Ubuntu - 基础命令
Ubuntu 16.04.4 LTS amd64
Copyright (c) 2002-2017 NetSarang Computer, Inc. All rights reserved.
Type `help' to learn how to use Xshell prompt.
[c:\~]$
Connecting to 192.168.221.103:22...
Connection established.
To escape to local shell, press 'Ctrl+Alt+]'.
Welcome to Ubuntu 16.04.4 LTS (GNU/Linux 4.13.0-36-generic x86_64)
* Documentation: https://help.ubuntu.com
* Management: https://landscape.canonical.com
* Support: https://ubuntu.com/advantage
0 packages can be updated.
0 updates are security updates.
New release '17.10' available.
Run 'do-release-upgrade' to upgrade to it.
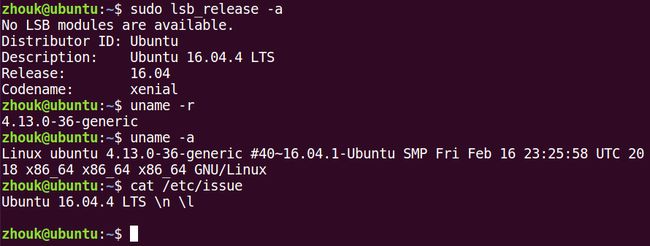
查看 Ubuntu 版本、内核版本号
lsb_release、cat /etc/issue查看Ubuntu的版本号uname -r、uname -a查看内核版本号
zhouk@ubuntu:~$ sudo lsb_release -a
No LSB modules are available.
Distributor ID: Ubuntu
Description: Ubuntu 16.04.4 LTS
Release: 16.04
Codename: xenial
zhouk@ubuntu:~$ uname -r
4.13.0-36-generic
zhouk@ubuntu:~$ uname -a
Linux ubuntu 4.13.0-36-generic #40~16.04.1-Ubuntu SMP Fri Feb 16 23:25:58 UTC 2018 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux
zhouk@ubuntu:~$ cat /etc/issue
Ubuntu 16.04.4 LTS \n \l
zhouk@ubuntu:~$对于以上命令行中,执行 $ sudo lsb_release -a 后出现 No LSB modules are available.,可能是需要安装 lsb-core
$ sudo apt-get install lsb-core
测试:
zhouk@ubuntu:~$ sudo lsb_release -a
LSB Version: core-9.20160110ubuntu0.2-amd64:core-9.20160110ubuntu0.2-noarch:security-9.20160110ubuntu0.2-amd64:security-9.20160110ubuntu0.2-noarch
Distributor ID: Ubuntu
Description: Ubuntu 16.04.4 LTS
Release: 16.04
Codename: xenial
zhouk@ubuntu:~$sudo、apt 等含义
sudo是superuser do的简写。sudo是Linux系统管理指令,是允许系统管理员让普通用户执行一些或者全部的root命令的一个工具,如sudo halt,sudo reboot,sudo su等等。这样不仅减少了root用户的登陆 和管理时间,同样也提高了安全性。apt是个很完整和先进的软件包管理程式,使用他能够让您,又简单,又准确的找到您要的的软件包, 并且安装或卸载都很简洁。 他还能够让您的任何软件都更新到最新状态,而且也能够用来对ubuntu进行升级。
~、/、$、# 等基础符号的含义:
zhouk@ubuntu:/$ cd home/
zhouk@ubuntu:/home$ ls
zhouk
zhouk@ubuntu:/home$ cd zhouk/
zhouk@ubuntu:~$ cd Documents/
zhouk@ubuntu:~/Documents$ sudo su
root@ubuntu:/home/zhouk/Documents# cd /
root@ubuntu:/# cd root/
root@ubuntu:~# 其中:
zhouk@ubuntu、root@ubuntu 代表 当前登录用户@机器名
~目录root用户的家目录是/root普通用户的家目录是/home/用户名
/目录(根目录)
zhouk@ubuntu:~$ cd / #普通用户的 ~目录切换到 /目录
zhouk@ubuntu:/$ cd home/zhouk/ #普通用户的 /目录切换到 ~目录
zhouk@ubuntu:~$
zhouk@ubuntu:/$ sudo su
[sudo] password for zhouk:
root@ubuntu:/# cd root/ #root用户的 /目录切换到 ~目录
root@ubuntu:~# cd / # root用户的 ~目录切换到 /目录
root@ubuntu:/# 命令提示符:
#是root权限下的命令提示符$是普通用户权限下的命令提示符
切换用户:
zhouk@localhost:~$ su root
Password:
root@localhost:/home/zhouk# su zhouk
zhouk@localhost:~$ sudo su
root@localhost:/home/zhouk#
AND
zhouk@localhost:~$ sudo su
[sudo] password for zhouk:
root@localhost:/home/zhouk# su zhouk
zhouk@localhost:~$ 创建、删除目录
- 创建
mkdir
zhouk@ubuntu:~$ ls
Desktop Documents Downloads examples.desktop Music Pictures Public Templates Videos
zhouk@ubuntu:~$ mkdir --help
Usage: mkdir [OPTION]... DIRECTORY...
Create the DIRECTORY(ies), if they do not already exist.
Mandatory arguments to long options are mandatory for short options too.
-m, --mode=MODE set file mode (as in chmod), not a=rwx - umask
-p, --parents no error if existing, make parent directories as needed
-v, --verbose print a message for each created directory
-Z set SELinux security context of each created directory
to the default type
--context[=CTX] like -Z, or if CTX is specified then set the SELinux
or SMACK security context to CTX
--help display this help and exit
--version output version information and exit
GNU coreutils online help:
or available locally via: info '(coreutils) mkdir invocation' 分析:
mkdir
mkdir -m
mkdir -p
mkdir -v
mkdir -Z- 删除
zhouk@ubuntu:~$ rm --help
Usage: rm [OPTION]... [FILE]...
Remove (unlink) the FILE(s).
-f, --force ignore nonexistent files and arguments, never prompt
-i prompt before every removal
-I prompt once before removing more than three files, or
when removing recursively; less intrusive than -i,
while still giving protection against most mistakes
--interactive[=WHEN] prompt according to WHEN: never, once (-I), or
always (-i); without WHEN, prompt always
--one-file-system when removing a hierarchy recursively, skip any
directory that is on a file system different from
that of the corresponding command line argument
--no-preserve-root do not treat '/' specially
--preserve-root do not remove '/' (default)
-r, -R, --recursive remove directories and their contents recursively
-d, --dir remove empty directories
-v, --verbose explain what is being done
--help display this help and exit
--version output version information and exit
By default, rm does not remove directories. Use the --recursive (-r or -R)
option to remove each listed directory, too, along with all of its contents.
To remove a file whose name starts with a '-', for example '-foo',
use one of these commands:
rm -- -foo
rm ./-foo
Note that if you use rm to remove a file, it might be possible to recover
some of its contents, given sufficient expertise and/or time. For greater
assurance that the contents are truly unrecoverable, consider using shred.
GNU coreutils online help: <http://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/>
Full documentation at: <http://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/rm>
or available locally via: info '(coreutils) rm invocation'分析:
rm示例:
zhouk@ubuntu:~$ ls
Desktop Documents Downloads examples.desktop Music Pictures Public Templates Videos
zhouk@ubuntu:~$ mkdir -v test
mkdir: created directory 'test'
zhouk@ubuntu:~$ ls
Desktop Downloads Music Public test
Documents examples.desktop Pictures Templates Videos
zhouk@ubuntu:~$ cd test/
zhouk@ubuntu:~/test$ ls
zhouk@ubuntu:~/test$ mkdir -v t1 t2 t3
mkdir: created directory 't1'
mkdir: created directory 't2'
mkdir: created directory 't3'
zhouk@ubuntu:~/test$ ls
t1 t2 t3
zhouk@ubuntu:~/test$ rm -rf t1
zhouk@ubuntu:~/test$ ls
t2 t3
zhouk@ubuntu:~/test$ cd ..
zhouk@ubuntu:~$ ls
Desktop Downloads Music Public test
Documents examples.desktop Pictures Templates Videos
zhouk@ubuntu:~$ rm -rf test
zhouk@ubuntu:~$ ls
Desktop Documents Downloads examples.desktop Music Pictures Public Templates Videos
zhouk@ubuntu:~$ 软件管理:
- APT以及dpkg常见用法如下:
- APT——Advanced Package Tool
| 命令 | 功能 |
|---|---|
/etc/apt/sources.list |
软件源设置 |
apt-get update |
更新软件源数据 |
apt-get upgrade |
更新已安装软件 |
apt-get dist-upgrade |
更新系统版本 |
apt-get -f install |
通过安装包或卸载包来修复依赖错误 |
apt-cache search foo |
搜索软件源数据 |
apt-get install foo |
解压安装软件包 |
apt-get --reinstall install foo |
重新安装软件包 |
apt-get remove foo |
删除软件包释放的内容 |
apt-get --purge remove foo |
卸载软件,同时清除该软件配置文件 |
apt-get autoclean |
删除不需要的包 |
apt-get clean |
删除所有已下载的包 |
apt-get build-dep foo |
自动安装编译一软件所需要的包 |
- dpkg——package manager for Debian
| 命令 | 功能 |
|---|---|
dpkg -I xx.deb |
显示DEB包信息 |
dpkg -c xx.deb |
显示DEB包文件列表 |
dpkg -i xx.deb |
安装DEB包 |
dpkg --root= |
安装DEB包(指定根目录) |
dpkg -l |
显示所有已安装软件 |
dpkg -s foo |
显示已安装包信息 |
dpkg -L foo |
显示已安装包文件列表 |
dpkg -r foo |
卸载包 |
dpkg -P foo |
卸载软件包并删除其配置文件 |
dpkg-reconfigure foo |
重新配置已安装程序 |
- 从软件源中编译软件流程(适用于少量代码改动或者配置修改)
| 命令 | 功能 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
apt-get source foo |
获取源码 | apt-get source rox-filer |
apt-get build-dep foo |
安装编译依赖 | apt-get build-dep rox-filer |
dpkg-source -x foo_version-revision.dsc |
解压源码 | dpkg-source -x rox_2.11-3.dsc |
| 修改源码部分 | nano ROX-Filer/src/main.c |
|
dpkg-buildpackage -rfakeroot -b |
创建包 | |
echo -e "foo hold" | dpkg --set-selections |
修改软件可升级状态 |