Spring --- IoC相关笔记
概述
spring 是分层的java se/ee 应用 full-stack 轻量级开源框架,以IoC (Inverse Of Control : 反转控制)和AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming:面向切面编程)为内核,提供了展示层Spring MVC 和吃阶层 Spring JDBC 以及业务层是事务管理层 等众多 企业级应用技术,还能整合世界开源众多的第三方框架 和类库,逐渐成为使用最多的Java EE企业集应用开源框架。
Spring 的优点
方便解耦,简化开发
通过spring 提供的IoC容器,可以将对象之间的依赖关系交由Spring来管理,避免硬编码所造成的过度程序耦合。
AOP编程的支持
通过Spring 的AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming)功能,方便进行切面的编程,许多不容易用传统OOP(Object Oriented Programming)实现的功能可以通过AOP应付。
声明式事务的支持
声明式 其实就是通过配置的方式实现事务声明。
方便程序的测试
方便继承各种优秀的框架
降低javaEE API的使用难度
入门案例 – IoC (解决程序间的依赖关系)
提要
程序的耦合
耦合:程序间的依赖关系,包括类之间的依赖关系,和方法之间的依赖关系
解耦 :降低程序间的依赖关系,实际开发中,应该做到:编译期不依赖,运行时才依赖
解耦思路:
第一步:使用反射来创建对象,从而避免new 关键字
第二部:通过读取配置文件来获取要创建文件的全限定类名
Bean : 在计算机英语中,有可重用组件的含义
JavaBean 用java语言编写的 可重归于组件
javaBean > 实体类
他就是创建我们的service 和 dao 对象的。
第一步:需要一个配置文件来配置我们的service 和 dao。
- 配置的内容:唯一标志 = 全限定类名(key = value)
IoC : 控制反转(Inverse Of Control )。把创建对象的权力交给框架,是框架的重要特征,并非面向对象的专用术语。它包括依赖注入(Dependency Injection,简称DI)和依赖查找(Dependency LookUp)
明确 IoC 在计算机程序中的作用:削减程序之间的耦合(解除我们代码之间的依赖关系)。
spring 中的 IoC就是为了是这些代码变得简单,简化这些代码
搭建步骤
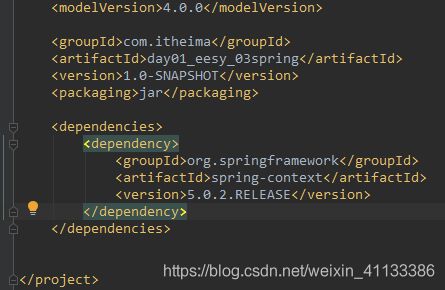
第一步:建立maven工程,导入坐标
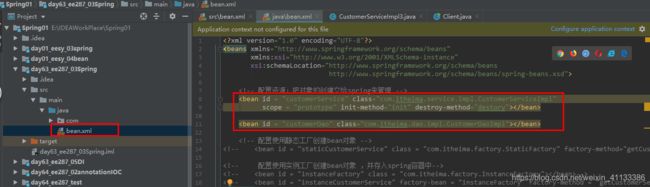
第二步:创建配置文件、导约束、配置资源
第三步:直接获取对象,两种方式
public class Client {
/*
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext : 它是只能加载类路径下的配置文件 我们用这个
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext : 它是可以加载磁盘任意位置的配置文件
Bean创建的两种规则:
BeanFactory: 单例对象适用
提供的是一种延迟加载思想来创建bean对象。bean对象什么时候用什么时候创建
ApplicationContext 多例对象适用
提供的是一种立即加载思想来创建bean对象。只要一解析完配置文件,就立即创建配置文件
bean 的三种创建方式
第一种方式:调用无参构造函数创建 (此种方式用的最多)
默认情况下,如果类中没有无参构造函数,则创建失败,会报异常
第二种方式:使用工厂中的方法创建对象
需要使用bean标签中的factory-method属性,指定静态工厂中创建对象的方法
第三种方式:使用实例工厂中的方法创建
bean 的作用范围:
它是可以通过配置的方式来调整作用范围。
配置的属性:bean标签的scope属性
属性的取值:
singleton:单例的(默认值)
prototype:多例的(当我们让spring接管structs2的action创建时,action必须配置此值)
request:作用范围是一次请求,和当前请求的转发
session:作用范围是一次会话
globalsession:作用范围是一次全局会话
bean的生命周期:
涉及两个属性:
init-method
destroy-method
单例:
出生:容器创建,对象就出生了
活着:只要容器在,对象就一直存在
死亡:容器销毁,对象消亡
多例:
出生:每次使用时创建对象
活着:只要对象在使用中就一直活着
死亡:当对象长时间不使用,并且也没有别的对象引用是时,有java的垃圾回收器回收
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.获取核心容器
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//2.根据bean的id获取对象
ICustomerService cs1 = (ICustomerService) ac.getBean("customerService");
CustomerDao cs2 = ac.getBean("customerDao", CustomerDao.class);
System.out.println(cs1);
System.out.println(cs2);
cs1.saveCustomer();
}
/* public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.获取容器
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource("bean.xml");
BeanFactory factory = new XmlBeanFactory(resource);
//2.根据bean的id获取对象
ICustomerService cs = (ICustomerService) factory.getBean("customerService");
CustomerDao dao = (CustomerDao) factory.getBean("customerDao");
cs.saveCustomer();
}*/
}
bean.xml 注入
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- spring 的依赖注入:
注入的方式有三种:
第一种:使用构造函数注入
第二种:使用set方法注入
第三种:使用注解注入
注入的数据类型有三种:
第一类:基本类型和String类型
第二类:其他Bean类型(必须在spring配置文件出现过的bean)
第三类:复杂类型(集合类型)
-->
<!-- 配构造函数注入
涉及的标签:constructor-arg
标签的属性:
type:指定参数的类型
index:指定参数的索引位置
name:指定参数的名称 一般用它
===================上面三个参数是指定给哪个参数赋值,下面两个属性是指定赋什么值======================
value:指定基本数据类型或String类型的数据
ref:指定其他bean类型数据
标签出现的位置:
写在bean标签的内部
-->
<bean id = "customerService" class="itheima.service.impl.CustomerServiceImpl" >
<constructor-arg name = "driver" value = "com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name = "port" value = "3306"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name = "today" ref = "now"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean id = "now" class = "java.util.Date"></bean>
<!-- set方法注入
涉及的标签:property
标签的属性:
name:指定参数的set方法名称 一般用它
===================上面三个参数是指定给哪个参数赋值,下面两个属性是指定赋什么值======================
value:指定基本数据类型或String类型的数据
ref:指定其他bean类型数据
标签出现的位置:
写在bean标签的内部
-->
<bean id = "customerService2" class="itheima.service.impl.CustomerServiceImpl2" >
<property name="driver" value = "com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="port" value = "3307"></property>
<property name="today" ref = "now"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 复杂类型注入
用于给list结构注入的标签有
list array set
用于map结构注入的标签
map props
结构相同,标签可以互换
-->
<bean id = "customerService3" class = "itheima.service.impl.CustomerServiceImpl3">
<property name="myStrs" >
<set >
<value>AAA</value>
<value>BBB</value>
<value>CCC</value>
</set>
</property>
<property name="myList">
<list>
<value>AAA</value>
<value>BBB</value>
<value>CCC</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="mySet">
<array>
<value>AAA</value>
<value>BBB</value>
<value>CCC</value>
</array>
</property>
<property name="myMap">
<map>
<entry key = "testD" value="DDD"></entry>
<entry key = "testE">
<value>EEE</value>
</entry>
</map>
</property>
<property name="myProps">
<props>
<prop key="prop1">111</prop>
<prop key="prop2">222</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
注解注入
有四种注解
1.用于创建bean对象,和 标签作用一样
@Component
作用:相当于配置了bean标签
它能出现的位置:类上面
属性:value。含义是指定bean的id。当不写时,它有默认值,默认值是:当前类的短名首字母该小写。
(全限定名:com.itheima.service.impl.CustomerServiceImpl)
(短名:customerServiceImpl)
由此注解衍生的三个注解:
@Controller 一般用于表现层的注解
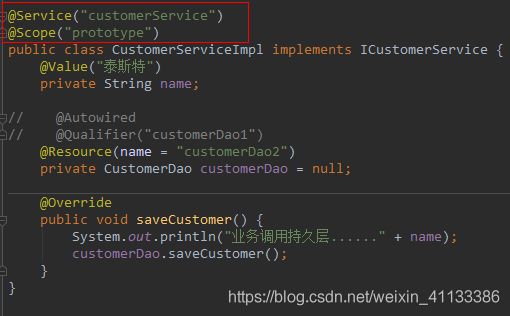
@Service 一般用于业务层
@Repository 一般用于持久层
它们和@Component的作用及属性一模一样2.用于注入数据的,和标签的作用一样
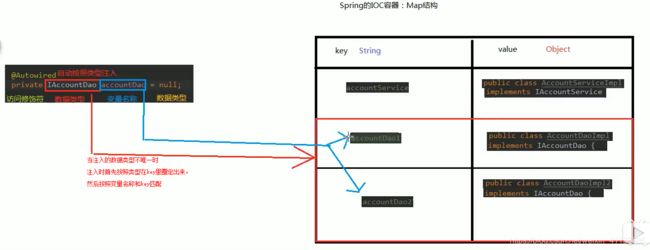
@AutoWired
作用:自动按照类型注入。只要有唯一类型匹配就能注入成功。
当我们使用注解方法注入时,set方法不是必须的
如果注入的bean在容器中类型不唯一时,他会把变量名称作为bean的id,在容器中查找,找到后也能注入
如果没有找到一致的bean的id,则报错
@Qualifier
作用:在自动按照类型注入的基础之上,在按照bean的id注入。
在给类成员注入数据时,不能独立使用。但是在给方法的形参注入数据时,可以独立使用
属性:
value:用于指定bean的id
@Resource
作用:直接按照bean的id注入
属性:
name:用于指定bean的id。
以上三个注解都是用于注入bean类型的。用于与注入基本类型和String类型注入需要使用Value
@Value
作用:用于注入基本类型和String类型数据。它可以借助spring的el表达式读取properties文件中的配置。
属性:
value:用于指定要注入的数据3.用于改变作用范围的,和属性功能一样
@Scope
作用:用于改变bean的作用范围
属性:
value:用于指定范围的取值
取值和xml中scope属性的取值是一样的。singleton prototype request session globalsession4.和生命周期相关的
PreDestory 用于指定销毁方法
PostConstruct 用于指定初始化方法5.spring的新注解
@Bean 它是把方法的返回值存入到spring容器中。
该注解有一个属性:name用于指定bean的id。当不指定时,它有默认值,默认值是方法名称。
@Configuration 把当前类看做spring的配置类
@ComponentScan 指定要扫描的包
@PropertySource(value={“classpath:config/jdbcConfig.properties”})说明这个是类路径
@Import 导入其他配置类
使用纯注解
public class JdbcTemplateDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.获取容器
// ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfiguration.class);
//2.跟id获取bean对象
JdbcTemplate jt = (JdbcTemplate) ac.getBean("jdbcTemplate");
//3.执行操作
jt.execute("insert into account(name,money)values('eee',2345)");
}
}
@Configuration //指定当前类是一个配置类
@ComponentScan("com.itheima") //用于通过注解指定spring再创建容器时要扫描的包
public class SpringConfiguration {
@Bean(name="jdbcTemplate")//用于把当前方法的返回值作为bean对象存入spring容器中。属性name用于指定bean的id,默认值是当前方法的名称
public JdbcTemplate createJdbcTemplate(DataSource dataSource){
return new JdbcTemplate(dataSource);
}
/**
* 创建数据源对象
*/
@Bean(name="dataSource")
@Scope("prototype")//datasource 有必要配置成为多例
public DataSource createDataSource(){
DriverManagerDataSource ds = new DriverManagerDataSource();
//jdbc也可以配置为注解,要用PropertySource注解,不过这种方法属于杀敌一千自损八百
ds.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
ds.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/eesy");
ds.setUsername("root");
ds.setPassword("123");
return ds;
}
}
spring整合junit
问题 当测试方法执行时,没有IoC容器,就算写了AutoWired注解,也无法注入
整合步骤:
第一步:拷贝spring提供的整合jar包 (再pom文件中直接导入坐标)
spring-test-4.2.4RELEASE.jar
第二步:使用junit提供的一个注解,把原有的main函数替换掉,换成spring提供的
@RunWith
要换的类:SpringJunit4ClassRunner
第三部:使用spring提供的注解告知spring,配置文件或者注解所在位置
@ContextConfiguration(locations={"classpath:bean.xml"})//配置文件
@ContextConfiguration(classes={SpringConfiguration.class})//注解所在位置
------------------------------------------------------------------------
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassPathRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes={SpringConfiguration.class})
public class CustomerServiceTest{
@Resource(name = "customerService")或者@Autowired
private ICustomerService cs;
@Test
public void testFindAllCustomer(){
List<Customer> list = cs.findAllCustomer();
for(Customer c : list)
System.out.println(c);
}
}