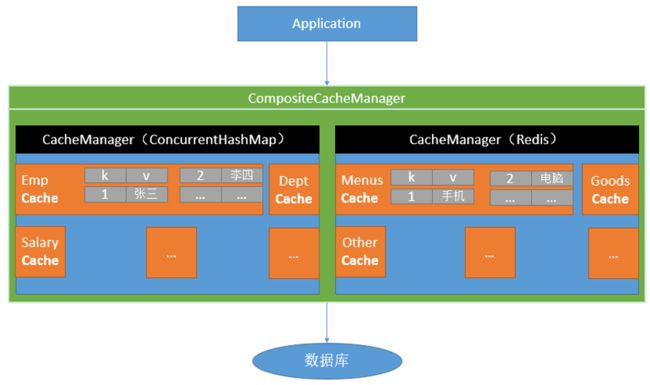
Spring Boot与缓存
Spring Boot与缓存
一、 JSR107
Java Caching定义了5个核心接口
-
CachingProvider
定义了创建、配置、获取、管理和控制多个CacheManager。一个应用可
以在运行期访问多个CachingProvider。 -
CacheManager
定义了创建、配置、获取、管理和控制多个唯一命名的Cache,这些Cache
存在于CacheManager的上下文中。一个CacheManager仅被一个CachingProvider所拥有。 -
Cache
一个类似Map的数据结构并临时存储以Key为索引的值。一个Cache仅被一个
CacheManager所拥有。 -
Entry
一个存储在Cache中的key-value对。
-
Expiry
每一个存储在Cache中的条目有一个定义的有效期。一旦超过这个时间,条目为过期的状态。一旦过期,条目将不可访问、更新和删除。缓存有效期可以通过ExpiryPolicy设置。
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-82C7xx8n-1598345189959)(https://niceseason.github.io/images/%E5%9B%BE%E7%89%871.png)]
二、 Spring缓存抽象
-
Spring从3.1开始定义了org.springframework.cache.Cache
和org.springframework.cache.CacheManager接口来统一不同的缓存技术;
**并支持使用JCache(JSR-107)**注解简化我们开发;Cache接口有以下功能:
- 为缓存的组件规范定义,包含缓存的各种操作集合;
-
Spring提供了各种xxxCache的实现;如RedisCache,EhCacheCache ,
ConcurrentMapCache等;
三、 重要缓存注解及概念
| Cache | 缓存接口,定义缓存操作。实现有:RedisCache、EhCacheCache、ConcurrentMapCache等 |
|---|---|
| CacheManager | 缓存管理器,管理各种缓存(Cache)组件 |
| @Cacheable | 根据方法的请求参数对其结果进行缓存 |
| @CacheEvict | 清空缓存 |
| @CachePut | 更新缓存 |
| @EnableCaching | 开启基于注解的缓存 |
| keyGenerator | 缓存数据时key生成策略 |
| serialize | 缓存数据时value序列化策略 |
1 . @Cacheable/@CachePut/@CacheEvict 主要的参数
-
value
缓存名称,字符串/字符数组形式;
如@Cacheable(value=”mycache”) 或者@Cacheable(value={”cache1”,”cache2”}
-
key
缓存的key,需要按照SpEL表达式编写,如果不指定则按照方法所有参数进行组合;
如@Cacheable(value=”testcache”,key=”#userName”)
-
keyGenerator
key的生成器;可以自己指定key的生成器的组件id
注意:key/keyGenerator:二选一使用;
(自定义KeyGenerator)
package com.wh.cache.config; import org.springframework.cache.interceptor.KeyGenerator; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.util.Arrays; /** * @author wh * @date 2020/8/25 1:37 * @description */ @Configuration public class MyCacheConfig { @Bean("myKeyGenerator") public KeyGenerator keyGenerator() { return new KeyGenerator() { @Override public Object generate(Object o, Method method, Object... params) { return method.getName() + "[" + Arrays.asList(params).toString() + "]"; } }; } } -
condition
缓存条件,使用SpEL编写,在调用方法之前之后都能判断;
如@Cacheable(value=”testcache”,condition=”#userName.length()>2”)
-
unless(@CachePut、@Cacheable)
用于否决缓存的条件,只在方法执行之后判断;
如@Cacheable(value=”testcache”,unless=”#result ==null”)
-
beforeInvocation(@CacheEvict)
是否在执行前清空缓存,默认为false,false情况下方法执行异常则不会清空;
如@CachEvict(value=”testcache”,beforeInvocation=true)
-
allEntries(@CacheEvict)
是否清空所有缓存内容,默认为false;
如@CachEvict(value=”testcache”,allEntries=true)
2 . 缓存可用的SpEL表达式
root
表示根对象,不可省略
-
被调用方法名 methodName
如 #root.methodName
-
被调用方法 method
如 #root.method.name
-
目标对象 target
如 #root.target
-
被调用的目标对象类 targetClass
如 #root.targetClass
-
被调用的方法的参数列表 args
如 #root.args[0]
-
方法调用使用的缓存列表 caches
如 #root.caches[0].name
参数名
方法参数的名字. 可以直接 #参数名 ,也可以使用 #p0或#a0 的形式,0代表参数的索引;
如 #iban 、 #a0 、 #p0
返回值
方法执行后的返回值(仅当方法执行之后的判断有效,如‘unless’ , @CachePut、@CacheEvict’的表达式beforeInvocation=false )
如 #result
四、 缓存使用
1. 基本使用步骤
- 引入spring-boot-starter-cache模块
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cacheartifactId>
dependency>
- @EnableCaching开启缓存
在主配置类上标注
- 使用缓存注解
如@Cacheable、@CachePut
- 切换为其他缓存
2. 搭建实验环境
-
导入数据库文件 创建出department和employee表
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `department`; CREATE TABLE `department` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `departmentName` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; -- ---------------------------- -- Table structure for employee -- ---------------------------- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `employee`; CREATE TABLE `employee` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `lastName` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL, `email` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL, `gender` int(2) DEFAULT NULL, `d_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8; -
创建javaBean封装数据
package com.wh.cache.pojo; import java.io.Serializable; /** * @author wh * @date 2020/8/24 23:23 * @description */ public class Department implements Serializable { private Integer id; private String departmentName; public Department() { super(); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } public Department(Integer id, String departmentName) { super(); this.id = id; this.departmentName = departmentName; } public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getDepartmentName() { return departmentName; } public void setDepartmentName(String departmentName) { this.departmentName = departmentName; } @Override public String toString() { return "Department [id=" + id + ", departmentName=" + departmentName + "]"; } } package com.wh.cache.pojo; import java.io.Serializable; /** * @author wh * @date 2020/8/24 23:23 * @description */ public class Employee implements Serializable { private Integer id; private String lastName; private String email; private Integer gender; //性别 1男 0女 private Integer dId; public Employee() { super(); } public Employee(Integer id, String lastName, String email, Integer gender, Integer dId) { super(); this.id = id; this.lastName = lastName; this.email = email; this.gender = gender; this.dId = dId; } public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getLastName() { return lastName; } public void setLastName(String lastName) { this.lastName = lastName; } public String getEmail() { return email; } public void setEmail(String email) { this.email = email; } public Integer getGender() { return gender; } public void setGender(Integer gender) { this.gender = gender; } public Integer getdId() { return dId; } public void setdId(Integer dId) { this.dId = dId; } @Override public String toString() { return "Employee [id=" + id + ", lastName=" + lastName + ", email=" + email + ", gender=" + gender + ", dId=" + dId + "]"; } } -
整合MyBatis操作数据库
配置数据源信息
spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=123456 spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springboot?serverTimezone=GMT spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver # 开启驼峰命名法(否则部分字段封装不了) mybatis.configuration.map-underscore-to-camel-case=true #打印sql logging.level.cn.edu.ustc.springboot.mapper=debug debug=true使用注解版的MyBatis;
@MapperScan指定需要扫描的mapper接口所在的包
-
主配置类开启@EnableCaching
3. 快速体验缓存
@Cacheable、@CachePut、@CacheEvict的使用
@Service
public class EmployeeService {
@Autowired
private EmployeeMapper employeeMapper;
@Cacheable(value={
"emp"},
key = "#id+#root.methodName+#root.caches[0].name",
condition = "#a0>1",
unless = "#p0==2"
)
public Employee getEmpById(Integer id) {
System.out.println("查询员工:"+id);
return employeeMapper.getEmpById(id);
}
@CachePut(value = {
"emp"},key = "#employee.id" )
public Employee updateEmp(Employee employee) {
System.out.println("更新员工"+employee);
employeeMapper.updateEmp(employee);
return employee;
}
@CacheEvict(value = {
"emp"},allEntries = true,beforeInvocation = true)
public Integer delEmp(Integer id){
int i=1/0;
System.out.println("删除员工:"+id);
employeeMapper.delEmp(id);
return id;
}
}
自定义KeyGenerator
使用时在注解属性内指定KeyGenerator=“myKeyGenerator”
@Configuration
public class MyCacheConfig {
@Bean("myKeyGenerator")
public KeyGenerator keyGenerator() {
return new KeyGenerator() {
@Override
public Object generate(Object o, Method method, Object... params) {
return method.getName() + "[" + Arrays.asList(params).toString() + "]";
}
};
}
}
@CacheConfig
标注在类上,用于抽取@Cacheable的公共属性
由于一个类中可能会使用多次@Cacheable等注解,所以各项属性可以抽取到@CacheConfig
@Caching
组合使用@Cacheable、@CachePut、@CacheEvict
@Caching(
cacheable = {
@Cacheable(/*value="emp",*/key = "#lastName")
},
put = {
@CachePut(/*value="emp",*/key = "#result.id"),
@CachePut(/*value="emp",*/key = "#result.email")
}
)
public Employee getEmpByLastName(String lastName){
return employeeMapper.getEmpByLastName(lastName);
}
4. 工作原理
缓存的自动配置类CacheAutoConfiguration向容器中导入了CacheConfigurationImportSelector,此类的selectImports()方法添加了许多配置类,其中SimpleCacheConfiguration默认生效
GenericCacheConfiguration
JCacheCacheConfiguration
EhCacheCacheConfiguration
HazelcastCacheConfiguration
InfinispanCacheConfiguration
CouchbaseCacheConfiguration
RedisCacheConfiguration
CaffeineCacheConfiguration
GuavaCacheConfiguration
SimpleCacheConfiguration【默认】
NoOpCacheConfiguration
@Import({
CacheConfigurationImportSelector.class, CacheManagerEntityManagerFactoryDependsOnPostProcessor.class })
public class CacheAutoConfiguration {
static class CacheConfigurationImportSelector implements ImportSelector {
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) {
CacheType[] types = CacheType.values();
String[] imports = new String[types.length];
for (int i = 0; i < types.length; i++) {
//将即将导入的各配置类存入字符数组内
imports[i] = CacheConfigurations.getConfigurationClass(types[i]);
}
return imports;
}
}
}
SimpleCacheConfiguration向容器中导入了ConcurrentMapCacheManager
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(CacheManager.class)
@Conditional(CacheCondition.class)
class SimpleCacheConfiguration {
//向容器中导入ConcurrentMapCacheManager
@Bean
ConcurrentMapCacheManager cacheManager(CacheProperties cacheProperties,
CacheManagerCustomizers cacheManagerCustomizers) {
ConcurrentMapCacheManager cacheManager = new ConcurrentMapCacheManager();
List<String> cacheNames = cacheProperties.getCacheNames();
if (!cacheNames.isEmpty()) {
cacheManager.setCacheNames(cacheNames);
}
return cacheManagerCustomizers.customize(cacheManager);
}
}
ConcurrentMapCacheManager使用ConcurrentMap以k-v的方式存储缓存缓存,下面以@Cacheable的运行流程为例说明ConcurrentMapCacheManager的作用。
@Cacheable的运行流程
-
方法运行之前,先去查询Cache(缓存组件),按照cacheNames指定的名字获取;
(CacheManager先获取相应的缓存),第一次获取缓存如果没有Cache组件会自动创建,并以cacheNames-cache对放入ConcurrentMap。 -
去Cache中查找缓存的内容,使用一个key,默认就是方法的参数;
key是按照某种策略生成的;默认是使用keyGenerator生成的,默认使用SimpleKeyGenerator生成key;SimpleKeyGenerator生成key的默认策略;
如果没有参数;key=new SimpleKey();
如果有一个参数:key=参数的值
如果有多个参数:key=new SimpleKey(params); -
没有查到缓存就调用目标方法;
-
将目标方法返回的结果,放进缓存中
@Cacheable标注的方法执行之前先来检查缓存中有没有这个数据,默认按照参数的值作为key去查询缓存,
如果没有就运行方法并将结果放入缓存;以后再来调用就可以直接使用缓存中的数据;
核心:
1)、使用CacheManager【ConcurrentMapCacheManager】按照名字得到Cache【ConcurrentMapCache】组件
2)、key使用keyGenerator生成的,默认是SimpleKeyGenerator
源码分析
默认使用ConcurrentMapCacheManager管理缓存,该类使用ConcurrentMap保存缓存,获取缓存如果没有Cache组件会自动创建,并以cacheNames-cache对放入ConcurrentMap。
public class ConcurrentMapCacheManager implements CacheManager, BeanClassLoaderAware {
private final ConcurrentMap<String, Cache> cacheMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private boolean dynamic = true;
//获取缓存
public Cache getCache(String name) {
Cache cache = this.cacheMap.get(name);
//如果没有缓存会自动创建
if (cache == null && this.dynamic) {
synchronized (this.cacheMap) {
cache = this.cacheMap.get(name);
if (cache == null) {
cache = createConcurrentMapCache(name);
this.cacheMap.put(name, cache);
}
}
}
return cache;
}
}
在@Cacheable标注方法执行前执行CacheAspectSupport的execute()方法,在该方法中会以一定的规则生成key,并尝试在缓存中通过该key获取值,若通过key获取到值则直接返回,不用执行@Cacheable标注方法,否则执行该方法获得返回值。
public abstract class CacheAspectSupport extends AbstractCacheInvoker
implements BeanFactoryAware, InitializingBean, SmartInitializingSingleton {
//在执行@Cacheable标注的方法前执行此方法
@Nullable
private Object execute(final CacheOperationInvoker invoker, Method method, CacheOperationContexts contexts) {
if (contexts.isSynchronized()) {
CacheOperationContext context = contexts.get(CacheableOperation.class).iterator().next();
if (isConditionPassing(context, CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT)) {
Object key = generateKey(context, CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT);
Cache cache = context.getCaches().iterator().next();
try {
return wrapCacheValue(method, cache.get(key, () -> unwrapReturnValue(invokeOperation(invoker))));
}
catch (Cache.ValueRetrievalException ex) {
throw (CacheOperationInvoker.ThrowableWrapper) ex.getCause();
}
}
else {
return invokeOperation(invoker);
}
}
processCacheEvicts(contexts.get(CacheEvictOperation.class), true,
CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT);
// 见findCachedItem方法
//此方法通过一定规则生成的key找cache,若没找到则返回null
Cache.ValueWrapper cacheHit = findCachedItem(contexts.get(CacheableOperation.class));
List<CachePutRequest> cachePutRequests = new LinkedList<>();
if (cacheHit == null) {
collectPutRequests(contexts.get(CacheableOperation.class),
CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT, cachePutRequests);
}
Object cacheValue;
Object returnValue;
if (cacheHit != null && !hasCachePut(contexts)) {
// 如果通过该key找到缓存,且无@cacheput,则直接返回cacheValue
cacheValue = cacheHit.get();
returnValue = wrapCacheValue(method, cacheValue);
}
else {
// 若通过该key未找到缓存,则执行@cacheable标注方法
returnValue = invokeOperation(invoker);
cacheValue = unwrapReturnValue(returnValue);
}
// Collect any explicit @CachePuts
collectPutRequests(contexts.get(CachePutOperation.class), cacheValue, cachePutRequests);
// Process any collected put requests, either from @CachePut or a @Cacheable miss
for (CachePutRequest cachePutRequest : cachePutRequests) {
cachePutRequest.apply(cacheValue);
}
// Process any late evictions
processCacheEvicts(contexts.get(CacheEvictOperation.class), false, cacheValue);
return returnValue;
}
@Nullable
private Cache.ValueWrapper findCachedItem(Collection<CacheOperationContext> contexts) {
Object result = CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT;
for (CacheOperationContext context : contexts) {
if (isConditionPassing(context, result)) {
//通过一定规则生成key值(生成规则见generateKey方法)
Object key = generateKey(context, result);
//通过生成的key寻找缓存
Cache.ValueWrapper cached = findInCaches(context, key);
if (cached != null) {
return cached;
}
else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No cache entry for key '" + key + "' in cache(s) " + context.getCacheNames());
}
}
}
}
return null;
}
//key的生成策略
@Nullable
protected Object generateKey(@Nullable Object result) {
//如果@Cacheable设置了属性key,则根据设置值生成key
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.metadata.operation.getKey())) {
EvaluationContext evaluationContext = createEvaluationContext(result);
return evaluator.key(this.metadata.operation.getKey(), this.metadata.methodKey, evaluationContext);
}
//否则使用keyGenerator生成key,默认keyGenerator为SimpleKeyGenerator
return this.metadata.keyGenerator.generate(this.target, this.metadata.method, this.args);
}
默认情况下使用SimpleKeyGenerator生成key
public class SimpleKeyGenerator implements KeyGenerator {
//SimpleKeyGenerator的生成规则
public static Object generateKey(Object... params) {
//若无参,则返回空key
if (params.length == 0) {
return SimpleKey.EMPTY;
}
if (params.length == 1) {
Object param = params[0];
if (param != null && !param.getClass().isArray()) {
//1个参数,则直接返回该参数
return param;
}
}
//多个参数返回数组
return new SimpleKey(params);
}
}
默认的缓存类ConcurrentMapCache,使用ConcurrentMap存储k-v
public class ConcurrentMapCache extends AbstractValueAdaptingCache {
private final String name;
//存储key-cacheValue
private final ConcurrentMap<Object, Object> store;
//通过key查找cacheValue
protected Object lookup(Object key) {
return this.store.get(key);
}
//方法调用完后将结果存入缓存中
public void put(Object key, @Nullable Object value) {
this.store.put(key, toStoreValue(value));
}
}
五、Redis与缓存
1. 环境搭建
导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redisartifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>io.lettucegroupId>
<artifactId>lettuce-coreartifactId>
exclusion>
exclusions>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clientsgroupId>
<artifactId>jedisartifactId>
dependency>
在spring.properties指定Redis服务器地址
#redis服务器主机地址
spring.redis.host=192.168.11.132
2. RedisTemplate
RedisAutoConfiguration向容器中导入了两个类RedisTemplate
Redis常见的五大数据类型
String(字符串)、List(列表)、Set(集合)、Hash(散列)、ZSet(有序集合)
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue()[String(字符串)]
stringRedisTemplate.opsForList()[List(列表)]
stringRedisTemplate.opsForSet()[Set(集合)]
stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash()[Hash(散列)]
stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet()[ZSet(有序集合)]
3. Redis缓存使用
在导入redis依赖后RedisCacheConfiguration类就会自动生效,创建RedisCacheManager,并使用RedisCache进行缓存数据,要缓存的对象的类要实现Serializable接口,默认情况下是以jdk序列化数据存在redis中,如下:
k:"emp::1"
v:
\xAC\xED\x00\x05sr\x00$cn.edu.ustc.springboot.bean.Employeeuqf\x03p\x9A\xCF\xE0\x02\x00\x05L\x00\x03dIdt\x00\x13Ljava/lang/Integer;L\x00\x05emailt\x00\x12Ljava/lang/String;L\x00\x06genderq\x00~\x00\x01L\x00\x02idq\x00~\x00\x01L\x00\x08lastNameq\x00~\x00\x02xpsr\x00\x11java.lang.Integer\x12\xE2\xA0\xA4\xF7\x81\x878\x02\x00\x01I\x00\x05valuexr\x00\x10java.lang.Number\x86\xAC\x95\x1D\x0B\x94\xE0\x8B\x02\x00\x00xp\x00\x00\x00\x03t\x00\x07cch
要想让对象以json形式存储在redis中,需要自定义RedisCacheManager,使用GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer类对value进行序列化
@Configuration
public class MyRedisConfig {
@Bean
RedisCacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory factory){
//创建默认RedisCacheWriter
RedisCacheWriter cacheWriter = RedisCacheWriter.nonLockingRedisCacheWriter(factory);
//创建默认RedisCacheConfiguration并使用GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer构造的 SerializationPair对value进行转换
//创建GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer的json序列化器
GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer jsonRedisSerializer = new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer();
//使用json序列化器构造出对转换Object类型的SerializationPair序列化对
RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair<Object> serializationPair = RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(jsonRedisSerializer);
//将可以把Object转换为json的SerializationPair传入RedisCacheConfiguration
//使得RedisCacheConfiguration在转换value时使用定制序列化器
RedisCacheConfiguration cacheConfiguration=RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig().serializeValuesWith(serializationPair);
RedisCacheManager cacheManager = new RedisCacheManager(cacheWriter,cacheConfiguration);
return cacheManager;
}
}
序列化数据如下:
k:"emp::3"
v:
{
"@class": "cn.edu.ustc.springboot.bean.Employee",
"id": 3,
"lastName": "aaa",
"email": "aaaa",
"gender": 1,
"dId": 5
}
注意,这里必须用GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer进行value的序列化解析,如果使用Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer,序列化的json没有"@class": "cn.edu.ustc.springboot.bean.Employee",在读取缓存时会报类型转换异常。
4. Redis缓存原理
配置类RedisCacheConfiguration向容器中导入了其定制的RedisCacheManager,在默认的RedisCacheManager的配置中,是使用jdk序列化value值
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnClass(RedisConnectionFactory.class)
@AutoConfigureAfter(RedisAutoConfiguration.class)
@ConditionalOnBean(RedisConnectionFactory.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(CacheManager.class)
@Conditional(CacheCondition.class)
class RedisCacheConfiguration {
//向容器中导入RedisCacheManager
@Bean
RedisCacheManager cacheManager(CacheProperties cacheProperties, CacheManagerCustomizers cacheManagerCustomizers,
ObjectProvider<org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration> redisCacheConfiguration,
ObjectProvider<RedisCacheManagerBuilderCustomizer> redisCacheManagerBuilderCustomizers,
RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory, ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
//使用determineConfiguration()的返回值生成RedisCacheManagerBuilder
//调用了RedisCacheManagerBuilder的cacheDefaults()方法(见下一代码块)
RedisCacheManagerBuilder builder = RedisCacheManager.builder(redisConnectionFactory).cacheDefaults(
determineConfiguration(cacheProperties, redisCacheConfiguration, resourceLoader.getClassLoader()));
List<String> cacheNames = cacheProperties.getCacheNames();
if (!cacheNames.isEmpty()) {
builder.initialCacheNames(new LinkedHashSet<>(cacheNames));
}
redisCacheManagerBuilderCustomizers.orderedStream().forEach((customizer) -> customizer.customize(builder));
//使用RedisCacheManagerBuilder的build()方法创建RedisCacheManager并进行定制操作
return cacheManagerCustomizers.customize(builder.build());
}
private org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration determineConfiguration(
CacheProperties cacheProperties,
ObjectProvider<org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration> redisCacheConfiguration,
ClassLoader classLoader) {
//determineConfiguration()调用了createConfiguration()
return redisCacheConfiguration.getIfAvailable(() -> createConfiguration(cacheProperties, classLoader));
}
//createConfiguration()定义了其序列化value的规则
private org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration createConfiguration(
CacheProperties cacheProperties, ClassLoader classLoader) {
Redis redisProperties = cacheProperties.getRedis();
org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration config = org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration
.defaultCacheConfig();
//使用jdk序列化器对value进行序列化
config = config.serializeValuesWith(
SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new JdkSerializationRedisSerializer(classLoader)));
//设置properties文件中设置的各项属性
if (redisProperties.getTimeToLive() != null) {
config = config.entryTtl(redisProperties.getTimeToLive());
}
if (redisProperties.getKeyPrefix() != null) {
config = config.prefixKeysWith(redisProperties.getKeyPrefix());
}
if (!redisProperties.isCacheNullValues()) {
config = config.disableCachingNullValues();
}
if (!redisProperties.isUseKeyPrefix()) {
config = config.disableKeyPrefix();
}
return config;
}
}
RedisCacheManager的直接构造类,该类保存了配置类RedisCacheConfiguration,该配置在会传递给RedisCacheManager
public static class RedisCacheManagerBuilder {
private final RedisCacheWriter cacheWriter;
//默认缓存配置使用RedisCacheConfiguration的默认配置
//该默认配置缓存时默认将k按字符串存储,v按jdk序列化数据存储(见下一代码块)
private RedisCacheConfiguration defaultCacheConfiguration = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig();
private final Map<String, RedisCacheConfiguration> initialCaches = new LinkedHashMap<>();
private boolean enableTransactions;
boolean allowInFlightCacheCreation = true;
private RedisCacheManagerBuilder(RedisCacheWriter cacheWriter) {
this.cacheWriter = cacheWriter;
}
//传入RedisCacheManagerBuilder使用的缓存配置规则RedisCacheConfiguration类
public RedisCacheManagerBuilder cacheDefaults(RedisCacheConfiguration defaultCacheConfiguration) {
Assert.notNull(defaultCacheConfiguration, "DefaultCacheConfiguration must not be null!");
this.defaultCacheConfiguration = defaultCacheConfiguration;
return this;
}
//使用默认defaultCacheConfiguration创建RedisCacheManager
public RedisCacheManager build() {
RedisCacheManager cm = new RedisCacheManager(cacheWriter, defaultCacheConfiguration, initialCaches,
allowInFlightCacheCreation);
cm.setTransactionAware(enableTransactions);
return cm;
}
RedisCacheConfiguration保存了许多缓存规则,这些规则都保存在RedisCacheManagerBuilder的RedisCacheConfiguration defaultCacheConfiguration属性中,并且当RedisCacheManagerBuilder创建RedisCacheManager传递过去
public class RedisCacheConfiguration {
private final Duration ttl;
private final boolean cacheNullValues;
private final CacheKeyPrefix keyPrefix;
private final boolean usePrefix;
private final SerializationPair<String> keySerializationPair;
private final SerializationPair<Object> valueSerializationPair;
private final ConversionService conversionService;
//默认缓存配置
public static RedisCacheConfiguration defaultCacheConfig(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
DefaultFormattingConversionService conversionService = new DefaultFormattingConversionService();
registerDefaultConverters(conversionService);
return new RedisCacheConfiguration(Duration.ZERO, true, true, CacheKeyPrefix.simple(),
SerializationPair.fromSerializer(RedisSerializer.string()),//key使用字符串
SerializationPair.fromSerializer(RedisSerializer.java(classLoader)), conversionService);
//value按jdk序列化存储
}
RedisCacheManager在创建RedisCache时将RedisCacheConfiguration传递过去,并在创建RedisCache时通过createRedisCache()起作用
public class RedisCacheManager extends AbstractTransactionSupportingCacheManager {
private final RedisCacheWriter cacheWriter;
private final RedisCacheConfiguration defaultCacheConfig;
private final Map<String, RedisCacheConfiguration> initialCacheConfiguration;
private final boolean allowInFlightCacheCreation;
protected RedisCache createRedisCache(String name, @Nullable RedisCacheConfiguration cacheConfig) {
//如果调用该方法时RedisCacheConfiguration有值则使用定制的,否则则使用默认的RedisCacheConfiguration defaultCacheConfig,即RedisCacheManagerBuilder传递过来的配置
return new RedisCache(name, cacheWriter, cacheConfig != null ? cacheConfig : defaultCacheConfig);
}
RedisCache,Redis缓存,具体负责将缓存数据序列化的地方,将RedisCacheConfiguration的序列化对SerializationPair提取出来并使用其定义的序列化方式分别对k和v进行序列化操作
public class RedisCache extends AbstractValueAdaptingCache {
private static final byte[] BINARY_NULL_VALUE = RedisSerializer.java().serialize(NullValue.INSTANCE);
private final String name;
private final RedisCacheWriter cacheWriter;
private final RedisCacheConfiguration cacheConfig;
private final ConversionService conversionService;
public void put(Object key, @Nullable Object value) {
Object cacheValue = preProcessCacheValue(value);
if (!isAllowNullValues() && cacheValue == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(String.format(
"Cache '%s' does not allow 'null' values. Avoid storing null via '@Cacheable(unless=\"#result == null\")' or configure RedisCache to allow 'null' via RedisCacheConfiguration.",
name));
}
//在put k-v时使用cacheConfig中的k-v序列化器分别对k-v进行序列化
cacheWriter.put(name, createAndConvertCacheKey(key), serializeCacheValue(cacheValue), cacheConfig.getTtl());
}
//从cacheConfig(即RedisCacheConfiguration)中获取KeySerializationPair并写入key值
protected byte[] serializeCacheKey(String cacheKey) {
return ByteUtils.getBytes(cacheConfig.getKeySerializationPair().write(cacheKey));
}
//从cacheConfig(即RedisCacheConfiguration)中获取ValueSerializationPair并写入key值
protected byte[] serializeCacheValue(Object value) {
if (isAllowNullValues() && value instanceof NullValue) {
return BINARY_NULL_VALUE;
}
return ByteUtils.getBytes(cacheConfig.getValueSerializationPair().write(value));
}
代码地址:https://gitee.com/monsterwh/springboot_project/tree/master/springboot_cache
视频地址:https://www.bilibili.com/video/av38657363?p=83