bp反向传播+3层全连接神经网络+softmax交叉熵损失+代码实现详解
引言
上学期选了"模式识别与机器学习"这门课,但是没有选"模式识别"这门硬课,略有遗憾,因此博主想利用假期补一补基础。
一、理论部分
如标题所述,本文探讨的是bp反向传播这一经典算法。算法分析如下:



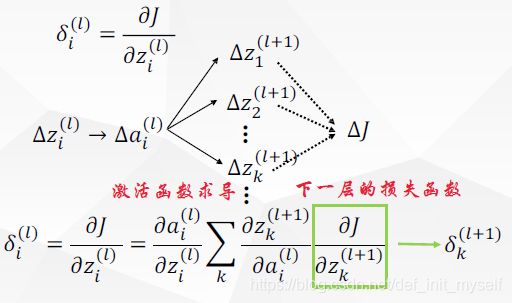

三、代码部分
1、初始化训练数据
from numpy import array,dot,exp,transpose,hstack,vstack,random,arange,linalg
from math import log10
###############训练样本###################
class1 = transpose(array([[1.58, 2.32, -5.8], [0.67, 1.58, -4.78], [1.04, 1.01, -3.63],
[-1.49, 2.18, -3.39], [-0.41, 1.21, -4.73], [1.39, 3.16, 2.87],
[1.20, 1.40, -1.89], [-0.92, 1.44, -3.22], [0.45, 1.33, -4.38],
[-0.76, 0.84, -1.96]], dtype=float).reshape(-1, 3))#在复制样本的时候首先改成标准格式,然后检查有没有小数点变成逗号的情况
class2 = transpose(array([[ 0.21, 0.03, -2.21], [0.37, 0.28, -1.8], [0.18, 1.22, 0.16],
[-0.24, 0.93, -1.01], [-1.18, 0.39, -0.39], [0.74, 0.96, -1.16],
[-0.38, 1.94, -0.48], [0.02, 0.72, -0.17], [0.44, 1.31, -0.14],
[0.46, 1.49, 0.68]], dtype=float).reshape(-1, 3))
class3 = transpose(array([[-1.54, 1.17, 0.64], [5.41, 3.45, -1.33], [1.55, 0.99, 2.69],
[1.86, 3.19, 1.51], [1.68, 1.79, -0.87], [3.51, -0.22, -1.39],
[1.40, -0.44, -0.92], [0.44, 0.83, 1.97], [0.25, 0.68, -0.99],
[0.66, -0.45, 0.08]], dtype=float).reshape(-1, 3))
data=hstack([class1,class2,class3])#按水平方向组合
###############样本标签###################
y1 = array([[1,0,0] * len(transpose(class1))]).reshape(len(transpose(class1)), 3)
y2 = array([[0,1,0] * len(transpose(class2))]).reshape(len(transpose(class2)), 3)
y3 = array([[0,0,1] * len(transpose(class3))]).reshape(len(transpose(class3)), 3)
lable = vstack([y1,y2,y3])#按垂直方向组合
2、定义激活函数
#############激活函数sigmoid##############
def sigmoid(x):
y = 1 / (1 + exp(-x))#numpy中可以直接对向量求exp
return y
#########激活函数sigmoid求导##############
def sigmoid_diff(x):
y = exp(-x) / pow((1 + exp(-x)), 2)
return y
#########softmax激活函数##############
def softmax(x):
y = exp(x) / linalg.norm(exp(x),ord=1)
return y
3、定义神经网络类
##############定义神经网络类##############
class neural_bp(object):
##############初始化网络结构##############
def __init__(self,num_input,num_hidden,num_output,data_input,lable_input):
###初始化权向量矩阵###
self.w1 = array([[0.2] * num_hidden * num_input]).reshape(num_hidden, num_input)#参考k-means中初始化矩阵的形式
self.w2 = array([[0.2] * num_hidden * num_output]).reshape(num_output, num_hidden)
self.b1 = array([[0.2] * num_hidden]).reshape(num_hidden, 1)
self.b2 = array([[0.2] * num_output]).reshape(num_output, 1)
###初始化输入###
self.data_input=data_input#样本输入
self.lable_input = lable_input
self.n = 0.
self.m = 0.
##############损失函数##############
def lossfunction(self):
###单个样本交叉熵损失###
loss=-log10(dot(self.lable_input, self.data_output_output))
return loss
##############神经元值##############
def neural_value(self):
self.data_hidden_input = dot(self.w1, self.data_input) + self.b1#隐层输入,即z
self.data_hidden_output = sigmoid(self.data_hidden_input)#经过激活函数后的输出,即a
self.data_output_input = dot(self.w2, self.data_hidden_output) + self.b2#输出层输入,y
self.data_output_output = softmax(self.data_output_input)#经过softmax激活后函数值
##############参数更新##############
def Parameter_update(self):
###w2 Forward Pass###
#为self.data_hidden_output
###w2 Backward Pass###
self.w2_loss_function =self.data_output_output - transpose(self.lable_input)#所有样本的最后一层误差函数为(3,30)
###w2_gradient###
self.w2_gradient = dot(self.w2_loss_function, transpose(self.data_hidden_output))#第一项为最后一层误差函数
###b2_gradient###
self.b2_gradient = self.w2_loss_function
###w1 Forward Pass###
#为data_input
###w1 Backward Pass###
self.data_hidden_input_diff = sigmoid_diff(self.data_hidden_input)#输出层输入的激活函数求导
self.w1_loss_diff = self.w2_loss_function
self.w1_loss_function = self.data_hidden_input_diff * dot(transpose(self.w2), self.w1_loss_diff)
###w1_gradient###
self.w1_gradient = dot(self.w1_loss_function, transpose(self.data_input))
###b1_gradient###
self.b1_gradient = self.w1_loss_function
###w_update###
self.w2 = self.w2 - 0.009 * self.w2_gradient
self.w1 = self.w1 - 0.09 * self.w1_gradient
self.b2 = self.b2 - 0.09 * self.b2_gradient
self.b1 = self.b1 - 0.09 * self.b1_gradient
#############样本测试##############
def test(self):
for i in range(30):
self.data_input = array(data[:,i]).reshape(3,1)#格式问题需要重新定义格式
self.lable_input = array(lable[i,:]).reshape(1,3)
self.neural_value()
self.a1 = list(self.data_output_output)
self.c1 = self.a1.index(max(self.a1))#保存最大值的位置
self.a2 = list(transpose(self.lable_input))#注意要加转置!
self.c2 = self.a2.index(max(self.a2))#保存最大值的位置
if self.c2 == self.c1:
self.n = self.n+1
self.m = self.m + 1
print self.n / self.m
4、主程序
if __name__ == '__main__':
n =3000
print n
d = neural_bp(3, 3, 3, array([0, 0, 0], dtype=float), array([0, 0, 0])) # 注意不能将初始化放在循环里
###样本集中随机抽取一列###
for i in range(n):
col_rand = arange(data.shape[1])
random.shuffle(col_rand)
data_col_rand = data[:, col_rand[0:1]]
###标签集中抽取对应行###
lable_row_rand = lable[col_rand[0:1],:]
d.data_input = data_col_rand
d.lable_input = lable_row_rand
d.neural_value()
d.Parameter_update()
if i ==n/4:
print d.lossfunction()
if i ==n/2:
print d.lossfunction()
if i ==3*n/4:
print d.lossfunction()
if i ==(n-1):
print d.lossfunction()
d.test()
四、小结
学习率0.09,迭代次数3000次时,实验可得分类正确率为0.8附近:
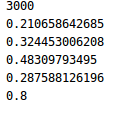
尚存在的问题:
(1)、仅使用sigmod函数作为激活函数
(2)、仅选择随机梯度下降,且学习率不一定合适
(3)、没有对梯度下降进行优化
(3)、未对训练样本就进行"训练集"“验证集”"测试集"的划分
(4)、未加入正则项
以上问题有时间的话会进行补充。
欢迎大家围观、补充、批评、指正!