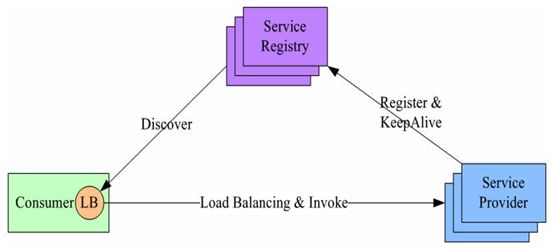
grpc-lb采用客户端进程内负载均衡方式,支持随机、轮询、一致性哈希三种负载均衡策略,并支持服务端权重。可采用etcd或consul作为注册中心。
项目地址:
https://github.com/liyue201/g...
基本架构如图,服务提供者起来后向注册中心注册自己的信息,ip、端口、权重等,并保持心跳。客户端监听注册中心,获取服务器列表,一旦服务器发生变化,客户端马上更新本地的服务器列表。客户端每个请求都通过负载均衡策略选择一个合适的服务器去访问。
随机负载均衡客户端例子:
package main
import (
etcd "github.com/coreos/etcd/client"
grpclb "github.com/liyue201/grpc-lb"
"github.com/liyue201/grpc-lb/examples/proto"
registry "github.com/liyue201/grpc-lb/registry/etcd"
"golang.org/x/net/context"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
"log"
)
func main() {
etcdConfg := etcd.Config{
Endpoints: []string{"http://120.24.44.201:4001"},
}
r := registry.NewResolver("/grpc-lb", "test", etcdConfg)
b := grpclb.NewBalancer(r, grpclb.NewRandomSelector())
c, err := grpc.Dial("", grpc.WithInsecure(), grpc.WithBalancer(b))
if err != nil {
log.Printf("grpc dial: %s", err)
return
}
defer c.Close()
client := proto.NewTestClient(c)
resp, err := client.Say(context.Background(), &proto.SayReq{Content: "random"})
if err != nil {
log.Println(err)
return
}
log.Printf(resp.Content)
}
轮询负载均衡,只需把NewRandomSelector改成NewRoundRobinSelector即可。
package main
import (
etcd "github.com/coreos/etcd/client"
grpclb "github.com/liyue201/grpc-lb"
"github.com/liyue201/grpc-lb/examples/proto"
registry "github.com/liyue201/grpc-lb/registry/etcd"
"golang.org/x/net/context"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
"log"
)
func main() {
etcdConfg := etcd.Config{
Endpoints: []string{"http://120.24.44.201:4001"},
}
r := registry.NewResolver("/grpc-lb", "test", etcdConfg)
b := grpclb.NewBalancer(r, grpclb.NewRoundRobinSelector())
c, err := grpc.Dial("", grpc.WithInsecure(), grpc.WithBalancer(b))
if err != nil {
log.Printf("grpc dial: %s", err)
return
}
defer c.Close()
client := proto.NewTestClient(c)
resp, err := client.Say(context.Background(), &proto.SayReq{Content: "round robin"})
if err != nil {
log.Println(err)
return
}
log.Printf(resp.Content)
}
一致性哈希负载均衡,需要给每个请求传一个哈希的参数,这个根据应用场景而定,就是下面这个例子中的hashData。
package main
import (
"fmt"
etcd "github.com/coreos/etcd/client"
grpclb "github.com/liyue201/grpc-lb"
"github.com/liyue201/grpc-lb/examples/proto"
registry "github.com/liyue201/grpc-lb/registry/etcd"
"golang.org/x/net/context"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
"log"
"time"
)
func main() {
etcdConfg := etcd.Config{
Endpoints: []string{"http://120.24.44.201:4001"},
}
r := registry.NewResolver("/grpc-lb", "test", etcdConfg)
b := grpclb.NewBalancer(r, grpclb.NewKetamaSelector(grpclb.DefaultKetamaKey))
c, err := grpc.Dial("", grpc.WithInsecure(), grpc.WithBalancer(b), grpc.WithTimeout(time.Second))
if err != nil {
log.Printf("grpc dial: %s", err)
return
}
client := proto.NewTestClient(c)
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
ctx := context.Background()
hashData := fmt.Sprintf("aaaa %d", i)
resp, err := client.Say(context.WithValue(ctx, grpclb.DefaultKetamaKey, hashData),
&proto.SayReq{Content: "ketama"})
if err != nil {
log.Println(err)
time.Sleep(time.Second)
continue
}
log.Printf(resp.Content)
time.Sleep(time.Second)
}
}服务端的代码如下, 使用以下命令运行3个服务进程,再启动客户端。
go run main.go -node node1 -port 28544
go run main.go -node node2 -port 18562
go run main.go -node node3 -port 27772
package main
import (
"flag"
"fmt"
etcd "github.com/coreos/etcd/client"
"github.com/liyue201/grpc-lb/examples/proto"
registry "github.com/liyue201/grpc-lb/registry/etcd"
"golang.org/x/net/context"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
"log"
"net"
"sync"
"time"
)
var nodeID = flag.String("node", "node1", "node ID")
var port = flag.Int("port", 8080, "listening port")
type RpcServer struct {
addr string
s *grpc.Server
}
func NewRpcServer(addr string) *RpcServer {
s := grpc.NewServer()
rs := &RpcServer{
addr: addr,
s: s,
}
return rs
}
func (s *RpcServer) Run() {
listener, err := net.Listen("tcp", s.addr)
if err != nil {
log.Printf("failed to listen: %v", err)
return
}
log.Printf("rpc listening on:%s", s.addr)
proto.RegisterTestServer(s.s, s)
s.s.Serve(listener)
}
func (s *RpcServer) Stop() {
s.s.GracefulStop()
}
func (s *RpcServer) Say(ctx context.Context, req *proto.SayReq) (*proto.SayResp, error) {
text := "Hello " + req.Content + ", I am " + *nodeID
log.Println(text)
return &proto.SayResp{Content: text}, nil
}
func StartService() {
etcdConfg := etcd.Config{
Endpoints: []string{"http://120.24.44.201:4001"},
}
registry, err := registry.NewRegistry(
registry.Option{
EtcdConfig: etcdConfg,
RegistryDir: "/grpc-lb",
ServiceName: "test",
NodeID: *nodeID,
NData: registry.NodeData{
Addr: fmt.Sprintf("127.0.0.1:%d", *port),
//Metadata: map[string]string{"weight": "1"}, //这里配置权重,不配置默认是1
},
Ttl: 10 * time.Second,
})
if err != nil {
log.Panic(err)
return
}
server := NewRpcServer(fmt.Sprintf("0.0.0.0:%d", *port))
wg := sync.WaitGroup{}
wg.Add(1)
go func() {
server.Run()
wg.Done()
}()
wg.Add(1)
go func() {
registry.Register()
wg.Done()
}()
//stop the server after one minute
//go func() {
// time.Sleep(time.Minute)
// server.Stop()
// registry.Deregister()
//}()
wg.Wait()
}
//go run main.go -node node1 -port 28544
//go run main.go -node node2 -port 18562
//go run main.go -node node3 -port 27772
func main() {
flag.Parse()
StartService()
}