mybatis-spring-boot-starter初始化原理及调用过程分析(一)
Springboot启动MapperScan注解处理及mybaits-spring-boot-autoconfigure自动配置容器初始化原理
首先关注MapperScan注解
@SpringBootApplication
@Slf4j
@MapperScan("com.example.mybatis.mybatisdemo.dao")
public class MybatisdemoApplication implements ApplicationRunner {
@Autowired
private DepartmentDOMapper departmentDOMapper;
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MybatisdemoApplication.class, args);
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Documented
@Import(MapperScannerRegistrar.class)
@Repeatable(MapperScans.class)
public @interface MapperScan {这里会导入MapperScannerRegistrar实例
public class MapperScannerRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar, ResourceLoaderAware {
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*
* @deprecated Since 2.0.2, this method not used never.
*/
@Override
@Deprecated
public void setResourceLoader(ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
// NOP
}
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
AnnotationAttributes mapperScanAttrs = AnnotationAttributes
.fromMap(importingClassMetadata.getAnnotationAttributes(MapperScan.class.getName()));
if (mapperScanAttrs != null) {
registerBeanDefinitions(importingClassMetadata, mapperScanAttrs, registry,
generateBaseBeanName(importingClassMetadata, 0));
}
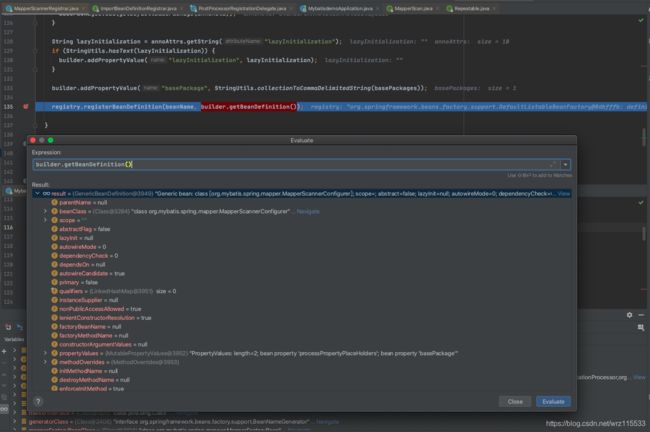
}这里的实现最终注册进来的Bean定义是MapperScannerConfigurer
之后看到MapperScannerConfigurer类,它实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,调用postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法,处理占位符,赋值,调用scan方法。注意这个时候sqlSessionFactory,跟sqlSessionTemplate都还没有值
public class MapperScannerConfigurer
implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor, InitializingBean, ApplicationContextAware, BeanNameAware {
private String basePackage;
private boolean addToConfig = true;
private String lazyInitialization;
private SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
...
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
if (this.processPropertyPlaceHolders) {
processPropertyPlaceHolders();
}
ClassPathMapperScanner scanner = new ClassPathMapperScanner(registry);
scanner.setAddToConfig(this.addToConfig);
scanner.setAnnotationClass(this.annotationClass);
scanner.setMarkerInterface(this.markerInterface);
scanner.setSqlSessionFactory(this.sqlSessionFactory);
scanner.setSqlSessionTemplate(this.sqlSessionTemplate);
scanner.setSqlSessionFactoryBeanName(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName);
scanner.setSqlSessionTemplateBeanName(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName);
scanner.setResourceLoader(this.applicationContext);
scanner.setBeanNameGenerator(this.nameGenerator);
scanner.setMapperFactoryBeanClass(this.mapperFactoryBeanClass);
if (StringUtils.hasText(lazyInitialization)) {
scanner.setLazyInitialization(Boolean.valueOf(lazyInitialization));
}
scanner.registerFilters();
scanner.scan(
StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(this.basePackage, ConfigurableApplicationContext.CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS));
}点进去看Scan方法,这里一步步看scan的逻辑
public int scan(String... basePackages) {
int beanCountAtScanStart = this.registry.getBeanDefinitionCount();
doScan(basePackages);
// Register annotation config processors, if necessary.
if (this.includeAnnotationConfig) {
AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(this.registry);
}
return (this.registry.getBeanDefinitionCount() - beanCountAtScanStart);
}@Override
public Set doScan(String... basePackages) {
Set beanDefinitions = super.doScan(basePackages);
if (beanDefinitions.isEmpty()) {
LOGGER.warn(() -> "No MyBatis mapper was found in '" + Arrays.toString(basePackages)
+ "' package. Please check your configuration.");
} else {
processBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitions);
}
return beanDefinitions;
} 这里super.doScan会执行超类ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner的方法进行一系列处理,最后获得所需Set
@Override
public T getObject() throws Exception {
return getSqlSession().getMapper(this.mapperInterface);
}去拿到对应的Mapper实例即MapperProxy代理对象。注意这个时候还没有sqlSessionFactory跟sqlSessionTemplate所以后面很多步骤这时还不会执行。
private void processBeanDefinitions(Set beanDefinitions) {
GenericBeanDefinition definition;
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : beanDefinitions) {
definition = (GenericBeanDefinition) holder.getBeanDefinition();
String beanClassName = definition.getBeanClassName();
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Creating MapperFactoryBean with name '" + holder.getBeanName() + "' and '" + beanClassName
+ "' mapperInterface");
// the mapper interface is the original class of the bean
// but, the actual class of the bean is MapperFactoryBean
definition.getConstructorArgumentValues().addGenericArgumentValue(beanClassName); // issue #59
definition.setBeanClass(this.mapperFactoryBeanClass);
definition.getPropertyValues().add("addToConfig", this.addToConfig);
boolean explicitFactoryUsed = false;
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName)) {
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionFactory",
new RuntimeBeanReference(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName));
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
} else if (this.sqlSessionFactory != null) {
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionFactory", this.sqlSessionFactory);
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
}
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName)) {
if (explicitFactoryUsed) {
LOGGER.warn(
() -> "Cannot use both: sqlSessionTemplate and sqlSessionFactory together. sqlSessionFactory is ignored.");
}
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionTemplate",
new RuntimeBeanReference(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName));
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
} else if (this.sqlSessionTemplate != null) {
if (explicitFactoryUsed) {
LOGGER.warn(
() -> "Cannot use both: sqlSessionTemplate and sqlSessionFactory together. sqlSessionFactory is ignored.");
}
definition.getPropertyValues().add("sqlSessionTemplate", this.sqlSessionTemplate);
explicitFactoryUsed = true;
}
if (!explicitFactoryUsed) {
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Enabling autowire by type for MapperFactoryBean with name '" + holder.getBeanName() + "'.");
definition.setAutowireMode(AbstractBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE);
}
definition.setLazyInit(lazyInitialization);
}
} 注意上述步骤都还是在533行的断点完成的,这个时候各种的autoconfiguration还没有执行。真正MybatisAutoConfiguration
执行要到551行finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory)处执行
看到MybatisAutoConfiguration在满足了上述限制条件后,会生层SqlSessionFactory跟SqlSessionTemplate的实例
@org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass({ SqlSessionFactory.class, SqlSessionFactoryBean.class })
@ConditionalOnSingleCandidate(DataSource.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(MybatisProperties.class)
@AutoConfigureAfter({ DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class, MybatisLanguageDriverAutoConfiguration.class })
public class MybatisAutoConfiguration implements InitializingBean {
...
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
SqlSessionFactoryBean factory = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
factory.setDataSource(dataSource);
factory.setVfs(SpringBootVFS.class);
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.properties.getConfigLocation())) {
factory.setConfigLocation(this.resourceLoader.getResource(this.properties.getConfigLocation()));
}
applyConfiguration(factory);
if (this.properties.getConfigurationProperties() != null) {
factory.setConfigurationProperties(this.properties.getConfigurationProperties());
}
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.interceptors)) {
factory.setPlugins(this.interceptors);
}
if (this.databaseIdProvider != null) {
factory.setDatabaseIdProvider(this.databaseIdProvider);
}
if (StringUtils.hasLength(this.properties.getTypeAliasesPackage())) {
factory.setTypeAliasesPackage(this.properties.getTypeAliasesPackage());
}
if (this.properties.getTypeAliasesSuperType() != null) {
factory.setTypeAliasesSuperType(this.properties.getTypeAliasesSuperType());
}
if (StringUtils.hasLength(this.properties.getTypeHandlersPackage())) {
factory.setTypeHandlersPackage(this.properties.getTypeHandlersPackage());
}
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.typeHandlers)) {
factory.setTypeHandlers(this.typeHandlers);
}
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.properties.resolveMapperLocations())) {
factory.setMapperLocations(this.properties.resolveMapperLocations());
}
Set factoryPropertyNames = Stream
.of(new BeanWrapperImpl(SqlSessionFactoryBean.class).getPropertyDescriptors()).map(PropertyDescriptor::getName)
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
Class defaultLanguageDriver = this.properties.getDefaultScriptingLanguageDriver();
if (factoryPropertyNames.contains("scriptingLanguageDrivers") && !ObjectUtils.isEmpty(this.languageDrivers)) {
// Need to mybatis-spring 2.0.2+
factory.setScriptingLanguageDrivers(this.languageDrivers);
if (defaultLanguageDriver == null && this.languageDrivers.length == 1) {
defaultLanguageDriver = this.languageDrivers[0].getClass();
}
}
if (factoryPropertyNames.contains("defaultScriptingLanguageDriver")) {
// Need to mybatis-spring 2.0.2+
factory.setDefaultScriptingLanguageDriver(defaultLanguageDriver);
}
return factory.getObject();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
ExecutorType executorType = this.properties.getExecutorType();
if (executorType != null) {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory, executorType);
} else {
return new SqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
}
} 这里重点关注下sqlSessionFactory的最后一步,fatory.getObject()这一步会把配置解析xml,一系列工作都干完,这个搞完你所有xml文件都解析完了。所有方法的mapedStatements,以及mapperRegistry对应的knownMappers(bindMapperForNamespace()加载)都已经加到配置文件里面。
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
notNull(dataSource, "Property 'dataSource' is required");
notNull(sqlSessionFactoryBuilder, "Property 'sqlSessionFactoryBuilder' is required");
state((configuration == null && configLocation == null) || !(configuration != null && configLocation != null),
"Property 'configuration' and 'configLocation' can not specified with together");
this.sqlSessionFactory = buildSqlSessionFactory();
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
...
if (this.mapperLocations != null) {
if (this.mapperLocations.length == 0) {
LOGGER.warn(() -> "Property 'mapperLocations' was specified but matching resources are not found.");
} else {
for (Resource mapperLocation : this.mapperLocations) {
if (mapperLocation == null) {
continue;
}
try {
XMLMapperBuilder xmlMapperBuilder = new XMLMapperBuilder(mapperLocation.getInputStream(),
targetConfiguration, mapperLocation.toString(), targetConfiguration.getSqlFragments());
xmlMapperBuilder.parse();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new NestedIOException("Failed to parse mapping resource: '" + mapperLocation + "'", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Parsed mapper file: '" + mapperLocation + "'");
}
}
} else {
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Property 'mapperLocations' was not specified.");
}
//---------------------------------------------
public void parse() {
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
bindMapperForNamespace();
}
parsePendingResultMaps();
parsePendingCacheRefs();
parsePendingStatements();
}
private void configurationElement(XNode context) {
try {
String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");
if (namespace == null || namespace.isEmpty()) {
throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty");
}
builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);
cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref"));
cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache"));
parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap"));
resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"));
sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"));
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing Mapper XML. The XML location is '" + resource + "'. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
private void bindMapperForNamespace() {
String namespace = builderAssistant.getCurrentNamespace();
if (namespace != null) {
Class boundType = null;
try {
boundType = Resources.classForName(namespace);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// ignore, bound type is not required
}
if (boundType != null && !configuration.hasMapper(boundType)) {
// Spring may not know the real resource name so we set a flag
// to prevent loading again this resource from the mapper interface
// look at MapperAnnotationBuilder#loadXmlResource
configuration.addLoadedResource("namespace:" + namespace);
configuration.addMapper(boundType);
}
}
}
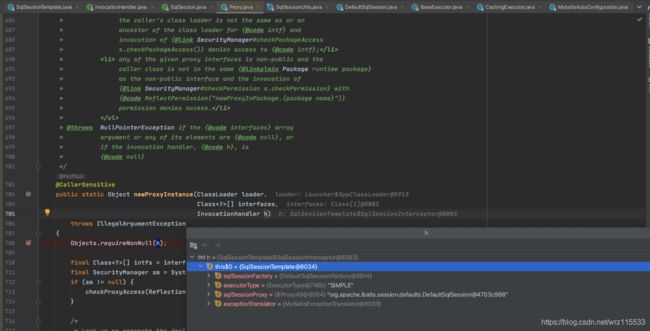
这里会把sqlSession等参数都赋值,这里其实藏了一个默认值,new SqlSessionInterceptor()的时候,因为SqlSessionInterceptor()是SqlSessionTemplate的内部类,其实会生成一个带有外部类四个参数的内部对象,而且这时候sqlSessionProxy会带上默认值,这里sqlSessionProxy就已经有org.apache.ibatis.session.defaults.DefaultSqlSession@79add732这个值了,它再通过Proxy的构造器方式把它再new出来一遍,参数就是SqlSessionInterceptor带入的外部类那个四个参数,包括上面的默认值。
public SqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType,
PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator) {
notNull(sqlSessionFactory, "Property 'sqlSessionFactory' is required");
notNull(executorType, "Property 'executorType' is required");
this.sqlSessionFactory = sqlSessionFactory;
this.executorType = executorType;
this.exceptionTranslator = exceptionTranslator;
this.sqlSessionProxy = (SqlSession) newProxyInstance(SqlSessionFactory.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[] { SqlSession.class }, new SqlSessionInterceptor());
}