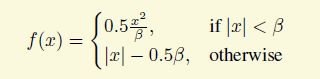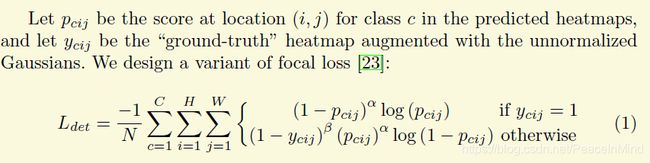物体检测论文杂读-非常少
对物体检测的工作不是特别熟悉,特别是不同工作对应的性能还没有记住。
Feature Selective Anchor-Free Module for Single-Shot Object Detection
Mask Scoring R-CNN
Generalized Intersection over Union: A Metric and A Loss for Bounding Box Regression
[2019-ICLR] Feature Intertwiner for Object Detection[paper][code]
In this paper, we address this problem via a new perspective. For each category, it is assumed that there are two sets in the feature space: one with more reliable information and the other with a less reliable source. We argue that the reliable set could guide the feature learning of the less reliable set during training - in the spirit of student mimicking teacher’s behavior and thus pushing towards a more compact class centroid in the high-dimensional space
[2019-AAAI] Gradient Harmonized Single-stage Detector [paper]
出发点非常清晰的工作,核心的疑惑是训练的过程中gradient norm的分布是否符合作者给出的相应分布。one stage 存在正负样本的极度不平衡。难易样本也是个问题。作者首先分析了一个已经收敛的one-stage detector样本的gradient norm的分布,发现easy sample(下图左边)和very hard sample(下图右边)的密度非常高,所以用这个信息来调整sample的权重。跟focal loss比较不用调gamma,但是提高的也不是特别明显,COCO上用RetinaNet-FPN-ResNeXt-101可以做到41.6
[201901-arxiv-未理解]RetinaMask: Learning to predict masks improves state-of-the-art single-shot detection for free [paper]
测试的时候是free的,但是训练的时候改了一些模块,并且加了mask的模块,因此训练代价肯定更高。作者主要优化了三个模块,有些还不是很理解。
1 including additional hard examples in training
有些比较畸形的框(长宽比很大的框)在之前的工作由于满足不了IOU的要求,所有有可能作为负样本或者不考虑。作者对这些框降低了IOU的要求,可以说是算是一个trick吧
2 making the loss function adaptive and more stable
框回归一般都用Smooth L1 loss,好控制一些outlier的loss不会太大, 另外考虑到连续性和可导性,公式一般是这样的,beta一般取1
作者提出了一种方案可以自动调整beta,如下图。均值减标准差什么的还是可以理解,但是不太理解均值减方差的物理意义
3 integrating instance mask prediction for the first time
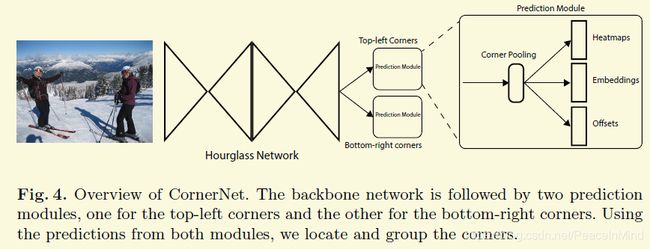
[2018-ECCV]CornerNet: Detecting Objects as Paired Keypoints[paper]
出发点:
大部分的one-stage detector 都需要anchor boxes,但是anchor boxes有两个缺点
1 anchor boxes的数量太多,比如在DSSD里面有40k,在retinaNet里面有100k。但是这么多里面只有少数的是正样本,很容易造成样本不均衡
2 anchor boxes引入了非常多的超参数和不同的设计,These include how many boxes, what sizes, and what aspect ratios.
方法:
这篇文章采用的是一种paired的关键点左上角点和右上角点形式来检测框。
1 embedding
当然可能由于有多个同样的物体,因此可能检测出多个点,那么需要一个embedding来让同一个物体的左上角点和右上角点的embedding距离最小。
2 正负样本设计
gt的一个点作为正样本,正样本附近的一些点也是负样本,不过这些点loss的权重要低些(高斯分布)
另外很显然这是一个样本不均衡问题,作者采用了focal loss,这个有点忘了,因为好像有报告指出focal loss的通用性不是很强
3 corner pooling
其实思想很简单,有些类似于做文字时候的global row pooling和global col pooling.
因为corner的点大部分都不在物体上。比如左上角,它得往右看和往下看能能决定位置,所以呢corner pooling就是一种很简单的截断pooling
4 offset真值怎么设计
看文章的图4,论文还会预测一个offset,但是关键是offset的gt或者在损失函数的体现好像完全没有提。