Android进阶主要知识总结下版
Android进阶
- 第五章
- Fragment(碎片)的静态
- Fragment(碎片)的动态用法
- Toolbar的使用
- Textinput Layout(增强型文本输入)
- Navigationview(导航抽屉)
- 第六章
- Tablayout实现顶部滑动数果
- Palette(颜色选择器)
- AppBarLayout(程序栏布局)
- FloatingActionButton与SnackBar
- BottomNavigationView(与底部导航)
- 第七章
- 线程
- 异步任务(AsyncTask)
- Service的启动和停止
- 绑定Service
- InterService的使用
第五章
Fragment(碎片)的静态
用法:Fragment是 Activity中用户界面的一个行为或者是一部,主要是为了便于大屏U的设计和实现。可以将 activity拆分成几个完全独立封装的可重用的组件,每个组件有自己的生命周期和ui布局。
展示:使用一个静态碎片
案例 :如图

.xml文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".UserOneFragmentActivity">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView28"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="30dp"
android:text="TextView"/>
<ListView
android:id="@+id/listView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"/>
</LinearLayout>
<!--注意fragment必须给id要不然会出现错误-->
<fragment
android:id="@+id/myFragment"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_weight="3"
android:name="com.hl.android004.MyFragment"
android:layout_height="match_parent"/>
</LinearLayout>
java代码:
//1.给ListView添加数据2.给碎片的的textView添加数据
public class UserOneFragmentActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
//1.声明
ListView listView;
//数据(列表的数据)
String[] data={"人工智能","大数据","云计算","物联网","AR","人工智能","大数据","云计算","物联网","AR"};
//碎片里的数据
String[] content={"人工智能知识","大数据知识","云计算知识","物联网知识","AR知识",
"人工智能知识","大数据知识","云计算知识","物联网知识","AR知识"};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_user_one_fragment);
//2.赋值
listView=findViewById(R.id.listView);
//3.创建一个数组适配器(去放数据)
ArrayAdapter arrayAdapter=new ArrayAdapter(
UserOneFragmentActivity.this,
R.layout.list_item,
data
);
//4.为listView添加数据
listView.setAdapter(arrayAdapter);
//2.给碎片的的textView添加数据
//(1)找到碎片
FragmentManager manager=getSupportFragmentManager();//碎片管理者
MyFragment myFragment=(MyFragment)manager.findFragmentById(R.id.myFragment);
//(2)找碎片的textView
final TextView textView = myFragment.getView().findViewById(R.id.textView29);
//(3)添加
listView.setOnItemClickListener(new AdapterView.OnItemClickListener() {
@Override
public void onItemClick(AdapterView<?> adapterView, View view, int position, long id) {
textView.setText(content[position]);
}
});
}
}list_item自定义布局:
<TextView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:gravity="center">
</TextView>使用到碎片,要新建一个Java类并且这个Java类还要继续Fragment,
下面要重写一个方法:
public View onCreateView
(@NonNull LayoutInflater inflater, @Nullable ViewGroup container,
@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState){
}参数1:你创建的这个视图的布局方式(一般就是你自己定义的碎片布局)
参数2:你创建的这个视图充当的角色,一般都是ViewGroup的名字(container)
参数3:你创建的这个视图是不是最外层的(根元素)【目前都是写false】
在重写的方法里,如果要为.xml里面的控件赋值,写的方式是,如下:
textView =view.findViewById(R.id.textView);Fragment(碎片)的动态用法
.xml文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".DTFragmentActivity"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:id="@+id/main">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:id="@+id/left">
<Button
android:id="@+id/button23"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="添加fragment" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>java代码:
public class DTFragmentActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
Button button;
LinearLayout linearLayout;
FragmentManager manager;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_dtfragment);
//赋值
button=findViewById(R.id.button23);
linearLayout=findViewById(R.id.left);
manager=getSupportFragmentManager();//获取碎片管理器
//给按钮设置点击事件
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
//1.要把放按钮的线性布局的宽度变成1/3
Resources resources=getResources();
linearLayout.setLayoutParams(
new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(
//拿到了原本的宽度/3,虽然高度不变但也得拿高度
resources.getDisplayMetrics().widthPixels/3,
resources.getDisplayMetrics().heightPixels
)
);
//2.添加fragment
//获取碎片事务类
FragmentTransaction transaction=manager.beginTransaction();
//添加(参数一:你要添加到的布局的id 参数二:你要添加的碎片)
transaction.replace(R.id.main,new DtFragment());
//设置手机回退键,移除fragment
transaction.addToBackStack(null);
//提交
transaction.commit();
}
});
}
}只要用到碎片就要新建一个Java类并且继承Fragment,还要重写一个方法
DtFragment java代码:
public class DtFragment extends Fragment {
FragmentManager manager;
@Nullable
@Override
public View onCreateView(@NonNull LayoutInflater inflater, @Nullable ViewGroup container, @Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view=inflater.inflate(R.layout.dt_fragment,container,false);
manager=getFragmentManager();
Button button=view.findViewById(R.id.button24);
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
//移除
FragmentTransaction transaction=manager.beginTransaction();
transaction.remove(DtFragment.this);
//提交
transaction.commit();
}
});
return view;
}
}
Toolbar的使用
Action Bar是 Activity开发的标配,但是从5.0开始逐由 Toolbar取代,主要因为Toolbar使用方式更加简单也更容易定制。
案例 :如图一

图二:

使用Toolbar步骤:
1.在资源文件中找到styles.xml文件
将:<style name="AppTheme" parent="Theme.AppCompat.Light.DarkActionBar">
改成:<style name="AppTheme" parent="Theme.AppCompat.Light.NoActionBar">.xml文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".ToolBarActivity"
android:orientation="vertical">
<androidx.appcompat.widget.Toolbar
android:id="@+id/toolbar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="?attr/colorPrimary"
android:minHeight="?attr/actionBarSize"
android:theme="?attr/actionBarTheme">
<Button
android:id="@+id/button25"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView31"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="TextView" />
</androidx.appcompat.widget.Toolbar>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:gravity="center"
android:background="#F1D686">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView30"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="TextView" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>java代码:
public class ToolBarActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
//1.声明
Toolbar toolbar;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_tool_bar);
//2.赋值
toolbar=findViewById(R.id.toolbar);
//添加logo
toolbar.setLogo(R.mipmap.ic_launcher);
//添加标题
toolbar.setTitle("主标题");
toolbar.setSubtitle("子标题");
//添加左边的图标
toolbar.setNavigationIcon(R.drawable.back);
setSupportActionBar(toolbar);//使系统支持toolbar
//设置回退键的单击事件
toolbar.setNavigationOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
finish();
}
});
//给菜单添加点击事件
toolbar.setOnMenuItemClickListener(new Toolbar.OnMenuItemClickListener() {
@Override
public boolean onMenuItemClick(MenuItem item) {
//item-可以知道你现在点的是哪一个菜单
Toast.makeText(ToolBarActivity.this,item.getTitle(),Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return true;
}
});
}
//加载自定义菜单【需要在res里面建一个menu资源文件】
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.menu1,menu);
return true;
}
}menu:
有几个菜单就有几个item,item必须需要标题
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<menu xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto">
<item
android:id="@+id/item1"
android:icon="@drawable/img03a"
android:title="菜单1"
app:showAsAction="always"/>
<item
android:id="@+id/item2"
android:icon="@drawable/img02"
android:title="菜单2"
app:showAsAction="always"/>
<item
android:id="@+id/item3"
android:icon="@drawable/img01"
android:title="菜单3"
app:showAsAction="never"/>
</menu>Textinput Layout(增强型文本输入)
Textlnputlayout=主作为 Edittexti的容器,使用这个组可以得到很好的输入框体验效果,可以显示正确、错误提示信息
语法:
相比传统单独使用 Edittext的做法,新増的容器 Textinputlayout拥有一些独特属性能够实现如下功能:
1、hint提示:输入框获取焦点时, Edittext通过hint属性设置的字符串内容将浮动显示在输入框左上方,用户进行输入操作时依旧能够看到提示信息
2、error提示:通常用户输入的内容需要经过验证,可以使用 Textinputlayout类提供的 set Errorenabled (boolean)和 setError( Charsequence)方法控制输入框左下方错误信息的显示与隐酸
3、character counter:通过 counterenabled和 countermaxlength属性可以统计
输入内容的字数,并显示在输入框右下角
4、Password visibility toggling:
当输入框内容为密码类信息时,可以通过 password ToggleEnabled属性或
者 setpasswordvisibilitytoggleenabled(boolean)方法在输入框右侧drawableRight的位置显示一个切换按钮,控制输入内容的显示与隐藏
案例:如图
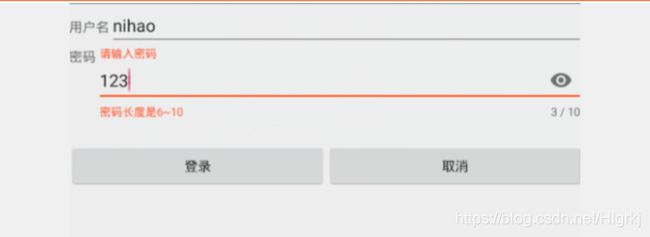
.xml文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".TextInputLayoutActivity"
android:orientation="vertical">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="用户名" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/editText3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:ems="10"
android:hint="请输入账号"
android:inputType="textPersonName" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView4"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="密码" />
<!--用于显示计数:
app:counterEnabled="true" 开启计数
app:counterMaxLength="10" 最大长度
app:passwordToggleEnabled="true" 开启小眼睛
android:inputType="textPassword" 密码保密
-->
<com.google.android.material.textfield.TextInputLayout
android:id="@+id/textInputLayout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
app:counterEnabled="true"
app:counterMaxLength="10"
app:passwordToggleEnabled="true">
<com.google.android.material.textfield.TextInputEditText
android:id="@+id/textInputEditText"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="请输入密码"
android:inputType="textPassword" />
</com.google.android.material.textfield.TextInputLayout>
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<Button
android:id="@+id/button3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="登录" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button4"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="取消" />
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>java代码:
public class TextInputLayoutActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
TextInputLayout textInputLayout;
TextInputEditText textInputEditText;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_text_input_layout);
textInputLayout=findViewById(R.id.textInputLayout);
textInputEditText=findViewById(R.id.textInputEditText);
//文本输入框
check();
}
public void check() {
//给文本框添加一个文本改变事件
textInputEditText.addTextChangedListener(new TextWatcher() {
@Override
public void beforeTextChanged(CharSequence charSequence, int start, int count, int after) {
//文本改变前
}
@Override
public void onTextChanged(CharSequence charSequence, int start, int before, int count) {
//文本改变时
}
@Override
public void afterTextChanged(Editable editable) {
//文本改变后
//获取输入的密码
//获取输入的密码
String pwd=textInputEditText.getText().toString();
if (pwd.length()>10||pwd.length()<6){
//显示错误信息
textInputLayout.setError("密码长度是6~10");
}else {
//取消错误信息
textInputLayout.setError("");
}
}
});
}
}
Navigationview(导航抽屉)
Navigation View在很多App上都已经可以看到其效果图,国内的比如知乎(侧拉菜单滑出来的那一部分属于 Navigation View)
案例:如图
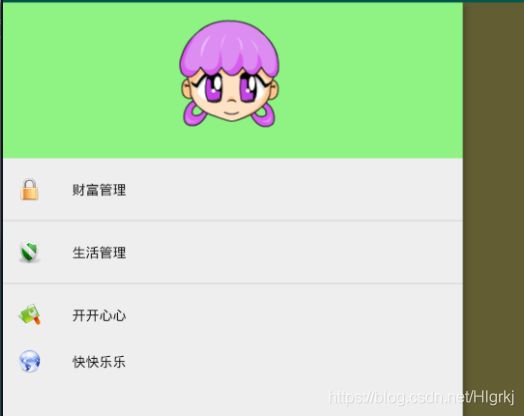
最外层要换成抽屉布局
.xml文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<!--1.抽屉导航【最外层一定是要用抽屉布局】-->
<androidx.drawerlayout.widget.DrawerLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".NavigationViewActivity">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:gravity="center"
android:background="#F5E87E">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView32"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="主界面" />
</LinearLayout>
<!--抽屉导航
android:layout_gravity="抽出来的方向left=start"
app:headerLayout="@layout/head" 调用自定义布局方式
app:menu="@menu/menu2" 调用菜单-->
<com.google.android.material.navigation.NavigationView
android:id="@+id/nav"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_gravity="left"
app:headerLayout="@layout/head"
app:menu="@menu/menu2"/>
</androidx.drawerlayout.widget.DrawerLayout>java代码:
public class NavigationViewActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
//1.声明
NavigationView navigationView;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_navigation_view);
navigationView=findViewById(R.id.nav);
//让导航的菜单图片上色
navigationView.setItemIconTintList(null);
//设置抽屉导航的菜单监听事件
navigationView.setNavigationItemSelectedListener(new NavigationView.OnNavigationItemSelectedListener() {
@Override
public boolean onNavigationItemSelected(@NonNull MenuItem item) {
Toast.makeText(NavigationViewActivity.this,item.getTitle(),Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return true;
}
});
}
}menu2:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<menu xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<!--一个菜单一个item-->
<!--下面要有一根线,加一个group组-->
<group android:id="@+id/g1">
<item
android:id="@+id/item1"
android:title="财富管理"
android:icon="@drawable/img01"
/>
</group>
<group android:id="@+id/g2">
<item
android:id="@+id/item2"
android:title="生活管理"
android:icon="@drawable/img02"
/>
</group>
<item
android:id="@+id/item3"
android:title="开开心心"
android:icon="@drawable/img03a"
/>
<item
android:id="@+id/item4"
android:title="快快乐乐"
android:icon="@drawable/img04"
/>
</menu>第六章
Tablayout实现顶部滑动数果
Tablayout主用作用实现顶部滑动效果。用于在一个 Activity上有多个界面的展示
案例:如图

图二:
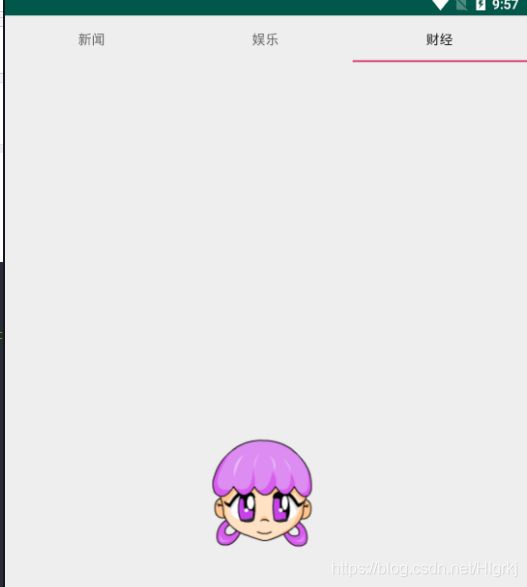
.xml文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".TabLayoutActivity"
android:orientation="vertical">
<com.google.android.material.tabs.TabLayout
android:id="@+id/tabLayout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
</com.google.android.material.tabs.TabLayout>
<androidx.viewpager.widget.ViewPager
android:id="@+id/viewPager"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
</LinearLayout>建好碎片,将每一个内容放在碎片里,碎片用List集合装起来,自己定义一个内部类的适配器来写方法
java代码:
//1.要把碎片加载到viewPager里,并且给tabLayout设置标题,要关联上
public class TabLayoutActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
TabLayout tableLayout;
ViewPager viewPager;
//准备数据
String[] titles={"新闻","娱乐","财经"};
List<Fragment> lists;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_tab_layout);
tableLayout=findViewById(R.id.tabLayout);
viewPager=findViewById(R.id.viewPager);
lists=new ArrayList<>();
lists.add(new MyFragment1());
lists.add(new MyFragment2());
lists.add(new MyFragment3());
//给viewPager添加数据
viewPager.setAdapter(new myAdapter(getSupportFragmentManager(),lists));
//关联
tableLayout.setupWithViewPager(viewPager);
}
//内部类(创建自定义pagerAdapter)
private class myAdapter extends FragmentPagerAdapter{
private List<Fragment> list;
//(快捷键出来alt+enter)
public myAdapter(@NonNull FragmentManager fm, List<Fragment> list) {
super(fm);
this.list=list;
}
@NonNull
@Override
public Fragment getItem(int position) {
//可以获取当前的碎片值
return list.get(position);
}
@Override
public int getCount() {
//拿到总数【你有多少个碎片】
return list.size();
}
@Nullable
@Override
public CharSequence getPageTitle(int position) {
return titles[position];
}
}
}Palette(颜色选择器)
这个Palette(颜色选择器) 是让toolbar的颜色根据图片的颜色变化
案例:如图

图二:

步骤:
1.加载Palette(颜色选择器)的依赖
【file-projectstructure-选中app之后点+LibraryDependency然后搜索palette依赖】
.xml文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<androidx.appcompat.widget.Toolbar
android:id="@+id/toolbar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="?attr/colorPrimary"
android:minHeight="?attr/actionBarSize"
android:theme="?attr/actionBarTheme">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:text="TextView" />
</androidx.appcompat.widget.Toolbar>
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:scaleType="fitXY"
app:srcCompat="@drawable/i1" />
</LinearLayout>java代码:
//1.点击图片实现图片切换,2.切换之后要根据图片的颜色改变toorBar的背景和文字颜色
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
Toolbar toolbar;
ImageView imageView;
TextView textView;
//准备图片【用于做切换的图片资源】
int[] img={R.drawable.i1,R.drawable.im1,R.drawable.img3,R.drawable.img4};
//定义图片的初始下标
int i=0;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
imageView=findViewById(R.id.imageView);
textView=findViewById(R.id.textView);
toolbar=findViewById(R.id.toolbar);
//设置点击事件
imageView.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
i++;
i=i%img.length;
imageView.setImageResource(img[i]);
//把图片转换成二进制图片(Bitmap类型)
Bitmap bitmap= BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(),img[i]);
//获取Palette的builder
Palette.Builder builder=Palette.from(bitmap);
//获取色板
Palette.Swatch swatch=builder.generate().getVibrantSwatch();
if (swatch!=null){
toolbar.setBackgroundColor(swatch.getRgb());
textView.setTextColor(swatch.getTitleTextColor());
}
}
});
}
}AppBarLayout(程序栏布局)
AppBarLayout是一种支持响应滚动手势的布局,用toolbar有收缩和扩展的效果
NestedScrollView(滑动的控件)
案例:如图
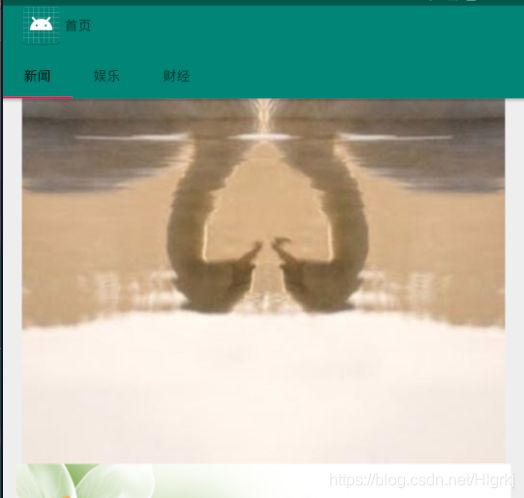
.xml文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.coordinatorlayout.widget.CoordinatorLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<com.google.android.material.appbar.AppBarLayout
android:id="@+id/appbar"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="match_parent">
<androidx.appcompat.widget.Toolbar
android:layout_height="?attr/actionBarSize"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
app:layout_scrollFlags="scroll|enterAlways">
<ImageView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:src="@mipmap/ic_launcher"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="首页"/>
</androidx.appcompat.widget.Toolbar>
<com.google.android.material.tabs.TabLayout
android:id="@+id/tabs"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:layout_scrollFlags="scroll|exitUntilCollapsed"
android:minHeight="40dp"
app:tabMode="scrollable">
</com.google.android.material.tabs.TabLayout>
</com.google.android.material.appbar.AppBarLayout>
<!-- android:clipToPadding="true" 去边距
android:fillViewport="true" 填充满-->
<androidx.core.widget.NestedScrollView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:clipToPadding="true"
android:fillViewport="true"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
app:layout_behavior="com.google.android.material.appbar.AppBarLayout$ScrollingViewBehavior">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".AppBarLayoutActivity">
<androidx.viewpager.widget.ViewPager
android:id="@+id/viewPager"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
</LinearLayout>
</androidx.core.widget.NestedScrollView>
<com.google.android.material.floatingactionbutton.FloatingActionButton
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:src="@android:drawable/ic_input_add"
android:layout_gravity="bottom|end"
android:layout_margin="16dp" />"
</androidx.coordinatorlayout.widget.CoordinatorLayout>java代码:
//1.要把三个碎片添加到viewPager里面 2.tabLayout关联viewPager里的页面
public class AppBarLayoutActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
ViewPager viewPager;
TabLayout tabLayout;
//准备三个碎片的数据
List<Fragment> lists;
//标题的准备
String[] titles={"新闻","娱乐","财经"};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_app_bar_layout);
viewPager=findViewById(R.id.viewPager);
tabLayout=findViewById(R.id.tabs);
lists=new ArrayList<>();
lists.add(new Fragment1());
lists.add(new Fragment2());
lists.add(new Fragment3());
//把集合的数据添加到viewPager里
viewPager.setAdapter(new MyAdapter(getSupportFragmentManager(),lists));
//关联viewPager和taLayout
tabLayout.setupWithViewPager(viewPager);
}
public class MyAdapter extends FragmentPagerAdapter{
private List<Fragment> list;
public MyAdapter(FragmentManager fm,List<Fragment> list) {
super(fm);
this.list=list;
}
@Override
public Fragment getItem(int position) {
return list.get(position);
}
@Override
public int getCount() {
return list.size();
}
@Nullable
@Override
public CharSequence getPageTitle(int position) {
return titles[position];
}
}
}FloatingActionButton与SnackBar
悬浮菜单按钮FloatingActionButton主要用于组件的悬浮显示,方便客户进行操作
SnackBar:
SnackBar用来替代Toast,SnackBar与Toast的主要区别是SnackBar可以滑动滚出,也可以处理用户交互(点击)事件而Toast不能
案例:如图

.xml文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@drawable/img3"
tools:context=".FloatingActionBtnActivity">
<com.google.android.material.floatingactionbutton.FloatingActionButton
android:id="@+id/floatingActionButton"
android:layout_width="231dp"
android:layout_height="337dp"
android:layout_alignParentEnd="true"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:layout_marginEnd="330dp"
android:layout_marginBottom="231dp"
android:clickable="true"
android:onClick="show1"
app:srcCompat="@android:drawable/btn_star_big_on" />
<com.google.android.material.floatingactionbutton.FloatingActionButton
android:id="@+id/floatingActionButton2"
android:layout_width="231dp"
android:layout_height="337dp"
android:layout_alignParentEnd="true"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:layout_marginEnd="22dp"
android:layout_marginBottom="236dp"
android:clickable="true"
android:onClick="show2"
app:srcCompat="@android:drawable/btn_star_big_on" />
</RelativeLayout>java代码:
public class FloatingActionBtnActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_floating_action_btn);
}
public void show1(View view){
Toast.makeText(FloatingActionBtnActivity.this,"这是Toast的提示!",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
public void show2(View view){
Snackbar.make(view,"这是Snackbar的提示!",Snackbar.LENGTH_SHORT)
.setAction("确认", new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
Toast.makeText(FloatingActionBtnActivity.this,"点击了确定按钮!",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
})
.setActionTextColor(getResources().getColor(R.color.colorPrimary))
.show();
}
}BottomNavigationView(与底部导航)
BottomNavigationView实现效果就是常见的app底部导航栏效果
案例:如图
.xml文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".BottomNavigationViewActivity">
<androidx.viewpager.widget.ViewPager
android:id="@+id/viewPager"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_height="0dp" />
<com.google.android.material.bottomnavigation.BottomNavigationView
android:id="@+id/bottomNavigationView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#ccc"
android:minHeight="60dp"
app:menu="@menu/menu_main"/>
</LinearLayout>java代码:
//1.要把四个碎片加载到viewPager 2.关联viewPager和底部导航菜单
public class BottomNavigationViewActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
ViewPager viewPager;
BottomNavigationView bottomNavigationView;
List<Fragment> lists;
//默认值就是null
MenuItem menuItem;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_bottom_navigation_view);
viewPager=findViewById(R.id.viewPager);
bottomNavigationView=findViewById(R.id.bottomNavigationView);
lists=new ArrayList<>();
lists.add(new Fragment2());
lists.add(new Fragment3());
lists.add(new Fragment4());
lists.add(new Fragment5());
//要用设配器给viewPage添加界面
viewPager.setAdapter(new myAdapter(getSupportFragmentManager(),lists));
//关联
//第一部分关联:选择底部导航菜单,要对应改变界面
bottomNavigationView.setOnNavigationItemSelectedListener(new BottomNavigationView.OnNavigationItemSelectedListener() {
@Override
public boolean onNavigationItemSelected(@NonNull MenuItem menuItem) {
//表示当前选中菜单之后要做的事【MenuItem menuItem:表示当前选中的菜单】
switch (menuItem.getItemId()){
case R.id.item1:
//页面设置为第一页
viewPager.setCurrentItem(0);
break;
case R.id.item2:
//页面设置为第二页
viewPager.setCurrentItem(1);
break;
case R.id.item3:
//页面设置为第三页
viewPager.setCurrentItem(2);
break;
case R.id.item4:
//页面设置为第四页
viewPager.setCurrentItem(3);
break;
}
return true;
}
});
//第二部分关联:改变当前的页面后,底部菜单选项也要发生变化
viewPager.addOnPageChangeListener(new ViewPager.OnPageChangeListener() {
@Override
public void onPageScrolled(int position, float positionOffset, int positionOffsetPixels) {
//页面滚动后(上下)
}
@Override
public void onPageSelected(int position) {
//页面被选中后
menuItem=bottomNavigationView.getMenu().getItem(position);
menuItem.setChecked(true);
}
@Override
public void onPageScrollStateChanged(int state) {
//页面状态改变
}
});
}
public class myAdapter extends FragmentPagerAdapter{
private List<Fragment> list;
public myAdapter(FragmentManager fm,List<Fragment> list) {
super(fm);
this.list=list;
}
@Override
public Fragment getItem(int position) {
return list.get(position);
}
@Override
public int getCount() {
return list.size();
}
}
}第七章
线程
在多线程OS中,通常是在一个进程中包括多个线程,每个线程都是作为利用CPU的基本单位,是花费最小开销的实体
比如:说一个人在吃饭的同时可以看电视也可以听歌,这个就要用到多线程
语法:启动
new Thread().start():
执行:
在 Activity中创建 handler对象,调用工作线程执行
案例:如图【时间随系统时间不断改变】
.xml文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".ThreadActivity">
<TableRow
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="2019-09-06 13:50"
android:textSize="20dp"
android:textColor="#000"/>
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<ImageView
android:layout_width="80dp"
android:layout_height="80dp"
android:src="@drawable/img01"/>
<ImageView
android:layout_width="80dp"
android:layout_height="80dp"
android:src="@drawable/img02"/>
<ImageView
android:layout_width="80dp"
android:layout_height="80dp"
android:src="@drawable/img04"/>
</LinearLayout>
</TableRow>
</TableLayout>java代码:
public class ThreadActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
TextView textView;
//标志位,定义当前页面是否启动
boolean flag=false; //表示未启动
//用到一个Handler类【要接收信息里面要重写一个方法】
//新建一个handler,用来接收来自子线程的信息,handler只能接收Message类型的数据,handler能发送也能接收。
//Handler可以接收多个子线程信息,通过代号来判断。
Handler handler=new Handler(){
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
if (msg.what==0x001){
textView.setText(msg.obj+"");
}
}
};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_thread);
textView=findViewById(R.id.textView);
flag=true; //页面启动
//新建一个线程【里面重写方法】一个线程配一个Handler类
new Thread(){
public void run(){
//你想要在这个线程中完成的事情(每隔一秒获取一次系统时间)【线程只拿系统时间,不是改变时间】
while (flag==true){
//创建一个格式化的类
SimpleDateFormat format=new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
//获取系统时间并且格式化
String time=format.format(System.currentTimeMillis());
//拿到的时间是一个常类型【System.currentTimeMillis()】
//发送数据
Message msg=new Message();//定义Message用于发送数据
msg.what=0x001; //代号【判断是否要接受它的信息】
msg.obj=time; //数据
handler.sendMessage(msg);//发送数据到handler
//睡眠一秒
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
super.run();
}
}.start();
}
//重写一个销毁方法
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
flag=false; //页面销毁
}
}异步任务(AsyncTask)
1.概念:
AsyncTask是 Handler+Thread的良好封装,是一种较轻量级的步类。
操作简单,方便.因为是已经封装了的,提供一些良好的接口,所以操作起来更为简单;通过某些操作,可以使 Asynctask停止异步任务,所以使于控制。
语法:
实现方法:private class MyTask extends AsyncTask
三个参数:
第一个执行后台任务需要的参数
第二个参数是任务的当前进度一般都是整型
第三个是参数指返回的结果类型
一个异步任务的执行一般包括以下几个步骤
讲解
- execute( Params. params),触发异步任务的执行。
- onpreexecute(),一般用来在执行后台任务前对Ui做一些标记。
- doInBackground( Params. params),用于执行较为费时的操作,在执行过程中可以调用
publishprogress( Progress. values)来更新进度信息 - onprogressupdate( Progress… values),此方法被执行,直将进度信息更新到Ui组件上
- onpostexecute( Result result),当后台操作结東时,此方法将会被调用。
案例:如图

.xml文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_marginLeft="60dp"
tools:context=".AsyncTaskActivity">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView"
android:layout_marginTop="130dp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="任务还未开启!"/>
<Button
android:layout_marginTop="30dp"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="开启任务"
android:onClick="startTask"/>
</LinearLayout>java代码:
public class AsyncTaskActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
TextView textView;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_async_task);
textView=findViewById(R.id.textView);
}
//开启任务按钮点击事件
public void startTask(View view){
//启动异步类
MyTask myTask=new MyTask(AsyncTaskActivity.this);
myTask.execute(new Integer(0));
}
//创建一个异步任务类
//三个参数:第一个执行后台任务需要的参数,第二个参数是任务的当前进度一般都是整型,第三个是参数指返回的结果类型
//需要下面四个方法,这个类才完整
private class MyTask extends AsyncTask<Integer,Integer,String>{
Context context;//进度对话框显示的位置
ProgressDialog progressDialog;//进度对话框
//构造防止【progressDialog=new ProgressDialog(context)】报空指针异常
public MyTask(Context context){
this.context=context;
}
//Integer当前的进度,...表示数组
@Override
protected String doInBackground(Integer... integers) {
//你要执行的任务
//获取当前的进度值
int i=integers[0];
//判断进度是否小于100,小于100进度每秒加1,等于一百更新完成
while (i<100){
i++;
//更新进度
publishProgress(i);
//睡眠一秒
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//它的返回值类型是根据上面的第三个参数决定
return "更新完成";
}
//执行任务之前的方法
@Override
protected void onPreExecute() {
//创建进度对话框
progressDialog=new ProgressDialog(context);
//设置进度对话框的图标
progressDialog.setIcon(R.mipmap.ic_launcher);
//设置标题
progressDialog.setTitle("提示");
//设置消息内容
progressDialog.setMessage("任务正在进行中,请稍后");
//设置进度条最大值
progressDialog.setMax(100);
//设置当前进度值
progressDialog.setProgress(60);
//设置进度条样式
progressDialog.setProgressStyle(ProgressDialog.STYLE_HORIZONTAL);
//显示
progressDialog.show();
//更改页面文本
textView.setText("任务正在进行中...");
}
//执行任务之后的方法
//String s接收的是return "更新完成"的值
@Override
protected void onPostExecute(String s) {
//进度对话框消失
progressDialog.dismiss();
//文字要改变
textView.setText(s);
}
//状态更新的方法【进度条的变化】
//跟protected String doInBackground(Integer... integers)参数意义差不多
@Override
protected void onProgressUpdate(Integer... values) {
//接收publishProgress(i)这个方法的值
progressDialog.setProgress(values[0]);
}
}
}Service的启动和停止
Android的四大组件:
活动(activity),用于表现功能;
服务(service),后台运行服务,不提供界面呈现;
广播接受者(Broadcast Receive),勇于接收广播;
内容提供者(Content Provider),支持多个应用中存储和读取数据,相当于数据库。
关于四大组件的详情信息链接:https://blog.csdn.net/xchaha/article/details/80398620
现在我们要学的是Service组件,对于Activity之前学的都差不多了
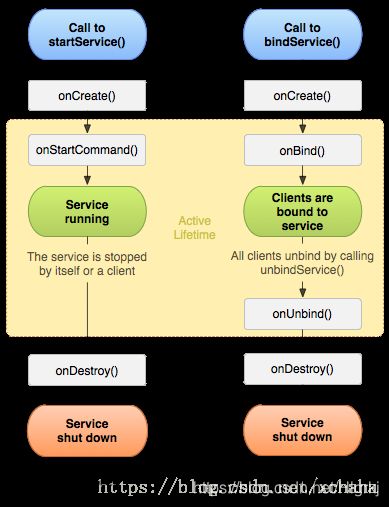
Service运行周期图
关于建service的步骤,service跟Activity一样建一个都会在配置文件中配置一个东西
今天我们学的是先建普通Service
MyService代码:
//跟Activity不同是service用于后台用于一些复杂的操作,后台数据的处理
//比如:游戏软件,弹出一个版本过低,需更新,这个就是service后台里面写了判断
//普通的service
public class MyService extends Service {
public MyService() {
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
// TODO: Return the communication channel to the service.【绑定】
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Not yet implemented");
}
//服务创建的方法
@Override
public void onCreate() {
//相当java里面的输出语句
Log.i("=====","创建");
super.onCreate();
}
//服务开始的方法
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
Log.i("=====","开始");
//接收到activity传过来的数据
String str=intent.getStringExtra("007");
Log.i("接收的数据",str);
return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
}
//服务销毁的方法
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
Log.i("=====","销毁");
super.onDestroy();
}
}.xml文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal"
tools:context=".ServiceActivity">
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="启动服务"
android:onClick="start"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="停止服务"
android:onClick="stop"/>
</LinearLayout>Activity的java代码:
//service不跟用户打交道,跟数据打交道
public class ServiceActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
Intent intent;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_service);
//这里不是用于跳转,用于service
intent=new Intent(ServiceActivity.this,MyService.class);
//传数据
intent.putExtra("007","hello service!");
}
public void start(View view){
//启动服务
startService(intent);
}
public void stop(View view){
//停止服务
stopService(intent);
}
}