Hive分区、分桶、类型、函数、运算符指令详解
内部表和外部表
一、内部表的概念
先在hive里建一张表,然后向这个表插入数据(用insert可以插入数据,也可以通过加载外部文件方式来插入数据),这样的表称之为hive的内部表
二、外部表的概念
- HDFS里已经有数据了,然后,通过hive创建一张表来管理这个文件数据。则这样表称之为外部表
- 注意,hive外部表管理的是HDFS里的某一个目录下的文件数据
三、外部表创建命令:
进入hive,执行:create external table stu (id int,name string) row format delimited fields terminated by ’ ’ location ‘/目录路径’
四、内部表和外部标的区别
- 对于内部表,在删除该表的时候,HDFS对应的目录节点会被删除
- 对于外部表,在删除该表的时候,HDFS对应的目录节点不会删除
基础命令详解
| 命令 | 作用 | 额外说明 |
|---|---|---|
| show databases; | 查看都有哪些数据库 | |
| create database park; | 创建park数据库 | 创建的数据库,实际是在Hadoop的HDFS文件系统里创建一个目录节点,统一存在: /user/hive/warehouse 目录下 |
| use park; | 进入park数据库 | |
| show tables; | 查看当前数据库下所有表 | |
| create table stu (id int,name string); | 创建stu表,以及相关的两个字段 | 1. hive里,表示字符串用的是string,不用char和varchar 2. 所创建的表,也是HDFS里的一个目录节点 |
| insert into stu values(1,‘zhang’) | 向stu表插入数据 | 1. HDFS不支持数据的修改和删除,因此已经插入的数据不能够再进行任何的改动 2. 在Hadoop2.0版本后支持了数据追加。实际上,insert into 语句执行的是追加操作 3. hive支持查询,行级别的插入。不支持行级别的删除和修改 4. hive的操作实际是执行一个job任务,调用的是Hadoop的MR 5. 插入完数据之后,发现HDFS stu目录节点下多了一个文件,文件里存了插入的数据,因此,hive存储的数据,是通过HDFS的文件来存储的。 |
| select * from stu | 查看表数据 | 也可以根据字段来查询,比如select id from stu |
| drop table stu | 删除表 | |
| load data local inpath ‘/home/software/1.txt’ into table stu; | 通过加载文件数据到指定的表里 | 1. 在执行完这个指令之后,发现hdfs stu目录下多了一个1.txt文件。由此可见,hive的工作原理实际上就是在管理hdfs上的文件,把文件里数据抽象成二维表结构,然后提供hql语句供程序员查询文件数据 2. 可以做这样的实验:不通过load 指令,而通过插件向stu目录下再上传一个文件,看下hive是否能将数据管理到stu表里。 |
| create table stu1(id int,name string) row format delimited fields terminated by ’ '; | 创建stu1表,并指定分割符 空格。 | |
| desc stu | 查看 stu表结构 | |
| create table stu2 like stu | 创建一张stu2表,表结构和stu表结构相同 | like只复制表结构,不复制数据 |
| insert overwrite table stu2 select * from stu | 把stu表数据插入到stu2表中 | |
| insert overwrite local directory ‘/home/stu’ row format delimited fields terminated by ’ ’ select * from stu; | 将stu表中查询的数据写到本地的/home/stu目录下 | |
| insert overwrite directory ‘/stu’ row format delimited fields terminated by ’ ’ select * from stu; | 将stu表中查询的数据写到HDFS的stu目录下 | |
| from stu insert overwrite table stu1 select * insert overwrite table stu2 select *; | 将stu表中查询的数据写到stu1以及stu2两张表中 | |
| alter table stu rename to stu2 | 为表stu重命名为stu2 | |
| alter table stu add columns (age int); | 为表stu增加一个列字段age,类型为int | |
| exit | 退出hive |
分区表指令
一、分区表概述
- 分区表可以通过添加指定的字段来提高Hive的查询效率
- 在数据量较大的情况下,往往会添加分区表来避免全表查询
二、分区表指令
| 指令 | 作用 | 额外说明 |
|---|---|---|
| create table book (id int, name string) partitioned by (category string) row format delimited fields terminated by ‘\t’; | 创建book表,以category作为分区 | 在创建分区表时,partitioned字段可以不在字段列表中。生成的表中自动就会具有该字段。 |
| load data local inpath ‘/home/cn.txt’ overwrite into table book partition (category=‘cn’); | 将本地文件cn.txt添加到book表中,分区字段为cn | 在HDFS下生成category=cn目录 |
| select * from book where category=‘cn’; | 查看分区为cn的数据 | |
| ALTER TABLE book add PARTITION (category = ‘jp’) location ‘/user/hive/warehouse/park.db/book/category=jp’; | 将指定的目录添加为分区字段 | |
| show partitions iteblog; | 查看分区 | |
| msck repair table book; | 修复分区 | |
| alter table book drop partition(category=‘cn’); | 删除分区 | |
| alter table book partition(category=‘french’) rename to partition (category=‘hh’); | 修改分区的名字 |
分桶表指令
一、概述
- 分桶表是一种更细粒度的数据分配方式
- 一个表既可以分区也可以分桶
- 分桶的主要作用是实现数据的抽样,方便进行数据测试
- 分桶表通过hash分桶算法,将数据分放在不同的桶(hdfs中的文件)中,方便后续获取
- 分桶表机制默认是不开启的,需要手动开启:set hive.enforce.bucketing=true;
- 分桶表不允许以外部文件方式导入数据,只能从另外一张表数据导入
二、分桶表语法
| 指令 | 作用 | 额外说明 |
|---|---|---|
| create table teacher(name string) clustered by (name) into 3 buckets row format delimited fields terminated by ’ '; | 创建teacher表,以name作为分桶机制,分为3个桶 | |
| insert overwrite table teacher select * from tmp; | 将tmp表中的数据添加到teacher表中 | 实际上是产生了3个文件用于存储不分桶的数据 |
| select * from teacher tablesample(bucket 1 out of 3 on name); | 进行抽样 | 抽样格式为:bucket x out of y on XXX 1. x表示抽样的起始桶,例如bucket 1 out of 3表示从第1 个桶开始抽取数据 2. y决定抽样的比例,要求必须是桶数的因子或者整数倍 a. 如果桶数为6,y为2,则表示抽取6/2=3个桶中的数据 b. 如果桶数为6,y为3,则表示抽取6/3=2个桶中的数据 c. 如果桶数为6,y为12,则表示抽取6/12=0.5个桶中的数据 3. 如果桶数为6,抽样为bucket 1 out of 3 on id表示从第1个桶开始抽样,抽取2个桶的数据,所以抽取的样本为1和4桶中的数据 |
数据类型
一、基本类型
| Hive中的类型 | Java中的类型 |
|---|---|
| tinyint | byte |
| smallint | short |
| int | int |
| bigint | long |
| boolean | boolean |
| float | float |
| double | double |
| string | String |
| timestamp | TimeStamp |
| binary | byte[] |
二、复杂类型
数组类型 array
案例一
原始数据:
100,200,300
200,300,500
建表语句:
create external table ex(vals array<int>) row format delimited fields terminated by '\t' collection items terminated by ',' location '/ex';
查询每行数组的个数,查询语句:
select size(vals) from ex;
注:hive 内置函数不具备查询某个具体行的数组元素。需要自定义函数来实现,但这样的需求在实际开发里很少,所以不需要在意。
案例二
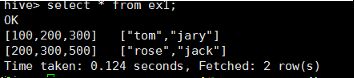
原始数据:
100,200,300 tom,jary
200,300,500 rose,jack
建表语句:
create external table ex1(info1 array<int>,info2 array<string>) row format delimited fields terminated by '\t' collection items terminated by ',' location '/ex';
map类型
案例一
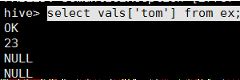
原始数据:
tom,23
rose,25
jary,28
建表语句:
create external table m1 (vals map<string,int>) row format delimited fields terminated by '\t' map keys terminated by ',' location '/map';
查询语句:
select vals['tom'] from m1;
案列二
原始数据:
tom 192.168.234.21
rose 192.168.234.21
tom 192.168.234.22
jary 192.168.234.21
tom 192.168.234.24
tom 192.168.234.21
rose 192.168.234.21
tom 192.168.234.22
jary 192.168.234.21
tom 192.168.234.22
tom 192.168.234.23
建表语句 :
create external table ex (vals map<string,string>) row format delimited fields terminated by '\t' map keys terminated by ' ' location '/ex';
注意:map类型,列的分割符必须是\t
查询语句
select vals['tom'] from ex where vals['tom'] is not null;
如果想做去重工作,可以调用distinct内置函数
select distinct(ip) from (select vals['tom'] ip from ex where vals['tom'] is not null)ex1;
或者
select distinct(vals['tom']) from m2 where vals['tom'] is not null;
struct 类型
原始数据:
tom 23
rose 22
jary 26
建表语句:
create external table ex (vals struct<name:string,age:int>)row format delimited collection items terminated by ' ' location '/ex';
查询语句:
select vals.age from ex where vals.name='tom';
内置函数
Hive实现了标准的sql,但在这之外,为了提升hive处理数据的能力,还额外提供了很多内置的函数,这些内置函数非常丰富,且可以直接使用,虽然不属于sql原生的语法,但大大的增强了hive处理数据的能力,是hive功能的重要组成部分。
运算符
一、关系运算符
| 运算符 | 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| A = B | 所有原始类型 | 如果A与B相等,返回true,否则返回false |
| A == B | 无 | 失败,因为无效的语法。 SQL使用”=”,不使用”==”。 |
| A <> B | 所有原始类型 | 如果A不等于B返回TRUE,否则返回FALSE。如果A或B值为”NULL”,结果返回”NULL”。 |
| A < B | 所有原始类型 | 如果A小于B返回TRUE,否则返回FALSE。如果A或B值为”NULL”,结果返回”NULL”。 |
| A <= B | 所有原始类型 | 如果A小于等于B返回TRUE,否则返回FALSE。如果A或B值为”NULL”,结果返回”NULL”。 |
| A > B | 所有原始类型 | 如果A大于B返回TRUE,否则返回FALSE。如果A或B值为”NULL”,结果返回”NULL”。 |
| A >= B | 所有原始类型 | 如果A大于等于B返回TRUE,否则返回FALSE。如果A或B值为”NULL”,结果返回”NULL”。 |
| A IS NULL | 所有类型 | 如果A值为”NULL”,返回TRUE,否则返回FALSE |
| A IS NOT NULL | 所有类型 | 如果A值不为”NULL”,返回TRUE,否则返回FALSE |
| A LIKE B | 字符串 | 如果A或B值为”NULL”,结果返回”NULL”。字符串A与B通过sql进行匹配,如果相符返回TRUE,不符返回FALSE。B字符串中 的””代表任一字符,”%”则代表多个任意字符。例如: (‘foobar’ like ‘foo’)返回FALSE,( ‘foobar’ like ‘foo _ _’或者 ‘foobar’ like ‘foo%’)则返回TURE |
| A RLIKE B | 字符串 | 如果A或B值为”NULL”,结果返回”NULL”。字符串A与B通过java进行匹配,如果相符返回TRUE,不符返回FALSE。例如:( ‘foobar’ rlike ‘foo’)返回FALSE,(’foobar’ rlike ‘^f.*r$’ )返回TRUE。 |
| A REGEXP B | 字符串 | 与RLIKE相同。 |
二、算数运算符
| 运算符 | 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| A + B | 所有数字类型 | A和B相加。结果的与操作数值有共同类型。例如每一个整数是一个浮点数,浮点数包含整数。所以,一个浮点数和一个整数相加结果也是一个浮点数。 |
| A – B | 所有数字类型 | A和B相减。结果的与操作数值有共同类型。 |
| A * B | 所有数字类型 | A和B相乘,结果的与操作数值有共同类型。需要说明的是,如果乘法造成溢出,将选择更高的类型。 |
| A / B | 所有数字类型 | A和B相除,结果是一个double(双精度)类型的结果。 |
| A % B | 所有数字类型 | A除以B余数与操作数值有共同类型。 |
| A & B | 所有数字类型 | 运算符查看两个参数的二进制表示法的值,并执行按位”与”操作。两个表达式的一位均为1时,则结果的该位为 1。否则,结果的该位为 0。 |
| A | B | 所有数字类型 |
| A ^ B | 所有数字类型 | 运算符查看两个参数的二进制表示法的值,并执行按位”异或”操作。当且仅当只有一个表达式的某位上为 1 时,结果的该位才为 1。否则结果的该位为 0。 |
| ~A | 所有数字类型 | 对一个表达式执行按位”非”(取反)。 |
三、逻辑运算符
| 运算符 | 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| A AND B | 布尔值 | A和B同时正确时,返回TRUE,否则FALSE。如果A或B值为NULL,返回NULL。 |
| A && B | 布尔值 | 与”A AND B”相同 |
| A OR B | 布尔值 | A或B正确,或两者同时正确返返回TRUE,否则FALSE。如果A和B值同时为NULL,返回NULL。 |
| A | B | 布尔值 |
| NOT A | 布尔值 | 如果A为NULL或错误的时候返回TURE,否则返回FALSE。 |
| ! A | 布尔值 | 与”NOT A”相同 |
函数
一、数学函数
| 返回类型 | 函数 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| BIGINT | round(double a) | 四舍五入 |
| DOUBLE | round(double a, int d) | 小数部分d位之后数字四舍五入,例如round(21.263,2),返回21.26 |
| BIGINT | floor(double a) | 对给定数据进行向下舍入最接近的整数。例如floor(21.2),返回21。 |
| BIGINT | ceil(double a), ceiling(double a) | 将参数向上舍入为最接近的整数。例如ceil(21.2),返回23. |
| double | rand(), rand(int seed) | 返回大于或等于0且小于1的平均分布随机数(依重新计算而变) |
| double | exp(double a) | 返回e的n次方 |
| double | ln(double a) | 返回给定数值的自然对数 |
| double | log10(double a) | 返回给定数值的以10为底自然对数 |
| double | log2(double a) | 返回给定数值的以2为底自然对数 |
| double | log(double base, double a) | 返回给定底数及指数返回自然对数 |
| double | pow(double a, double p) power(double a, double p) | 返回某数的乘幂 |
| double | sqrt(double a) | 返回数值的平方根 |
| string | bin(BIGINT a) | 返回二进制格式 |
| string | hex(BIGINT a) hex(string a) | 将整数或字符转换为十六进制格式 |
| string | unhex(string a) | 十六进制字符转换由数字表示的字符。 |
| string | conv(BIGINT num, int from_base, int to_base) | 将指定数值,由原来的度量体系转换为指定的试题体系。例如CONV(‘a’,16,2),返回 |
| double | abs(double a) | 取绝对值 |
| int double | pmod(int a, int b) pmod(double a, double b) | 返回a除b的余数的绝对值 |
| double | sin(double a) | 返回给定角度的正弦值 |
| double | asin(double a) | 返回x的反正弦,即是X。如果X是在-1到1的正弦值,返回NULL。 |
| double | cos(double a) | 返回余弦 |
| double | acos(double a) | 返回X的反余弦,即余弦是X,,如果-1<= A <= 1,否则返回null. |
| int double | positive(int a) positive(double a) | 返回A的值,例如positive(2),返回2。 |
| int double | negative(int a) negative(double a) | 返回A的相反数,例如negative(2),返回-2。 |
二、类型转换函数
| 返回类型 | 函数 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 指定 “type” | cast(expr as ) | 类型转换。例如将字符”1″转换为整数:cast(’1′ as bigint),如果转换失败返回NULL。 |
三、日期函数
| 返回类型 | 函数 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| string | from_unixtime(bigint unixtime[, string format]) | UNIX_TIMESTAMP参数表示返回一个值’YYYY- MM – DD HH:MM:SS’或YYYYMMDDHHMMSS.uuuuuu格式,这取决于是否是在一个字符串或数字语境中使用的功能。该值表示在当前的时区。 |
| bigint | unix_timestamp() | 如果不带参数的调用,返回一个Unix时间戳(从’1970- 01 – 0100:00:00′到现在的UTC秒数)为无符号整数。 |
| bigint | unix_timestamp(string date) | 指定日期参数调用UNIX_TIMESTAMP(),它返回参数值’1970- 01 – 0100:00:00′到指定日期的秒数。 |
| bigint | unix_timestamp(string date, string pattern) | 指定时间输入格式,返回到1970年秒数:unix_timestamp(’2009-03-20′, ‘yyyy-MM-dd’) = 1237532400 |
| string | to_date(string timestamp) | 返回时间中的年月日: to_date(“1970-01-01 00:00:00″) = “1970-01-01″ |
| string | to_dates(string date) | 给定一个日期date,返回一个天数(0年以来的天数) |
| int | year(string date) | 返回指定时间的年份,范围在1000到9999,或为”零”日期的0。 |
| int | month(string date) | 返回指定时间的月份,范围为1至12月,或0一个月的一部分,如’0000-00-00′或’2008-00-00′的日期。 |
| int | day(string date) dayofmonth(date) | 返回指定时间的日期 |
| int | hour(string date) | 返回指定时间的小时,范围为0到23。 |
| int | minute(string date) | 返回指定时间的分钟,范围为0到59。 |
| int | second(string date) | 返回指定时间的秒,范围为0到59。 |
| int | weekofyear(string date) | 返回指定日期所在一年中的星期号,范围为0到53。 |
| int | datediff(string enddate, string startdate) | 两个时间参数的日期之差。 |
| int | date_add(string startdate, int days) | 给定时间,在此基础上加上指定的时间段。 |
| int | date_sub(string startdate, int days) | 给定时间,在此基础上减去指定的时间段。 |
四、条件函数
| 返回类型 | 函数 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| T | if(boolean testCondition, T valueTrue, T valueFalseOrNull) | 判断是否满足条件,如果满足返回一个值,如果不满足则返回另一个值。 |
| T | COALESCE(T v1, T v2, …) | 返回一组数据中,第一个不为NULL的值,如果均为NULL,返回NULL。 |
| T | CASE a WHEN b THEN c [WHEN d THEN e]* [ELSE f] END | 当a=b时,返回c;当a=d时,返回e,否则返回f。 |
| T | CASE WHEN a THEN b [WHEN c THEN d]* [ELSE e] END | 当值为a时返回b,当值为c时返回d。否则返回e。 |
五、字符串函数
| 返回类型 | 函数 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| int | length(string A) | 返回字符串的长度 |
| string | reverse(string A) | 返回倒序字符串 |
| string | concat(string A, string B…) | 连接多个字符串,合并为一个字符串,可以接受任意数量的输入字符串 |
| string | concat_ws(string SEP, string A, string B…) | 链接多个字符串,字符串之间以指定的分隔符分开。 |
| string | substr(string A, int start) substring(string A, int start) | 从文本字符串中指定的起始位置后的字符。 |
| string | substr(string A, int start, int len) substring(string A, int start, int len) | 从文本字符串中指定的位置指定长度的字符。 |
| string | upper(string A) ucase(string A) | 将文本字符串转换成字母全部大写形式 |
| string | lower(string A) lcase(string A) | 将文本字符串转换成字母全部小写形式 |
| string | trim(string A) | 删除字符串两端的空格,字符之间的空格保留 |
| string | ltrim(string A) | 删除字符串左边的空格,其他的空格保留 |
| string | rtrim(string A) | 删除字符串右边的空格,其他的空格保留 |
| string | regexp_replace(string A, string B, string C) | 字符串A中的B字符被C字符替代 |
| string | regexp_extract(string subject, string pattern, int index) | 通过下标返回正则表达式指定的部分。regexp_extract(‘foothebar’, ‘foo(.*?)(bar)’, 2) returns ‘bar.’ |
| string | parse_url(string urlString, string partToExtract [, string keyToExtract]) | 返回URL指定的部分。parse_url(‘http://facebook.com/path1/p.php?k1=v1&k2=v2#Ref1′, ‘HOST’) 返回:’facebook.com’ |
| string | get_json_object(string json_string, string path) | select a.timestamp, get_json_object(a.appevents, ‘ . e v e n t i d ’ ) , g e t j s o n o b j e c t ( a . a p p e n v e t s , ‘ .eventid’), get_json_object(a.appenvets, ‘ .eventid’),getjsonobject(a.appenvets,‘.eventname’) from log a; |
| string | space(int n) | 返回指定数量的空格 |
| string | repeat(string str, int n) | 重复N次字符串 |
| int | ascii(string str) | 返回字符串中首字符的数字值 |
| string | lpad(string str, int len, string pad) | 返回指定长度的字符串,给定字符串长度小于指定长度时,由指定字符从左侧填补。 |
| string | rpad(string str, int len, string pad) | 返回指定长度的字符串,给定字符串长度小于指定长度时,由指定字符从右侧填补。 |
| array | split(string str, string pat) | 将字符串转换为数组。 |
| int | find_in_set(string str, string strList) | 返回字符串str第一次在strlist出现的位置。如果任一参数为NULL,返回NULL;如果第一个参数包含逗号,返回0。 |
| array |
sentences(string str, string lang, string locale) | 将字符串中内容按语句分组,每个单词间以逗号分隔,最后返回数组。 例如sentences(‘Hello there! How are you?’) 返回:( (“Hello”, “there”), (“How”, “are”, “you”) ) |
| array |
ngrams(array |
SELECT ngrams(sentences(lower(tweet)), 2, 100 [, 1000]) FROM twitter; |
| array |
context_ngrams(array |
SELECT context_ngrams(sentences(lower(tweet)), array(null,null), 100, [, 1000]) FROM twitter; |
六、聚合函数
| 返回类型 | 函数 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| bigint | count(*) , count(expr), count(DISTINCT expr[, expr_., expr_.]) | 返回记录条数。 |
| double | sum(col), sum(DISTINCT col) | 求和 |
| double | avg(col), avg(DISTINCT col) | 求平均值 |
| double | min(col) | 返回指定列中最小值 |
| double | max(col) | 返回指定列中最大值 |
| double | var_pop(col) | 返回指定列的方差 |
| double | var_samp(col) | 返回指定列的样本方差 |
| double | stddev_pop(col) | 返回指定列的偏差 |
| double | stddev_samp(col) | 返回指定列的样本偏差 |
| double | covar_pop(col1, col2) | 两列数值协方差 |
| double | covar_samp(col1, col2) | 两列数值样本协方差 |
| double | corr(col1, col2) | 返回两列数值的相关系数 |
| double | percentile(col, p) | 返回数值区域的百分比数值点。0<=P<=1,否则返回NULL,不支持浮点型数值。 |
| array | percentile(col, array(p~1,\ [, p,2,]…)) | 返回数值区域的一组百分比值分别对应的数值点。0<=P<=1,否则返回NULL,不支持浮点型数值。 |
| double | percentile_approx(col, p[, B]) | Returns an approximate pth percentile of a numeric column (including floating point types) in the group. The B parameter controls approximation accuracy at the cost of memory. Higher values yield better approximations, and the default is 10,000. When the number of distinct values in col is smaller than B, this gives an exact percentile value. |
| array | percentile_approx(col, array(p~1, [, p,2_]…) [, B]) | Same as above, but accepts and returns an array of percentile values instead of a single one. |
| array |
histogram_numeric(col, b) | Computes a histogram of a numeric column in the group using b non-uniformly spaced bins. The output is an array of size b of double-valued (x,y) coordinates that represent the bin centers and heights |
| array | collect_set(col) | 返回无重复记录 |
explode 详解
一、概述
- explode 命令可以将行数据,按指定规则切分出多行
- 用explode做行切分,注意表里只有一列,并且行数据是string类型,因为只有字符类型才能做切分
二、示例
原始数据:
100,200,300
200,300,500
要求:
要将上面两行数据根据逗号拆分成多行(每个数字占一行)
实现步骤
- 上传HDFS,并创建对应的外部表,执行:
create external table ex1 (num string) location '/ex';
- 通过explode指令来做行切分,执行:
select explode(split(num,',')) from ex1;