主要作用是初始化Instrumentation,创建Context(ContextImpl),然后通过Instrumentation创建Application并执行Application.onCreate().
这里先来理清下面几个类的作用:Instrumentation,ContextImpl ,Application,**LoadedApk **
Instrumentation:对于一个应用进程,该类会优先被创建出来,然后通过他来创建其他组件;另外,它还是系统与组件交互的桥梁,因而通过他可以监听组件和系统之间的各种交互了。
**Context ** : 是一个接口,通过他能够访问整个应用的全局信息如资源了类了等等,它还可以启动activity、broadcast以及接收intents。
Application:保存了整个应用的状态。
**LoadedApk **:保存了整个APK的相关信息。
1.4 ActivityThread.getSystemContext()
public ContextImpl getSystemContext() {
synchronized (this) {
if (mSystemContext == null) {
mSystemContext = ContextImpl.createSystemContext(this);
}
return mSystemContext;
}
}
1.5 ContextImpl.createSystemContext()
static ContextImpl createSystemContext(ActivityThread mainThread) {
// LoadedApk初始化
LoadedApk packageInfo = new LoadedApk(mainThread);
// ContextImpl初始化
ContextImpl context = new ContextImpl(null, mainThread,
packageInfo, null, null, false, null, null, Display.INVALID_DISPLAY);
// 资源信息相关
context.mResources.updateConfiguration(context.mResourcesManager.getConfiguration(),
context.mResourcesManager.getDisplayMetricsLocked());
return context;
}
1.6 系统APK(framework-res.apk)对应的LoadedApk初始化
/**
* Create information about the system package.
* system package : framework-res.apk,packagename为android
* Must call {@link #installSystemApplicationInfo} later.
*/
LoadedApk(ActivityThread activityThread) {
mActivityThread = activityThread;
mApplicationInfo = new ApplicationInfo();
// packageName为"android",这个APK为framework-res.apk
mApplicationInfo.packageName = "android";
mPackageName = "android";
mAppDir = null;
mResDir = null;
mSplitAppDirs = null;
mSplitResDirs = null;
mOverlayDirs = null;
mSharedLibraries = null;
mDataDir = null;
mDataDirFile = null;
mLibDir = null;
mBaseClassLoader = null;
mSecurityViolation = false;
mIncludeCode = true;
mRegisterPackage = false;
mClassLoader = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();
mResources = Resources.getSystem();
}
1.7 ContextImpl初始化
/**
*ActivityThread mainThread = mainThread
*LoadedApk packageInfo = packageInfo
*boolean restricted = false
*int createDisplayWithId = Display.INVALID_DISPLAY
*/
private ContextImpl(ContextImpl container, ActivityThread mainThread,
LoadedApk packageInfo, IBinder activityToken, UserHandle user, boolean restricted,
Display display, Configuration overrideConfiguration, int createDisplayWithId) {
mOuterContext = this;
mMainThread = mainThread;// ActivityThread赋值
mActivityToken = activityToken;
mRestricted = restricted;
if (user == null) {
user = Process.myUserHandle();
}
mUser = user;
mPackageInfo = packageInfo;// LoadedApk赋值
mResourcesManager = ResourcesManager.getInstance();
final int displayId = (createDisplayWithId != Display.INVALID_DISPLAY)
? createDisplayWithId
: (display != null) ? display.getDisplayId() : Display.DEFAULT_DISPLAY;
CompatibilityInfo compatInfo = null;
if (container != null) {
compatInfo = container.getDisplayAdjustments(displayId).getCompatibilityInfo();
}
if (compatInfo == null) {
compatInfo = (displayId == Display.DEFAULT_DISPLAY)
? packageInfo.getCompatibilityInfo()
: CompatibilityInfo.DEFAULT_COMPATIBILITY_INFO;
}
mDisplayAdjustments.setCompatibilityInfo(compatInfo);
mDisplayAdjustments.setConfiguration(overrideConfiguration);
mDisplay = (createDisplayWithId == Display.INVALID_DISPLAY) ? display
: ResourcesManager.getInstance().getAdjustedDisplay(displayId, mDisplayAdjustments);
// resources初始化
Resources resources = packageInfo.getResources(mainThread);
if (resources != null) {
if (displayId != Display.DEFAULT_DISPLAY
|| overrideConfiguration != null
|| (compatInfo != null && compatInfo.applicationScale
!= resources.getCompatibilityInfo().applicationScale)) {
resources = mResourcesManager.getTopLevelResources(packageInfo.getResDir(),
packageInfo.getSplitResDirs(), packageInfo.getOverlayDirs(),
packageInfo.getApplicationInfo().sharedLibraryFiles, displayId,
overrideConfiguration, compatInfo);
}
}
mResources = resources;// 赋值
if (container != null) {
mBasePackageName = container.mBasePackageName;
mOpPackageName = container.mOpPackageName;
} else {
mBasePackageName = packageInfo.mPackageName;
ApplicationInfo ainfo = packageInfo.getApplicationInfo();
if (ainfo.uid == Process.SYSTEM_UID && ainfo.uid != Process.myUid()) {
// Special case: system components allow themselves to be loaded in to other
// processes. For purposes of app ops, we must then consider the context as
// belonging to the package of this process, not the system itself, otherwise
// the package+uid verifications in app ops will fail.
mOpPackageName = ActivityThread.currentPackageName();
} else {
mOpPackageName = mBasePackageName;
}
}
mContentResolver = new ApplicationContentResolver(this, mainThread, user);
}
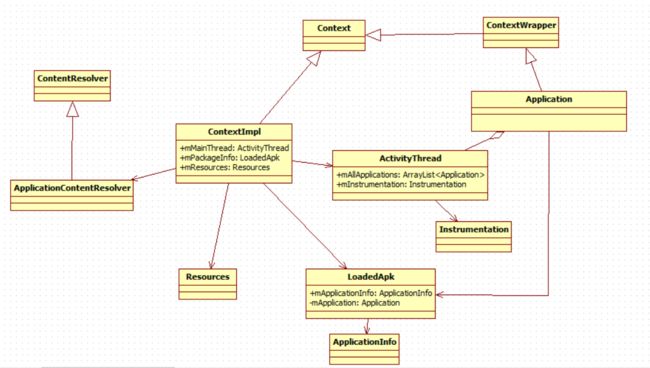
主要是相关变量初始化,涉及的相关类关系如下:
SystemServer.createSystemContext()分析到这里就基本结束了,从这里可以看到,SystemServer.createSystemContext()主要是创建了ActivityThread,获取了Context,这个Context是系统进程(framework-res.apk)运行的环境。另外,从代码中也可以看到:
1)ActivityThread中用了一个集合来保存Application,说明一个进程里面可以包含多个Application;
具体实现:在APK的AndroidManifext.xml中配置
2)Application是在LoadedApk中通过Intrumentation创建出来的(LoadedApk.makeApplication()-->Instrumentation.newApplication()-->Application.attach()),Application通过attach()方法持有LoadedApk对象,Application和LoadedApk是一一对应的关系。