Metal系列四:Demo清屏加三角形
首先贴出Apple的官方Demo:地址
https://developer.apple.com/documentation/metal/devices_and_commands
首先由个Metal的准备阶段,在准备阶段中,我们准备以下内容:
1.MTLDevice 获取默认设备
2.MTLCommandQueue 命令队列
1.声明全局变量
{
id<MTLDevice> _device;
id<MTLCommandQueue> _commandQueue;
}
2.初始化
- (nonnull instancetype)initWithMetalKitView:(nonnull MTKView *)mtkView
{
self = [super init];
if(self)
{
_device = mtkView.device;
_commandQueue = [_device newCommandQueue];
}
return self;
}
- 使用MetalKit
/// Called whenever the view needs to render
- (void)drawInMTKView:(nonnull MTKView *)view
{
Color color = [self makeFancyColor];
view.clearColor = MTLClearColorMake(color.red, color.green, color.blue, color.alpha);
//为每个渲染传递创建一个新的命令缓冲区到当前drawable
// Create a new command buffer for each render pass to the current drawable
id<MTLCommandBuffer> commandBuffer = [_commandQueue commandBuffer];
commandBuffer.label = @"MyCommand";
//获取从视图的drawable生成的渲染过程描述符
// Obtain a render pass descriptor, generated from the view's drawable
MTLRenderPassDescriptor *renderPassDescriptor = view.currentRenderPassDescriptor;
// If you've successfully obtained a render pass descriptor, you can render to
// the drawable; otherwise you skip any rendering this frame because you have no
// drawable to draw to
//如果您已成功获得渲染过程描述符,则可以渲染到drawable; 否则你跳过任何渲染这个帧,因为你没有可绘制的绘图
if(renderPassDescriptor != nil)
{
id<MTLRenderCommandEncoder> renderEncoder = [commandBuffer renderCommandEncoderWithDescriptor:renderPassDescriptor];
renderEncoder.label = @"MyRenderEncoder";
//我们通常会使用渲染命令编码器来绘制对象,但是出于本示例的目的,我们所需要的只是当我们创建编码器时Metal隐式执行的GPU清除命令
// We would normally use the render command encoder to draw our objects, but for
// the purposes of this sample, all we need is the GPU clear command that
// Metal implicitly performs when we create the encoder.
//由于我们没有绘制任何内容,请指明我们已完成使用此编码器
// Since we aren't drawing anything, indicate we're finished using this encoder
[renderEncoder endEncoding];
//添加最终命令以将清除的drawable呈现给屏幕
// Add a final command to present the cleared drawable to the screen
[commandBuffer presentDrawable:view.currentDrawable];
}
// Finalize rendering here and submit the command buffer to the GPU
[commandBuffer commit];
}
如果不用MetalKit,那么需要自己管理CAMetalLayer,而且在Apple中的示例代码中,是执行了可多次渲染,初学者可只执行一次。
从图中可以看出RenderCommandEncoder承载着GPU需要的所有信息。
我们所谓的 Command,被用我们可以编码、理解的形式,配置到 Command Encoder 上,然后 Command Encoder 将我们描述的高级指令,编码转换成 GPU 可以理解的低级指令,写入 Command Buffer 中。
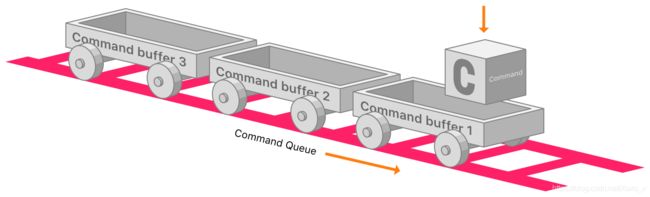
提交给 GPU 的 Command Buffer,就包含了这次渲染所需要的信息。
一个commandBuffer中包含多个commandEncoder
一个队列包含多个commandBuffer
在每个pipline中,回事这样有序的commandEncoder被处理
三角形的绘制需要用到vertexshader、fragmentshader
// Vertex shader outputs and fragment shader inputs
typedef struct
{
// The [[position]] attribute of this member indicates that this value is the clip space
// position of the vertex when this structure is returned from the vertex function
float4 clipSpacePosition [[position]];
// Since this member does not have a special attribute, the rasterizer interpolates
// its value with the values of the other triangle vertices and then passes
// the interpolated value to the fragment shader for each fragment in the triangle
float4 color;
} RasterizerData;
// Vertex function
vertex RasterizerData
vertexShader(uint vertexID [[vertex_id]],
constant AAPLVertex *vertices [[buffer(AAPLVertexInputIndexVertices)]],
constant vector_uint2 *viewportSizePointer [[buffer(AAPLVertexInputIndexViewportSize)]])
{
RasterizerData out;
// Initialize our output clip space position
out.clipSpacePosition = vector_float4(0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
// Index into our array of positions to get the current vertex
// Our positions are specified in pixel dimensions (i.e. a value of 100 is 100 pixels from
// the origin)
float2 pixelSpacePosition = vertices[vertexID].position.xy;
// Dereference viewportSizePointer and cast to float so we can do floating-point division
vector_float2 viewportSize = vector_float2(*viewportSizePointer);
// The output position of every vertex shader is in clip-space (also known as normalized device
// coordinate space, or NDC). A value of (-1.0, -1.0) in clip-space represents the
// lower-left corner of the viewport whereas (1.0, 1.0) represents the upper-right corner of
// the viewport.
// Calculate and write x and y values to our clip-space position. In order to convert from
// positions in pixel space to positions in clip-space, we divide the pixel coordinates by
// half the size of the viewport.
out.clipSpacePosition.xy = pixelSpacePosition / (viewportSize / 2.0);
// Pass our input color straight to our output color. This value will be interpolated
// with the other color values of the vertices that make up the triangle to produce
// the color value for each fragment in our fragment shader
out.color = vertices[vertexID].color;
return out;
}
// Fragment function
fragment float4 fragmentShader(RasterizerData in [[stage_in]])
{
// We return the color we just set which will be written to our color attachment.
return in.color;
}
在Metal Shader Language中有一些关键字比如:
vertex_id
buffer(0)
等,用于描述内容。
同OpenGL ES一样,我们要编译shader、链接shader、这一步在渲染管线中完成。
func setupPipeline() {
let library = device.makeDefaultLibrary()!
let vertexFunction = library.makeFunction(name: "vertexShader")
let fragmentFunction = library.makeFunction(name: "fragmentShader")
let pipelineDescriptor = MTLRenderPipelineDescriptor()
pipelineDescriptor.vertexFunction = vertexFunction
pipelineDescriptor.fragmentFunction = fragmentFunction
pipelineDescriptor.colorAttachments[0].pixelFormat = metalLayer.pixelFormat
pipelineState = try! device.makeRenderPipelineState(descriptor: pipelineDescriptor)
每一个commandEncoder都对应一个轻资源MTLRenderPassDescriptor,(用完即毁)、获取方式
let renderPassDescripor = MTLRenderPassDescriptor()
renderPassDescripor.colorAttachments[0].clearColor = MTLClearColorMake(0.48, 0.74, 0.92, 1)
renderPassDescripor.colorAttachments[0].texture = drawable.texture
renderPassDescripor.colorAttachments[0].loadAction = .clear
renderPassDescripor.colorAttachments[0].storeAction = .store
colorAttachments:颜色组件信息,一个三角形,只需要设置第一个值
获取commandEncoder,commandEncoder也是轻量级的
let commandBuffer = commonQueue.makeCommandBuffer()!
let commandEncoder = commandBuffer.makeRenderCommandEncoder(descriptor: renderPassDescripor)!
完整的render状态大概是这样的:
func render() {
guard let drawable = metalLayer.nextDrawable() else {
return
}
let renderPassDescripor = MTLRenderPassDescriptor()
renderPassDescripor.colorAttachments[0].clearColor = MTLClearColorMake(0.48, 0.74, 0.92, 1)
renderPassDescripor.colorAttachments[0].texture = drawable.texture
renderPassDescripor.colorAttachments[0].loadAction = .clear
renderPassDescripor.colorAttachments[0].storeAction = .store
let commandBuffer = commonQueue.makeCommandBuffer()!
let commandEncoder = commandBuffer.makeRenderCommandEncoder(descriptor: renderPassDescripor)!
commandEncoder.setRenderPipelineState(pipelineState)
let vertices = [YLZVertex(position: [ 0.5, -0.5], color: [1, 0, 0, 1]),
YLZVertex(position: [-0.5, -0.5], color: [0, 1, 0, 1]),
YLZVertex(position: [ 0.0, 0.5], color: [0, 0, 1, 1])]
if #available(iOS 8.3, *) {
commandEncoder.setVertexBytes(vertices, length: MemoryLayout<YLZVertex>.size * 3, index: Int(1))
} else {
// Fallback on earlier versions
}
commandEncoder.drawPrimitives(type: .lineStrip, vertexStart: 2, vertexCount: 2)
commandEncoder.endEncoding()
commandBuffer.present(drawable)
commandBuffer.commit()
}
一位大神的Demo地址:https://github.com/colin1994/Metal-Practice