redis源码浅析--七-redisObject对象(上)(对象的类型与编码)
环境说明:redis源码版本 5.0.3;我在阅读源码过程做了注释,git地址:https://gitee.com/xiaoangg/redis_annotation
参考书籍:《redis的设计与实现》
redis提供5种数据类型:字符串、列表、哈希、集合、有序集合;
实际上每种数据类型都有自己底层的内部编码实现;如set数据结构的底层编码方式有 压缩列表、跳表
这样做的好处就是
1.可以针对不通的场景使用不同编码方式,不同的编码能够在各自场景下发挥优势;
2.当开发更优的编码方式时,可以无需改动外部数据结构和命令情况下 升级编码方式;
一 对象类型 与编码
redis中每个对象都是由redisObject来表示,redisObject定义位于server.h中;
//redisObjec结构体来表示string、hash、list、set、zset五种数据类型
typedef struct redisObject {
//4位的type表示具体的数据类型()。Redis中共有5中数据类型(string、hash、list、set、zset)。
//2^4 = 16足以表示这些类型
unsigned type:4;
//4位的encoding表示该类型的物理编码方式,同一种数据类型可能有不同的编码方式
unsigned encoding:4;
//lru 属性保存了对象最后一次被命令访问的时间
unsigned lru:LRU_BITS; /* LRU time (relative to global lru_clock) or
* LFU data (least significant 8 bits frequency
* and most significant 16 bits access time). */
int refcount;//refcount表示对象的引用计数
void *ptr;//ptr指针指向真正的存储结构
} robj;1. 类型type属性;
type占用4个bit,可以表示2^4个值;
type的值可以是: 0:字符串对象、1:列表对象、2:集合对象、3:有序集合对象、4:哈希对象
//redis的五种数据类型
/* The actual Redis Object */
#define OBJ_STRING 0 /* String object. */
#define OBJ_LIST 1 /* List object. */
#define OBJ_SET 2 /* Set object. */
#define OBJ_ZSET 3 /* Sorted set object. */
#define OBJ_HASH 4 /* Hash object. */
2.编码和底层实现 encoding属性;
同样encoding占用4个bit,可以表示2^4个值;
encoding 记录对象所使用的编码方式,是使用什么数据结构实现的;
encoding的值可以是以下宏定义中的任何一种:
/* Objects encoding. Some kind of objects like Strings and Hashes can be
* internally represented in multiple ways. The 'encoding' field of the object
* is set to one of this fields for this object. */
#define OBJ_ENCODING_RAW 0 /* Raw representation */ //简单动态字符串
#define OBJ_ENCODING_INT 1 /* Encoded as integer */ //long类型整数
#define OBJ_ENCODING_HT 2 /* Encoded as hash table */ //字典
#define OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPMAP 3 /* Encoded as zipmap */
#define OBJ_ENCODING_LINKEDLIST 4 /* No longer used: old list encoding. */ //双向链表
#define OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST 5 /* Encoded as ziplist */ //压缩列表
#define OBJ_ENCODING_INTSET 6 /* Encoded as intset */ //整数集合
#define OBJ_ENCODING_SKIPLIST 7 /* Encoded as skiplist *///跳表
#define OBJ_ENCODING_EMBSTR 8 /* Embedded sds string encoding */ //编码的简单字符串; EMBSTR是专门保存简短字符串的一种优化编码方式
#define OBJ_ENCODING_QUICKLIST 9 /* Encoded as linked list of ziplists */ //快速链表
#define OBJ_ENCODING_STREAM 10 /* Encoded as a radix tree of listpacks *///todo 每种type可用的编码方式 以及优缺点
| 类型(type) | 编码(encoding) | 描述 | 优缺点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| OBJ_STRING | OBJ_ENCODING_RAW |
//简单动态字符串 |
|
| OBJ_ENCODING_INT |
//long类型整数 |
||
| OBJ_ENCODING_EMBSTR |
//编码的简单字符串; EMBSTR是专门保存简短字符串的一种优化编码方式 |
||
| OBJ_LIST | OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST | //压缩列表 | |
| OBJ_ENCODING_LINKEDLIST | //双向链表 | ||
| OBJ_ENCODING_QUICKLIST | 快速列表 | Redis中的列表对象在版本3.2之前,列表底层的编码是ziplist和linkedlist实现的,但是在版本3.2之后,重新引入了一个 quicklist 的数据结构,列表的底层都由quicklist实现。 | |
| OBJ_HASH | OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST | //压缩列表 | |
| OBJ_ENCODING_HT | //字典 | ||
| OBJ_SET | OBJ_ENCODING_INTSET | //整数集合 | |
| OBJ_ENCODING_HT | //字典 | ||
| OBJ_ZSET | OBJ_ENCODING_ZIPLIST | //压缩列表 | |
| OBJ_ENCODING_SKIPLIST | //跳表 |
tips:使用object encoding 命令可以查看一个对象的编码
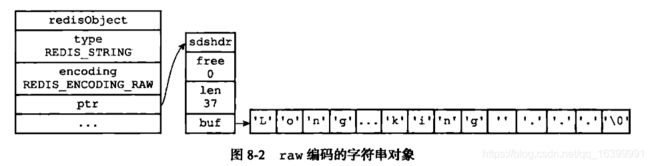
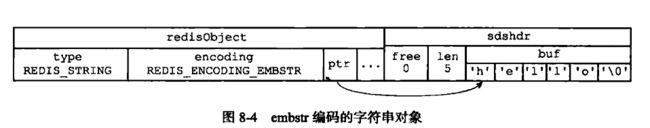
二 字符串对象
字符串的编码方式可以是int、raw、或者embstr;
| 编码 | 使用条件 | 优缺点 |
|---|---|---|
| int | 字符串对象保存的是整数 | |
| raw | 值是一个字符串,并且 字符串的长度大于44字节 | 创建/释放对象 需要两次内存操作; |
| embstr | 值是一个字符串,并且字符串的长度小于等于44字节 | 创建/释放对象 需要一次内存操作; embstr编码的字符对象所有数据保存在一块连续的内存里,所以更高效;
|
以tryObjectEncoding 函数为入口,可以看到编码的整个过程:
//尝试对字符串进行编码,以节省空间
/* Try to encode a string object in order to save space */
robj *tryObjectEncoding(robj *o) {
long value;
sds s = o->ptr;
size_t len;
/* Make sure this is a string object, the only type we encode
* in this function. Other types use encoded memory efficient
* representations but are handled by the commands implementing
* the type. */
serverAssertWithInfo(NULL,o,o->type == OBJ_STRING);
/* We try some specialized encoding only for objects that are
* RAW or EMBSTR encoded, in other words objects that are still
* in represented by an actually array of chars. */
if (!sdsEncodedObject(o)) return o;
//共享对象 不会进行编码
/* It's not safe to encode shared objects: shared objects can be shared
* everywhere in the "object space" of Redis and may end in places where
* they are not handled. We handle them only as values in the keyspace. */
if (o->refcount > 1) return o;
/* Check if we can represent this string as a long integer.
* Note that we are sure that a string larger than 20 chars is not
* representable as a 32 nor 64 bit integer. */
//检查字符串时候可以转化成整数;(字符串如果大于20位,64位存不下,所以一定不能转换)
len = sdslen(s);
if (len <= 20 && string2l(s,len,&value)) {
/* This object is encodable as a long. Try to use a shared object.
* Note that we avoid using shared integers when maxmemory is used
* because every object needs to have a private LRU field for the LRU
* algorithm to work well. */
if ((server.maxmemory == 0 ||
!(server.maxmemory_policy & MAXMEMORY_FLAG_NO_SHARED_INTEGERS)) &&
value >= 0 &&
value < OBJ_SHARED_INTEGERS)
{
decrRefCount(o);
incrRefCount(shared.integers[value]);
return shared.integers[value];
} else {
if (o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_RAW) sdsfree(o->ptr);
o->encoding = OBJ_ENCODING_INT;
o->ptr = (void*) value;
return o;
}
}
/*
如果字符串很小 并且 是使用 RAW编码的
尝试使用 更高效的 EMBSTR编码方式
*/
/* If the string is small and is still RAW encoded,
* try the EMBSTR encoding which is more efficient.
* In this representation the object and the SDS string are allocated
* in the same chunk of memory to save space and cache misses. */
if (len <= OBJ_ENCODING_EMBSTR_SIZE_LIMIT) {
robj *emb;
if (o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_EMBSTR) return o;
emb = createEmbeddedStringObject(s,sdslen(s)); //创建 EMB 编码的对象
decrRefCount(o);
return emb;
}
/*
不能使用 long 和embstr编码方式
*/
/* We can't encode the object...
*
* Do the last try, and at least optimize the SDS string inside
* the string object to require little space, in case there
* is more than 10% of free space at the end of the SDS string.
*
* We do that only for relatively large strings as this branch
* is only entered if the length of the string is greater than
* OBJ_ENCODING_EMBSTR_SIZE_LIMIT. */
if (o->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_RAW &&
sdsavail(s) > len/10)
{
o->ptr = sdsRemoveFreeSpace(o->ptr);
}
/* Return the original object. */
return o;
}
三 哈希对象
hash对象的编码的可以是ziplist或者是hashtable;
- 使用ziplist作为底层编码时,程序先将保存“键”的列表节点压如表尾,再将保存“值”的列表节点压如表尾;
- 使用hashtable作为底层编码时,每个“键”都使用一个键值对都使用一个字典对象来保存;
3 .1编码转换
当满足以下两个条件时,使用ziplist编码:
- hash对象保存的所有键值对的键和值字符串长度都小于64字节
- 键值对数量小于512;
不能满足时则使用hashtable编码;
注:以上两个条件是可以修改的;
只支持ziplist转hashtale;
/*
可以已hset命令为输入 阅读编码转换的工程
.......
*/
/* 检查是否需要编码转换 Check if the ziplist needs to be converted to a hash table */
if (hashTypeLength(o) > server.hash_max_ziplist_entries)
hashTypeConvert(o, OBJ_ENCODING_HT);
/*
.......
*/
四 集合对象
集合对象的编码方式可以是 intset或者是hashtable
- intset作为底层编码,所有元素都被保存在整数集合里
- hash作为底层实现时,元素都是字符串对象,存储hash键中,hash值设为NULL
4.1 编码转换
使用intset 的编码条件:
- 集合所有元素都是整数
- 集合元素个数少于512
不能满足时,使用hashtabl作为底层实现
//编码转换条件
/* Add the specified value into a set.
*
* If the value was already member of the set, nothing is done and 0 is
* returned, otherwise the new element is added and 1 is returned. */
int setTypeAdd(robj *subject, sds value) {
long long llval;
if (subject->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_HT) {
dict *ht = subject->ptr;
dictEntry *de = dictAddRaw(ht,value,NULL);
if (de) {
dictSetKey(ht,de,sdsdup(value));
dictSetVal(ht,de,NULL);
return 1;
}
} else if (subject->encoding == OBJ_ENCODING_INTSET) {
if (isSdsRepresentableAsLongLong(value,&llval) == C_OK) {
uint8_t success = 0;
subject->ptr = intsetAdd(subject->ptr,llval,&success);
if (success) {
/* Convert to regular set when the intset contains
* too many entries. */
if (intsetLen(subject->ptr) > server.set_max_intset_entries)
setTypeConvert(subject,OBJ_ENCODING_HT);
return 1;
}
} else {
/* Failed to get integer from object, convert to regular set. */
setTypeConvert(subject,OBJ_ENCODING_HT);
/* The set *was* an intset and this value is not integer
* encodable, so dictAdd should always work. */
serverAssert(dictAdd(subject->ptr,sdsdup(value),NULL) == DICT_OK);
return 1;
}
} else {
serverPanic("Unknown set encoding");
}
return 0;
}
五 有序集合对象
有序集合编码可以是ziplist或者是skiplist
当ziplist作为有序集合实现时:
- 每个集合元素使用两个紧挨在一起的压缩列表节点来保存,第一个节点保存元素member,第二压缩列表节点保存分值;
- 压缩列表元素按照分值从小到大进行排序
5.1编码转换
当同时满足以下两个条件时,使用ziplist编码
- 有序集合元素小于128
- 有序集合所有元素长度都小于64字节
tips:以上两个限制条件是可以根据配置来修改的
以zsetAdd函数作为入口阅读,可看到编码转换条件和转换过程
#define OBJ_ZSET_MAX_ZIPLIST_ENTRIES 128
#define OBJ_ZSET_MAX_ZIPLIST_VALUE 64
int zsetAdd(robj *zobj, double score, sds ele, int *flags, double *newscore) {
.....
if (zzlLength(zobj->ptr) > server.zset_max_ziplist_entries)//触发编码转换
zsetConvert(zobj,OBJ_ENCODING_SKIPLIST);
if (sdslen(ele) > server.zset_max_ziplist_value) //触发编码转换
zsetConvert(zobj,OBJ_ENCODING_SKIPLIST);
if (newscore) *newscore = score;
*flags |= ZADD_ADDED;
return 1;
......
return 0; /* Never reached. */
}