通用的Bitmap压缩算法,进一步节约内存(推荐)
前几天我写了一篇通过压缩Bitmap,减少OOM的文章,那篇文章的目的是按照imageview的大小来压缩bitmap,让bitmap的大小正好是imageview。但是那种算法的通用性比较差,仅仅能适合fit_xy的情况。对此我进一步分析了下这个问题,并且参考了Volley的源码,最终得出了结论:如果你要让这个压缩后的bitmap完全适合多种imageview拉伸模式,你就必须重写拉伸模式的算法,但这过于小题大做了。讨巧一点的办法就是让这个imageview不完全按照imageview的长宽进行压缩,而仅仅按照imageview的长或宽按比例缩小,得到的是一张和原图比率一样的小图,让imageview加载这个小图就行了。世上没有十全十美的事情,你这个虽然讨巧了,但问题也就来了,在某些模式下可能会有一部分图片没有显示在屏幕上,浪费了一点点内存,在cent模式下,原图的显示效果和小图的显示效果完全不一样。
总结:考虑到多种因素,我还是决定使用比较讨巧的做法,因为它通用性比较高,浪费内存的情况有,但浪费的内存很少(几kb),一般情况下我们不用center模式进行图片的显示,所以我们完全可以考虑这个方式。
工具类:
我参考了volley的代码,重新构建了工具类,下面直接贴出工具类的代码:
package com.kale.bitmaptest; import android.content.res.Resources; import android.graphics.Bitmap; import android.graphics.BitmapFactory; public class BitUtils { private static int mDesiredWidth; private static int mDesiredHeight; /** * @description 从Resources中加载图片 * * @param res * @param resId * @param reqWidth * @param reqHeight * @return */ public static Bitmap decodeSampledBitmapFromResource(Resources res, int resId, int reqWidth, int reqHeight) { BitmapFactory.Options options = new BitmapFactory.Options(); // 设置成了true,不占用内存,只获取bitmap宽高 options.inJustDecodeBounds = true; // 初始化options对象 BitmapFactory.decodeResource(res, resId, options); // 得到计算好的options,目标宽、目标高 options = getBestOptions(options, reqWidth, reqHeight); Bitmap src = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(res, resId, options); // 载入一个稍大的缩略图 return createScaleBitmap(src, mDesiredWidth, mDesiredHeight); // 进一步得到目标大小的缩略图 } /** * @description 从SD卡上加载图片 * * @param pathName * @param reqWidth * @param reqHeight * @return */ public static Bitmap decodeSampledBitmapFromFile(String pathName, int reqWidth, int reqHeight) { BitmapFactory.Options options = new BitmapFactory.Options(); options.inJustDecodeBounds = true; BitmapFactory.decodeFile(pathName, options); options = getBestOptions(options, reqWidth, reqHeight); Bitmap src = BitmapFactory.decodeFile(pathName, options); return createScaleBitmap(src, mDesiredWidth, mDesiredHeight); } /** * @description 计算目标宽度,目标高度,inSampleSize * * @param options * @param reqWidth * @param reqHeight * @return BitmapFactory.Options对象 */ private static BitmapFactory.Options getBestOptions(BitmapFactory.Options options, int reqWidth, int reqHeight) { // 读取图片长宽 int actualWidth = options.outWidth; int actualHeight = options.outHeight; // Then compute the dimensions we would ideally like to decode to. mDesiredWidth = getResizedDimension(reqWidth, reqHeight, actualWidth, actualHeight); mDesiredHeight = getResizedDimension(reqHeight, reqWidth, actualHeight, actualWidth); // 根据现在得到计算inSampleSize options.inSampleSize = calculateBestInSampleSize(actualWidth, actualHeight, mDesiredWidth, mDesiredHeight); // 使用获取到的inSampleSize值再次解析图片 options.inJustDecodeBounds = false; return options; } /** * Scales one side of a rectangle to fit aspect ratio. 最终得到重新测量的尺寸 * * @param maxPrimary * Maximum size of the primary dimension (i.e. width for max * width), or zero to maintain aspect ratio with secondary * dimension * @param maxSecondary * Maximum size of the secondary dimension, or zero to maintain * aspect ratio with primary dimension * @param actualPrimary * Actual size of the primary dimension * @param actualSecondary * Actual size of the secondary dimension */ private static int getResizedDimension(int maxPrimary, int maxSecondary, int actualPrimary, int actualSecondary) { double ratio = (double) actualSecondary / (double) actualPrimary; int resized = maxPrimary; if (resized * ratio > maxSecondary) { resized = (int) (maxSecondary / ratio); } return resized; } /** * Returns the largest power-of-two divisor for use in downscaling a bitmap * that will not result in the scaling past the desired dimensions. * * @param actualWidth * Actual width of the bitmap * @param actualHeight * Actual height of the bitmap * @param desiredWidth * Desired width of the bitmap * @param desiredHeight * Desired height of the bitmap */ // Visible for testing. private static int calculateBestInSampleSize(int actualWidth, int actualHeight, int desiredWidth, int desiredHeight) { double wr = (double) actualWidth / desiredWidth; double hr = (double) actualHeight / desiredHeight; double ratio = Math.min(wr, hr); float inSampleSize = 1.0f; while ((inSampleSize * 2) <= ratio) { inSampleSize *= 2; } return (int) inSampleSize; } /** * @description 通过传入的bitmap,进行压缩,得到符合标准的bitmap * * @param src * @param dstWidth * @param dstHeight * @return */ private static Bitmap createScaleBitmap(Bitmap tempBitmap, int desiredWidth, int desiredHeight) { // If necessary, scale down to the maximal acceptable size. if (tempBitmap != null && (tempBitmap.getWidth() > desiredWidth || tempBitmap.getHeight() > desiredHeight)) { // 如果是放大图片,filter决定是否平滑,如果是缩小图片,filter无影响 Bitmap bitmap = Bitmap.createScaledBitmap(tempBitmap, desiredWidth, desiredHeight, true); tempBitmap.recycle(); // 释放Bitmap的native像素数组 return bitmap; } else { return tempBitmap; // 如果没有缩放,那么不回收 } } }
这个工具类构造的思想和原本的构造思想完全一致,差别之处在于这里的图片是等比缩放的。
测试代码:
public void loadBitmap(boolean exactable) { int bmSize = 0; Bitmap bm = null; if (exactable) { // 通过工具类来产生一个符合ImageView的缩略图 bm = BitUtils.decodeSampledBitmapFromResource(getResources(), R.drawable.saber, iv.getWidth(), iv.getHeight()); } else { // 直接加载原图 bm = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.drawable.saber); } iv.setImageBitmap(bm);
bmSize += bm.getByteCount(); // 得到bitmap的大小 int kb = bmSize / 1024; int mb = kb / 1024; kb = kb % 1024; Log.d("Bitmap", "bitmap w = " + bm.getWidth() + " h = " + bm.getHeight()); Log.d("Bitmap", "bitmap size = " + mb + "MB " + kb + "KB"); Toast.makeText(this, "bitmap size = " + mb + "MB " + kb + "KB", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show(); }
通过加载原图和加载缩略图进行比较,最终在log打印出图片的宽高和图片内存占用。
测试结果:
布局文件:

<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:padding="16dp" tools:context="${relativePackage}.${activityClass}" > <ImageView android:id="@+id/imageView" android:layout_width="100dp" android:layout_height="100dp" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" android:layout_centerVertical="true" android:src="@drawable/ic_launcher" /> <Button android:id="@+id/original_button" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignParentBottom="true" android:onClick="butonListener" android:text="加载原图" /> <Button android:id="@+id/clip_button" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignBaseline="@+id/original_button" android:layout_alignBottom="@+id/original_button" android:layout_alignParentRight="true" android:onClick="butonListener" android:text="加载缩略图" /> </RelativeLayout>
前题:我的手机定义的imageview是100dp,实际是200pix。加载图片的实际大小:850 x 1200
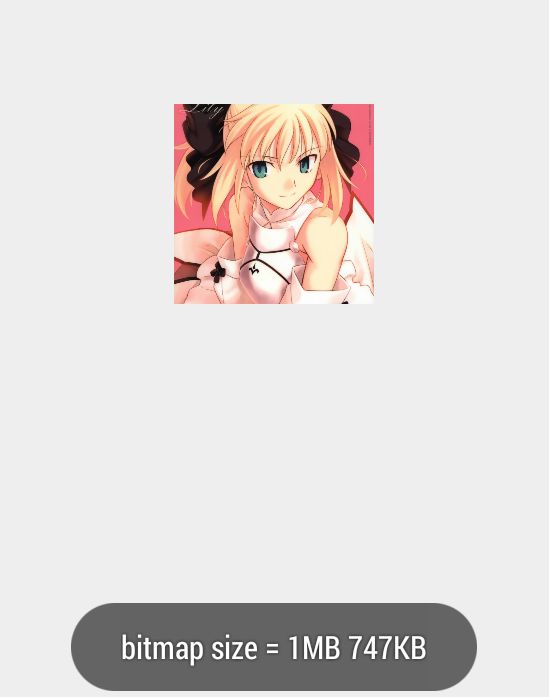
① 加载原图
bitmap宽 = 567,高 = 800;
内存占用:1M 747KB
解释:最终得到的图片大小和原始图片不同,这里应该是BitmapFactory在解码时就已经做了压缩,算是自带的一个智能压缩方案吧。
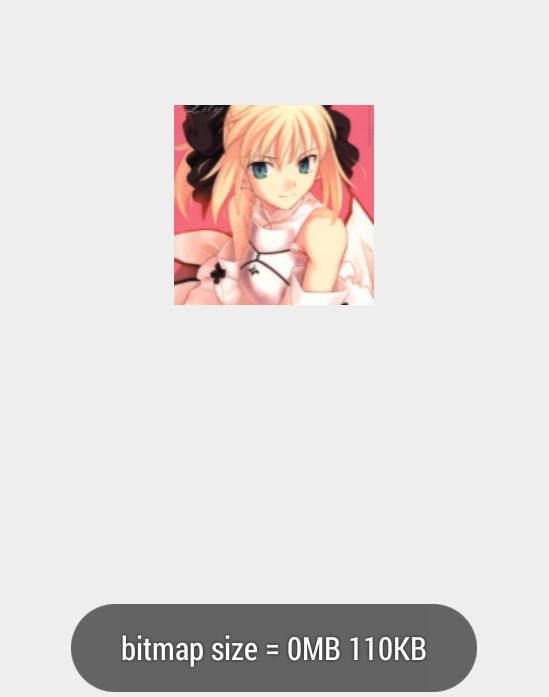
② 用工具类加载缩略图
bitmap宽 = 141,高 = 200;
内存占用:110KB
解释:目标的imageview宽、高均为100dp,在我手机上换算为200pix,这里做了等比缩放处理,所以高为200.最后我们也明显的看出,用这种方式得到的图片比较小,不会轻易出现OOM
完整的activity代码:

package com.kale.bitmaptest; import android.app.Activity; import android.app.ActivityManager; import android.content.Context; import android.graphics.Bitmap; import android.graphics.BitmapFactory; import android.os.Bundle; import android.util.Log; import android.view.View; import android.widget.ImageView; import android.widget.ImageView.ScaleType; import android.widget.Toast; public class MainActivity extends Activity { ImageView iv; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); iv = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.imageView); iv.setScaleType(ScaleType.CENTER_CROP); // center 变了 getMemoryCacheSize(); } public void butonListener(View v) { switch (v.getId()) { case R.id.original_button: loadBitmap(false); // 加载原图 break; case R.id.clip_button: loadBitmap(true); // 加载缩略图 break; } } public void loadBitmap(boolean exactable) { int bmSize = 0; Bitmap bm = null; if (exactable) { // 通过工具类来产生一个符合ImageView的缩略图 bm = BitUtils.decodeSampledBitmapFromResource(getResources(), R.drawable.saber, iv.getWidth(), iv.getHeight()); } else { // 直接加载原图 bm = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.drawable.saber); } iv.setImageBitmap(bm); bmSize += bm.getByteCount(); // 得到bitmap的大小 int kb = bmSize / 1024; int mb = kb / 1024; kb = kb % 1024; Log.d("Bitmap", "bitmap w = " + bm.getWidth() + " h = " + bm.getHeight()); Log.d("Bitmap", "bitmap size = " + mb + "MB " + kb + "KB"); Toast.makeText(this, "bitmap size = " + mb + "MB " + kb + "KB", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show(); } public int getMemoryCacheSize() { // Get memory class of this device, exceeding this amount will throw an // OutOfMemory exception. final int memClass = ((ActivityManager) getSystemService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE)).getMemoryClass(); System.out.println("memory = " + memClass + "M"); return memClass; } public int dip2px(float dpValue) { final float scale = getResources().getDisplayMetrics().density; return (int) (dpValue * scale + 0.5f); } }
利弊:
利:
节约内存,降低出现OOM的几率
弊:
降低了图片的清晰度,不适用于center模式的imageview。
左边的是加载的缩略图,右边的是加载的原图。右边的图片明显比坐标的清晰,但锐化过于严重了,左边的虽然小,但是较为模糊。
如果你用了android studio,你可以很明显的看出内存的变化:
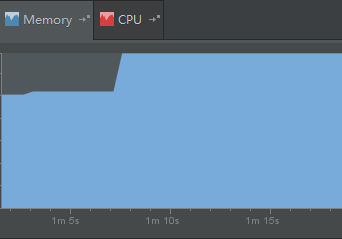
Android Studio下的测试代码:
package com.example.jack.loadbitmap; import com.kale.lib.activity.KaleBaseActivity; import com.kale.lib.utils.BitmapUtil; import com.kale.lib.utils.EasyToast; import android.graphics.Bitmap; import android.graphics.BitmapFactory; import android.util.Log; import android.view.View; import android.widget.Button; import android.widget.ImageView; public class MainActivity extends KaleBaseActivity { ImageView mImageView; Button loadOriginPicBtn; Button loadThumbPicBtn; @Override protected int getContentViewId() { return R.layout.activity_main; } @Override protected void findViews() { mImageView = getView(R.id.imageView); loadOriginPicBtn = getView(R.id.loadOriginal_button); loadThumbPicBtn = getView(R.id.loadThumb_button); } @Override protected void setViews() { // 加载原始的图片 loadOriginPicBtn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.drawable.saber); setBitmapToImageView(bitmap); } }); // 加载压缩后的图片 loadThumbPicBtn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { Bitmap bitmap = BitmapUtil.decodeSampledBitmapFromResource(getResources(), R.drawable.saber, mImageView.getWidth(), mImageView.getHeight()); setBitmapToImageView(bitmap); } }); } private void setBitmapToImageView(Bitmap bitmap) { mImageView.setImageBitmap(bitmap); int bmSize = BitmapUtil.getBitmapSize(bitmap); int mb = bmSize / 1024 / 1024; int kb = bmSize /1014 % 1024; String bitmapSizeStr = mb + "MB " + kb + "KB"; Log.d("Bitmap", "bitmap w = " + bitmap.getWidth() + " h = " + bitmap.getHeight()); Log.d("Bitmap", bitmapSizeStr); EasyToast.makeText(mContext, "bitmap size = " + bitmapSizeStr); } }
源码下载:
http://download.csdn.net/detail/shark0017/8412329
利用AS构建的工程(推荐):http://download.csdn.net/detail/shark0017/8671957
参考自:
http://www.open-open.com/lib/view/open1329994992015.html
