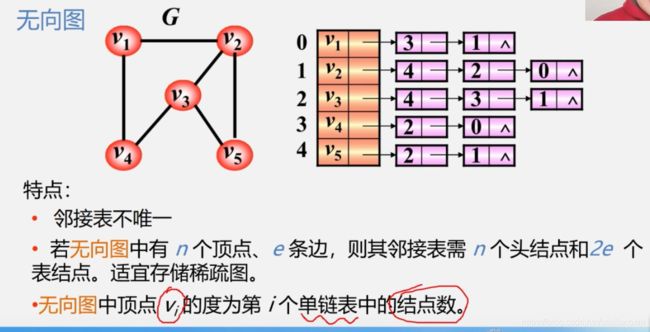
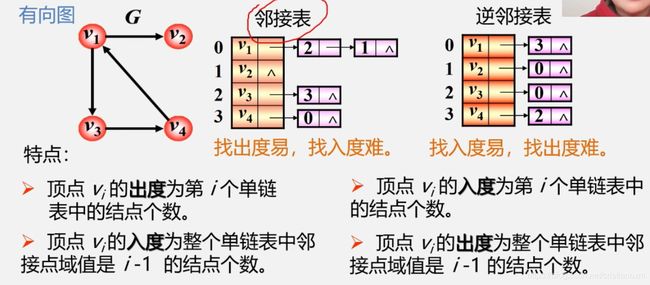
图的两种存储形式(邻接矩阵、邻接表)
图可以使用两种存储结构,分别是邻接矩阵和邻接表。
注意:一个图所对应的邻接矩阵唯一,所对应的邻接表不唯一
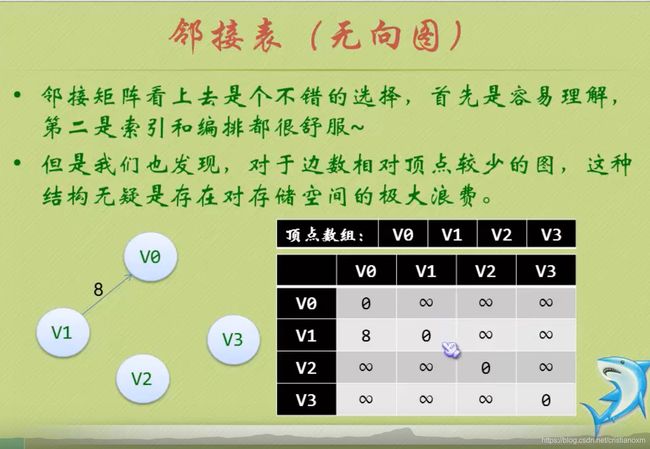
一、邻接矩阵
邻接矩阵以矩阵的形式存储图所有顶点间的关系。邻接矩阵具有以下特点:
- 1.邻接矩阵是正矩阵,即横纵维数相等。
- 2.矩阵的每一行或一列代表一个顶点,
行与列的交点对应这两个顶点的边。 - 3.矩阵的点代表边的属性,
1代表有边,0代表无边,所以矩阵的对角线都是0,因为对角线上对应的横纵轴代表相同的顶点,边没有意义。 - 4.如果是无向图,那么矩阵是对称矩阵;
如果是有向图则不一定是对称矩阵。

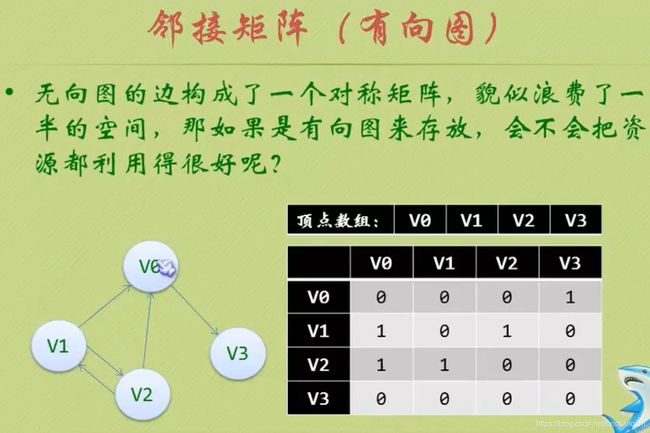
- 5.如果是有权图,
矩阵点数值可以是权值。 - 6.邻接矩阵表示图的
关系非常清晰,但消耗空间较大。
- 7.代码实现(Java)
邻接矩阵无向图:
public class MatrixNDG {
int size;//图顶点个数
char[] vertexs;//图顶点名称
int[][] matrix;//图关系矩阵
public MatrixNDG(char[] vertexs,char[][] edges){
size=vertexs.length;
matrix=new int[size][size];//设定图关系矩阵大小
this.vertexs=vertexs;
for(char[] c:edges){//设置矩阵值
int p1 = getPosition(c[0]);//根据顶点名称确定对应矩阵下标
int p2 = getPosition(c[1]);
matrix[p1][p2] = 1;//无向图,在两个对称位置存储
matrix[p2][p1] = 1;
}
}
//图的遍历输出
public void print(){
for(int[] i:matrix){
for(int j:i){
System.out.print(j+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
//根据顶点名称获取对应的矩阵下标
private int getPosition(char ch) {
for(int i=0; i<vertexs.length; i++)
if(vertexs[i]==ch)
return i;
return -1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] vexs = {'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G','H','I','J','K'};
char[][] edges = new char[][]{
{'A', 'C'},
{'A', 'D'},
{'A', 'F'},
{'B', 'C'},
{'C', 'D'},
{'E', 'G'},
{'D', 'G'},
{'I','J'},
{'J','G'},};
MatrixNDG pG;
// 自定义"图"(输入矩阵队列)
// 采用已有的"图"
for(int i=0;i<10000;i++){
pG = new MatrixNDG(vexs, edges);
//pG.print(); // 打印图
}
}
邻接矩阵有向图:
public class MatrixDG {
int size;
char[] vertexs;
int[][] matrix;
public MatrixDG(char[] vertexs,char[][] edges){
size=vertexs.length;
matrix=new int[size][size];
this.vertexs=vertexs;
//和邻接矩阵无向图差别仅仅在这里
for(char[] c:edges){
int p1 = getPosition(c[0]);
int p2 = getPosition(c[1]);
matrix[p1][p2] = 1;
}
}
public void print(){
for(int[] i:matrix){
for(int j:i){
System.out.print(j+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
private int getPosition(char ch) {
for(int i=0; i<vertexs.length; i++)
if(vertexs[i]==ch)
return i;
return -1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
char[] vexs = {'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G','H','I','J','K'};
char[][] edges = new char[][]{
{'A', 'C'},
{'A', 'D'},
{'A', 'F'},
{'B', 'C'},
{'C', 'D'},
{'E', 'G'},
{'D', 'G'},
{'I','J'},
{'J','G'},};
MatrixDG pG;
// 自定义"图"(输入矩阵队列)
//pG = new MatrixUDG();
// 采用已有的"图"
pG = new MatrixDG(vexs, edges);
pG.print();
}
}
二、邻接表
- 1.邻接表示一个有但链表组成的数组
- 2.图中的每一个顶点都有一个链,数组的大小等于图中顶点的个数。
- 3.无向图的链的第一个元素是本顶点,后继分别连接着和这个顶点相连的顶点;
有向图的链第一个顶点是本顶点,后继是以本顶点为起点的边的终点。 - 4.邻接表虽然在空间上有很大的优势,但是
对于一个有向图,如果需要查找每个顶点的入度就需要遍历整个邻接表,在效率上很低下的。因此才有了逆邻接表的诞生。
注意:
邻接表:反映的是顶点出度的情况。
逆邻接表:反映的是顶点的入度情况。
- 5.如果是有权图,可以在节点元素中设置权值属性
- 6.邻接链表
关系表示不如邻接矩阵清晰,数据结构相对复杂,但节省空间。 - 7.代码实现(java)
邻接表无向图:
public class ListNDG {
Vertex[] vertexLists;//邻接表数组
int size;
class Vertex{//邻接表节点类,单链表数据结构
char ch;
Vertex next;
Vertex(char ch){//初始化方法
this.ch=ch;
}
void add(char ch){//加到链表尾
Vertex node=this;
while(node.next!=null){
node=node.next;
}
node.next=new Vertex(ch);
}
}
public ListNDG(char[] vertexs,char[][] edges){
size=vertexs.length;
this.vertexLists=new Vertex[size];//确定邻接表大小
//设置邻接表头节点
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
this.vertexLists[i]=new Vertex(vertexs[i]);
}
//存储边信息
for(char[] c:edges){
int p1=getPosition(c[0]);
vertexLists[p1].add(c[1]);
int p2=getPosition(c[1]);
vertexLists[p2].add(c[0]);
}
}
//跟据顶点名称获取链表下标
private int getPosition(char ch) {
for(int i=0; i<size; i++)
if(vertexLists[i].ch==ch)
return i;
return -1;
}
//遍历输出邻接表
public void print(){
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
Vertex temp=vertexLists[i];
while(temp!=null){
System.out.print(temp.ch+" ");
temp=temp.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
char[] vexs = {'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G','H','I','J','K'};
char[][] edges = new char[][]{
{'A', 'C'},
{'A', 'D'},
{'A', 'F'},
{'B', 'C'},
{'C', 'D'},
{'E', 'G'},
{'D', 'G'},
{'I','J'},
{'J','G'},};
ListNDG pG;
for(int i=0;i<10000;i++){
pG = new ListNDG(vexs, edges);
//pG.print(); // 打印图
}
}
}
邻接表有向图:
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class ListDG2 {
LinkedList<Character>[] vertexLists;
int size;
public ListDG2(char[] vertexs,char[][] edges){
size=vertexs.length;
this.vertexLists=new LinkedList[size];
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
this.vertexLists[i]=new LinkedList<Character>();
vertexLists[i].add(vertexs[i]);
}
for(char[] c:edges){
int p=getPosition(c[0]);
this.vertexLists[p].add(c[1]);
}
}
private int getPosition(char ch) {
for(int i=0; i<size; i++)
if(vertexLists[i].get(0)==ch)
return i;
return -1;
}
public void print(){
for(int i=0;i<size;i++){
LinkedList<Character> temp=vertexLists[i];
for(int j=0;j<temp.size();j++){
System.out.print(temp.get(j)+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
char[] vexs = {'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G','H','I','J','K'};
char[][] edges = new char[][]{
{'A', 'C'},
{'A', 'D'},
{'A', 'F'},
{'B', 'C'},
{'C', 'D'},
{'E', 'G'},
{'D', 'G'},
{'I','J'},
{'J','G'},};
ListDG2 pG;
for(int i=0;i<10000;i++){
pG = new ListDG2(vexs, edges);
//pG.print(); // 打印图
}
}
}
本文参考