MyBatis_MyBatis之逆向工程
1.引入
我们在编写数据库的持久化操作的时候,我们先知道数据库的数据表内容,然后我们会根据数据库表的字段信息去编写对应的javaBean内容,然后根据这一些内容写出查询所需的sql,然后我们会在根据javaBean内容去编写映射文件内容。那么这一个过程在使用java和MyBatis的时候基本上每一个数据库表都需要进行的操作。那么如果有一个技术能够做到把这一个过程直接实现出来。那么就可以把我们需要做的功能内容就会节省下来很多。那么下面我们一起来看一下MyBatis提供的逆向过程操作。
2.MyBatis逆向工程介绍
MyBatis Generator,简称MBG,是一个专门为MyBatis框架使用者定 制的代码生成器,可以快速的根据表生成对应的 映射文件,接口,以及bean类。支持基本的增删 改查,以及QBC风格的条件查询。但是表连接、 存储过程等这些复杂sql的定义需要我们手工编写。
相关的官方文档地址信息:
http://www.mybatis.org/generator/
官方工程地址:
https://github.com/mybatis/generator/releases
3.如何实现一个逆向工程
(1).导入逆向工程所需要使用的jar包:mybatis-generator-core-1.3.2.jar
(2).在项目的根路径下面编写mgb配置文件mbg.xml
(3).执行逆向生成代码(可以使用多个方法实现,这里使用执行代码的方式)
public class MyBatisTest {
@Test
public void testMbg() throws Exception {
List warnings = new ArrayList();
boolean overwrite = true;
File configFile = new File("mbg.xml");
ConfigurationParser cp = new ConfigurationParser(warnings);
Configuration config = cp.parseConfiguration(configFile);
DefaultShellCallback callback = new DefaultShellCallback(overwrite);
MyBatisGenerator myBatisGenerator = new MyBatisGenerator(config,
callback, warnings);
myBatisGenerator.generate(null);
}
} (4).执行情况
4.生成内容说明
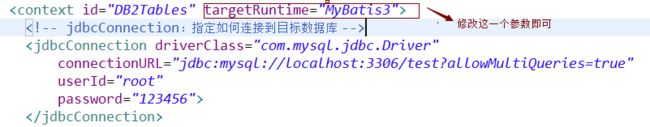
(1).我们在逆向工程中所指定的是targetRuntime="MyBatis3Simple"这是简易版本的。如果需要生成有较为复杂的需要指定targetRuntime="MyBatis3"。
(2).在生成的实体对象中,仅仅只生成成员变量对应的getXxx()和setXxx()方法。一般需要添加对象对应的toString()方法。
(3).实体对象对应的映射文件需要在mybatis-config.xml中注册,不然无法使用。
5.生成内容测试
(1).简易版本提供的基本的操作方法
public interface AdminMapper {
int deleteByPrimaryKey(Integer id);
int insert(Admin record);
Admin selectByPrimaryKey(Integer id);
List selectAll();
int updateByPrimaryKey(Admin record);
}
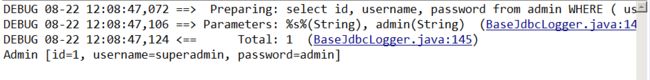
//简易版本提供了基础的增删查改的操作。 (2).简单测试:List
@Test
public void testMbgMethod() throws Exception{
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = getSqlSessionFactory();
SqlSession openSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try {
AdminMapper mapper = openSession.getMapper(AdminMapper.class);
List lt = mapper.selectAll();
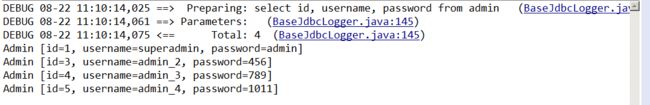
for(Admin ad:lt){
System.out.println(ad);
}
} finally {
openSession.close();
}
} 测试结果
6.生成复杂逆向工程内容
(1).修改设生成的配置文件内容:mbg.xml
(2).其他参数不变,如上述3中一样。
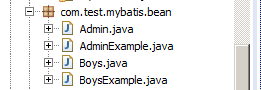
(3).生成内容查看:
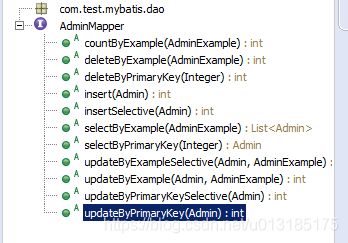
我们发现实体对象中每一个实体对象都多出来了一个对应的ObjExample实体,并且每一个实体对象的操作方法都变多了。这里面生成的ObjExample实体其实就是用于该对象较为复杂的查询的时候使用。
(4).内容测试
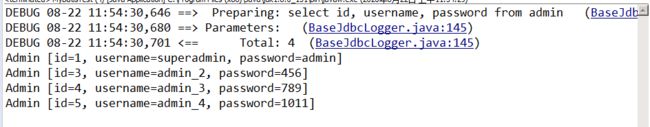
①:查询所有内容
public void testMbgMethod() throws Exception{
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = getSqlSessionFactory();
SqlSession openSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try {
AdminMapper mapper = openSession.getMapper(AdminMapper.class);
//xxxExample就是封装查询条件的
List lt = mapper.selectByExample(null);
for(Admin ad:lt){
System.out.println(ad);
}
} finally {
openSession.close();
}
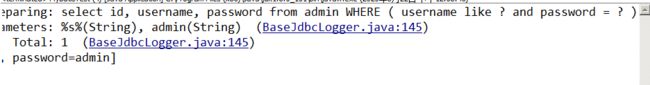
} ②条件查询测试:查询用户名中有特殊字母s的用户名和密码为admin的管理员信息
@Test
public void testMbgMethod() throws Exception{
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = getSqlSessionFactory();
SqlSession openSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try {
AdminMapper mapper = openSession.getMapper(AdminMapper.class);
//封装员工查询条件的example
AdminExample example = new AdminExample();
//创建一个Criteria,这个Criteria就是拼装查询条件
Criteria criteria = example.createCriteria();
criteria.andUsernameLike("%s%");
criteria.andPasswordEqualTo("admin");
//调用查询
List lt = mapper.selectByExample(example);
for(Admin ad:lt){
System.out.println(ad);
}
} finally {
openSession.close();
}
}
查询结果:
//我们发现其实这样的复杂查询就是拼接了一个内部查询