【雷丰阳】Spring纯注解版 bean的生命周期
Spring纯注解开发(雷丰阳)
本文为个人学习笔记:
资料来源:
个人学习尚硅谷 雷丰阳老师的视频 自己总结
学习视频:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1gW411W7wy
组件添加
@Configuration
// 配置类 等于之前的配置文件
@Configuration // 告诉Spring 这是一个配置类
public class MainConfig {
/**
* 功能描述: 配置person
* @Param: []
* @Return: com.jsu.pojo.Person
* @Author: Jsu
*
*
* 类型为 class="com.jsu.pojo.Person" 返回值类型 Person
* id="person" == person
*/
@Bean // 给容器中主注册一个bean
public Person person(){
return new Person("su",20);// 自己随便定义的person类 只有两个属性
}
}
@Test
public void testMain01() {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig.class);
Person bean = applicationContext.getBean(Person.class);
System.out.println(bean);
String[] names = applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String name : names) {
System.out.println("bean --- --- " + name);
}
}
@ComponentScan
@ComponentScan 什么都不填的话 默认是本包
包扫描 只要是标注了@component @controller @service @repository
<context:component-scan base-package="com.jsu"></context:component-scan>
value: 指定要扫描的包
excludeFilters: 扫描的时候按照什么规则排除那些组件
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,classes = {Controller.class, Service.class})
includeFilters : 扫描的时候只让那些组件接收扫描
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,classes = {Repository.class,})
使用includeFilters时候 记得加上 useDefaultFilters = false
@ComponentScans 里面放ComponentScan数组
FilterType.ANNOTATION 按照注解
FilterType.ASSIGNABLE_TYPE 按照给定的类型 type = FilterType.ASSIGNABLE_TYPE,classes = {PersonService.class}
FilterType.ASPECTJ 使用ASPECTJ表达式
FilterType.REGEX 使用正则表达式
FilterType.CUSTOM 自定义过滤规则
// 配置类 等于之前的配置文件
@Configuration // 告诉Spring 这是一个配置类
@ComponentScan(value = "com.jsu",excludeFilters = {
// @ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ASSIGNABLE_TYPE,classes = {PersonService.class})
},
includeFilters = {
@ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM,classes = {MyTypeFilter.class}),
// @ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.ANNOTATION,classes = {Repository.class,})
},useDefaultFilters = false)
public class MainConfig {
@Bean // 给容器中主注册一个bean
public Person person(){
return new Person("su",20);
}
}
// @ComponentScan.Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM,classes = {MyTypeFilter.class}) 自定义过滤规则
public class MyTypeFilter implements TypeFilter {
/**
* 功能描述:
* metadataReader : 读取到的当前正在扫描的包
* metadataReaderFactory : 可以获取到其他任何类的信息的
* @Param: [metadataReader, metadataReaderFactory]
* @Return: boolean
* @Author: Jsu
*/
@Override
public boolean match(MetadataReader metadataReader, MetadataReaderFactory metadataReaderFactory) throws IOException {
// 获取到当前类的注解的信息
AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata = metadataReader.getAnnotationMetadata();
// 获取当前正在扫描的类 的类信息
ClassMetadata classMetadata = metadataReader.getClassMetadata();
// 获取当前类资源(类路径)
Resource resource = metadataReader.getResource();
// 类名
String className = classMetadata.getClassName();
System.out.println("--->" + className);
if (className.contains("er")){
return true; //匹配成功 包含在容器中
}
return false;
}
}
@Conditional
@Conditional({Condition(数组)})
按照一定的条件进行判断,满足条件给容器中注册bean
问题升级:
当系统为windows系统的时候 输出Bill Gates
当系统为linux系统的时候 输出Linux
Conditional 可以放在类上 : 意思是 当不满足条件 就整个配置都不注册组件
@Configuration
public class MainConfig2 {
@Conditional({WindowsConditional.class})
@Bean("bill")
public Person person01(){
return new Person("Bill Gates",62);
}
@Conditional({LinuxConditional.class})
@Bean("linux")
public Person person02(){
return new Person("Linux",48);
}
}
public class LinuxConditional implements Condition {
/**
* 功能描述: 判断是否是Linux 系统
* ConditionContext : 判断条件恩使用的上下文环境
* AnnotatedTypeMetadata: 注释信息
* @Param: [context, metadata]
* @Return: boolean
* @Author: Jsu
*/
@Override
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
// 判断是否是Linux 系统
// 能获取到iod使用的beanFactory
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
// 获取到类加载器
ClassLoader classLoader = context.getClassLoader();
// 获取当前环境信息
Environment environment = context.getEnvironment();
// 获取到bean定义的注册类
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = context.getRegistry();
// 操作系统 使用environment
String property = environment.getProperty("os.name");
if (property.contains("linux")){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
public class WindowsConditional implements Condition {
/**
* 功能描述: 判断是否是windows 系统
* ConditionContext : 判断条件恩使用的上下文环境
* AnnotatedTypeMetadata: 注释信息
* @Param: [context, metadata]
* @Return: boolean
* @Author: Jsu
*/
@Override
public boolean matches(ConditionContext context, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
// 获取当前环境信息
Environment environment = context.getEnvironment();
// 操作系统 使用environment
String property = environment.getProperty("os.name");
if (property.contains("Windows")){
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
@Test
public void testMain03() {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig2.class);
/**
* 问题升级:
* 当系统为windows系统的时候 输出Bill Gates
* 当系统为linux系统的时候 输出Linux
*/
Environment environment = applicationContext.getEnvironment();
String property = environment.getProperty("os.name"); // 获取当前系统
System.out.println(property); //Windows 10
String[] beanNamesForType = applicationContext.getBeanNamesForType(Person.class);
for (String s : beanNamesForType) {
System.out.println(s);
}
Map<String, Person> beansOfType = applicationContext.getBeansOfType(Person.class);
System.out.println(beansOfType);
}
@Scope
public class MainConfig2 {
/**
* 默认单实例化 ,对其进行修改
*
* @see @ConfigurableBeanFactory#SCOPE_PROTOTYPE prototype
* @see @ConfigurableBeanFactory#SCOPE_SINGLETON singleton
* @see @org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext#SCOPE_REQUEST
* @see @org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext#SCOPE_SESSION
* 常用:
* prototype :多实例
* ioc容器启动并不会去调用方法创建对象放在容器中
* 每次获取的时候才会调用方法创建对象
* singleton :单实例(默认值)
* ioc容器在启动的时候 就会调用方法去创建对象 放到ioc容器中
* 以后每次获取就是直接从容器(map.get)中拿
* 不用:
* request : 同一次请求创建一个实例
* session :同一个session创建一个实例
* 懒加载:
* 单实例bean :默认在容器启动的时候创建对象;
* 懒加载:容器启动不创建对象。第一次使用(获取) Bean创建对象,并初始化;
* @Lazy: 单例模式时候 刚启动的时候从容器中先不获取,当实例化的时候在获取
*/
@Scope("prototype")
@Bean
public Person person() {
return new Person();
}
@Test
public void testMain02() {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig2.class);
String[] names = applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String name : names) {
System.out.println("bean --- --- " + name);
}
Object bean1 = applicationContext.getBean("person");
Object bean2 = applicationContext.getBean("person");
System.out.println(bean1 == bean2);
}
@import
/**
* 给容器中注册组件
* 1、包扫描+组件标注注解 @Controller @Service @Repository @Component
* 2、@Bean 导入的第三方包里面的组件
* 3、@Import 快速给容器导一个组件
* 1、 @Import() 导入组件 id默认是组件的全类名
* 也可以导入多个
* 2、ImportSelector: 返回需要导入的组件的全类名数组
* 可以将自己写的ImportSelector中返回的数组的内容 注入到容器中
* 3、ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar : 手动注册bean到容器中
*/
@Import({Color.class,Person.class, MyImportSelector.class, MyImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar.class})
public class MyImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar {
/**
* 功能描述:
* AnnotationMetadata : 当前类的注解信息
* BeanDefinitionRegistry :BeanDefinition的注册类
* 把所需要添加到容器中的bean,调用
* BeanDefinitionRegistry.registerBeanDefinitions 手工注册进来
* @Param: [importingClassMetadata, registry]
* @Return: void
* @Author: Jsu
*/
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
boolean red = registry.containsBeanDefinition("com.jsu.pojo.Red");
boolean blue = registry.containsBeanDefinition("com.jsu.pojo.Blue");
if (red && blue){ // 判断容器中是否有com.jsu.pojo.Red和com.jsu.pojo.Blue
// 指定bean的定义信息:bean的类型 bean...
RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(RainBow.class);
// 注册一个bean 指定bean名
registry.registerBeanDefinition("rainBow",beanDefinition);
}
}
// 自定义逻辑返回需要导入的组件
public class MyImportSelector implements ImportSelector {
/**
* 功能描述: 返回值就是导入到容器中的组件全类名
* AnnotationMetadata 当标注Import注解的类的所有注解信息
* @Param: [importingClassMetadata]
* @Return: java.lang.String[]
* @Author: Jsu
*/
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) {
return new String[]{"com.jsu.pojo.Blue","com.jsu.pojo.Red"};
}
}
使用Spring提供的FactoryBean(工厂bean)
// 使用Spring提供的FactoryBean(工厂bean)
// 1、默认获取的是工厂bean调用的getObject创建的对象
// 2、要获取工厂bean本身,我们需要给id前面加上一个 &
// &colorFactoryBean
@Configuration
public class MainConfig2 {
@Bean
public ColorFactoryBean colorFactoryBean(){
return new ColorFactoryBean();
}
}
// 创建一个spring定义的工厂bean
public class ColorFactoryBean implements FactoryBean<Color> {
/**
* 功能描述: 返回一个color对象 返回到容器中
* @Param: []
* @Return: com.jsu.pojo.Color
* @Author: Jsu
*/
@Override
public Color getObject() throws Exception {
System.out.println("ColorFactoryBean getObject...... ");
return new Color();
}
/**
* 功能描述: 返回的类型
* @Param: []
* @Return: java.lang.Class
* @Author: Jsu
*/
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return Color.class;
}
/**
* 功能描述: 是否是单例
* true:单实例 在容器中保存一份
* false:多实例 每次获取都会创建一个新的bean 调用getObject方法
* @Param: []
* @Return: boolean
* @Author: Jsu
*/
@Override
public boolean isSingleton() {
return false;
}
}
@Test
public void testImport(){
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfig2.class);
String[] beanDefinitionNames = applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String name : beanDefinitionNames) {
System.out.println(name);
}
// 工厂调用 获取的是调用getObject创建的对象
Object colorFactory = applicationContext.getBean("colorFactoryBean");
Object colorFactory2 = applicationContext.getBean("colorFactoryBean");
System.out.println("bean的类型: "+ colorFactory.getClass());
//bean的类型: class com.jsu.pojo.Color
System.out.println(colorFactory == colorFactory2); // false
// ColorFactoryBean getObject......
// ColorFactoryBean getObject......
// bean的类型: class com.jsu.pojo.Color
// Spring 在FactoryBean中注册 标明当有& 说明是拿工厂bean的本身对象
Object colorFactory3 = applicationContext.getBean("&colorFactoryBean");
System.out.println("bean的类型: "+ colorFactory3.getClass());
}
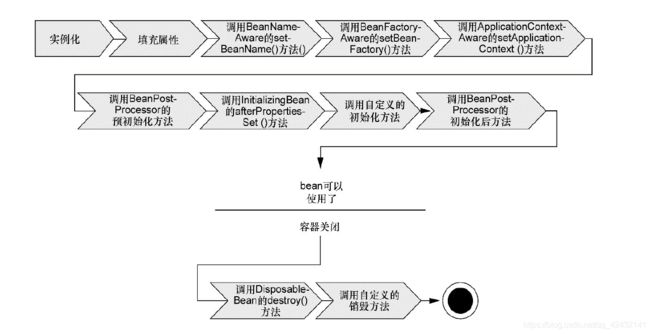
Bean的生命周期
bean的生命周期:
bean的创建 --- 初始化 --- 销毁的过程
1. Spring对bean进行实例化;
2. Spring将值和bean的引用注入到bean对应的属性中;
3. 加载xxxAware接口
1)、如果bean实现了BeanNameAware接口,Spring将bean的ID传递给setBean-Name()方法;
2)、如果bean实现了BeanFactoryAware接口,Spring将调用setBeanFactory()方法,将BeanFactory容器实例传入;
3)、如果bean实现了ApplicationContextAware接口,Spring将调用setApplicationcontext()方法,将bean所在的应用上下文的引用传入进来;
4.如果bean实现了BeanPostProcessor接口,Spring将调用它们的post-ProcessBeforeInitialization()方法;
5.如果bean实现了InitializingBean接口,Spring将调用它们的after-Propertiesset()方法。类似地,如果bean使用init-method声明了初始化方法,该方法也会被调用;
6.如果bean实现了BeanPostProcessor接口,Spring将调用它们的post-ProcessAfterInitialization()方法;
7.此时,bean已经准备就绪,可以被应用程序使用了,它们将一直驻留在应用上下文中,直到该应用上下文被销毁;
8.如果bean实现了DisposableBean接口,Spring将调用它的destroy()接口方法。同样,如果bean使用destroy-method声明了销毁方法,该方法也会被调用。
容器管理bean的生命周期
我们可以自定义初始化和销毁的方法;
容器在bean进行到当前生命周期的时候来调用我们自定义的初始化和销毁方法
构造(对象创建)
单实例:在容器启动的时候创建对象
多实例:在每次获取的时候创建对象
1、指定初始化和销毁方法
@Configuration
public class MainConfigOfLifeCycle {
// 指定init-method 和 destroy-method 两个方法
@Bean(initMethod = "init",destroyMethod = "destroy")
public Car car(){
return new Car();
}
}
public class Car {
public Car() {
System.out.println("car constructor .... ");
}
public void init(){
System.out.println("car init ...");
}
public void destroy(){
System.out.println("car destroy ...");
}
}
@Test
public void test01( ){
// 创建ioc容器 在创建容器的时候 所有的单实例都会创建完成
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfigOfLifeCycle.class);
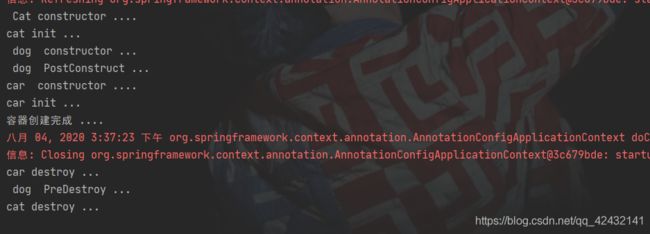
System.out.println("容器创建完成 .... ");
// car constructor ....
// car init ...
// 容器创建完成 ....
applicationContext.close();
// car destroy ...
}
、
2、通过让Bean 实现InitializingBean(定义初始化逻辑)DisposableBean(定义销毁逻辑)
@ComponentScan("com.jsu.pojo")
@Configuration
public class MainConfigOfLifeCycle {
@Bean(initMethod = "init",destroyMethod = "destroy")
public Car car(){
return new Car();
}
}
@Component
public class Cat implements InitializingBean , DisposableBean {
public Cat() {
System.out.println(" Cat constructor .... ");
}
/**
* 功能描述: 销毁
*/
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("cat destroy ...");
}
/**
* 功能描述: 初始化
*/
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("cat init ...");
}
}
@Test
public void test02( ){
// 创建ioc容器 在创建容器的时候 所有的单实例都会创建完成
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfigOfLifeCycle.class);
System.out.println("容器创建完成 .... ");
applicationContext.close();
}
3、可以使用JSR250:
@PostConstruct: 在bean创建完成并且属性赋值完成,来执行初始化方法
@PreDestroy: 在bean销毁之前通知我们进行清理工作
@Component
public class Dog {
public Dog() {
System.out.println(" dog constructor ... ");
}
@PostConstruct // 对象创建并赋值之后
public void init(){
System.out.println(" dog PostConstruct ... ");
}
@PreDestroy //在容器移除对象之前
public void destroy( ){
System.out.println(" dog PreDestroy ... ");
}
}
// 测试类还是上面的那个
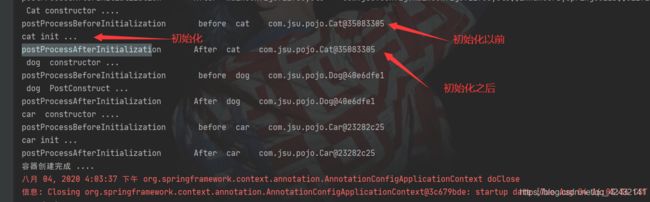
4、BeanPostProcessor bean的后置处理器
// BeanPostProcessor[interface]: bean的后置处理器
// 在bean初始化前后进行一些处理工作
// postProcessBeforeInitialization : 初始化之前进行后置处理工作
// postProcessAfterInitialization : 初始化之后进行后置处理工作
@Component // 将后置处理器 加入到容器中
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
/**
* 功能描述:
* @Param: [o, s]
* Object o: 刚创建的实例
* String s:创建好bean的名字
* @Return: java.lang.Object 可以是the original (传入的 )or a wrapped one(被封装的);
* @Author: Jsu
*/
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object o, String s) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("postProcessBeforeInitialization before " + s +" " +o);
return o;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object o, String s) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("postProcessAfterInitialization After " + s +" " +o);
return o;
}
}
//测试类还是上面的
组件赋值
@PropertySource
以前导入外部文本文件
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:person.properties"></context>
现在使用注解版
使用@PropertySource 读取外部配置文件中的k/v 保存到与逆行环境变量中
@PropertySource(value = {"classpath:/person.properties"}) 是个数组 可填多个
@PropertySource(value = {"classpath:/person.properties"}) // 是个数组 可填多个
@Configuration
public class MainConfigOfPropertyValues {
@Bean
public Person person(){
return new Person();
}
}
// 实体类
public class Person {
// 使用@Value赋值;
// 1、基本数值
// 2、可以写SpEL; #{}
// 3、可以写${ };取出配置文件[properties]中的值(在运行环境变量里面的值)`
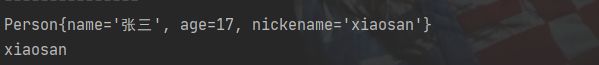
@Value("张三")
private String name;
@Value("#{20-3}")
private Integer age;
@Value("${person.nickname}")
private String nickename;
}
# 配置文件
person.nickname=xiaosan
// 测试类
public class Main_PropertyValues {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfigOfPropertyValues.class);
public void printBeans(AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext){
String[] beanDefinitionNames = applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String name : beanDefinitionNames) {
System.out.println(name);
}
}
@Test
public void test01(){
printBeans(applicationContext);
System.out.println("---------------");
Person person = (Person) applicationContext.getBean("person");
System.out.println(person);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = applicationContext.getEnvironment();
String property = environment.getProperty("person.nickname");
System.out.println(property);
applicationContext.close();
}
}
自动装配
@Autowired
自动装配
Spring利用依赖注入(DI),完成对IOC容器中各个组件的依赖关系赋值
1、@Autowired : 自动注入
1)、默认优先按照类型去容器中找对应的组件
applicationContext.getBean(PersonDao.class); (找到就赋值)
2)、如果找到多个相同类型的组件,再将属性的名称作为组件的id去容器中查找
3)、@Qualifier( "bookDao" ):使用@Qualifier指定需要装配的组件的id,而不是使用属性名
4)、自动装配默认-定要将属性赋值好,没有就会报错;
可以通过 @Autowired(required=false) 找到就注入 找不到就算了 默认是true 找不到就报错
5)、@Primary 让spring进行自动装配的时候。默认使用首选的bean
当加上@Primary 的时候 @Qualifier就不能添加了
public class PersonService {
@Autowired
PersonDao personDao;
}
2、Spring还支持@Resource(JSR250)和 Inject(JSR330)[java规范的东西]
@Resoure:
可以和@Autowired一样实现自动装配功能;默认是按照组件名称进行装配的
不能和@Qualifier 以及 @Autowired(required=false)一起用
name : 可以指定组件
@Inject
需要导包 javax。inject
和@Autowired功能一样 可以和@Qualifier一起用
没有属性 required=false
// dao层
@Repository
public class PersonDao {
public void print(){
System.out.println("dao ..");
}
}
// service层
@Service
public class PersonService {
@Autowired
PersonDao personDao;
public void print(){
System.out.println(personDao);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "PersonService{" +
"personDao=" + personDao +
'}';
}
}
// 配置类
@ComponentScan({"com.jsu.service","com.jsu.dao","com.jsu.controller"})
@Configuration
public class MainConfigOfAutowired {
}
// 测试类
public class Main_Autowired {
@Test
public void test01(){
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MainConfigOfAutowired.class);
PersonService bean = applicationContext.getBean(PersonService.class);
System.out.println(bean);
PersonDao bean2 = applicationContext.getBean(PersonDao.class);
System.out.println(bean2);
// 两个地址相同 说明是一个PersonDao
applicationContext.close();
}
}
当有两个注入的时候怎么办?
// personDao2
@ComponentScan({"com.jsu.service","com.jsu.dao","com.jsu.controller"})
@Configuration
public class MainConfigOfAutowired {
@Bean("personDao2")
public PersonDao personDao(){
PersonDao personDao = new PersonDao();
personDao.setLabel("2");
return personDao;
}
}
// personDao
@Repository
public class PersonDao {
private String label="1";
public String getLabel() {
return label;
}
public void setLabel(String label) {
this.label = label;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "PersonDao{" +
"label='" + label + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
@Service
public class PersonService {
// @Qualifier("personDao") 加上这个注解后 可指定需要装配的组件的id,而不是使用属性名
@Autowired
PersonDao personDao; // 注入哪个就是哪个
PersonDao personDao2; //
@Override
public String toString() {
return "PersonService{" +
"personDao=" + personDao2 +
'}';
}
}
@Resource @Inject
Spring还支持@Resource(JSR250)和 Inject(JSR330)[java规范的东西]
@Resoure:
可以和@Autowired一样实现自动装配功能;默认是按照组件名称进行装配的
不能和@Qualifier 以及 @Autowired(required=false)一起用
name : 可以指定组件
@Inject
需要导包 javax。inject
和@Autowired功能一样 可以和@Qualifier一起用
没有属性 required=false
3、@Autowired : 构造器,参数,方法,属性
都是从容器中获取参数组件的值
1、 当标注在方法上的时候 【@Bean + 方法参数 参数从容器中获取】
2、 当标注在构造器的时候 【如果组件只有一个有参构造器,这个有参构造器的@Autowired可以省略,参数位置的组件还是可以自动获取】
3、 当标注在参数的时候
@Profile
/**
* Profile:
* Spring为我们提供的可以根据当前环境,动态激活和切换一系列的组件的功能
* 开发环境 、 测试环境 、 生产环境
* 数据源(/A)(/B)(/C)
* @Profile
* 指定组件在哪个环境的情况下才能被注册到容器中,不指定,任何环境下都可以注册这个组件
* 1、 加了环境标识的bean 只有这个环境能被激活 默认是default
* 2、 当写在配置类上的时候 只有是指定的环境的时候,整个配置类里面的所有配置才能生效
*/
@PropertySource("classpath:/dbconfig.properties")
@Configuration
public class MainConfigOfProfile {
@Value("${db.user}")
private String user;
@Value("${db.password}")
private String password;
@Value("${db.driverClass}")
private String driverClass;
@Value("${db.jdbcUrl}")
private String jdbcUrl;
@Profile("test")
@Bean("dataSource")
public DataSource dataSource() throws Exception {
ComboPooledDataSource dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
dataSource.setUser(user);
dataSource.setPassword(password);
dataSource.setJdbcUrl(jdbcUrl);
dataSource.setDriverClass(driverClass);
return dataSource;
}
@Profile("dev")
@Bean("dataSourceDev")
public DataSource dataSourceDev() throws Exception {
ComboPooledDataSource dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
dataSource.setUser(user);
dataSource.setPassword(password);
dataSource.setJdbcUrl(jdbcUrl);
dataSource.setDriverClass(driverClass);
return dataSource;
}
@Profile("pro")
@Bean("dataSourcePro")
public DataSource dataSourcePro() throws Exception {
ComboPooledDataSource dataSource = new ComboPooledDataSource();
dataSource.setUser(user);
dataSource.setPassword(password);
dataSource.setJdbcUrl(jdbcUrl);
dataSource.setDriverClass(driverClass);
return dataSource;
}
}
# c3p0连接池配置
db.user=root
db.password=000
db.driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
db.jdbcUrl=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test
// 测试类
public class Main_Profile {
// 如何改变环境?
// 1、在虚拟机参数位置加载 -Dspring.profiles.active=test
// 2、代码方式
@Test
public void test01() {
/**
* 使用有参构造的时候执行流程
* public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Class... annotatedClasses) {
* this();
* register(annotatedClasses);
* refresh();
* }
* 下面是无参构造 内容自己写
*/
// 2、代码方式
// 无参构造 创建一个applicationContext
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
// 设置需要激活的环境
applicationContext.getEnvironment().setActiveProfiles("test","dev");
// 配置主配置类
applicationContext.register(MainConfigOfProfile.class);
// 启动构造器
applicationContext.refresh();
String[] beanNamesForType = applicationContext.getBeanNamesForType(DataSource.class);
for (String s : beanNamesForType) {
System.out.println(s);
}
applicationContext.close();
}
}
本文为个人学习笔记:
资料来源:
个人学习尚硅谷 雷丰阳老师的视频 自己总结
学习视频:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1gW411W7wy