Netty应用篇
本博客是在阅读《Netty权威指南》以后整理出来的一篇。
一、 Netty服务端
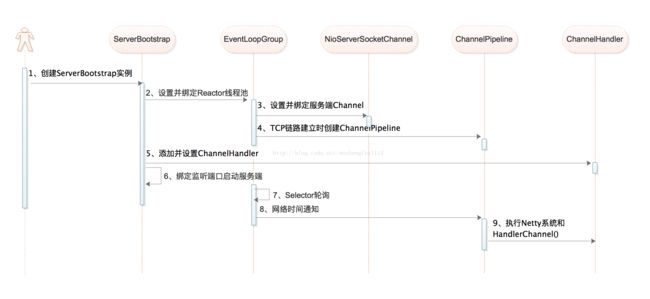
1. 时序图
2. 服务端启动步骤
1) 创建ServerBootstrap实例
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap= new ServerBootstrap();ServerBootstrap是netty服务端的启动辅助类,提供了一系列的方法用于设置服务端启动的相关参数,底层通过门面模式对各种能力进行抽象和封装,尽量不需要用户跟过多的底层API打交道,以降低用户的开发难度。
2) 设置并绑定Reactor线程池
EventLoopGroup bossGroup= new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup= new NioEventLoopGroup();
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)Netty的Reactor线程池是EventLoopGroup,它实际上是EventLoop的数据。EventLoop的职责是处理所有注册到本线程Selector(多路复用器)上的Channel,Selector的轮询操作由绑定的EventLoop线程run方法驱动,在一个循环体内循环执行。EventLoop不仅处理网络IO事件,还负责处理用户自定义的Task和定时任务,如此线程模型就统一了。
3) 设置并绑定服务端Channel
serverBootstrap channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)作为NIO的服务端,Netty自然是需要创建ServerSocketChannel的。NioServerSocketChannel是Netty对原生NIO类库的封装实现,对用户而言,不需要关心服务端Channel的底层实现细节和工作原理,只需要指定具体使用那种服务端Channel即可。
serverBootstrap.handler(newLoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO)).childHandler(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
publicvoid initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throwsIOException {
}
}); 4) 链路建立的时候创建并初始化ChannelPipeline
serverBootstrap.childHandler(newChannelInitializer() {
@Override
publicvoid initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throwsIOException {
//add ChannelHandler
}
}); ChannelPipeline并不是NIO服务端必须的,它本质上是一个负责处理网络事件的责任链,负责管理和执行ChannelHandler。网络事件以流的形式在ChannelPipeline中流转,由ChannelPipeline根据ChannelHandler的执行策略进行调度。典型的网络事件如下:
Ø 链路注册
Ø 链路激活
Ø 链路断开
Ø 接收到请求消息
Ø 请求消息接收并处理完毕
Ø 发送应答消息
Ø 链路发生异常
Ø 发生用户自定义事件
5) 添加并设置ChannelHandler
ch.pipeline().addLast(newNettyMessageDecoder(1024 * 1024, 4, 4));
ch.pipeline().addLast(newNettyMessageEncoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast("readTimeoutHandler",new ReadTimeoutHandler(50));
ch.pipeline().addLast(newLoginAuthRespHandler());
ch.pipeline().addLast("HeartBeatHandler",new HeartBeatRespHandler());
ChannelHandler是Netty提供给用户定制和扩展的关键接口,利用ChannelHandler用户可以完成大多数的功能定制,例如消息编解码、心跳、安全认证、TSL/SSL认证、流量控制、流量整形等。以下是Netty提供的常用的系统Channel。
Ø ByteToMessageCodec:系统编解码框架
Ø LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder:基于长度的半包解码器
Ø LoggingHandler:码流日志打印Handler
Ø SslHandler:SSL安全认证Handler
Ø IdleStateHandler:链路空闲检测Handler
Ø ChannelTrafficShapingHandler:流量整形Handler
Ø Base64Decoder和Base64Encoder:Base64编解码
6) 绑定并启动监听端口
serverBootstrap.bind(NettyConstant.REMOTEIP,NettyConstant.PORT);在绑定监听端口之前,系统会做一系列的初始化和检测工作,完成之后,会启动监听端口,并将ServerSocketChannel注册到Selector上监听客户端连接。
7) Selector轮询
由NioEventLoop负责调度并执行Selector轮询操作,选择准备就绪的Channel集合,相关代码如下:
private void select(boolean oldWakenUp)throws IOException {
Selector selector= this.selector;
try {
intselectCnt = 0;
longcurrentTimeNanos = System.nanoTime();
long selectDeadLineNanos = currentTimeNanos + delayNanos(currentTimeNanos);
for(;;) {
long timeoutMillis = (selectDeadLineNanos - currentTimeNanos + 500000L) / 1000000L;
if (timeoutMillis<= 0) {
if (selectCnt== 0) {
selector.selectNow();
selectCnt = 1;
}
break;
}
// If a task was submitted when wakenUpvalue was true, the task didn't get a chance to call
// Selector#wakeup. So we need tocheck task queue again before executing select operation.
// If we don't, the task might be pendeduntil select operation was timed out.
// It might be pended until idle timeout ifIdleStateHandler existed in pipeline.
if (hasTasks() && wakenUp.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
selector.selectNow();
selectCnt = 1;
break;
}
int selectedKeys = selector.select(timeoutMillis);
selectCnt ++;
if (selectedKeys!= 0 || oldWakenUp || wakenUp.get()|| hasTasks() || hasScheduledTasks()) {
// -Selected something,
// -waken up by user, or
// -the task queue has a pending task.
// -a scheduled task is ready for processing
break;
}
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
//Thread was interrupted so reset selected keys and break so we not run into abusy loop.
//As this is most likely a bug in the handler of the user or it's client librarywe will
// also log it.
//
//See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/2426
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Selector.select() returnedprematurely because Thread.currentThread().interrupt()was called. Use NioEventLoop.shutdownGracefully()to shutdown the NioEventLoop.");
}
selectCnt = 1;
break;
}
long time =System.nanoTime();
if (time -TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.toNanos(timeoutMillis) >= currentTimeNanos){
//timeoutMillis elapsed without anything selected.
selectCnt = 1;
} else if (SELECTOR_AUTO_REBUILD_THRESHOLD> 0 &&
selectCnt >= SELECTOR_AUTO_REBUILD_THRESHOLD){
//The selector returned prematurely many times in a row.
//Rebuild the selector to work around the problem.
logger.warn("Selector.select() returned prematurely {} times ina row; rebuilding Selector {}.",
selectCnt, selector);
rebuildSelector();
selector = this.selector;
//Select again to populate selectedKeys.
selector.selectNow();
selectCnt = 1;
break;
}
currentTimeNanos = time;
}
if(selectCnt > MIN_PREMATURE_SELECTOR_RETURNS){
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Selector.select() returned prematurely {} times ina row for Selector {}.",selectCnt - 1, selector);
}
}
} catch(CancelledKeyException e) {
if(logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(CancelledKeyException.class.getSimpleName() + "raised by a Selector {} - JDK bug?", selector, e);
}
// Harmless exception - log anyway
}
}
8) 当轮询到准备继续的Channel之后,就由Reactor线程NioEventLoop执行ChannelPipeline的相应方法,并最终调度并执行ChannelHandler
9) 执行Netty系统的ChannelHandler和用户添加的定制化ChannelHandler
说明:后几个步骤,都被Netty封装并处理了,所以并不需要我们做过多的事情。
3. 示例代码
EventLoopGroup bossGroup= new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup= new NioEventLoopGroup();
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap= new ServerBootstrap();
serverBootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 100).handler(newLoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO))
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
public voidinitChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws IOException {
ch.pipeline().addLast(newNettyMessageDecoder(1024 * 1024, 4, 4));
ch.pipeline().addLast(newNettyMessageEncoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast("readTimeoutHandler",new ReadTimeoutHandler(50));
ch.pipeline().addLast(newLoginAuthRespHandler());
ch.pipeline().addLast("HeartBeatHandler",new HeartBeatRespHandler());
}
});
// 绑定端口,同步等待成功
serverBootstrap.bind(NettyConstant.REMOTEIP,NettyConstant.PORT).sync();
System.out.println("Netty server start ok : " +(NettyConstant.REMOTEIP + " : " + NettyConstant.PORT));
二、 Netty客户端
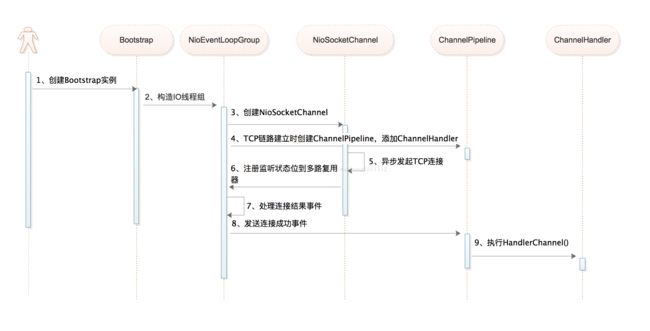
1. 时序图
2. 服务端启动步骤
因为Client有很多步骤做的事情和Server比较类似,所以下面的描述较为简单。
1) 创建Bootstrap实例
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
2) 创建客户端连接、用于IO读写的Reactor线程组(NioEventLoopgroup)
EventLoopGroup group =new NioEventLoopGroup();
bootstrap.group(group);默认为IO线程个数为CPU核数的2倍
3) 创建NioSocketChannel
通过Bootstrap的ChannelFactor和用户指定的Channel类型创建用于客户端连接的NioSocketChannel。
bootstrap. channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
4) 创建ChannelPipeline,添加ChannelHandler
bootstrap.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY,true).handler(newChannelInitializer() {
@Override
publicvoid initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throwsException {
//add ChannelHandler
ch.pipeline().addLast(new NettyMessageDecoder(1024 * 1024, 4, 4));
ch.pipeline().addLast("MessageEncoder", new NettyMessageEncoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast("readTimeoutHandler", new ReadTimeoutHandler(50));
ch.pipeline().addLast("HeartBeatHandler", new HeartBeatReqHandler());
}
}); 5) 异步发起TCP连接,判断连接是否成功。
如果成功,则直接将NioSocketChannel注册到多路复用器上,监听读操作位,用户数据报读取和消息发送;如果没有连接成功,则注册连接监听位到多路复用器,等待连接结果。
bootstrap.connect(newInetSocketAddress(host, port), newInetSocketAddress(NettyConstant.LOCALIP,NettyConstant.LOCAL_PORT)).sync();
6) 注册对应的网络监听状态位到多路复用器
7) 由多路复用器轮询各Channel,处理连接结果
8) 如果连接成功,设置Future结果,发送连接成功事件,触发ChannelPipeline执行
9) 有ChannelPipeline执行ChannelHandler,执行业务逻辑。
以下为HeartBeatReqHandler的示例代码:
@Override
public voidchannelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx,Object msg) throwsException {
NettyMessage message= (NettyMessage) msg;
// 握手成功,主动发送心跳消息
if (message.getHeader() != null&& message.getHeader().getType() ==MessageType.LOGIN_RESP.value()) {
heartBeat= ctx.executor().scheduleAtFixedRate(new HeartBeatReqHandler.HeartBeatTask(ctx), 0, 5000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} else if (message.getHeader()!= null && message.getHeader().getType()== MessageType.HEARTBEAT_RESP.value()) {
System.out.println("Client receive server heart beatmessage : ---> " + message);
} else
ctx.fireChannelRead(msg);
}
说明:后几个步骤,都被Netty封装并处理了,所以并不需要我们做过多的事情。
3. 示例代码
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(group).channel(NioSocketChannel.class).option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer() {
@Override
public voidinitChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast(newNettyMessageDecoder(1024 * 1024, 4, 4));
ch.pipeline().addLast("MessageEncoder",new NettyMessageEncoder());
ch.pipeline().addLast("readTimeoutHandler",new ReadTimeoutHandler(50));
ch.pipeline().addLast("HeartBeatHandler",new HeartBeatReqHandler());
}
});
// 发起异步连接操作
ChannelFuture future =bootstrap.connect(newInetSocketAddress(host, port),
newInetSocketAddress(NettyConstant.LOCALIP,NettyConstant.LOCAL_PORT)).sync();
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();