Spring——IoC核心(基于XML)、DI核心(基于XML)
目录
- 一、IoC容器
- 1、BeanFactory和ApplicationContext两者的区别
- 2、Bean实例化的四种方式
- 2.1、使用构造器实例化(无参构造器)
- 2.2、静态工厂方法实例化(了解)
- 2.3、实例工厂方法实例化(了解))
- 2.4、实现FactoryBean接口实例化
- 3、Bean作用域
- 4、Bean的初始化和销毁
- 5、Bean的实例化过程
- 二、DI操作
- 1、什么是注入操作?
- 2、XML自动装配(不推荐)
- 3、Setter方法注入(重点)
- 3.1、注入常量
- 3.2、注入对象
- 3.3、注入集合
- 4、构造器注入
- 5、Bean元素继承
- 6、属性占位符
![]()
Spring系列
- Spring — Spring简介、入门、配置 , IoC和DI思想
- Spring — IoC核心(基于XML)、DI核心(基于XML)
- Spring — 使用IoC和DI模拟注册案例、注解配置IoC和DI
- Spring — 静态代理、动态代理、拦截器思想
- Spring — AOP思想、AOP开发、Pointcut语法、注解配置AOP
- Spring — DAO层、Spring JDBC、Spring事务控制
- Spring — XML配置事务、注解+XML、纯注解的配置方式
- Spring整合MyBatis
- Spring Java Config — 组件注册相关注解
- Spring Java Config — 常用注解
一、IoC容器
跳转到目录
在上一篇文章中已经介绍过了IoC的思想,这里不再赘述!
Spring IoC容器 (Container):
-
BeanFactory: Spring最底层的接口, 只提供了IoC的功能, 负责创建、组装、管理bean,所以一般不适用BeanFactory, 推荐使用ApplicationContext(应用上下文)
-
ApplicationContext : ApplicationContext接口继承了BeanFactory, 还提供了AOP继承、国际化处理、事件传播、统一资源价值等功能; 可以查看该接口的继承体系;
1、BeanFactory和ApplicationContext两者的区别
跳转到目录
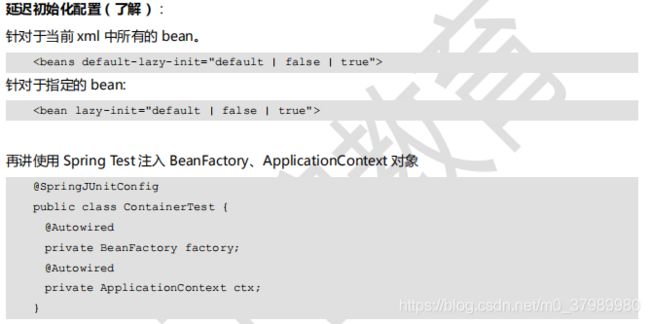
bean的创建时机不同:
-
BeanFactory有
延迟初始化(懒加载)的特点,在创建Spring容器的时候,不会立刻去创建容器,管理Bean对象,而是要等到从容器中获取对象的时候,才去创建对象. -
ApplicationContext在创建Spring容器的时候,会把容器中管理的Bean立刻初始化,而不会等到获取Bean的时候才初始化.
// Person
@Data
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
public Person(){
System.out.println("Person对象创建啦!");
}
}
// person.xml
<!-- 使用IoC来管理对象的创建和依赖注入-->
<bean id="person" class="com.sunny.domain.Person">
<property name="name" value="CoderZYGui"/>
<property name="age" value="23"/>
</bean>
// PersonTest(非Spring Test)
public class PersonTest {
// 使用BeanFactory创建Spring IoC容器
/**
* --------------------------------
* Person对象创建啦!
* Person(name=CoderZYGui, age=23)
*
* 结论: BeanFactory有延迟初始化(懒加载)的特点,在创建Spring容器的时候,不会立刻去创建容器,
* 管理Bean对象,而是要等到从容器中获取对象的时候,才去创建对象.
*/
@Test
public void test1(){
Resource resource = new ClassPathResource("xmls/person.xml");
BeanFactory factory = new XmlBeanFactory(resource);
System.out.println("--------------------------------");
Person person = factory.getBean("person", Person.class);
System.out.println(person);
}
// 使用ApplicationContext创建Spring IoC容器
/**
* Person对象创建啦!
* --------------------------------
* Person(name=CoderZYGui, age=23)
*
* 结论: 在创建Spring容器的时候,会把容器中管理的Bean立刻初始化,而不会等到获取Bean的时候才初始化.
*/
@Test
public void test2(){
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("xmls/person.xml");
System.out.println("--------------------------------");
Person person = ctx.getBean("person", Person.class);
System.out.println(person);
}
2、Bean实例化的四种方式
跳转到目录
- 构造器实例化(无参构造器),使用最多
- 静态工厂方法实例化(了解)
- 实例工厂方法实例化(了解)
- 实现FactoryBean接口实例化:实例工厂的变种
2.1、使用构造器实例化(无参构造器)
跳转到目录
// 类
public class Cat1 {
public Cat1(){
System.out.println("构建Cat1");
}
}
// createBean.xml
<!--1、构造器实例化(无参构造器),使用最多-->
<bean id="cat1" class="com.sunny.createbean._01_constructor.Cat1"/>
2.2、静态工厂方法实例化(了解)
跳转到目录
// 类
public class Cat2 {
}
// Cat2工厂
public class Cat2Factory {
public static Cat2 createInstance(){
Cat2 cat2 = new Cat2();
return cat2;
}
}
// createBean.xml
<!--2、静态工厂方法实例化(了解)
以前使用静态工厂方法: Cat2 cat2 = Cat2Factory.createInstance();来创建,
现在只不过把这种方式,设置到配置文件中来了
-->
<bean id="cat2" class="com.sunny.createbean._02_static_factory.Cat2Factory"
factory-method="createInstance"/>
2.3、实例工厂方法实例化(了解)
跳转到目录
// 类
public class Cat3 {
}
// Cat3工厂
public class Cat3Factory {
public Cat3 createInstance(){
Cat3 cat3 = new Cat3();
return cat3;
}
}
// createBean.xml
<!--3、实例工厂方法实例化(了解)
第一个bean是创建实例工厂对象,第二个bean是通过实例工厂对象调用工厂方法创建Cat3的对象
-->
<bean id="cat3Factory" class="com.sunny.createbean._03_instance_factory.Cat3Factory"/>
<bean id="cat3" factory-bean="cat3Factory" factory-method="createInstance"/>
2.4、实现FactoryBean接口实例化
跳转到目录
// 类
public class Cat4 {
}
// Cat4工厂
public class Cat4Factory implements FactoryBean<Cat4> {
private String name;
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
// 实例工厂的方法(对比方式三,这种方式固定了工厂实例方法)
public Cat4 getObject() throws Exception {
System.out.println("name=:" + name);
Cat4 cat4 = new Cat4();
return cat4;
}
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return Cat4.class;
}
}
// createBean.xml
<!--4、实现FactoryBean接口实例化:实例工厂的变种
Cat4Factory工厂类的创建实例的方法已经固定实现了,Cat4Factory通过实现方法getObject来
创建Cat4的对象
-->
<bean id="cat4" class="com.sunny.createbean._04_factory_bean.Cat4Factory">
<property name="name" value="猫猫4"/>
</bean>
测试
Spring Test(基于Junit4)
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class SpringJunit4 {
// @Autowired:表示从Spring IoC容器中根据类型找到对应的bean,并自动注入到某个字段上
// ------- 4种Bean实例化的方式---------
@Autowired
private Cat1 cat1;
@Autowired
private Cat2 cat2;
@Autowired
private Cat3 cat3;
@Autowired
private Cat4 cat4;
// 不使用Spring容器的时候,使用这4种方式的实例化步骤
@Test
public void testOld() throws Exception {
// 使用构造器_实例化bean
Cat1 cat1 = new Cat1();
// 使用静态工厂方法_实例化bean
Cat2 cat2 = Cat2Factory.createInstance();
// 使用实例工厂方法_实例化bean
Cat3 cat3 = new Cat3Factory().createInstance();
// 实现FactoryBean接口实例化_实例化bean
Cat4 cat4 = new Cat4Factory().getObject();
}
@Test
public void test2(){
System.out.println(cat1);
System.out.println(cat2);
System.out.println(cat3);
System.out.println(cat4);
}
}
3、Bean作用域
跳转到目录
在Spring容器中是指其创建的Bean对象相对于其他Bean对象的请求可见范围,语法格式:
<bean id="" class="" scope="作用域"/>
singleton: 单例, 在Spring IoC容器中仅存在一个Bean实例(默认缺省就是scope)prototype: 多里, 每次从容器中调用Bean时,都返回一个新的实例,每次调用getBean()时,相当于执行 new XxxBean(), 不会在容器启动时创建对象.
// 类
public class Dog {
}
// Dog.xml
<!--Bean的作用域,
单例: 缺省是singleton,从容器中拿到的对象都是同一个对象
多例: prototype, 从容器拿到的对象不是同一个对象
-->
<bean id="dog" class="com.sunny.scope.Dog" scope="singleton"/>
// Spring Test
// ----------bean的scope范围-----------------
// 表示从容器中拿到实例化的dog对象
@Autowired
private Dog dog1;
@Autowired
private Dog dog2;
@Test
public void test3(){
// 因为bean的scope默认就是singleton,所以容器生成的Dog对象就是同一个
System.out.println(dog1);
System.out.println(dog2);
}
4、Bean的初始化和销毁
跳转到目录
比如DataSource、SqlSessionFactory 最终都需要关闭资源; 在Bean销毁之前都要调用close方法, 而在Spring IoC容器中可以帮我们管理对象的创建, 如何帮我们管理对象在创建之后的初始化操作和回收资源的操作呢,语法如下:
<bean id="" class="" init-method="该类初始化方法名"
destroy-method="该类销毁方法名"/>
- init-method: 调用ds对象的初始化方法,在初始化执行之前,立刻执行
- destroy-method: 调用ds对象的销毁方法,在销毁执行之前,调用
使用Spring IoC容器时的操作
测试使用的是Spring Test
MyDataSource类
/**
* 模拟数据库连接池
* 当使用连接池的时候,都需要初始化和销毁,使用Spring IoC容器后,如何
* 让容器帮助我们进行初始化和销毁呢?
*/
public class MyDataSource {
public MyDataSource(){
System.out.println("创建对象...");
}
public void open(){
System.out.println("开启资源...");
}
public void close(){
System.out.println("销毁资源...");
}
public void doWork(){
System.out.println("工作...");
}
}
// mydatasource.xml
<!--
init-method: 调用ds对象的初始化方法,在初始化执行之前,立刻执行
destroy-method: 调用ds对象的销毁方法,在销毁执行之前,调用
-->
<bean id="ds" class="com.sunny.lifecycle.MyDataSource" init-method="open"
destroy-method="close"/>
//Spring Test测试
// ------bean的初始化和销毁--------
// 没有使用Spring容器的操作
@Test
public void testOld1(){
// 创建对象
MyDataSource ds = new MyDataSource();
System.out.println("-------");
// 初始化操作
ds.open();
// 工作
ds.doWork();
// 销毁
ds.close();
}
// 使用Spring容器的方式
@Autowired
private MyDataSource ds;
@Test
public void test4(){
ds.doWork();
}
使用普通的测试方法
在这里没有打印出销毁资源,这就是普通测试和Spring测试的区别;
- Spring测试会正常释放资源
- 普通的单元测试不会正常释放资源,这时就需要手动来释放资源了
xml文件和类同上.
public class MyDataSourceTest {
/**
* 在这里没有打印出销毁资源,这就是普通测试和Spring测试的区别;
* Spring测试会正常释放资源
* 普通的单元测试不会正常释放资源,这时就需要手动来释放资源了
*/
@Test
public void test(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("xmls/mydatasource.xml");
MyDataSource ds = ctx.getBean("ds", MyDataSource.class);
ds.doWork();
ds.close(); // 手动释放资源
}
@Test
public void test1(){
@Cleanup //使用第三方框架lombok中的Clearup注解来释放.
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("xmls/mydatasource.xml");
MyDataSource ds = ctx.getBean("ds", MyDataSource.class);
ds.doWork();
}
@Test
public void test2(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("xmls/mydatasource.xml");
MyDataSource ds = ctx.getBean("ds", MyDataSource.class);
ds.doWork();
// 这种方式是将Spring线程作为JVM的子线程,当JVM关闭后,该Spring线程也会被关闭
ctx.registerShutdownHook();
}
}
5、Bean的实例化过程
跳转到目录
bean的声明周期: bean从出生–>销毁的整个过程
<bean id="" class="" init-method="该类初始化方法名"
destroy-method="该类销毁方法名"/>
1、启动Spring容器
2、创建Bean对象 ----> 实际是在调用Bean对象的构造器
3、给Bean添加属性
4、调用Bean对象的初始化init-method
5、getBean获取某个bean对象,调用bean对象的某一个方法
6、调用Bean对象的销毁方法destory-method
7、Spring容器销毁
二、DI操作
跳转到目录
1、 什么是注入操作?
- setter方法注入
- 构造器注入
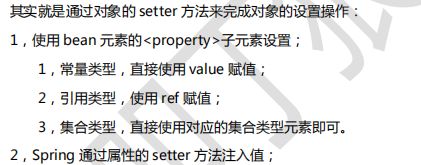
注入值类型:
- 常量值(简单类型) -----
value 元素 - 对象 -----
ref元素 - 集合 -----
对象集合类型元素
2、XML自动装配(不推荐)
跳转到目录
- 设置
autowire属性<bean id="person2" class="Person的全限定名" autowire="byName"/> - autowire属性: 让Spring按照一定的规则方式自己去找合适的对象,并完成DI注入操作.

注意:- 如果按照
byName自动注入,要求所有的属性名字和id的名字必须保证一种规范的命名 - 如果安装
byType注入,如果Spring容器中同一个类型有多个实例,报 bean不是唯一类型错误;
- 如果按照
// 需求: 让Spring帮我们创建Person对象,而Person对象还需要依赖Dog对象;所以需要创建两个Bean
public class Person {
private Dog dog;
public void setDog(Dog dog){
this.dog = dog;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" + "dog=" + dog + '}';
}
}
// .xml
<bean id="dog1" class="com.sunny._01_xml_autowired.Dog"/>
<bean id="person2" class="com.sunny._01_xml_autowired.Person" autowire="byName"/>
// Spring Test测试
// @Autowired:表示从Spring IoC容器中根据类型找到对应的bean,并自动注入到某个字段上
@Autowired
private Person person;
@Test
public void test(){
System.out.println(person);
}
3、Setter方法注入(重点)
3.1、注入常量
跳转到目录
注入常量值,也称之为注入简单类型 :
<property name="对象属性名称" value="注入的值"/>
// 类
@Setter
@ToString
public class Employee {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private BigDecimal salary;
}
3.2、注入对象
跳转到目录
注入对象,就是把一个对象,通过setter方法设置给另一个对象:
<property name="对象属性名称" ref="被注入对象的bean的id"/>
// 类
public class Cat {
}
public class Person {
private Cat c1;
public void setC1(Cat c1) {
this.c1 = c1;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person1{" +
"c1=" + c1 +
'}';
}
}
3.3、注入集合
跳转到目录
注入集合,就是把一个集合类型的数据,通过setter方法设置给另一个对象:
<property name="集合类型">
<set>
<value>set1value>
<value>set2value>
set>
property>
// 类
@Setter
public class CollectionBean {
private Set<String> set;
private List<String> list;
private String[] array;
private Map<String, String> map;
private Properties prop;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "CollectionBean{" +
"\nset=" + set +
", \nlist=" + list +
", \narray=" + Arrays.toString(array) +
", \nmap=" + map +
", \nprop=" + prop +
'}';
}
}
XML文件
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="employee" class="com.sunny._02_di_setter.Employee">
<property name="name" value="coder"/>
<property name="age" value="23"/>
<property name="salary" value="188.00"/>
bean>
<bean id="cat" class="com.sunny._02_di_setter.Cat"/>
<bean id="person" class="com.sunny._02_di_setter.Person">
<property name="c1" ref="cat"/>
bean>
<bean id="collectionBean" class="com.sunny._02_di_setter.CollectionBean">
<property name="set">
<set>
<value>set1value>
<value>set2value>
set>
property>
<property name="list">
<list>
<value>list1value>
<value>list2value>
list>
property>
<property name="array">
<array>
<value>array1value>
<value>array2value>
array>
property>
<property name="map">
<map>
<entry key="key1" value="value1"/>
<entry key="key2" value="value2"/>
map>
property>
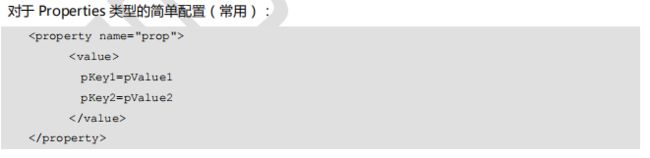
<property name="prop">
<value>
k1=v1
k2=v2
k3=v3
value>
property>
bean>
beans>
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class DiSetterTest {
// @Autowired:表示从Spring IoC容器中根据类型找到对应的bean,并自动注入到某个字段上
@Autowired
private Employee employee;
@Autowired
private Person person;
@Autowired
private CollectionBean cb;
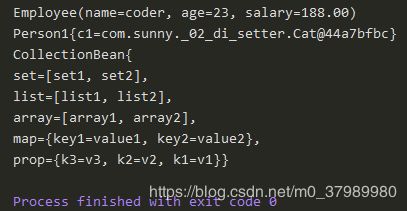
@Test
public void test1(){
System.out.println(employee);
System.out.println(person);
System.out.println(cb);
}
}
4、构造器注入
跳转到目录
// 注入常量的类
@ToString
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Employee1 {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private BigDecimal salary;
}
// 注入对象的类
public class Cat1 {
}
public class Person1 {
private Cat1 c1;
public Person1(Cat1 c1) {
this.c1 = c1;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person1{" +
"c1=" + c1 +
'}';
}
}
// 注入集合类型的类
@AllArgsConstructor //生成全参数构造器
@ToString
public class CollectionBean1 {
private Set<String> set;
private List<String> list;
private String[] array;
private Map<String, String> map;
private Properties prop;
}
xml文件
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="employee1" class="com.sunny._03_di_constructor.Employee1">
<constructor-arg name="name" value="zygui"/>
<constructor-arg name="age" value="23"/>
<constructor-arg name="salary">
<null/>
constructor-arg>
bean>
<bean id="cat1" class="com.sunny._03_di_constructor.Cat1"/>
<bean id="perosn1" class="com.sunny._03_di_constructor.Person1">
<constructor-arg name="c1" ref="cat1"/>
bean>
<bean id="collectionBean1" class="com.sunny._03_di_constructor.CollectionBean1">
<constructor-arg name="set">
<set>
<value>set1value>
<value>set2value>
set>
constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="list">
<list>
<value>list1value>
<value>list2value>
list>
constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="array">
<array>
<value>array1value>
<value>array2value>
array>
constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="map">
<map>
<entry key="key1" value="value1"/>
<entry key="key2" value="value2"/>
map>
constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="prop">
<value>
k1=v1
k2=v2
k3=v3
value>
constructor-arg>
bean>
beans>
测试类
// @Autowired:表示从Spring IoC容器中根据类型找到对应的bean,并自动注入到某个字段上
@Autowired
private Employee1 emp;
@Autowired
private Person1 p1;
@Autowired
private CollectionBean1 cb1;
@Test
public void test1(){
System.out.println(emp);
System.out.println(p1);
System.out.println(cb1);
}
5、Bean元素继承
跳转到目录
多个bean元素共同配置的抽取,实则是bean配置的拷贝,和Java的继承不同
- Java继承: 把多个类共同的代码抽取到父类中
- bean元素的继承: 把多个bean元素
共同的属性配置抽取到另一个公用的bean元素中
Java类
@Setter
@ToString
public class SomeBean1 {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Double weight;
}
@Setter
@ToString
public class SomeBean2 {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Double height;
}
xml配置
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="baseBean" abstract="true">
<property name="name" value="Tom"/>
<property name="age" value="23"/>
bean>
<bean id="someBean1" class="com.sunny._04_bean_tag_inheritance.SomeBean1" parent="baseBean">
<property name="name" value="lucy"/>
<property name="weight" value="60.0"/>
bean>
<bean id="someBean2" class="com.sunny._04_bean_tag_inheritance.SomeBean2" parent="baseBean">
<property name="height" value="175.0"/>
bean>
beans>
6、属性占位符
跳转到目录
举一个查询数据库的例子:
- 表结构
CREATE TABLE `student` (
`id` bigint(20) NOT NULL,
`name` varchar(40) NOT NULL,
`age` int(11) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
1、原始版本
- 查询数据库信息的测试方法
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class PropertyPlaceholderTest {
private DruidDataSource ds;
@Test
public void test() throws Exception{
ds = new DruidDataSource();
ds.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
ds.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring");
ds.setUsername("root");
ds.setPassword("1111");
ds.setInitialSize(2);
@Cleanup
Connection conn = ds.getConnection();
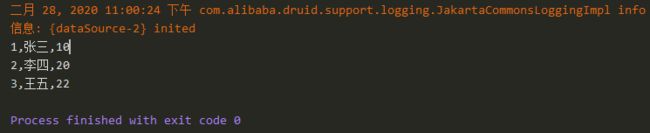
String sql = "SELECT id, name, age FROM student";
@Cleanup
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
@Cleanup
ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()){
System.out.print(rs.getLong("id")+",");
System.out.print(rs.getString("name")+",");
System.out.println(rs.getInt("age"));
}
}
}
注意: @Cleanup是第三方框架lombok的注解,该注解的作用自动资源管理, 并处理一些异常.
成功查询到数据库中的信息
但是从上面代码可以发现, 我们可以将这一坨代码,交给Spring IoC容器来处理,让IoC来构建我们的dataSource对象; 让DI来给这个对象注入属性值;
2、Spring IoC容器管理版本
- 测试类
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class PropertyPlaceholderTest {
// @Autowired:表示从Spring IoC容器中根据类型找到对应的bean,并自动注入到某个字段上
@Autowired
private DruidDataSource ds;
@Test
public void test() throws Exception{
@Cleanup
Connection conn = ds.getConnection();
String sql = "SELECT id, name, age FROM student";
@Cleanup
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
@Cleanup
ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery();
while (rs.next()){
System.out.print(rs.getLong("id")+",");
System.out.print(rs.getString("name")+",");
System.out.println(rs.getInt("age"));
}
}
}
- db.properties
jdbc.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=1111
jdbc.initialSize=2
- xml文件
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties"/>
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource"
init-method="init" destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
<property name="initialSize" value="${jdbc.initialSize}"/>
bean>
beans>
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties"/>