HDU - Largest Rectangle in a Histogram(单调栈)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1506
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Problem Description
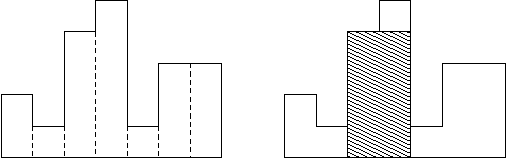
A histogram is a polygon composed of a sequence of rectangles aligned at a common base line. The rectangles have equal widths but may have different heights. For example, the figure on the left shows the histogram that consists of rectangles with the heights 2, 1, 4, 5, 1, 3, 3, measured in units where 1 is the width of the rectangles:
Usually, histograms are used to represent discrete distributions, e.g., the frequencies of characters in texts. Note that the order of the rectangles, i.e., their heights, is important. Calculate the area of the largest rectangle in a histogram that is aligned at the common base line, too. The figure on the right shows the largest aligned rectangle for the depicted histogram.
Input
The input contains several test cases. Each test case describes a histogram and starts with an integer n, denoting the number of rectangles it is composed of. You may assume that 1 <= n <= 100000. Then follow n integers h1, ..., hn, where 0 <= hi <= 1000000000. These numbers denote the heights of the rectangles of the histogram in left-to-right order. The width of each rectangle is 1. A zero follows the input for the last test case.
Output
For each test case output on a single line the area of the largest rectangle in the specified histogram. Remember that this rectangle must be aligned at the common base line.
Sample Input
7 2 1 4 5 1 3 3
4 1000 1000 1000 1000
0
Sample Output
8
4000
Problem solving report:
Description: 有一堆宽度恒为1、高度不定的长方形排成一列,找出最大面积的长方形。。
Problem solving: 单调栈。栈内每个单位存入两个元素:该单位高度height和对应可控宽度width,对于每个大于等于栈顶直接入栈的元素,width=1;对于需要先弹栈再入栈的元素,其width=弹栈所有元素width之和+1,因为被弹栈的元素的高度均大于等于当前元素,所以其可控范围应加上被其弹栈元素的width;在弹栈过程中,记录一个width为本次弹栈到当前为止弹出的宽度,因为是单增栈,所以每个高度均可限制其后被弹栈元素的宽度,所以其对应的面积为s=width*height[i],取max即可。
Accepted Code:
#include
using namespace std;
struct edge {
int height, width;
edge(const int& h, const int& w) {
height = h, width = w;
}
};
int main() {
long long max_;
int n, height, width;
while (scanf("%d", &n), n) {
max_ = 0;
stack S;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
width = 0;
scanf("%d", &height);
while (!S.empty() && S.top().height >= height) {
width += S.top().width;
max_ = max(max_, 1ll * S.top().height * width);
S.pop();
}
S.push(edge(height, width + 1));
}
width = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
while (!S.empty()) {
width += S.top().width;
max_ = max(max_, 1ll * S.top().height * width);
S.pop();
}
}
printf("%lld\n", max_);
}
return 0;
}