Hadoop详解(四)——Shuffle原理,Partitioner分区原理,Combiner编程,常见的MR算法
Partitioner编程
Partition简介
shuffle是通过分区partitioner 分配给Reduce的 一个Reducer对应一个记录文件
Partitioner是shuffle的一部分
partitioner执行时机:在mapper执行完成,Reducer还没有执行的时候,mapper的输出就是partitioner的输入 即
partitioner 分区主要是用来提高效率的 例如从全国基站的数据中查找北京基站的数据,如果计算时不分区全国的数据都放在一起,查询的时候就相当于全表扫描 效率非常低,如果在第一次进行Mapreducer计算的时候按照省市进行分区,每个城市的基站数据都存储在对应的每个文件,那么下次再进行查询的时候直接从北京分区里直接查找 效率很高。
分区的依据是具体业务需求,可以按照省市分区,时间进行分区等。
如果不手动进行分区,Hadoop有一个默认的分区规则
Partitioner是shuffle的一部分
partitioner执行时机:在mapper执行完成,Reducer还没有执行的时候,mapper的输出就是partitioner的输入 即
partitioner 分区主要是用来提高效率的 例如从全国基站的数据中查找北京基站的数据,如果计算时不分区全国的数据都放在一起,查询的时候就相当于全表扫描 效率非常低,如果在第一次进行Mapreducer计算的时候按照省市进行分区,每个城市的基站数据都存储在对应的每个文件,那么下次再进行查询的时候直接从北京分区里直接查找 效率很高。
分区的依据是具体业务需求,可以按照省市分区,时间进行分区等。
如果不手动进行分区,Hadoop有一个默认的分区规则
Partitioner是partitioner的基类,如果需要定制partitioner也需要继承该类。HashPartitioner是mapreduce的默认partitioner。计算方法是which reducer=(key.hashCode() & Integer.MAX_VALUE) % numReduceTasks,得到当前的目的reducer。
Partitioner原理
以上流程省略了shuffle的过程
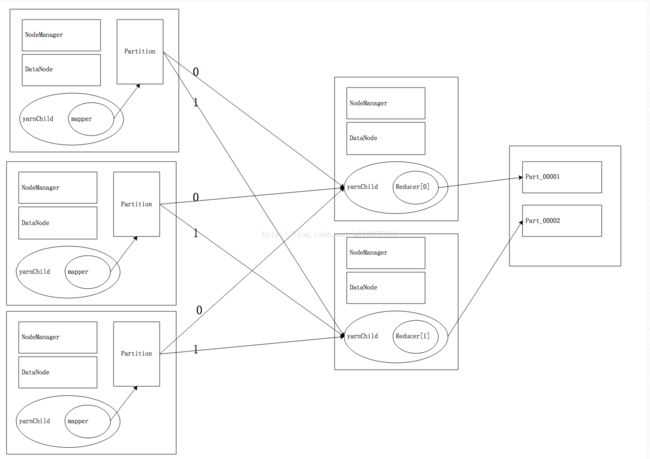
DataNode在此处用于下载jar
NodeManager用于运行Yarn 由YarnChild运行Mapper或Reducer
当启动一个Reducer时会分配一个分区号 默认是按数字分区
Partitioner是Shuffle的一部分,当Partition的返回值是N时 会将shuffle的结果输出给对应的分区号为N的Reducer
一个Reducer对应一个分区文件 Reducer计算完毕后就会按照分区号写入对应的分区文件
DataNode在此处用于下载jar
NodeManager用于运行Yarn 由YarnChild运行Mapper或Reducer
当启动一个Reducer时会分配一个分区号 默认是按数字分区
Partitioner是Shuffle的一部分,当Partition的返回值是N时 会将shuffle的结果输出给对应的分区号为N的Reducer
一个Reducer对应一个分区文件 Reducer计算完毕后就会按照分区号写入对应的分区文件
Partitioner编程
① 先分析一下具体的业务逻辑,确定大概有多少个分区
② 首先书写一个类,它要继承org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner这个类
③ 重写public int getPartition这个方法,根据具体逻辑,读数据库或者配置返回相同的数字
④ 在main方法中设置Partioner的类,job.setPartitionerClass(DataPartitioner.class);
⑤ 设置Reducer的数量,job.setNumReduceTasks(6);
② 首先书写一个类,它要继承org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner这个类
③ 重写public int getPartition这个方法,根据具体逻辑,读数据库或者配置返回相同的数字
④ 在main方法中设置Partioner的类,job.setPartitionerClass(DataPartitioner.class);
⑤ 设置Reducer的数量,job.setNumReduceTasks(6);
实例如下:
日志数据:HTTP_20130313143750.dat
1363157985066 13726230503 00-FD-07-A4-72-B8:CMCC 120.196.100.82 i02.c.aliimg.com 24 27 2481 24681 200
1363157995052 13826544101 5C-0E-8B-C7-F1-E0:CMCC 120.197.40.4 4 0 264 0 200
1363157991076 13926435656 20-10-7A-28-CC-0A:CMCC 120.196.100.99 2 4 132 1512 200
1363154400022 13926251106 5C-0E-8B-8B-B1-50:CMCC 120.197.40.4 4 0 240 0 200
1363157993044 18211575961 94-71-AC-CD-E6-18:CMCC-EASY 120.196.100.99 iface.qiyi.com 视频网站 15 12 1527 2106 200
1363157995074 84138413 5C-0E-8B-8C-E8-20:7DaysInn 120.197.40.4 122.72.52.12 20 16 4116 1432 200
1363157993055 13560439658 C4-17-FE-BA-DE-D9:CMCC 120.196.100.99 18 15 1116 954 200
1363157995033 15920133257 5C-0E-8B-C7-BA-20:CMCC 120.197.40.4 sug.so.360.cn 信息安全 20 20 3156 2936 200
1363157983019 13719199419 68-A1-B7-03-07-B1:CMCC-EASY 120.196.100.82 4 0 240 0 200
1363157984041 13660577991 5C-0E-8B-92-5C-20:CMCC-EASY 120.197.40.4 s19.cnzz.com 站点统计 24 9 6960 690 200
1363157973098 15013685858 5C-0E-8B-C7-F7-90:CMCC 120.197.40.4 rank.ie.sogou.com 搜索引擎 28 27 3659 3538 200
1363157986029 15989002119 E8-99-C4-4E-93-E0:CMCC-EASY 120.196.100.99 www.umeng.com 站点统计 3 3 1938 180 200
1363157992093 13560439658 C4-17-FE-BA-DE-D9:CMCC 120.196.100.99 15 9 918 4938 200
1363157986041 13480253104 5C-0E-8B-C7-FC-80:CMCC-EASY 120.197.40.4 3 3 180 180 200
1363157984040 13602846565 5C-0E-8B-8B-B6-00:CMCC 120.197.40.4 2052.flash2-http.qq.com 综合门户 15 12 1938 2910 200
1363157995093 13922314466 00-FD-07-A2-EC-BA:CMCC 120.196.100.82 img.qfc.cn 12 12 3008 3720 200
1363157982040 13502468823 5C-0A-5B-6A-0B-D4:CMCC-EASY 120.196.100.99 y0.ifengimg.com 综合门户 57 102 7335 110349 200
1363157986072 18320173382 84-25-DB-4F-10-1A:CMCC-EASY 120.196.100.99 input.shouji.sogou.com 搜索引擎 21 18 9531 2412 200
1363157990043 13925057413 00-1F-64-E1-E6-9A:CMCC 120.196.100.55 t3.baidu.com 搜索引擎 69 63 11058 48243 200
1363157988072 13760778710 00-FD-07-A4-7B-08:CMCC 120.196.100.82 2 2 120 120 200
1363157985066 13726238888 00-FD-07-A4-72-B8:CMCC 120.196.100.82 i02.c.aliimg.com 24 27 2481 24681 200
1363157993055 13560436666 C4-17-FE-BA-DE-D9:CMCC 120.196.100.99 18 15 1116 954 200这种映射关系在实际开发中一般存储在数据库中,通过web项目的Service查询数据库得到
需求:统计每个手机号的上行总流量,下行总流量,总流量,并按照手机号进行分区存储。
代码如下:
DataBean(自定义Bean)
package liuxun.hadoop.mr.dc;
import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Writable;
public class DataBean implements Writable {
private String tel;
private long upPayLoad;
private long downPayLoad;
private long totalPayLoad;
public DataBean() {
}
public DataBean(String tel, long upPayLoad, long downPayLoad) {
this.tel = tel;
this.upPayLoad = upPayLoad;
this.downPayLoad = downPayLoad;
this.totalPayLoad = upPayLoad + downPayLoad;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return this.upPayLoad + "\t" + this.downPayLoad + "\t" + this.totalPayLoad;
}
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
this.tel = in.readUTF();
this.upPayLoad = in.readLong();
this.downPayLoad = in.readLong();
this.totalPayLoad = in.readLong();
}
// 注意两点:写入的顺序和写入的类型
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
out.writeUTF(tel);
out.writeLong(upPayLoad);
out.writeLong(downPayLoad);
out.writeLong(totalPayLoad);
}
public String getTel() {
return tel;
}
public void setTel(String tel) {
this.tel = tel;
}
public long getUpPayLoad() {
return upPayLoad;
}
public void setUpPayLoad(long upPayLoad) {
this.upPayLoad = upPayLoad;
}
public long getDownPayLoad() {
return downPayLoad;
}
public void setDownPayLoad(long downPayLoad) {
this.downPayLoad = downPayLoad;
}
public long getTotalPayLoad() {
return totalPayLoad;
}
public void setTotalPayLoad(long totalPayLoad) {
this.totalPayLoad = totalPayLoad;
}
}
DataCountPartition (编写计算模型)
package liuxun.hadoop.mr.dc;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
public class DataCountPartition {
public static class DCMapper extends Mapper {
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
// accept
String line = value.toString();
// split
String[] fields = line.split("\t");
String tel = fields[1];
long up = Long.parseLong(fields[8]);
long down = Long.parseLong(fields[9]);
DataBean bean = new DataBean(tel, up, down);
// send
context.write(new Text(tel), bean);
}
}
public static class DCReducer extends Reducer {
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable values, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
long up_sum = 0;
long down_sum = 0;
for (DataBean bean : values) {
up_sum += bean.getUpPayLoad();
down_sum += bean.getDownPayLoad();
}
DataBean bean = new DataBean("", up_sum, down_sum);
context.write(key, bean);
}
}
public static class ProviderPartitioner extends Partitioner {
private static Map prividerMap = new HashMap();
static {
// 实际开发时是从数据库加载这种映射关系的
// 1:中国移动 2:中国联通 3:中国电信
prividerMap.put("135", 1);
prividerMap.put("136", 1);
prividerMap.put("137", 1);
prividerMap.put("150", 2);
prividerMap.put("159", 2);
prividerMap.put("182", 3);
prividerMap.put("183", 3);
}
// 此方法的返回值是分区号
// key: mapper一次输出的key 这里是手机号
// key: mapper一次输出的Value 这里是DataBean
// numPartitions:分区数量,由Reducer的数量决定,启动几个Reducer就会有几个partition
@Override
public int getPartition(Text key, DataBean value, int numPartitions) {
// 根据手机号得到运营商 此处根据key进行分区,实际开发中也可以根据value进行分区
String account = key.toString();
String sub_acc = account.substring(0, 3);
Integer code = prividerMap.get(sub_acc);
if (code == null) {
code =0;
}
return code;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);
job.setJarByClass(DataCountPartition.class);
job.setMapperClass(DCMapper.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(DataBean.class);
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0]));
job.setReducerClass(DCReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(DataBean.class);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
job.setPartitionerClass(ProviderPartitioner.class);
// 设置启动Reducer的数量
job.setNumReduceTasks(Integer.parseInt(args[2]));
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
}
① 首先将日志数据上传至HDFS
② 将以上程序打包成WCP.jar —>上传至Linux主机—>hadoop jar /日志地址 /统计结果地址 /reducer数量
hadoop fs -put HTTP_20130313143750.dat /log.txt
hadoop jar WCP.jar /log.txt /logResult 4
hadoop jar WCP.jar /log.txt /logResult 4
查看统计结果
[root@hadoop0 Desktop]# hadoop fs -ls /logResult
Found 5 items
-rw-r--r-- 1 root supergroup 0 2017-08-31 19:02 /logResult/_SUCCESS
-rw-r--r-- 1 root supergroup 175 2017-08-31 19:02 /logResult/part-r-00000
-rw-r--r-- 1 root supergroup 241 2017-08-31 19:02 /logResult/part-r-00001
-rw-r--r-- 1 root supergroup 80 2017-08-31 19:02 /logResult/part-r-00002
-rw-r--r-- 1 root supergroup 55 2017-08-31 19:02 /logResult/part-r-00003
[root@hadoop0 Desktop]# hadoop fs -cat /logResult/part-r-00000
13480253104 180 180 360
13826544101 264 0 264
13922314466 3008 3720 6728
13925057413 11058 48243 59301
13926251106 240 0 240
13926435656 132 1512 1644
84138413 4116 1432 5548
[root@hadoop0 Desktop]# hadoop fs -cat /logResult/part-r-00001
13502468823 7335 110349 117684
13560436666 1116 954 2070
13560439658 2034 5892 7926
13602846565 1938 2910 4848
13660577991 6960 690 7650
13719199419 240 0 240
13726230503 2481 24681 27162
13726238888 2481 24681 27162
13760778710 120 120 240
[root@hadoop0 Desktop]# hadoop fs -cat /logResult/part-r-00002
15013685858 3659 3538 7197
15920133257 3156 2936 6092
15989002119 1938 180 2118
[root@hadoop0 Desktop]# hadoop fs -cat /logResult/part-r-00003
18211575961 1527 2106 3633
18320173382 9531 2412 11943
Found 5 items
-rw-r--r-- 1 root supergroup 0 2017-08-31 19:02 /logResult/_SUCCESS
-rw-r--r-- 1 root supergroup 175 2017-08-31 19:02 /logResult/part-r-00000
-rw-r--r-- 1 root supergroup 241 2017-08-31 19:02 /logResult/part-r-00001
-rw-r--r-- 1 root supergroup 80 2017-08-31 19:02 /logResult/part-r-00002
-rw-r--r-- 1 root supergroup 55 2017-08-31 19:02 /logResult/part-r-00003
[root@hadoop0 Desktop]# hadoop fs -cat /logResult/part-r-00000
13480253104 180 180 360
13826544101 264 0 264
13922314466 3008 3720 6728
13925057413 11058 48243 59301
13926251106 240 0 240
13926435656 132 1512 1644
84138413 4116 1432 5548
[root@hadoop0 Desktop]# hadoop fs -cat /logResult/part-r-00001
13502468823 7335 110349 117684
13560436666 1116 954 2070
13560439658 2034 5892 7926
13602846565 1938 2910 4848
13660577991 6960 690 7650
13719199419 240 0 240
13726230503 2481 24681 27162
13726238888 2481 24681 27162
13760778710 120 120 240
[root@hadoop0 Desktop]# hadoop fs -cat /logResult/part-r-00002
15013685858 3659 3538 7197
15920133257 3156 2936 6092
15989002119 1938 180 2118
[root@hadoop0 Desktop]# hadoop fs -cat /logResult/part-r-00003
18211575961 1527 2106 3633
18320173382 9531 2412 11943
注意:
分区的程序不可在Eclipse上运行,因为在Eclipse上运行的是本地模式,始终只会启动一个mapper和一个reducer 不能实现分区
指定分区数如果小于写入所需的最大分区数量 会抛出异常
如果大于写入所需的最大分区数量 不会抛异常 但是多余的分区不会存储数据
所以在指定分区的时候数量要大于或等于最所需的最大分区数量
指定分区数如果小于写入所需的最大分区数量 会抛出异常
如果大于写入所需的最大分区数量 不会抛异常 但是多余的分区不会存储数据
所以在指定分区的时候数量要大于或等于最所需的最大分区数量
排序
如果没有自定义排序规则则 如果k2的类型是Text默认按照k2的字典顺序进行排序
MapReducer 实现原理就是迭代式编程,如果一个MapReduce无法完成具体的需求,可以实现多个MapReduce,就是可以将一个MapReduce的输出的内容作为中间结果作为另一个MapReducer的输入
如果要实现排序 参数中的Bean对象要实现WritableComparable接口 此接口是Writable的子接口
MapReducer 实现原理就是迭代式编程,如果一个MapReduce无法完成具体的需求,可以实现多个MapReduce,就是可以将一个MapReduce的输出的内容作为中间结果作为另一个MapReducer的输入
如果要实现排序 参数中的Bean对象要实现WritableComparable接口 此接口是Writable的子接口
注意:如果业务比较复杂,可以编写多个MapReduce迭代编程处理
实例:
交易信息trade_info
[email protected] 6000 0 2014-02-20
[email protected] 2000 0 2014-02-20
[email protected] 0 100 2014-02-20
[email protected] 3000 0 2014-02-20
[email protected] 9000 0 2014-02-20
[email protected] 0 200 2014-02-20
代码编写:
① 自定义BeanInfo实现WritableComparable接口,并重写compareTo方法和toString方法
package liuxun.hadoop.mr.sort;
import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
public class InfoBean implements WritableComparable {
private String account; // 账号
private double income; // 收入
private double expenses;// 支出
private double surplus; // 结余
public void set(String account,double income,double expenses) {
this.account = account;
this.income = income;
this.expenses = expenses;
this.surplus = this.income - this.expenses;
}
// 序列化
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
out.writeUTF(account);
out.writeDouble(income);
out.writeDouble(expenses);
out.writeDouble(surplus);
}
// 反序列化
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
this.account = in.readUTF();
this.income = in.readDouble();
this.expenses = in.readDouble();
this.surplus = in.readDouble();
}
public int compareTo(InfoBean o) {
if (this.income == o.getIncome()) {
return this.expenses > o.getExpenses() ? 1 : -1;
}else {
return this.income > o.getIncome() ? -1 :1;
}
}
public String getAccount() {
return account;
}
public void setAccount(String account) {
this.account = account;
}
public double getIncome() {
return income;
}
public void setIncome(double income) {
this.income = income;
}
public double getExpenses() {
return expenses;
}
public void setExpenses(double expenses) {
this.expenses = expenses;
}
public double getSurplus() {
return surplus;
}
public void setSurplus(double surplus) {
this.surplus = surplus;
}
// 注意:toString方法决定了Bean写入文件的顺序
@Override
public String toString() {
return income+"\t"+expenses+"\t"+surplus+"\t";
}
} package liuxun.hadoop.mr.sort;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
public class SumStep {
public static class SumMapper extends Mapper {
private Text k = new Text();
private InfoBean v = new InfoBean();
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String line = value.toString();
String[] fields = line.split("\t");
String account = fields[0];
double in = Double.parseDouble(fields[1]);
double out = Double.parseDouble(fields[2]);
k.set(account);
v.set(account, in, out);
context.write(k, v);
}
}
public static class SumReducer extends Reducer{
private InfoBean v = new InfoBean();
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable value,Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
double in_sum = 0;
double out_sum = 0;
for (InfoBean bean : value) {
in_sum += bean.getIncome();
out_sum += bean.getExpenses();
}
v.set("", in_sum, out_sum);
context.write(key, v);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf);
job.setJarByClass(SumStep.class);
job.setMapperClass(SumMapper.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(InfoBean.class);
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0]));
job.setReducerClass(SumReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(InfoBean.class);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
} package liuxun.hadoop.mr.sort;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
public class SortStep {
public static class SortMapper extends Mapper {
private InfoBean k = new InfoBean();
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String line = value.toString();
String[] fields = line.split("\t");
String account = fields[0];
double in = Double.parseDouble(fields[1]);
double out = Double.parseDouble(fields[2]);
k.set(account, in, out);
context.write(k, NullWritable.get());
}
}
public static class SortReducer extends Reducer {
private Text k = new Text();
@Override
protected void reduce(InfoBean bean, Iterable value, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String account = bean.getAccount();
k.set(account);
context.write(k, bean);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf );
job.setJarByClass(SortStep.class);
job.setMapperClass(SortMapper.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(InfoBean.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0]));
job.setReducerClass(SortReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(InfoBean.class);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
}
首先将trade_info上传至HDFS
再对统计程序进行打包 SumStep.jar
其次对排序程序打包 SortStep.jar
将jar包上传至Linux主机,步骤如下:
hadoop fs -put trade_info.txt /trade_info
hadoop jar SumStep.jar /trade_info /sumResult
hadoop jar SortStep.jar /sumResult /sortResult
[root@hadoop0 Desktop]# hadoop fs -cat /sortResult/part-r-00000
[email protected] 9000.0 0.0 9000.0
[email protected] 9000.0 200.0 8800.0
[email protected] 2000.0 100.0 1900.0
hadoop jar SumStep.jar /trade_info /sumResult
hadoop jar SortStep.jar /sumResult /sortResult
[root@hadoop0 Desktop]# hadoop fs -cat /sortResult/part-r-00000
[email protected] 9000.0 0.0 9000.0
[email protected] 9000.0 200.0 8800.0
[email protected] 2000.0 100.0 1900.0
Combiners编程
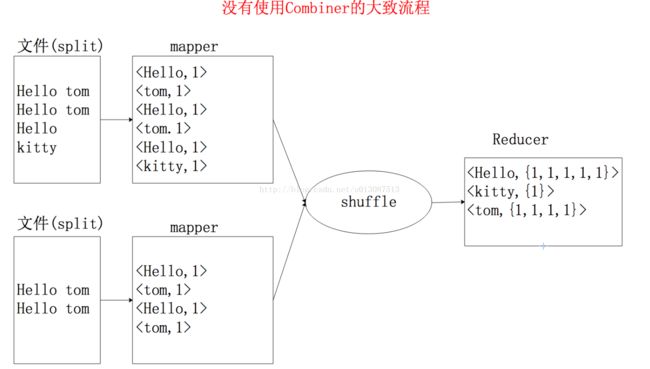
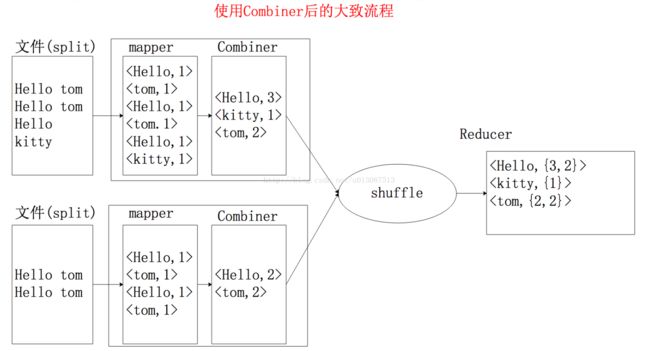
每一个map可能会产生大量的输出,combiner的作用就是在map端对输出先做一次合并,以减少传输到reducer的数据量。
combiner最基本是实现本地key的归并,combiner最基本是实现本地key的归并,combiner有类似于本地reducer的功能。如果不使用combiner,那么所有的结果都是Reduce完成,效率会相对低下。使用combiner,先完成的map会在本地聚合,提升速度。
注意:Combiner的输出是Reducer的输入,如果combiner是可插拔的,添加combiner绝对不能改变最终计算结果。所以在可插拔的情况下Combiner只应该用于那种和Reduce的输入key/value与输出key/value类型完全一致,且不影响最终结果的场景。比如累加,最大值等。
注意:
如果数据量大的时候使用Combiner的情况效率高
如果数据量很小的话 有可能会更慢 毕竟又增加了一个部分
如果Combiner是可插拔的(有Combiner或没有Combine都不会影响运行结果),那么Combiner的功能和Reducer的功能就是相同的。
Combine也可以是不可插拔的,例如实际开发中经常使用Combine在Mapper端做数据过滤。
例如求总的平均数 Combine就不能和Reducer一样
如果一样:
a.txt 3 6 3 Combine:12/3=4
b.txt 2 5 Combine:7/2=3.5
Reducer:(4+3.5)/2=3.75 != 3.8
只可以按照以下的方式运算:
a.txt 3 6 3 Combine:12 3
b.txt 2 5 Combine:7 2
Reducer:(12+7)/(3+2)=3.8
实例:例如WordCount程序就是 Combiner和Reducer功能相同 可插拔的,流程分析如下:
① 没有使用Combiner的情况
② 使用Combiner的情况
注意:Combiner的实现和Reduce相同,都是继承Reducer类。
使用方式 job.setCombinerClass(WCReducer.class);
当Combiner和Reducer的功能相同时,即可插拔的,这种情况下Reducer类即是Combiner
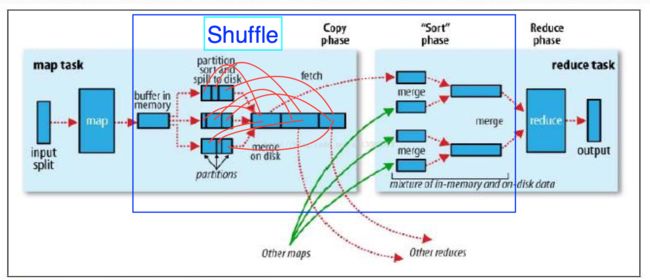
Shuffle原理******
一个切片对应一个map ,每一个map对应一个在内存中的环形缓冲区,用来存储map的输出,缓冲区的大小默认是100M
当map向环形缓冲区写入数据达到一定阀值,就是超出一定范围(80%) 就会启动一个后台线程将缓冲区数据溢写到磁盘,注意:不仅仅是将数据存入到磁盘,而是经过很复杂的过程,写入磁盘之前首先将数据按照分区规则进行分区,如果没有指定分区规则,就会按照Hadoop默认的分区规则进行分区,然后按照排序规则对分区内的数据按照k2(map输出的key即reducer输入的key)进行排序 ,如果k2是Text类型 则按照k2的字典顺序的排序规则,如果是Bean按照自定义的排序规则排序,然后得到多个分区且排序的小文件。分区是按照分区号排序,分区内的数据是按照k2的排序规则进行排序,小文件内可以有多个分区。由于map向缓存区中存数据速度远远比缓冲区向磁盘写数据的速度,所以当缓冲区中的数据达到80%,map就会阻塞,停止向缓冲区存入数据,直到缓冲区中的数据写入到多个小文件并清空缓冲区,才让map继续向缓冲区存入数据,之所以写入多个小文件,是因为文件越小排序的速度越快。注意:一个分区如果过大可能存在于多个小文件之中。在得到多个分区且排序的小文件后要进行合并,合并规则是按照分区号将多个小文件中的部分分区数据合并成对应分区号的完整分区数据里面,在合并的同时再对分区内的多个部分数据按照k2排序规则进行一次排序。
小文件1:[1号分区[1,1,3,4], 2号分区[2,3], 3号分区[1,5]]
小文件2:[1号分区[3,2], 2号分区[1,2,3], 3号分区[6,7]]
小文件3:[1号分区[4,5], 2号分区[6], 3号分区[3,4,8]]
(这里的数据1,2,3.....代表以key排序的键值对 假设1代表 2: 3:)
注意:小文件中的内容按分区号排序,分区内容按照k2进行排序,但是分区中的内容并没有按照key值进行合并。
合并后的大文件:
大文件:[1号分区[,,,,然后得到了一个分区且排序的大文件,并向上级汇报信息后,map的任务就完成了。
接着对应分区号的Reduce会从多个Map输出的大文件中取出对应分区的数据然后合并,进行排序 合并成多个排序的文件,最后进行合并排序计算后写入到对应的分区中 写入到HDFS内。
当map向环形缓冲区写入数据达到一定阀值,就是超出一定范围(80%) 就会启动一个后台线程将缓冲区数据溢写到磁盘,注意:不仅仅是将数据存入到磁盘,而是经过很复杂的过程,写入磁盘之前首先将数据按照分区规则进行分区,如果没有指定分区规则,就会按照Hadoop默认的分区规则进行分区,然后按照排序规则对分区内的数据按照k2(map输出的key即reducer输入的key)进行排序 ,如果k2是Text类型 则按照k2的字典顺序的排序规则,如果是Bean按照自定义的排序规则排序,然后得到多个分区且排序的小文件。分区是按照分区号排序,分区内的数据是按照k2的排序规则进行排序,小文件内可以有多个分区。由于map向缓存区中存数据速度远远比缓冲区向磁盘写数据的速度,所以当缓冲区中的数据达到80%,map就会阻塞,停止向缓冲区存入数据,直到缓冲区中的数据写入到多个小文件并清空缓冲区,才让map继续向缓冲区存入数据,之所以写入多个小文件,是因为文件越小排序的速度越快。注意:一个分区如果过大可能存在于多个小文件之中。在得到多个分区且排序的小文件后要进行合并,合并规则是按照分区号将多个小文件中的部分分区数据合并成对应分区号的完整分区数据里面,在合并的同时再对分区内的多个部分数据按照k2排序规则进行一次排序。
小文件1:[1号分区[1,1,3,4], 2号分区[2,3], 3号分区[1,5]]
小文件2:[1号分区[3,2], 2号分区[1,2,3], 3号分区[6,7]]
小文件3:[1号分区[4,5], 2号分区[6], 3号分区[3,4,8]]
(这里的数据1,2,3.....代表以key排序的键值对 假设1代表
注意:小文件中的内容按分区号排序,分区内容按照k2进行排序,但是分区中的内容并没有按照key值进行合并。
合并后的大文件:
大文件:[1号分区[
接着对应分区号的Reduce会从多个Map输出的大文件中取出对应分区的数据然后合并,进行排序 合并成多个排序的文件,最后进行合并排序计算后写入到对应的分区中 写入到HDFS内。
默认的分区规则
默认的分区规则类:HashPartitioner(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.partition)

&是二进制“与”运算,参加运算的两个数的二进制按位进行运算,运算的规律是:
0 & 0=0
0 & 1=0
1 & 0=0
1 & 1=1
对于参加运算的数要换算为二进制进行运算,例如3 & 2的结果是2,过程如下:
3 & 2
=0111 & 0010
=0010
=2
与的计算规则是,如果两个二进制数都为真(或为1),其结果为真,如果两位数中有一位为假(或为0)者结果为假
按照key的哈希值和最大整型数进行与操作然后对启动的Reducer数量进行取余操作 得到分区号
如果不指定Reducer的数量,默认只启动一个Reducer 则取余结果均为0,所以最终结果只会存入到0号分区
假设:启动reducer的数量为4
1 % 4 = 1
2 % 4 = 2
3 % 4 = 3
4 % 4 = 0
5 % 4 = 1
6 % 4 = 2
…… 获取的分区号始终在0~3之间 每个分区号出现的概率相当
此算法的好处就是可以将数据均匀的分布到每个Reducer,不至于使某个Reducer的压力过大。(每个Reducer对应磁盘上的一个分区文件)


&是二进制“与”运算,参加运算的两个数的二进制按位进行运算,运算的规律是:
0 & 0=0
0 & 1=0
1 & 0=0
1 & 1=1
对于参加运算的数要换算为二进制进行运算,例如3 & 2的结果是2,过程如下:
3 & 2
=0111 & 0010
=0010
=2
与的计算规则是,如果两个二进制数都为真(或为1),其结果为真,如果两位数中有一位为假(或为0)者结果为假
按照key的哈希值和最大整型数进行与操作然后对启动的Reducer数量进行取余操作 得到分区号
如果不指定Reducer的数量,默认只启动一个Reducer 则取余结果均为0,所以最终结果只会存入到0号分区
假设:启动reducer的数量为4
1 % 4 = 1
2 % 4 = 2
3 % 4 = 3
4 % 4 = 0
5 % 4 = 1
6 % 4 = 2
…… 获取的分区号始终在0~3之间 每个分区号出现的概率相当
此算法的好处就是可以将数据均匀的分布到每个Reducer,不至于使某个Reducer的压力过大。(每个Reducer对应磁盘上的一个分区文件)
Hadoop1.0~Hadoop2.0演变
1.0中Hadoop的核心是JobTracker,它既要监控全局的任务又要负责资源的分配,所谓的资源分配就是决定在哪些机器上运行MapReducer。这会导致JobTracker的压力非常大。
在Hadoop2.0之后,就将JobTracker进行了拆分,将资源的分配交给了ReourceManager完成,将任务的监控交给了AppMater, 只要启动了一个计算任务(MapReduce)就会启动一个AppMaster。
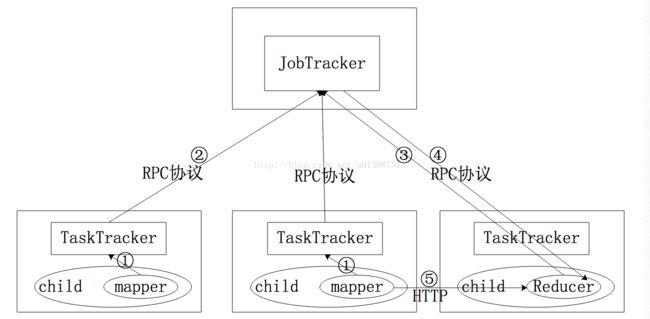
Hadoop1.0通讯过程
JobTracker将任务切片分配给每个TaskTracker,每个TaskTracker可以启动多个child,child会启动一个Reducer或Mapper来完成任务。当其中一个Mapper完成分配的任务后会将Mapper输出结果的描述信息(输出的数据的存储位置 例如数据在哪个文件路径,哪个分区)汇报给自己的TaskTracker,TaskTracker会将此信息通过RPC协议传递给JobTracker,而Reducer会启动一个后台进程不断的向JobTracker询问任务信息,从而从JobTracker获取Mapper输出数据的描述信息,然后根据描述信息通过Http协议从指定的位置下载到本地 进行运算。
注意:由于reducer可能执行失败,因此TaskTracker并没有在第一个reducer检索到map输出时就立即从磁盘删除它们,TaskTracker会一直等待,直到JobTracker告知它可以删除map的输出。
注意:由于reducer可能执行失败,因此TaskTracker并没有在第一个reducer检索到map输出时就立即从磁盘删除它们,TaskTracker会一直等待,直到JobTracker告知它可以删除map的输出。
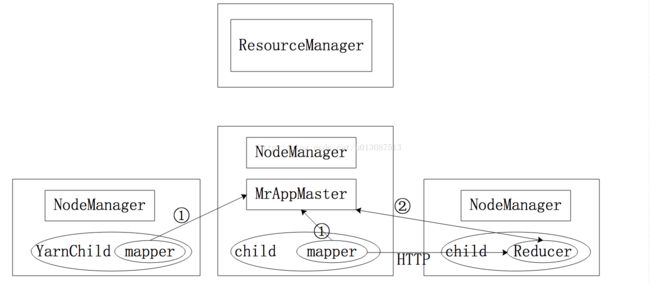
Hadoop2.0通讯过程
Hadoop2.0之后由ResourceManager(Yarn的老大)负责任务的分配,NodeManager(Yarn的小弟)负责管理当前节点的状态,一台主机只会有一个NodeManager,NodeManager可以启动多个YarnChild,每个YarnChild 负责启动Map和Reduce完成任务。每次启动一个计算任务都会在其中的一个NodeManager所管理的节点中开启一个MrAppMaster负责监控当前计算的所有任务切片,当mapper完成任务后会直接将结果描述信息通过RPC汇报给MrAppMaster,而Reducer会不断的访问MrAppMaster获取Mapper输出结果的描述信息,根据描述信息找到输出结果的位置,再通过Http协议下载到本地并执行计算任务。
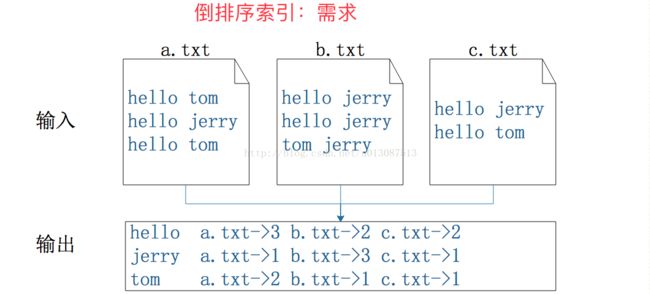
MR实现倒排序索引
要想知道当前读取的数据存在于哪个文件中,可以通过mapper的map()方法中的context对象获取输入的任务切片对象InputSplit 它是一个抽象类,要转成FIleSplit
FileSplit inputSplit = (FileSplit) context.getInputSplit();
注意:在使用字符串拼接时,如果涉及到多线程要使用StringBuffer,StringBuffer和StringBuilder都可做字符串的拼接,但是,StringBuffer是线程安全的 速度相对较慢,StringBuilder是不是线程安全的,但是速度较快。
根据输入和输出的信息逆向推理:
FileSplit inputSplit = (FileSplit) context.getInputSplit();
注意:在使用字符串拼接时,如果涉及到多线程要使用StringBuffer,StringBuffer和StringBuilder都可做字符串的拼接,但是,StringBuffer是线程安全的 速度相对较慢,StringBuilder是不是线程安全的,但是速度较快。
根据输入和输出的信息逆向推理:
推断的伪代码如下
Map阶段
<0,"hello tom">
....
context.write("hello->a.txt",1);
context.write("hello->a.txt",1);
context.write("hello->a.txt",1);
context.write("hello->b.txt",1);
context.write("hello->b.txt",1);
context.write("hello->c.txt",1);
context.write("hello->c.txt",1);
--------------------------------------------------------
combiner阶段
<"hello->a.txt",1>
<"hello->a.txt",1>
<"hello->a.txt",1>
<"hello->b.txt",1>
<"hello->b.txt",1>
<"hello->c.txt",1>
<"hello->c.txt",1>
context.write("hello","a.txt->3”);
context.write("hello","b.txt->2”);
context.write("hello”,”c.txt->2”);
--------------------------------------------------------
Reducer阶段
<"hello",{"a.txt->3”,”b.txt->2”,”c.txt->2”}>
context.write("hello","a.txt->3 b.txt->2 c.txt->2”);
-------------------------------------------------------
hello a.txt->3 b.txt->2 c.txt->2
.......
Map阶段
<0,"hello tom">
....
context.write("hello->a.txt",1);
context.write("hello->a.txt",1);
context.write("hello->a.txt",1);
context.write("hello->b.txt",1);
context.write("hello->b.txt",1);
context.write("hello->c.txt",1);
context.write("hello->c.txt",1);
--------------------------------------------------------
combiner阶段
<"hello->a.txt",1>
<"hello->a.txt",1>
<"hello->a.txt",1>
<"hello->b.txt",1>
<"hello->b.txt",1>
<"hello->c.txt",1>
<"hello->c.txt",1>
context.write("hello","a.txt->3”);
context.write("hello","b.txt->2”);
context.write("hello”,”c.txt->2”);
--------------------------------------------------------
Reducer阶段
<"hello",{"a.txt->3”,”b.txt->2”,”c.txt->2”}>
context.write("hello","a.txt->3 b.txt->2 c.txt->2”);
-------------------------------------------------------
hello a.txt->3 b.txt->2 c.txt->2
.......
代码实现:
InverseIndex
package liuxun.hadoop.mr.ii;
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputSplit;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileSplit;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
/**
* 反向索引
*
* @author liuxun
*
*/
public class InverseIndex {
public static class IndexMapper extends Mapper{
private Text k = new Text();
private Text v = new Text();
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value,Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String line = value.toString();
String[] words = line.split(" ");
// 可以从context中获取当前读取输入切片的信息
FileSplit inputSplit = (FileSplit) context.getInputSplit();
String path = inputSplit.getPath().toString();// 格式是:hdfs://hostName:9000/directory ../filename
// 获取截取的部分 /directory.../filename
for (String word : words) {
k.set(word+"->"+path);
v.set("1");
context.write(k, v);
}
}
}
public static class IndexCombiner extends Reducer{
private Text k = new Text();
private Text v = new Text();
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable values, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String[] wordAndPath = key.toString().split("->");
String word = wordAndPath[0];
String path = wordAndPath[1];
int counter = 0;
for (Text t : values) {
counter += Integer.parseInt(t.toString());
}
k.set(word);
v.set(path+"->"+counter);
context.write(k,v);
}
}
public static class IndexReducer extends Reducer{
private Text v = new Text();
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable values, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
StringBuilder resultBuilder = new StringBuilder();
for (Text t : values) {
resultBuilder.append((t.toString()+"\t").toCharArray());
}
v.set(resultBuilder.toString());
context.write(key,v );
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
Job job =Job.getInstance(conf);
job.setJarByClass(InverseIndex.class);
job.setMapperClass(IndexMapper.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class);
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(args[0]));
job.setCombinerClass(IndexCombiner.class);
job.setReducerClass(IndexReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(Text.class);
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(args[1]));
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
}