VxWorks解析ELF格式VxWorks镜像过程
文章目录
- VxWorks解析ELF格式VxWorks镜像过程
- 1 VxWorks 解析ELF镜像流程
- 1.1 VxWorks镜像类型
- 1.2 ELF 解析函数 bootElfModule 加载过程
- 1.3 bootElfModule 调用过程图
- 1.4 bootElfModule函数详解
- 2 ELF文件结构描述
- 2.1 readelf 命令介绍
- 2.2 ELF文件头描述
- 2.3 ELF文件中的程序头
VxWorks解析ELF格式VxWorks镜像过程
1 VxWorks 解析ELF镜像流程
1.1 VxWorks镜像类型
本文所介绍的VxWorks镜像类型为ELF格式,并且VxWorks的启动方式为可加载型,可以通过博文VxWorks可加载型启动方式流程梳理详细了解VxWorks启动的相关内容
1.2 ELF 解析函数 bootElfModule 加载过程
/********************************************************************************
* bootElfInit - initialize the system for elf load modules
*
* This routine initialises VxWorks to use ELF format for
* boot loading modules.
*
* RETURNS:
* OK, or
* ERROR if XXX
*
* SEE ALSO: loadModuleAt()
*/
STATUS bootElfInit()
{
bootLoadRoutine = bootElfModule;
return (OK);
}
该函数在 文件 usrConfig.c 中的 usrRoot 中被调用即:
#ifdef INCLUDE_ELF
bootElfInit ();
#endif
上层主要通过接口
/******************************************************************************
*
* bootLoadModule - bootstrap load an object module into memory
*
* This routine is the underlying routine to loadModuleAt(). This interface
* allows specification of the the symbol table used to resolve undefined
* external references and to which to add new symbols.
*
* RETURNS:
* OK, or
* ERROR if can't read file or not enough memory or illegal file format
*
* NOMANUAL
*/
STATUS bootLoadModule ( FAST int fd, /* fd from which to read module */ FUNCPTR *pEntry /* entry point of module */)
{
if (bootLoadRoutine == NULL)
{
errnoSet (S_bootLoadLib_ROUTINE_NOT_INSTALLED);
return (ERROR);
}
else
{
return ((bootLoadRoutine) (fd, pEntry));
}
}
调用bootElfModule进行解析VxWorks镜像文件。
1.3 bootElfModule 调用过程图
1.4 bootElfModule函数详解
/*******************************************************************************
*
* bootElfModule - load an object module into memory
*
* This routine loads an object module in ELF format from the specified
* file, and places the code, data, and BSS at the locations specified within
* the file. The entry point of the module is returned in . This
* routine is generally used for bootstrap loading.
*
* RETURNS:
* OK, or
* ERROR if the routine cannot read the file
*
* SEE ALSO: loadModuleAt()
*/
LOCAL STATUS bootElfModule
(
int fd,
FUNCPTR *pEntry /* entry point of module */
)
{
Elf32_Ehdr ehdr;
Elf32_Phdr *pPhdr, *pph;
int i;
int segment = 0;
unsigned int nbytes;
/*读取ELF文件头*/
if (elfHdrRead (fd, &ehdr) != OK)
{
errnoSet (S_loadElfLib_HDR_READ);
return (ERROR);
}
/* check the program header validity 检查程序段的有效性*/
if (ehdr.e_phoff == 0 ||
ehdr.e_phnum == 0 || ehdr.e_phentsize != sizeof(Elf32_Phdr))
{
errnoSet (S_loadElfLib_HDR_ERROR);
return (ERROR);
}
/* read the program header 读取程序段的头 */
nbytes = ehdr.e_phnum * ehdr.e_phentsize;
if ((pPhdr = (Elf32_Phdr *) malloc (nbytes)) == NULL)
{
errnoSet (S_loadElfLib_PHDR_MALLOC);
return (ERROR);
}
if (lseek (fd, ehdr.e_phoff, L_SET) == ERROR ||
read (fd, (char *) pPhdr, nbytes) != nbytes)
{
errnoSet (S_loadElfLib_PHDR_READ);
fail:
free (pPhdr);
return (ERROR);
}
/* read each loadable segment 读取每一个程序段 并加载到内存指定位置 即: pEntry 位置 */
for (i = 0, pph = pPhdr; i < ehdr.e_phnum; i++, pph++)
{
if (pph->p_type == PT_LOAD)
{
/* This segment is to be loaded, so do it */
printf ("%s%ld", segment++ == 0 ? "" : " + ", pph->p_memsz);
/* load the bits that are present in the file */
if (pph->p_filesz) {
if (lseek (fd, pph->p_offset, L_SET) != pph->p_offset ||
read (fd, (char *) pph->p_vaddr, pph->p_filesz) != pph->p_filesz)
{
errnoSet (S_loadElfLib_READ_SECTIONS);
goto fail;
}
}
// 接下来者两步不能省略
/* zap the bits that didn't appear in the file */
if (pph->p_filesz < pph->p_memsz)
bzero ((char *) (pph->p_vaddr+pph->p_filesz),
pph->p_memsz - pph->p_filesz);
/* if we might end up executing this we need to flush the cache */
if (pph->p_flags & PF_X)
CACHE_TEXT_UPDATE ((char *)pph->p_vaddr, pph->p_memsz);
}
}
printf ("\n");
*pEntry = (FUNCPTR) ehdr.e_entry;
free (pPhdr);
return (OK);
}
2 ELF文件结构描述
2.1 readelf 命令介绍
在了解ELF文件结构之前,我们应该先熟悉一个工具,那就是 readelf工具,该工具可以读出ELF 文件的相关信息,至于 readelf的用法可以通过 readelf -H进行查看,这里贴出相关的信息:
用法:readelf <选项> elf-文件
显示关于 ELF 格式文件内容的信息
Options are:
-a --all Equivalent to: -h -l -S -s -r -d -V -A -I
-h --file-header Display the ELF file header
-l --program-headers Display the program headers
--segments An alias for --program-headers
-S --section-headers Display the sections' header
--sections An alias for --section-headers
-g --section-groups Display the section groups
-t --section-details Display the section details
-e --headers Equivalent to: -h -l -S
-s --syms Display the symbol table
--symbols An alias for --syms
--dyn-syms Display the dynamic symbol table
-n --notes Display the core notes (if present)
-r --relocs Display the relocations (if present)
-u --unwind Display the unwind info (if present)
-d --dynamic Display the dynamic section (if present)
-V --version-info Display the version sections (if present)
-A --arch-specific Display architecture specific information (if any)
-c --archive-index Display the symbol/file index in an archive
-D --use-dynamic Use the dynamic section info when displaying symbols
-x --hex-dump=
Dump the contents of section as bytes
-p --string-dump=
Dump the contents of section as strings
-R --relocated-dump=
Dump the contents of section as relocated bytes
-z --decompress Decompress section before dumping it
-w[lLiaprmfFsoRtUuTgAckK] or
--debug-dump[=rawline,=decodedline,=info,=abbrev,=pubnames,=aranges,=macro,=frames,
=frames-interp,=str,=loc,=Ranges,=pubtypes,
=gdb_index,=trace_info,=trace_abbrev,=trace_aranges,
=addr,=cu_index,=links,=follow-links]
Display the contents of DWARF debug sections
--dwarf-depth=N Do not display DIEs at depth N or greater
--dwarf-start=N Display DIEs starting with N, at the same depth
or deeper
-I --histogram Display histogram of bucket list lengths
-W --wide Allow output width to exceed 80 characters
@ Read options from
-H --help Display this information
-v --version Display the version number of readelf
2.2 ELF文件头描述
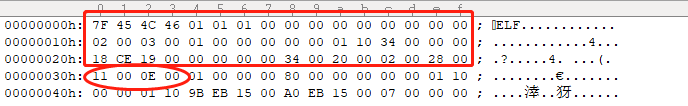
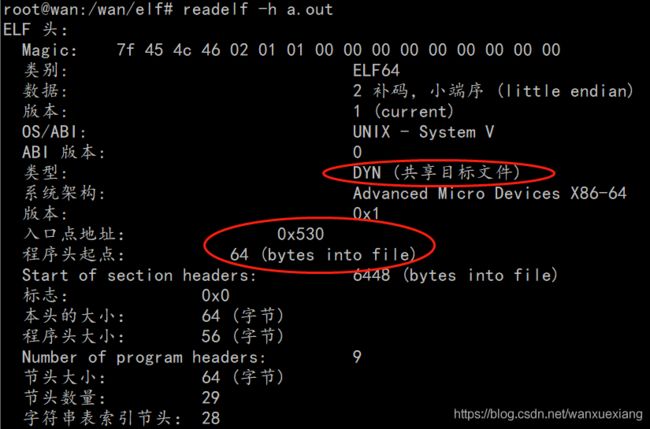
通过readelf -h 文件可以读出 ELF 文件头的信息,具体示例如下:
root@wan:/wan/elf# readelf -h vxWorks
ELF 头:
Magic: 7f 45 4c 46 01 01 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
类别: ELF32
数据: 2 补码,小端序 (little endian)
版本: 1 (current)
OS/ABI: UNIX - System V
ABI 版本: 0
类型: EXEC (可执行文件)
系统架构: Intel 80386
版本: 0x1
入口点地址: 0x10010000
程序头起点: 52 (bytes into file)
Start of section headers: 1691160 (bytes into file)
标志: 0x0
本头的大小: 52 (字节)
程序头大小: 32 (字节)
Number of program headers: 2
节头大小: 40 (字节)
节头数量: 17
字符串表索引节头: 14
在Linux 可以在 /usr/include/elf.h 中查看 ELF对应的结构体以及结构体每个字段的含义,以ELF32位为例:
#define EI_NIDENT (16)
/* ELF types definition */
typedef unsigned long Elf32_Addr; /* unsigned program address */
typedef unsigned short Elf32_Half; /* unsigned medium integer */
typedef unsigned long Elf32_Off; /* unsigned file offset */
typedef long Elf32_Sword; /* signed large integer */
typedef unsigned long Elf32_Word; /* unsigned large integer */
#define ELF32_FSZ_ADDR 4
#define ELF32_FSZ_HALF 2
#define ELF32_FSZ_OFF 4
#define ELF32_FSZ_SWORD 4
#define ELF32_FSZ_WORD 4
/* ELF header */
#define EI_NIDENT 16 /* identification size */
typedef struct
{
unsigned char e_ident[EI_NIDENT]; /* Magic number and other info */
Elf32_Half e_type; /* Object file type */
Elf32_Half e_machine; /* Architecture */
Elf32_Word e_version; /* Object file version */
Elf32_Addr e_entry; /* Entry point virtual address */
Elf32_Off e_phoff; /* Program header table file offset */
Elf32_Off e_shoff; /* Section header table file offset */
Elf32_Word e_flags; /* Processor-specific flags */
Elf32_Half e_ehsize; /* ELF header size in bytes */
Elf32_Half e_phentsize; /* Program header table entry size */
Elf32_Half e_phnum; /* Program header table entry count */
Elf32_Half e_shentsize; /* Section header table entry size */
Elf32_Half e_shnum; /* Section header table entry count */
Elf32_Half e_shstrndx; /* Section header string table index */
} Elf32_Ehdr;
下面以 VxWorks镜像为例,依次讲解结构体各个成员的含义:
- e_ident
开头16个字节为 ELF文件的魔幻数和一些其他的信息,通常前4个字节是固定的,分别7f 45 4c 46 - e_type
ELF 文件的类型
/* Legal values for e_type (object file type). */
#define ET_NONE 0 /* No file type */
#define ET_REL 1 /* Relocatable file */
#define ET_EXEC 2 /* Executable file */
#define ET_DYN 3 /* Shared object file */
#define ET_CORE 4 /* Core file */
#define ET_NUM 5 /* Number of defined types */
#define ET_LOOS 0xfe00 /* OS-specific range start */
#define ET_HIOS 0xfeff /* OS-specific range end */
#define ET_LOPROC 0xff00 /* Processor-specific range start */
#define ET_HIPROC 0xffff /* Processor-specific range end */
ET_REL(relocatable):重定位文件,该文件(整个文件)被当做(标记为)一段可执行的代码,有时也称为目标文件。可重定位目标文件通常是还未被链接可执行程序的一段位置独立的代码(position independent code)。通常我们遇到的 *.a *.o就是重定位为文件。
查看如下实例:

ET_DYN:共享目标文件。ELF类型为dynamic,即动态可链接的目标文件,通常是 *.so 或者程序的可执行文件

ET_EXEC(executable):可执行文件,即程序,是一个进程开始执行的入口
ET_CORE:核心文件,在程序崩溃或者进程传递了一个SIGSEGV信号(分段违规)时,会在核心文件中记录整个进程的镜像信息。可以使用GDB读取这类文件来辅助调试并查找程序崩溃的原因

- e_machine
程序运行的硬件平台
这些通常在elf.h头文件中定义,举几个常见的例子:
/* Target machine definitions */
#define EM_NONE 0 /* no machine */
#define EM_M32 1 /* AT&T WE 32100 */
#define EM_SPARC 2 /* Sun SPARC */
#define EM_386 3 /* Intel 80386 */
#define EM_68K 4 /* Motorola 68000 */
#define EM_88K 5 /* Motorola 88000 */
#define EM_486 6 /* Intel 80486 */
#define EM_860 7 /* Intel i860 */
#define EM_MIPS 8 /* MIPS family */
#define EM_PPC_OLD 17 /* PowerPC family - EABI draft 1.0 */
#define EM_SPARC32PLUS 18 /* Sun's "v8plus" */
#define EM_960 19 /* Intel i960 family */
#define EM_PPC 20 /* PowerPC family */
#define EM_ARM 40 /* ARM/Thumb family */
#define EM_SH 42 /* Hitachi SH family */
#define EM_MCORE 39 /* MCORE family */
#define EM_FRV 0x5441 /* Fujitsu FR-V (Venus) family */
- e_version
目标文件的版本 通常定义如下
/* Legal values for e_version (version). */
#define EV_NONE 0 /* Invalid ELF version */
#define EV_CURRENT 1 /* Current version */
#define EV_NUM 2
-
e_entry
Entry point virtual address 即:程序入口点的虚拟地址。 -
e_phoff
程序头偏移地址 -
e_shoff
/* Section header table file offset */ -
e_flags
/* Processor-specific flags */ -
e_ehsize
/* ELF header size in bytes */ -
e_phentsize
/* Program header table entry size */ -
e_phnum
/* Program header table entry count */ -
e_shentsize
/* Section header table entry size */ -
e_shnum
/* Section header table entry count */ -
e_shstrndx
/* Section header string table index */
2.3 ELF文件中的程序头
程序头部表(Program Header Table),如果存在的话,告诉系统如何创建进程映像。
程序头部(Program Header)描述与程序执行直接相关的目标文件结构信息。用来在文件中定位各个段的映像。同时包含其他一些用来为程序创建映像所必须的信息。
可执行文件或者共享目标文件的程序头部是一个结构数组,每个结构描述了一个段或者系统准备程序执行所必须的其他信息。目标文件的“段”包含一个或者多个“节区”,也就是“段内容(Segment Contents)”。程序头部仅对可执行文件和共享目标文件有意义。
可以通过readelf -l 查看程序头的相关信息
root@wan:/wan/elf# readelf -l vxWorks
Elf 文件类型为 EXEC (可执行文件)
Entry point 0x10010000
There are 2 program headers, starting at offset 52
程序头:
Type Offset VirtAddr PhysAddr FileSiz MemSiz Flg Align
LOAD 0x000080 0x10010000 0x10010000 0x15eb9b 0x15eba0 RWE 0x20
LOAD 0x160000 0x10170000 0x10170000 0x0ecd0 0x2b310 RW 0x10000
Section to Segment mapping:
段节...
00 .text .wrs_build_vars .sdata2
01 .data .bss
程序头相关的结构体如下:
typedef struct {
Elf32_Word p_type; //此数组元素描述的段的类型,或者如何解释此数组元素的信息。
Elf32_Off p_offset; //此成员给出从文件头到该段第一个字节的偏移
Elf32_Addr p_vaddr; //此成员给出段的第一个字节将被放到内存中的虚拟地址
Elf32_Addr p_paddr; //此成员仅用于与物理地址相关的系统中。System V忽略所有应用程序的物理地址信息。
Elf32_Word p_filesz; //此成员给出段在文件映像中所占的字节数。可以为0。
Elf32_Word p_memsz; //此成员给出段在内存映像中占用的字节数。可以为0。
Elf32_Word p_flags; //此成员给出与段相关的标志。
Elf32_Word p_align; //此成员给出段在文件中和内存中如何对齐。
} Elf32_phdr;