这次主要就介绍android动画,android动画目前分为三种形式,Tween Animation 这个只能应用于view对象上面的,Drawable Animation这个是帧动画,就是类似我们有一些列的图片依次播放图片时出现的动画,Property Animation 这个是属性动画,这也是在android3.0之后引进的动画,在手机的版本上是android4.0就可以使用这个动画,下面我们主要就是针对这三种情况进行介绍。
Tween Animation
这个动画在Property Animation之前使用最多的,当然在android4.0之后也是有很多人使用这个动画来弄一些简单的动画效果,Tween Animation主要是包括四种动画实现效果:
- AlphaAniamtion:渐变效果,这个是一个透明度的动画效果
AlphaAnimation(float fromAlpha,float toAlpha)
这个就是AlphaAnimation的构造函数,fromAlpha表示的是动画初始时的透明度,toAlpha表示的是动画结束时的透明度,这个取值范围是0~1,0表示的是完全透明,1表示的是完全不透明
- ScaleAnimation:图片进行放大缩小的动画效果,
ScaleAnimation(float fromX, float toX, float fromY,float toY, int pivotXType, float pivotXValue, int pivotYType, float pivotYValue)
上面就是这个Scale参数的情况,这个参数是最多的,fromX:起始X坐标上的伸缩尺寸,toX:结束X坐标上的伸缩尺寸,fromY:起始Y坐标上的伸缩尺寸,toY:结束Y坐标上的伸缩尺寸,关于这个伸缩尺寸,0表示的就是看不见,1表示原始大小,依此类推,1.5表示的就是1.5倍
pivotXType和pivotYType分别表示在X和Y轴上伸缩模式。这里有三个值:
Animation.ABSOLUTE:这个表示的是绝对坐标
Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF:相对于自己的坐标
Animation.RELATIVE_TO_PARENT:相对于父控件
上面这些说的都是这个动画效果相对于哪一个点来进行变化的,Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF这个就相对于自己的坐标,就是说这个坐标原始坐标是在你设置view的左上角,Animation.RELATIVE_TO_PARENT相对于父控件的坐标,这个大多数指的就是手机上的坐标原点。Animation.ABSOLUTE绝对坐标说的就是具体相对哪个一个点,比如(100,200),就是表示相对坐标点在(100,200)这个点来进行动画。
pivotXValue和pivotYValue值就是相对上面的值设置的,表示的是相对于哪一个点来进行放大缩小的动画,对于Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF和Animation.RELATIVE_TO_PARENT
(0,0)表示的是原点,(0.5f,0.5f)表示的中间点这个对于Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF相对于view控件的中间点,Animation.RELATIVE_TO_PARENT就是值该view上父控件的中间点,(1,1)表示的就是右下角的坐标。这个我们可以多多试试就知道效果了。
一般情况下使用是Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF,选择点是(0.5f,0.5f)就是该view的中间点,这样图片变化看起来不会产生很奇怪的感觉。
- TranslateAnimation:view在水平方向和垂直方向进行移动动画效果
TranslateAnimation(fromXDelta, toXDelta, fromYDelta, toYDelta)
fromXDelta和fromYDelta分别表示在X和Y轴上面的起始坐标,(0,0)这个表示的就是当前view的坐标,toXDelta和toYDelta分别表示最终目标,如果只是X轴移动或者Y轴移动,那么可以把对应不移动的坐标设置为0。
- RotateAnimation:旋转动画效果
RotateAnimation(fromDegrees, toDegrees, pivotXType, pivotXValue, pivotYType, pivotYValue)
fromDegrees和toDegrees分别表示的起始角度和结束角度,比如(0,45)这个就是表示从默认状态旋转到45度的意思。剩下的参数上面已经介绍过来,比如下面的代码:
RotateAnimation rotate=new RotateAnimation(0, 50, Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0.5f, Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0.5f);
表示就是从默认状态旋转到50度,旋转的中心点就是这个view的中心点(Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF表示的以自身为参考点,0.5f表示就是一般)
上面介绍就是这个Tween Animation动画效果,分别是透明度的变化,放大缩小,移动以及旋转动画效果,这些动画除了上面的构造函数之外当然还有一些公共的其它方法,下面就介绍一下:
setDuration(long durationMillis)
这个表示的是设置动画的显示时间,就是这个动画从初始状态到结束状态所需要的时间,durationMillis参数为动画显示时间的长短,单位是毫秒。
setStartOffset(long startOffset)
这个表示的是动画的开始时间,startOffset表示就是动画的开始时间,单位毫秒(有时候我们在startAnimation之后可能不希望立即取执行这个动画,需要等待一会再进行动画就可以使用这个
setFillAfter(boolean fillAfter)
这个表示的动画结束之后是否保留结束的位置,这个值默认是flase表示动画结束之后不保留动画的位置,就是说在我们进行动画效果结束之后又会自动恢复到原始的状态,true表示就是保留动画结束时的状态,这个值一般都是要设置为true的
startAnimation(Animation animation)
这个是在view对象上使用的,表示开始进行动画,参数就是我们上面说的那四种(注意上面的四种类型都是继承于Animation的),比如我现在有一个ImageView对象image,那么我现在要开始动画时就是用imageView.startAnimation(rotateAnimation);就可以进行动画了,
setInterpolator(Interpolator i)
这个表示的设置动画的变化速度,这里android提供很多类型的Interpolator类型的变化器
1。setInterpolator(new AccelerateInterpolator(float factor):这个AccelerateInterpolator表示的是加速,factor参数可以设置为加速的倍数,数值越大动画的速度越快,当然也可以是默认的new AccelerateInterpolator()默认这个参数为1。我们来看一下源码:
/** * An interpolator where the rate of change starts out slowly and * and then accelerates. * */ public class AccelerateInterpolator implements Interpolator { private final float mFactor; private final double mDoubleFactor; public AccelerateInterpolator() { mFactor = 1.0f; mDoubleFactor = 2.0; } /** * Constructor * * @param factor Degree to which the animation should be eased. Seting * factor to 1.0f produces a y=x^2 parabola. Increasing factor above * 1.0f exaggerates the ease-in effect (i.e., it starts even * slower and ends evens faster) */ public AccelerateInterpolator(float factor) { mFactor = factor; mDoubleFactor = 2 * mFactor; } public AccelerateInterpolator(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, com.android.internal.R.styleable.AccelerateInterpolator); mFactor = a.getFloat(com.android.internal.R.styleable.AccelerateInterpolator_factor, 1.0f); mDoubleFactor = 2 * mFactor; a.recycle(); } public float getInterpolation(float input) { if (mFactor == 1.0f) { return input * input; } else { return (float)Math.pow(input, mDoubleFactor); } } }
上面那个就是AccelerateInterpolator的源码,这个源码中有两个构造函数一个带参数一个不带参数的,从上面代码中getInterpolation这个方法是最重要的,那么跟踪一下这个方法调用是在Animation.java类中的getTransformation()方法
public boolean getTransformation(long currentTime, Transformation outTransformation) { if (mStartTime == -1) { mStartTime = currentTime; } final long startOffset = getStartOffset(); final long duration = mDuration; float normalizedTime; if (duration != 0) { normalizedTime = ((float) (currentTime - (mStartTime + startOffset))) / (float) duration; } else { // time is a step-change with a zero duration normalizedTime = currentTime < mStartTime ? 0.0f : 1.0f; } final boolean expired = normalizedTime >= 1.0f; mMore = !expired; if (!mFillEnabled) normalizedTime = Math.max(Math.min(normalizedTime, 1.0f), 0.0f); if ((normalizedTime >= 0.0f || mFillBefore) && (normalizedTime <= 1.0f || mFillAfter)) { if (!mStarted) { fireAnimationStart(); mStarted = true; if (USE_CLOSEGUARD) { guard.open("cancel or detach or getTransformation"); } } if (mFillEnabled) normalizedTime = Math.max(Math.min(normalizedTime, 1.0f), 0.0f); if (mCycleFlip) { normalizedTime = 1.0f - normalizedTime; } final float interpolatedTime = mInterpolator.getInterpolation(normalizedTime); applyTransformation(interpolatedTime, outTransformation); }
。。。。。。。。。
return mMore; }
上面就是getTransformation()方法,在这个方法中也看到之前设置的getStartOffset()以及mDuration等等,在下面发现这么一句话
final float interpolatedTime = mInterpolator.getInterpolation(normalizedTime);mInterpolator对象创建也是在这个类里面
public void setInterpolator(Interpolator i) { mInterpolator = i; }
看上面就是我们代码中设置的,那么来看看这个getInterpolation里面参数的值,从上面源码中知道mFillEnabled和mCycleFlip默认值都是flase,一般情况下我们都不会去设置这两个值都是取默认值的,if (mFillEnabled) normalizedTime = Math.max(Math.min(normalizedTime, 1.0f), 0.0f);这个设置了normalizedTime的值,就是下面要用做getInterpolation参数值,从上面的代码中可以发现normalizedTime这个值是不小于0的,Math.max(Math.min(normalizedTime, 1.0f), 0.0f)表示取值范围就是0~1,也就是手这个getInterpolation(float input)这个input参数的变化就是在指定的动画事件内从0到1递增变化。
我们来看看Interpolator这个类
package android.view.animation; import android.animation.TimeInterpolator; /** * An interpolator defines the rate of change of an animation. This allows * the basic animation effects (alpha, scale, translate, rotate) to be * accelerated, decelerated, repeated, etc. */ public interface Interpolator extends TimeInterpolator { // A new interface, TimeInterpolator, was introduced for the new android.animation // package. This older Interpolator interface extends TimeInterpolator so that users of // the new Animator-based animations can use either the old Interpolator implementations or // new classes that implement TimeInterpolator directly. }
再看这个TimeInterpolator类
/* * Copyright (C) 2010 The Android Open Source Project * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package android.animation; /** * A time interpolator defines the rate of change of an animation. This allows animations * to have non-linear motion, such as acceleration and deceleration. */ public interface TimeInterpolator { /** * Maps a value representing the elapsed fraction of an animation to a value that represents * the interpolated fraction. This interpolated value is then multiplied by the change in * value of an animation to derive the animated value at the current elapsed animation time. * * @param input A value between 0 and 1.0 indicating our current point * in the animation where 0 represents the start and 1.0 represents * the end * @return The interpolation value. This value can be more than 1.0 for * interpolators which overshoot their targets, or less than 0 for * interpolators that undershoot their targets. */ float getInterpolation(float input); }
从这段代码中我们得出结论就是所有的变化器都是继承于Interpolator接口,而且都实现了float getInterpolation(float input);这个方法,那么我们就要弄清楚这个getTransformation()方法在哪里调用,我们说过StartAnimation是view对象调用那么我们在View.java里面
public void startAnimation(Animation animation) { animation.setStartTime(Animation.START_ON_FIRST_FRAME); setAnimation(animation); invalidateParentCaches(); invalidate(true); }
这段代码中最后一句就是更新,看一下
/** * This method is called by ViewGroup.drawChild() to have each child view draw itself. * This draw() method is an implementation detail and is not intended to be overridden or * to be called from anywhere else other than ViewGroup.drawChild(). */ boolean draw(Canvas canvas, ViewGroup parent, long drawingTime) { boolean useDisplayListProperties = mAttachInfo != null && mAttachInfo.mHardwareAccelerated; boolean more = false; final boolean childHasIdentityMatrix = hasIdentityMatrix(); final int flags = parent.mGroupFlags; if ((flags & ViewGroup.FLAG_CLEAR_TRANSFORMATION) == ViewGroup.FLAG_CLEAR_TRANSFORMATION) { parent.getChildTransformation().clear(); parent.mGroupFlags &= ~ViewGroup.FLAG_CLEAR_TRANSFORMATION; } Transformation transformToApply = null; boolean concatMatrix = false; boolean scalingRequired = false; boolean caching; int layerType = getLayerType(); final boolean hardwareAccelerated = canvas.isHardwareAccelerated(); if ((flags & ViewGroup.FLAG_CHILDREN_DRAWN_WITH_CACHE) != 0 || (flags & ViewGroup.FLAG_ALWAYS_DRAWN_WITH_CACHE) != 0) { caching = true; // Auto-scaled apps are not hw-accelerated, no need to set scaling flag on DisplayList if (mAttachInfo != null) scalingRequired = mAttachInfo.mScalingRequired; } else { caching = (layerType != LAYER_TYPE_NONE) || hardwareAccelerated; } final Animation a = getAnimation(); if (a != null) { more = drawAnimation(parent, drawingTime, a, scalingRequired); concatMatrix = a.willChangeTransformationMatrix(); if (concatMatrix) { mPrivateFlags3 |= PFLAG3_VIEW_IS_ANIMATING_TRANSFORM; } transformToApply = parent.getChildTransformation(); } else { 。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。
上面这段代码中有这么一句话 more = drawAnimation(parent, drawingTime, a, scalingRequired),这个函数就是
private boolean drawAnimation(ViewGroup parent, long drawingTime, Animation a, boolean scalingRequired) { Transformation invalidationTransform; final int flags = parent.mGroupFlags; final boolean initialized = a.isInitialized(); if (!initialized) { a.initialize(mRight - mLeft, mBottom - mTop, parent.getWidth(), parent.getHeight()); a.initializeInvalidateRegion(0, 0, mRight - mLeft, mBottom - mTop); if (mAttachInfo != null) a.setListenerHandler(mAttachInfo.mHandler); onAnimationStart(); } final Transformation t = parent.getChildTransformation(); boolean more = a.getTransformation(drawingTime, t, 1f);
。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。
看到上面的drawAnimation方法中就有a.getTransformation(drawingTime, t, 1f);这个方法,我们也就明白了这个getTransformation()方法是在startAnimation()之后调用的。
2。setInterpolator(new AccelerateDecelerateInterpolator()):这个AccelerateDecelerateInterpolator表示的是先加速后减速的动画
/** * An interpolator where the rate of change starts and ends slowly but * accelerates through the middle. * */ public class AccelerateDecelerateInterpolator implements Interpolator { public AccelerateDecelerateInterpolator() { } @SuppressWarnings({"UnusedDeclaration"}) public AccelerateDecelerateInterpolator(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { } public float getInterpolation(float input) { return (float)(Math.cos((input + 1) * Math.PI) / 2.0f) + 0.5f; } }
3。setInterpolator(new DecelerateInterpolator(float factor)):这个表示的就是减速,factor和上面的加速参数是一个意思,只不过作用是相反的,也可以不带参数new DecelerateInterpolator()这样
/** * An interpolator where the rate of change starts out quickly and * and then decelerates. * */ public class DecelerateInterpolator implements Interpolator { public DecelerateInterpolator() { } /** * Constructor * * @param factor Degree to which the animation should be eased. Setting factor to 1.0f produces * an upside-down y=x^2 parabola. Increasing factor above 1.0f makes exaggerates the * ease-out effect (i.e., it starts even faster and ends evens slower) */ public DecelerateInterpolator(float factor) { mFactor = factor; } public DecelerateInterpolator(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, com.android.internal.R.styleable.DecelerateInterpolator); mFactor = a.getFloat(com.android.internal.R.styleable.DecelerateInterpolator_factor, 1.0f); a.recycle(); } public float getInterpolation(float input) { float result; if (mFactor == 1.0f) { result = (float)(1.0f - (1.0f - input) * (1.0f - input)); } else { result = (float)(1.0f - Math.pow((1.0f - input), 2 * mFactor)); } return result; } private float mFactor = 1.0f; }
4。setInterpolator(new CycleInterpolator()):动画循环播放特定次数,速率改变沿着正弦曲线
/** * Repeats the animation for a specified number of cycles. The * rate of change follows a sinusoidal pattern. * */ public class CycleInterpolator implements Interpolator { public CycleInterpolator(float cycles) { mCycles = cycles; } public CycleInterpolator(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, com.android.internal.R.styleable.CycleInterpolator); mCycles = a.getFloat(com.android.internal.R.styleable.CycleInterpolator_cycles, 1.0f); a.recycle(); } public float getInterpolation(float input) { return (float)(Math.sin(2 * mCycles * Math.PI * input)); } private float mCycles; }
5。setInterpolator(new LinearInterpolator()):表示匀速
/** * An interpolator where the rate of change is constant * */ public class LinearInterpolator implements Interpolator { public LinearInterpolator() { } public LinearInterpolator(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { } public float getInterpolation(float input) { return input; } }
6。setInterpolator(new OvershootInterpolator()) 超越,最后超出目的值然后缓慢改变到目的值
/** * An interpolator where the change flings forward and overshoots the last value * then comes back. */ public class OvershootInterpolator implements Interpolator { private final float mTension; public OvershootInterpolator() { mTension = 2.0f; } /** * @param tension Amount of overshoot. When tension equals 0.0f, there is * no overshoot and the interpolator becomes a simple * deceleration interpolator. */ public OvershootInterpolator(float tension) { mTension = tension; } public OvershootInterpolator(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, com.android.internal.R.styleable.OvershootInterpolator); mTension = a.getFloat(com.android.internal.R.styleable.OvershootInterpolator_tension, 2.0f); a.recycle(); } public float getInterpolation(float t) { // _o(t) = t * t * ((tension + 1) * t + tension) // o(t) = _o(t - 1) + 1 t -= 1.0f; return t * t * ((mTension + 1) * t + mTension) + 1.0f; } }
7。setInterpolator(new BounceInterpolator()):跳跃,快到目的值时值会跳跃,如目的值100,后面的值可能依次为85,77,70,80,90,100
/** * An interpolator where the change bounces at the end. */ public class BounceInterpolator implements Interpolator { public BounceInterpolator() { } @SuppressWarnings({"UnusedDeclaration"}) public BounceInterpolator(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { } private static float bounce(float t) { return t * t * 8.0f; } public float getInterpolation(float t) { // _b(t) = t * t * 8 // bs(t) = _b(t) for t < 0.3535 // bs(t) = _b(t - 0.54719) + 0.7 for t < 0.7408 // bs(t) = _b(t - 0.8526) + 0.9 for t < 0.9644 // bs(t) = _b(t - 1.0435) + 0.95 for t <= 1.0 // b(t) = bs(t * 1.1226) t *= 1.1226f; if (t < 0.3535f) return bounce(t); else if (t < 0.7408f) return bounce(t - 0.54719f) + 0.7f; else if (t < 0.9644f) return bounce(t - 0.8526f) + 0.9f; else return bounce(t - 1.0435f) + 0.95f; } }
8。setInterpolator(new AnticipateOvershootInterpolator()):反向加超越,先向相反方向改变,再加速播放,会超出目的值然后缓慢移动至目的值
/** * An interpolator where the change starts backward then flings forward and overshoots * the target value and finally goes back to the final value. */ public class AnticipateOvershootInterpolator implements Interpolator { private final float mTension; public AnticipateOvershootInterpolator() { mTension = 2.0f * 1.5f; } /** * @param tension Amount of anticipation/overshoot. When tension equals 0.0f, * there is no anticipation/overshoot and the interpolator becomes * a simple acceleration/deceleration interpolator. */ public AnticipateOvershootInterpolator(float tension) { mTension = tension * 1.5f; } /** * @param tension Amount of anticipation/overshoot. When tension equals 0.0f, * there is no anticipation/overshoot and the interpolator becomes * a simple acceleration/deceleration interpolator. * @param extraTension Amount by which to multiply the tension. For instance, * to get the same overshoot as an OvershootInterpolator with * a tension of 2.0f, you would use an extraTension of 1.5f. */ public AnticipateOvershootInterpolator(float tension, float extraTension) { mTension = tension * extraTension; } public AnticipateOvershootInterpolator(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, AnticipateOvershootInterpolator); mTension = a.getFloat(AnticipateOvershootInterpolator_tension, 2.0f) * a.getFloat(AnticipateOvershootInterpolator_extraTension, 1.5f); a.recycle(); } private static float a(float t, float s) { return t * t * ((s + 1) * t - s); } private static float o(float t, float s) { return t * t * ((s + 1) * t + s); } public float getInterpolation(float t) { // a(t, s) = t * t * ((s + 1) * t - s) // o(t, s) = t * t * ((s + 1) * t + s) // f(t) = 0.5 * a(t * 2, tension * extraTension), when t < 0.5 // f(t) = 0.5 * (o(t * 2 - 2, tension * extraTension) + 2), when t <= 1.0 if (t < 0.5f) return 0.5f * a(t * 2.0f, mTension); else return 0.5f * (o(t * 2.0f - 2.0f, mTension) + 2.0f); } }
9。setInterpolator(new AnticipateInterpolator()):反向 ,先向相反方向改变一段再加速播放
/** * An interpolator where the change starts backward then flings forward. */ public class AnticipateInterpolator implements Interpolator { private final float mTension; public AnticipateInterpolator() { mTension = 2.0f; } /** * @param tension Amount of anticipation. When tension equals 0.0f, there is * no anticipation and the interpolator becomes a simple * acceleration interpolator. */ public AnticipateInterpolator(float tension) { mTension = tension; } public AnticipateInterpolator(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, com.android.internal.R.styleable.AnticipateInterpolator); mTension = a.getFloat(com.android.internal.R.styleable.AnticipateInterpolator_tension, 2.0f); a.recycle(); } public float getInterpolation(float t) { // a(t) = t * t * ((tension + 1) * t - tension) return t * t * ((mTension + 1) * t - mTension); } }
就上面这么多了,按照上面的代码我们也可以自定义我们符合我们自己的Interpolator,定义方法就是写一个类继承于Interpolator接口,并且去实现getInterpolation()方法,在该方法里面做相应的运算。
常用的方法就上面这些,来看一下一个ScaleAnimation用法,其它类似:
private ScaleAnimation scale(){ ScaleAnimation scaleAnimation=new ScaleAnimation(0, 1, 0, 1, Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0.5f, Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0.5f); scaleAnimation.setDuration(1000); scaleAnimation.setStartOffset(0); scaleAnimation.setInterpolator(new AccelerateInterpolator()); scaleAnimation.setFillAfter(true); return scaleAnimation; }
开启这个动画在一个按钮上面
imageView=(ImageView) findViewById(R.id.image); scaleBtn.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub imageView.startAnimation(scale()); } });
上面这个就实现图片放大缩小的效果
如果我们想要实现两种以上的动画如何处理呢,这个时候我们就可以使用AnimationSet这个类实现多个动画叠加效果,
AnimationSet(boolean shareInterpolator);
这个参数设为false表示可以在每个添加到AnimationSet中的Animation都使用Interpolator,且效果都能清楚的观察。设置为true如果在添加到AnimationSet中的Animation设置Interpolator将无效果,通过设置AnimationSet的Interpolator可以设置所有动画的Interpolator且所有动画的Interpolator都一样。
private AnimationSet allAnimation(){ AnimationSet set=new AnimationSet(boolean shareInterpolator); TranslateAnimation translate=new TranslateAnimation(0, 100, 0, 100); RotateAnimation rotate=new RotateAnimation(0, 50, Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0.5f, Animation.RELATIVE_TO_SELF, 0.5f); set.addAnimation(translate); set.addAnimation(rotate); set.setInterpolator(new AnticipateOvershootInterpolator()); set.setFillAfter(true); set.setDuration(1000); set.setStartOffset(100); return set; }
我们看到addAnimation就是添加动画效果,其它方法和那个是一样的
我们在使用的过程有时候需要监听动画的开始和结束,AnimationListener这个就是动画监听
set.setAnimationListener(new AnimationListener() { @Override public void onAnimationStart(Animation animation) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } @Override public void onAnimationRepeat(Animation animation) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } @Override public void onAnimationEnd(Animation animation) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } });
看上面的意思就会明白那个是表示动画的开始,那个是动画结束了
这个我们可以在res/anim目录中通过xml来写动画
xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<set xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<alpha
android:fromAlpha="0"
android:toAlpha="1"
android:duration="1000"
/>
<translate
android:interpolator="@android:anim/accelerate_decelerate_interpolator"
android:fromXDelta="0"
android:toXDelta="100"
android:fromYDelta="0"
android:toYDelta="100"
android:startOffset="50"
android:duration="1000"
/>
set>
上面就是xml写的,那么如何加载呢?看下面的代码
Animation an=AnimationUtils.loadAnimation(AnimationTest.this, R.anim.itchqanimator); imageView.startAnimation(an);
这个就是加载xml里面的动画的
Property Animation
这个是属性动画,是android4.0引入手机中(android 3.0中就有了只是3.0主要的在平板电脑上使用的),我们上面讲解的那种tween Animation动画改变的是view绘制,而没有改变View对象本身,比如,你有一个Button,坐标 (100,100),Width:200,Height:50,而你有一个动画使其变为Width:100,Height:100,你会发现动画过程中触 发按钮点击的区域仍是(100,100)-(300,150)。而在Property Animation中,改变的是对象的实际属性,而且Property Animation不止可以应用于View,还可以应用于任何对象。
ValueAnimator类就是这个的包含Property Animation的动画所以核心功能,如动画的时间,开始,结束的属性值等等,当时对于ValueAnimator来说我们一般都不会直接使用这个,我们都是直接使用ValueAnimator的子类就是ObjectAnimator。
ObjectAnimator是继承于ValueAnimator的,使用这个ObjectAnimator是有条件限制的
1。对象应该有一个setter函数:set
2。创建ObjectAnimation对象一般是
ObjectAnimator objectAnimator=ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(valueBtn, "alpha", 1f,0f);
像ofFloat之类的工场方法,第一个参数为对象名(这个也就是我们的view类了),第二个为属性名,后面的参数为可变参 数,如果values…参数只设置了一个值的话,那么会假定为目的值,属性值的变化范围为当前值到目的值,为了获得当前值,该对象要有相应属性的 getter方法:get
3。如果有getter方法,其应返回值类型应与相应的setter方法的参数类型一致。正常情况驼峰命名法都是get和set方法对应的出现
valueBtn=(Button) findViewById(R.id.valueAnimation); valueBtn.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub ObjectAnimator objectAnimator=ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(valueBtn, "alpha", 1f,0f); objectAnimator.setDuration(1000); objectAnimator.start(); } });
这个就是ObjectAnimator简单的用法,通过这个我们也可以监听动画的开始和结束,上面有介绍过AnimatorListener的监听,如下:
objectAnimator.addListener(new AnimatorListener() { @Override public void onAnimationStart(Animator animation) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } @Override public void onAnimationRepeat(Animator animation) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } @Override public void onAnimationEnd(Animator animation) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } @Override public void onAnimationCancel(Animator animation) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } });
当是我们有时候不需要取监听动画的取消或者重复,这些代码在这里显然是多余的,这个时候我们就可以使用AnimatorListenerAdapter这个适配器来进行监听了,如下
objectAnimator.addListener(new AnimatorListenerAdapter() { @Override public void onAnimationEnd(Animator animation) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub super.onAnimationEnd(animation); } @Override public void onAnimationStart(Animator animation) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub super.onAnimationStart(animation); } });
这个就只关心我们的动画开始和介绍,其它就不需要了,代码看起来简洁了很多。ObjectAnimator当然也有setInterpolator()和setStartDelay()等一系列方法,这些的话就和我们上面的说的tween Animation动画方法是一样的。如果我们想要同时实现很多个动画就需要AnimatorSet这个类来实现,如下代码:
AnimatorSet set=new AnimatorSet(); ObjectAnimator alphaAnimator=ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(valueBtn, "alpha", 0f,1f); ObjectAnimator xAnimator=ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(valueBtn, "translationX", 0f,5f,10f); ObjectAnimator yAnimator=ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(valueBtn, "translationY", 0f,5f,10f); ObjectAnimator rotateYAnimator=ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(valueBtn, "rotationX", 0f,90f); set.play(alphaAnimator).before(xAnimator); set.play(xAnimator).with(yAnimator); set.play(yAnimator).after(rotateYAnimator); set.setDuration(2000); set.start();
上面就是使用AnimatorSet方法,这个方法提供了before,with,after方法,按上面代码的意思就是alphaAnimator先执行,之后到xAnimator,yAnimator和xAnimator是同时执行的,执行完yAnimator和xAnimator之后就执行rotateYAnimator,看上面的字面意思也很容易理解了。
在实现过程中经常使用一些动画属性:
1。translationX,translationY,x,y
这些translationX和x,TranslationY和y是用区别的,下面来看看这个区别在哪里(我们这里以X坐标为例)
valueBtn=(Button) findViewById(R.id.valueAnimation); Log.i("itchq", "valueBtn.getLeft()="+valueBtn.getLeft()); Log.i("itchq", "valueBtn.getX()="+valueBtn.getX()); Log.i("itchq", "valueBtn.getTranslationX()="+valueBtn.getTranslationX());
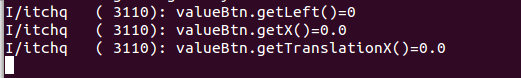
上面的代码中看一默认打印的信息是:
这个默认都是为0的,当我使用translationX动画之后
ObjectAnimator objectAnimator=ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(valueBtn, "translationX", 0f,100f); objectAnimator.setDuration(1000); objectAnimator.start(); objectAnimator.addListener(new AnimatorListenerAdapter() { @Override public void onAnimationEnd(Animator animation) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Log.i("itchq", "valueBtn.getLeft()="+valueBtn.getLeft()); Log.i("itchq", "valueBtn.getX()="+valueBtn.getX()); Log.i("itchq", "valueBtn.getTranslationX()="+valueBtn.getTranslationX()); } });
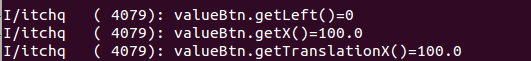
动画结束之后打印的信息如下
这个时候我们再使用x动画之后
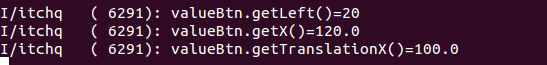
还是一样的,这个主要是因为这个getLeft为0,那么我们这个时候把getLeft设置为20时,当是translationX时动画之后打出的log是
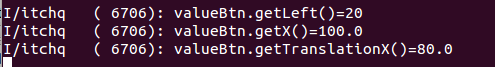
这个时候的x不再是100了而是120了,再设置为x,看一下结果
这个时候的getTranslationX()不再是100了,而是80,所以无论啥样应用动画,getLeft的值是不会变的,而TranslationX的值是为最终位置于布局时初始位置的差,即“最终位置-getLeft()",而x为最终位置之和,即”getLeft()+getTranslationX()“,所以当getLeft为0的时候就会发现两个值是相等的。
2。rotation,rotationX,rotationY:旋转,rotation用于2D旋转角度,3D中用到后两个
3。scaleX,scaleY:缩放
4。alpha:透明度
Keyframe
keyFrame是一个 时间/值 对,通过它可以定义一个在特定时间的特定状态,而且在两个keyFrame之间可以定义不同的Interpolator,就相当多个动画的拼接,第一个动 画的结束点是第二个动画的开始点。KeyFrame是抽象类,要通过ofInt(),ofFloat(),ofObject()获得适当的 KeyFrame,然后通过PropertyValuesHolder.ofKeyframe获得PropertyValuesHolder对象,如以下代码:
Keyframe kf0 = Keyframe.ofInt(0, 400); Keyframe kf1 = Keyframe.ofInt(0.25f, 200); Keyframe kf2 = Keyframe.ofInt(0.5f, 400); Keyframe kf4 = Keyframe.ofInt(0.75f, 100); Keyframe kf3 = Keyframe.ofInt(1f, 500); PropertyValuesHolder pvhRotation = PropertyValuesHolder.ofKeyframe("width", kf0, kf1, kf2, kf4, kf3); ObjectAnimator widthAnim = ObjectAnimator.ofPropertyValuesHolder(valueBtn, pvhRotation); widthAnim.setDuration(2000); widthAnim.start();
上述代码的意思为:设置valueBtn对象的width属性值使其:
开始时 Width=400
动画开始1/4时 Width=200
动画开始1/2时 Width=400
动画开始3/4时 Width=100
动画结束时 Width=500
第一个参数为时间百分比,第二个参数是在第一个参数的时间时的属性值。定义了一些Keyframe后,通过PropertyValuesHolder类的方法ofKeyframe封装,然后通过ObjectAnimator.ofPropertyValuesHolder获得Animator。
PropertyValuesHolder
如果需要对一个View的多个属性进行动画可以用ViewPropertyAnimator类,该类对多属性动画进行了优化,会合并一些invalidate()来减少刷新视图
PropertyValuesHolder pvhX = PropertyValuesHolder.ofFloat("x", 50f);
PropertyValuesHolder pvhY = PropertyValuesHolder.ofFloat("y", 100f);
ObjectAnimator x_yAnimator=ObjectAnimator.ofPropertyValuesHolder(valueBtn, pvhX, pvhY);
x_yAnimator.setDuration(1000);
x_yAnimator.start();
上面这段代码就是同时进行X轴和Y轴的动画