javascript BOM
一.什么是BOM:
BOM(Browser Object Model)的意思是浏览器对象模型。BOM方法一般指的都是在浏览器(window)中的方法。
二.常见的BOM方法/事件:
1.open('网址','打开方式'):打开一个新的窗口,例如:
<body>
<button id="btn">弹出新窗口button>
<script>
document.getElementById('btn').onclick = function(){
window.open('https://www.baidu.com/',",'height=500,width=611,scrollbars=yes,status =yes'");
}
script>注:
A.在使用该方法时要注意查看浏览器是否拦截了当前页面打开的新窗口

B.网址为空时打开的是空白页面
C.打开方式默认为新窗口方式_blank,此外还有_self
D.此方法的返回值是新窗口的window对象
2.close()方法:关闭窗口
注:该方法具有浏览器兼容性问题,火狐是禁止代码关闭浏览器的,chrome是直接关闭,ie下是询问关闭),因此很少会使用,但是可以关闭由于代码打开的新窗口
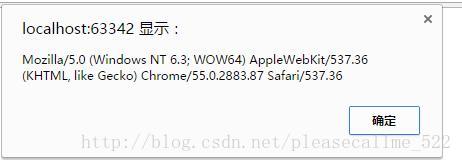
3..navigator.userAgent:查看浏览器信息(内核,版本等)
<body>
<button id="btn">弹出新窗口button>
<script>
document.getElementById('btn').onclick = function(){
alert(window.navigator.userAgent);
}
script>
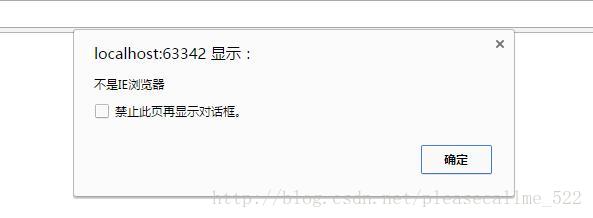
body>补充:window.navigator.userAgent.indexOf('MSIE'):判断当前浏览器是否为IE浏览器,返回-1时不是IE浏览器
<body>
<button id="btn">弹出新窗口button>
<script>
document.getElementById('btn').onclick = function(){
if(window.navigator.userAgent.indexOf('MSIE') == -1){
alert('不是IE浏览器');
}else{
alert('是IE浏览器');
}
}
script>
body>4..location:返回当前网址的url
<body>
<button id="btn">弹出新窗口button>
<script>
document.getElementById('btn').onclick = function(){
alert(window.location)
}
script>
body>补充:window.location.href='网址'直接跳转到另一个页面
<body>
<button id="btn">弹出新窗口button>
<script>
document.getElementById('btn').onclick = function(){
window.location.href = 'https://www.baidu.com';
}
script>
body>window.location.href = '网址'是在原页面上直接打开新页面,即新页面打开后替换原页面;而window.open('网址')是在保存原页面的前提下打开一个新窗口,即新页面打开后原页面还在
5..location.search:返回url ?后面的内容
6..location.hash: 返回url#后面的内容
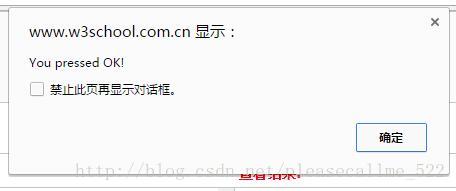
7.confirm()方法:用于显示一个带有指定消息和 OK 及取消按钮的对话框。括号里可以带参数,参数将显示在对话框上。当点击“确定”时函数返回值为true,点击“取消”时函数返回值为false,例如:
<html>
<head>
<script type="text/javascript">
function show_confirm()
{
var r=confirm("Press a button!");
if (r==true)
{
alert("You pressed OK!");
}
else
{
alert("You pressed Cancel!");
}
}
script>
head>
<body>
<input type="button" onclick="show_confirm()" value="Show a confirm box" />
body>
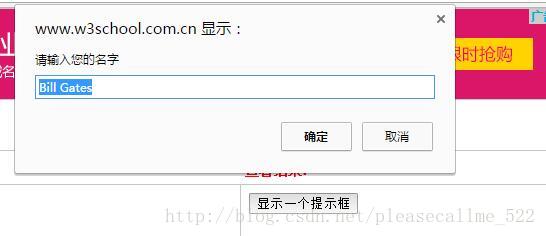
html>8.prompt()方法:用于显示可提示用户进行输入的对话框,例如:
<html>
<head>
<script type="text/javascript">
function disp_prompt()
{
var name=prompt("请输入您的名字","Bill Gates")
if (name!=null && name!="")
{
document.write("你好," + name + "!今天过得好吗?")
}
}
script>
head>
<body>
<input type="button" onclick="disp_prompt()" value="显示一个提示框" />
body>
html>
9..onload:页面加载完成时发生的事件
10..onscroll:页面滚动条滚动时发生的事件
11..onresize:页面尺寸发生变化时发生的事件
注:onscroll/.onresize不是按照1像素来触发事件,而是单位时间触发
三.浏览器里的尺寸
1.可视区(浏览器窗口)尺寸:
document.documentElement.clientWidth
document.documentElement.clientHeight
//注意:document没有尺寸,要从文档元素documentElement上取2.滚动距离(可视区到页面顶部/左部距离):
//chrome下有效
document.body.scrollTop/scrollLeft
//其他浏览器下有效
document.documentElement.scrollTop/scrollLeft因此为了解决兼容性问题,通常写成如下形式:
var scrollTop = document.body.scrollTop/scrollLeft || document.documentElement.scrollTop/scrollLeft3.内容高度(盒子内部包括溢出部分的宽度/高度):
document.body.scrollWidth/Height4.文档高度
document.documentElement.offsetHeight //不推荐(在ie7及以下浏览器中可能会变成距可视区的高度)
document.body.offsetHeight //推荐
document.documentElement.offsetHeight在ie7及以下会表现为可视区的高度,因此用第二个正确