SpringBoot深入(二)--SpringBoot启动过程分析
版权声明:作者原创,转载请注明出处。
本系列文章目录地址:http://blog.csdn.net/u011961421/article/details/79416510
前言
前一篇分析了SpringBoot如何启动以及内置web容器,这篇我们一起看一下SpringBoot的整个启动过程,废话不多说,正文开始。
正文
一、SpringBoot的启动类是**application,以注解@SpringBootApplication注明。
@SpringBootApplication
public class CmsApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(CmsApplication.class, args);
}
}SpringBootApplication注解是@Configuration,@EnableAutoConfiguration,@ComponentScan三个注解的集成,分别表示Springbean的配置bean,开启自动配置spring的上下文,组件扫描的路径,这也是为什么*application.java需要放在根路径的原因,这样@ComponentScan扫描的才是整个项目。
二、该启动类默认只有一个main方法,调用的是SpringApplication.run方法,下面我们来看一下SpringApplication这个类。
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Object source, String... args) {
return run(new Object[]{source}, args);
}
...
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Object[] sources, String[] args) {
return (new SpringApplication(sources)).run(args);//sources为具体的CmsApplication.class类
}
...抽出其中两个直接调用的run方法,可以看出静态方法SpringApplication.run最终创建了一个SpringApplication,并运行其中run方法。
查看起构造方法:
public SpringApplication(Object... sources) {
this.bannerMode = Mode.CONSOLE;
this.logStartupInfo = true;
this.addCommandLineProperties = true;
this.headless = true;
this.registerShutdownHook = true;
this.additionalProfiles = new HashSet();
this.initialize(sources);
}
...构造方法设置了基础值后调用initialize方法进行初始化,如下:
private void initialize(Object[] sources) {
if (sources != null && sources.length > 0) {
this.sources.addAll(Arrays.asList(sources));
}
this.webEnvironment = this.deduceWebEnvironment();
this.setInitializers(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
this.setListeners(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
this.mainApplicationClass = this.deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
...初始化方法主要做了几步:
1.将source放入SpringApplication的sources属性中管理,sources是一个LinkedHashSet(),这意味着我们可以同时创建多个自定义不重复的Application,但是目前只有一个。
2.判断是否是web程序(javax.servlet.Servlet和org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext都必须在类加载器中存在),并设置到webEnvironment属性中 。
3.从spring.factories中找出ApplicationContextInitializer并设置到初始化器initializers。
4.从spring.factories中找出ApplicationListener,并实例化后设置到SpringApplication的监听器listeners属性中。这个过程就是找出所有的应用程序事件监听器。
5.找出的main方法的类(这里是CmsApplication),并返回Class对象。
默认情况下,initialize方法从spring.factories文件中找出的key为ApplicationContextInitializer的类有:
- org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationContextInitializer
- org.springframework.boot.context.ContextIdApplicationContextInitializer
- org.springframework.boot.context.ConfigurationWarningsApplicationContextInitializer
- org.springframework.boot.context.web.ServerPortInfoApplicationContextInitializer
- org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.logging.AutoConfigurationReportLoggingInitializer
key为ApplicationListener的有:
- org.springframework.boot.context.config.ConfigFileApplicationListener
- org.springframework.boot.context.config.AnsiOutputApplicationListener
- org.springframework.boot.logging.LoggingApplicationListener
- org.springframework.boot.logging.ClasspathLoggingApplicationListener
- org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.BackgroundPreinitializer
- org.springframework.boot.context.config.DelegatingApplicationListener
- org.springframework.boot.builder.ParentContextCloserApplicationListener
- org.springframework.boot.context.FileEncodingApplicationListener
- org.springframework.boot.liquibase.LiquibaseServiceLocatorApplicationListener
三、SpringApplication构造和初始化完成后,便是运行其run方法
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();// 构造一个任务执行观察器
stopWatch.start();// 开始执行,记录开始时间
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
FailureAnalyzers analyzers = null;
this.configureHeadlessProperty();
// 获取SpringApplicationRunListeners,内部只有一个EventPublishingRunListener
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = this.getRunListeners(args);
// 封装成SpringApplicationEvent事件然后广播出去给SpringApplication中的listeners所监听,启动监听
listeners.starting();
try {
// 构造一个应用程序参数持有类
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
// 加载配置环境
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = this.prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
Banner printedBanner = this.printBanner(environment);
// 创建Spring容器(使用BeanUtils.instantiate)
context = this.createApplicationContext();
// 若容器创建失败,分析输出失败原因
new FailureAnalyzers(context);
// 设置容器配置环境,监听等
this.prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
// 刷新容器
this.refreshContext(context);
this.afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
// 广播出ApplicationReadyEvent事件给相应的监听器执行
listeners.finished(context, (Throwable)null);
stopWatch.stop();// 执行结束,记录执行时间
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
(new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)).logStarted(this.getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
return context;// 返回Spring容器
} catch (Throwable var9) {
this.handleRunFailure(context, listeners, (FailureAnalyzers)analyzers, var9);
throw new IllegalStateException(var9);
}
}run方法过程分析如上,该方法几个关键步骤如下:
1.创建了应用的监听器SpringApplicationRunListeners并开始监听
2.加载SpringBoot配置环境(ConfigurableEnvironment),如果是通过web容器发布,会加载StandardEnvironment,其最终也是继承了ConfigurableEnvironment,类图如下

可以看出,*Environment最终都实现了PropertyResolver接口,我们平时通过environment对象获取配置文件中指定Key对应的value方法时,就是调用了propertyResolver接口的getProperty方法。
3.配置环境(Environment)加入到监听器对象中(SpringApplicationRunListeners)
4.创建Spring容器:ConfigurableApplicationContext(应用配置上下文),我们可以看一下创建方法
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
Class contextClass = this.applicationContextClass;
if (contextClass == null) {
try {
contextClass = Class.forName(this.webEnvironment ? "org.springframework.boot.context.embedded.AnnotationConfigEmbeddedWebApplicationContext" : "org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException var3) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Unable create a default ApplicationContext, please specify an ApplicationContextClass", var3);
}
}
return (ConfigurableApplicationContext)BeanUtils.instantiate(contextClass);
}方法会先获取显式设置的应用上下文(applicationContextClass),如果不存在,再加载默认的环境配置(通过是否是web environment判断),默认选择AnnotationConfigApplicationContext注解上下文(通过扫描所有注解类来加载bean),最后通过BeanUtils实例化上下文对象,并返回,ConfigurableApplicationContext类图如下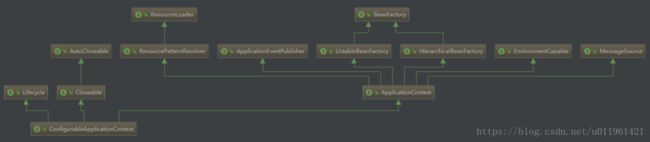
主要看其继承的两个方向:
LifeCycle:生命周期类,定义了start启动、stop结束、isRunning是否运行中等生命周期空值方法
ApplicationContext:应用上下文类,其主要继承了beanFactory(bean的工厂类)。
5.回到run方法内,设置容器prepareContext方法,将listeners、environment、applicationArguments、banner等重要组件与上下文对象关联
6.刷新容器,refresh()方法,初始化方法如下:
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
Object var1 = this.startupShutdownMonitor;
synchronized(this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
this.prepareRefresh();
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.obtainFreshBeanFactory();
this.prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
this.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
this.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
this.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
this.initMessageSource();
this.initApplicationEventMulticaster();
this.onRefresh();
this.registerListeners();
this.finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
this.finishRefresh();
} catch (BeansException var9) {
if (this.logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
this.logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - cancelling refresh attempt: " + var9);
}
this.destroyBeans();
this.cancelRefresh(var9);
throw var9;
} finally {
this.resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}refresh()方法做了很多核心工作比如BeanFactory的设置,BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的执行、BeanPostProcessor接口的执行、自动化配置类的解析、spring.factories的加载、bean的实例化、条件注解的解析、国际化的初始化等等。这部分内容会在之后的文章中分析。
7.广播出ApplicationReadyEvent,执行结束返回ConfigurableApplicationContext。
至此,SpringBoot启动完成,回顾整体流程,Springboot的启动,主要创建了配置环境(environment)、事件监听(listeners)、应用上下文(applicationContext),并基于以上条件,在容器中开始实例化我们需要的Bean。
参考资料链接
https://www.jianshu.com/p/d51e1896a5f7
https://www.cnblogs.com/trgl/p/7353782.html