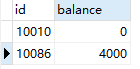Spring——XML配置事务、注解+XML、纯注解的配置方式
目录
- 一、基于 xml 配置声明式事务
- 1、解决银行转账问题
- 2、事务方法 tx:method 属性配置
- 3、CRUD通用事务配置
- 二、基于 注解 配置声明式事务
- 三、基于 纯注解(JavaConfig) 配置声明式事务
- 四、选择开发方式
![]()
Spring系列
- Spring — Spring简介、入门、配置 , IoC和DI思想
- Spring — IoC核心(基于XML)、DI核心(基于XML)
- Spring — 使用IoC和DI模拟注册案例、注解配置IoC和DI
- Spring — 静态代理、动态代理、拦截器思想
- Spring — AOP思想、AOP开发、Pointcut语法、注解配置AOP
- Spring — DAO层、Spring JDBC、Spring事务控制
- Spring — XML配置事务、注解+XML、纯注解的配置方式
- Spring整合MyBatis
- Spring Java Config — 组件注册相关注解
- Spring Java Config — 常用注解
一、基于 xml 配置声明式事务
跳转到目录
1、解决银行转账问题
跳转到目录
在上面引出事务的代码基础上,只需要修改xml配置文件
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
https://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties"/>
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource"
init-method="init" destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
<property name="initialSize" value="${jdbc.initialSize}"/>
bean>
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
bean>
<bean id="accountService" class="com.sunny.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl">
<property name="dao" ref="accountDao"/>
bean>
<bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
bean>
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="txManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="trans"/>
tx:attributes>
tx:advice>
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="txPointcut" expression="execution(* com.sunny.service.*Service.*(..))"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="txPointcut"/>
aop:config>
beans>
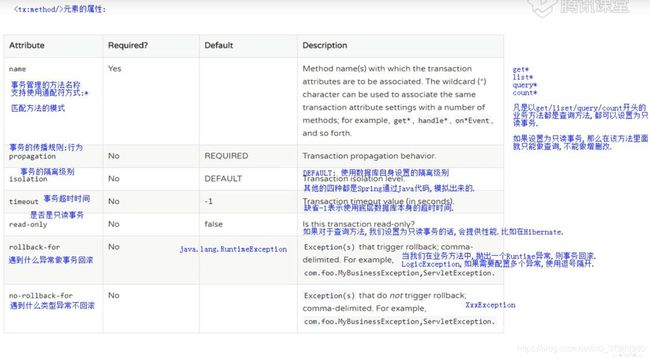
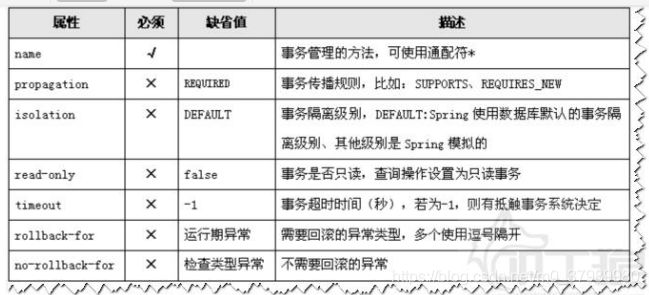
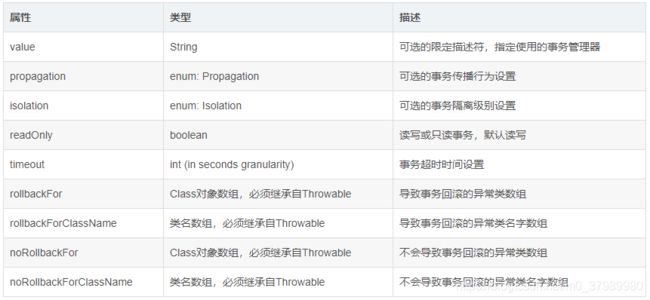
2、事务方法 tx:method 属性配置
跳转到目录
- 事务配置
- 属性id:自定义唯一表示
- transaction-manager属性:事务管理类,配置事务管理类的id属性值
- 事务属性配置
- 属性name:方法名
- 属性read-only:是否只读事务,查询都是只读,其他是非只读
- 属性propagation:事务的传播行为,默认配置REQUIRED或者SUPPORTS
- 属性isolation:事务隔离级别,默认配置DEFAULT
- 属性timeout:事务超时时间,配置-1
- 属性no-rollback-for:遇到什么异常不回滚,配置异常类名,多个类逗号分开
- 属性rollback-for:遇到什么异常回滚
- 以上回滚属性不配置,遇到异常就回滚
- aop切面配置
- 属性advice-ref:引用通知,配置tx:advice标签的属性值
- 属性pointcut:切点配置
3、CRUD通用事务配置
跳转到目录
<tx:advice id="crudAdvice" transaction-manager="txManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="get*" read-only="true" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="list*" read-only="true" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="query*" read-only="true" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
<tx:method name="*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
tx:attributes>
tx:advice>
二、基于 注解 配置声明式事务
跳转到目录
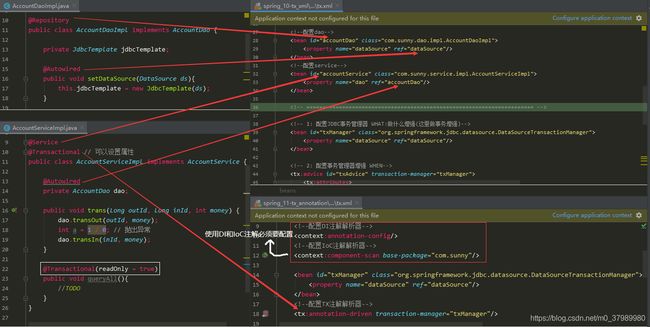
基于注解配置事务:在Service中,使用 @Transactional注解
- @Transactional 可以作用于接口、接口方法、类以及类方法上。当作用于类上时,该类中的所有
public方法将都具有该类型的事务属性,同时,我们也可以在方法级别使用该标注来覆盖类级别的定义(比如在查询方法上单独设置@Transactional(readOnly=true)。
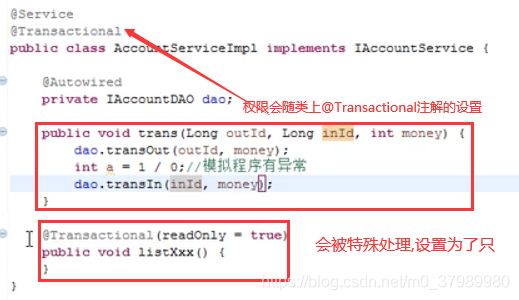
- @Transactional 注解可以作用于接口、
接口方法、类以及类方法上,但是 Spring 建议不要在接口或者接口方法上使用该注解,因为这只有在使用基于接口的代理时它才会生效。另外, @Transactional 注解应该只被应用到 public 方法上,这是由 Spring AOP 的本质决定的。如果你在 protected、private 或者默认可见性的方法上使用 @Transactional 注解,这将被忽略,也不会抛出任何异常。
Java代码
@Repository
public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao {
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Autowired
public void setDataSource(DataSource ds){
this.jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate(ds);
}
public void transOut(Long outId, int money) {
String sql = "UPDATE account SET balance = balance - ? WHERE id = ?";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql, money, outId);
}
public void transIn(Long inId, int money) {
String sql = "UPDATE account SET balance = balance + ? WHERE id = ?";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql, money, inId);
}
}
@Service
@Transactional
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
@Autowired
private AccountDao dao;
public void trans(Long outId, Long inId, int money) {
dao.transOut(outId, money);
int a = 1 / 0; // 抛出异常
dao.transIn(inId, money);
}
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public void queryAll(){
//TODO
}
}
xml配置: 必须要配置 TX注解解析器!
<context:annotation-config/>
<context:component-scan base-package="com.sunny"/>
<bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
bean>
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="txManager"/>
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties"/>
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource"
init-method="init" destroy-method="close">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}"/>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"/>
<property name="initialSize" value="${jdbc.initialSize}"/>
bean>
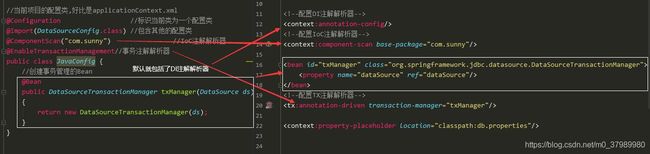
三、基于 纯注解(JavaConfig) 配置声明式事务
跳转到目录
- @Configuration标识当前类是Spring的一个配置类
- @ComponentScan替代xml中的
- @Import引入其他配置类,被引入的配置类可以不加@Configuration注解
- @PropertySource:引入外部properties文件,注意加classpath:
- @Value对成员变量赋值
- @Bean将一个方法的返回值对象加入到Spring的容器当中管理
- @Qualifier可以使用在方法上,表明对应的形参引入/注入的对象类型
直接删除xml的配置文件,取而代之的是一个Config类
@Transactional注解,取代tx标签
@EnableTransactionManagement注解,开启事务注解
-
@Configuration标识当前类为一个配置类, 当前项目的配置类,好比是applicationContext.xml -
@Import(Xxx.class)在主配置类中包含Xxx的配置类 -
@PropertySource("classpath:db.properties")读取配置文件 -
@Bean("Xxx")相当于
该类是一个配置类,它的作用和bean.xml是一样的
spring中的新注解
Configuration
作用:指定当前类是一个配置类
细节:当配置类作为AnnotationConfigApplicationContext对象创建的参数时,该注解可以不写。
ComponentScan
作用:用于通过注解指定spring在创建容器时要扫描的包
属性:
value:它和basePackages的作用是一样的,都是用于指定创建容器时要扫描的包。
我们使用此注解就等同于在xml中配置了:
Java代码
//@Repository("accountDaoImpl")
@Repository // 默认是 accountDaoImpl,相当于类名首字母小写,相当于Java配置类
//当前项目的配置类,好比是applicationContext.xml
@Configuration //标识当前类为一个配置类
@Import(DataSourceConfig.class) //包含其他的配置类
@ComponentScan("com.sunny") //IoC注解解析器
@EnableTransactionManagement//事务注解解析器
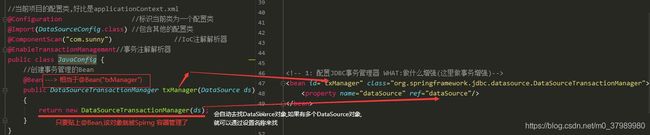
public class JavaConfig {
//创建事务管理的Bean
@Bean
public DataSourceTransactionManager txManager(DataSource ds) {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(ds);
}
}
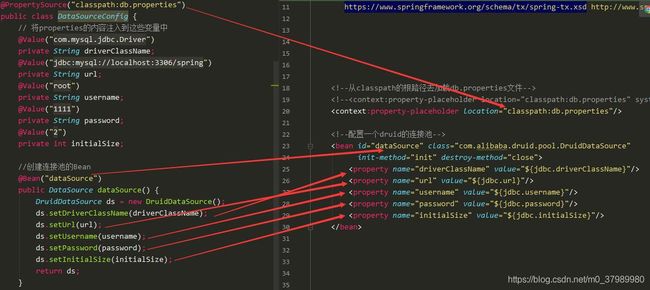
// 当前项目的连接池的配置类
@Configuration
@PropertySource("classpath:db.properties")
public class DataSourceConfig {
// 将properties的内容注入到这些变量中
@Value("${jdbc.driverClassName}")
private String driverClassName;
@Value("${jdbc.url}")
private String url;
@Value("${jdbc.username}")
private String username;
@Value("${jdbc.password}")
private String password;
@Value("${jdbc.initialSize}")
private int initialSize;
//创建连接池的Bean
@Bean("dataSource")
public DataSource dataSource() {
DruidDataSource ds = new DruidDataSource();
ds.setDriverClassName(driverClassName);
ds.setUrl(url);
ds.setUsername(username);
ds.setPassword(password);
ds.setInitialSize(initialSize);
return ds;
}
}
测试类
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes=JavaConfig.class)
public class SpringTxTest {
@Autowired
private AccountService service;
@Test
public void test1(){
service.trans(10086L, 10010L, 1000);
}
}
成功!