Nginx分享
一起学习nginx
- 一起学习nginx
- 1.nginx介绍
- 2.nginx优点
- 3.nginx安装
- 4.nginx常用命令
- 5.nginx基本配置
- 5.1 默认配置
- 5.2 虚拟目录
- 5.3 日志格式
- 6.nginx模块
- 6.1 http_stub_status_module(状态检查)
- 6.2 ngx_http_sub_module(响应内容过滤器)
- 6.3 ngx_http_limit_conn_module、ngx_http_limit_req_module(请求限制)
- 6.4 ngx_http_access_module、ngx_http_auth_basic_module(访问控制)
- 6.5 ngx_http_gzip_module、ngx_http_headers_module、ngx_http_referer_module(静态服务)
- 6.6 ngx_http_proxy_module,ngx_http_upstream_module,ngx_http_upstream_check_module(代理服务)
- 6.7 ngx_http_rewrite_module(重定向)
- 6.8 ngx_http_ssl_module(https)
- 6.9 nginx-rtmp-module
- 6.10 ngx_http_autoindex_module(目录索引)
- 6.11 ngx_http_map_module
- 6.12 ngx_http_geo_module、ngx_http_geoip_module
- 6.13 ngx_http_secure_link_module
- 6.14 ngx_stream_core_module(待实践)
- 6.15 ngx_http_mirror_module 流量拷贝(待实践)
- 7.扩展
- 7.1 location语法
- 7.2 root 、alias的区别
- 7.3 try_files的用法
- 7.4 nginx日志切割
- 7.5 nginx + php-fpm + php (ngx_http_fastcgi_module)
- 7.5 nginx + keepalive 高可用
- 7.6 nginx+upsync+consul 构建动态nginx配置系统
- 7.7 nginx + docker
- 7.8 nginx + lua
- 8.nginx优化
- 9.结束
1.nginx介绍
地址:http://nginx.org/
文档:http://nginx.org/en/docs/
摘自于官网 http://nginx.org/en/#basic_http_features:
nginx [engine x] is an HTTP and reverse proxy server, a mail proxy server, and a generic TCP/UDP proxy server, originally written by Igor Sysoev.
2.nginx优点
轻量级;
默认采用I/O多路复用的epoll模型处理io事件;
支持sendfile,高效传输文件.实现“零拷贝”;
实现cpu亲和性,尽量长时间的使worker进程运行在指定的cpu上,减少切换cpu导致的cpu缓存不能被使用;
3.nginx安装
yum 安装 :yum install nginx
源码 安装
# wget http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.15.2.tar.gz
-- 新建用户和组
# groupadd nginx
# useradd nginx -g nginx
-- 编译,安装
# yum -y install gcc gcc-c++ zlib zlib-devel pcre-devel openssl openssl-devel
# ./configure \
--group=nginx \
--user=nginx \
--prefix=/app/nginx-1.15.2 \
--error-log-path=/app/nginx-1.15.2/log/error.log \
--http-log-path=/app/nginx-1.15.2/log/access.log \
--pid-path=/app/nginx-1.15.2/nginx.pid \
--with-http_stub_status_module \
--with-http_ssl_module \
--with-http_gzip_static_module \
--with-http_sub_module \
--with-http_realip_module \
--with-pcre
# make & make install
Linux 服务启动脚本:nginx.sh
# cp nginx /etc/init.d
# chkconfig --add nginx
# chkconfig --level 2345 nginx on4.nginx常用命令
# nginx [-?hvVtq] [-s signal] [-c filename] [-p prefix] [-g directives]
-v : 显示版本信息并退出
-V : 显示版本和配置选项信息,然后退出
-t : 检测配置文件是否有语法错误,然后退出
-s signal : 给一个 nginx 主进程发送信号:stop(快速停止), quit(从容停止), reload(重新加载配置文件,平滑重启)
-c filename : 指定配置文件
除了nginx -s 之外,也可以
ps -ef | grep nginx
kill -QUIT 主进程号 :从容停止Nginx
kill -TERM 主进程号 :快速停止Nginx
pkill -9 nginx :强制停止Nginx
kill -HUP 主进程号 : 重新加载配置文件,平滑重启
# ps -ef|grep nginx|grep 'master process' |grep -v grep|awk '{print $2}' | xargs kill -HUP
# kill -HUP 'cat /app/nginx/nginx.pid'5.nginx基本配置
5.1 默认配置
# 设置nginx worker工作用户
user nobody;
# 设置nginx 工作进程数量,一般设置为和cpu核数一样
worker_processes 1;
# 错误日志 级别
error_log logs/error.log info;
# 启动进程指定pid
pid logs/nginx.pid;
#工作模式及每个worker进程的最大并发链接数
events {
use epoll;
worker_connections 1024;
}
#http默认配置
http {
#文件扩展名与类型映射表
include mime.types;
#默认文件类型
default_type application/octet-stream;
#日志格式
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#访问日志 log_format的名字
access_log logs/access.log main;
#开启sendfile
sendfile on;
#访问超时时间
keepalive_timeout 65;
#压缩
#gzip on;
server {
listen 80;
server_name default;
access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
error_page 404 /404.html;
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}
#server {
#...
#}
}
5.2 虚拟目录
- Nginx基于端口的虚拟主机配置
Nginx基于ip的虚拟主机配置
# ifconfig eth0:0 192.168.79.128 # ifconfig eth0:1 192.168.79.129 listen 192.168.79.128:80; listen 192.168.79.129:80;Nginx基于域名的虚拟主机配置
http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/server_names.html
nginx.conf 增加:include /app/nginx-1.15.2/conf/vhost/*.conf;
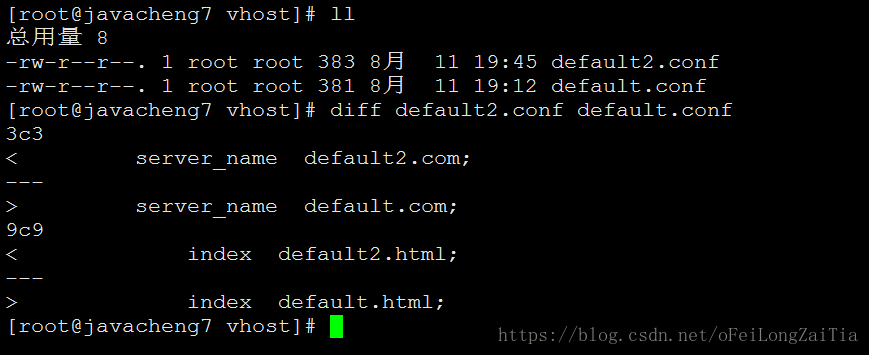
即可实现同端口不同域名的访问。
Nginx 的虚拟主机是通过HTTP请求中的Host值来找到对应的虚拟主机配置,如果找不到呢?那 Nginx 就会将请求送到指定了 default_server 的 节点来处理,如果没有指定为 default_server 的话,按照nginx默认加载顺序加载.
listen 80 default_server ;5.3 日志格式
nginx内置变量
http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_core_module.html#variables
#定义日志
log_format logJson '{"timestamp": "$time_local", '
'"fields": { '
'"remote_addr": "$remote_addr", '
'"remote_user": "$remote_user", '
'"body_bytes_sent": "$body_bytes_sent", '
'"request_time": "$request_time", '
'"status": "$status", '
'"request": "$request", '
'"request_method": "$request_method", '
'"http_referrer": "$http_referer", '
'"body_bytes_sent":"$body_bytes_sent", '
'"http_x_forwarded_for": "$http_x_forwarded_for", '
'"http_user_agent": "$http_user_agent" }}';
include /app/nginx-1.15.2/conf/log_json_format.conf;6.nginx模块
6.1 http_stub_status_module(状态检查)
server {
listen 80;
server_name m1.com;
location /status {
stub_status on;
access_log off;
allow 127.0.0.1;
allow 192.168.79.1;
deny all;
}
}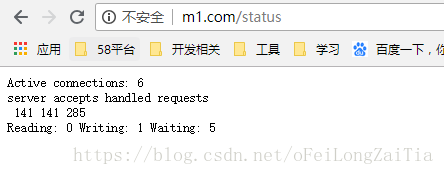
第一个 server 表示Nginx启动到现在共处理了 141 个连接
第二个 accepts 表示Nginx启动到现在共成功创建 141 次握手
第三个 handled requests 表示总共处理了 285 次请求
6.2 ngx_http_sub_module(响应内容过滤器)
server {
listen 80;
server_name m2.com;
location / {
root html;
index default4.html;
sub_filter_types *;
sub_filter 'hello' 'foo';
sub_filter 'word' 'bar';
sub_filter_once off;
}
}sub_filter指令: sub_filter string(原字符串) replacement(用于替换的字符串);
支持正则,replacement是 新的字符串,它里面可以带变量。
sub_filter_once指令:sub_filter_once on | off;
用于设置字符串替换次数,默认只替换一次。如果是on,默认只替换第一次匹配到的到字 符,如果是off,那么所有匹配到的字符都会被替换;
sub_filter_types指令:sub_filter_types *
用于指定需要被替换的MIME类型,默认为“text/html”,如果制定为*,那么所有的;
可用在反向代理之后,替换
6.3 ngx_http_limit_conn_module、ngx_http_limit_req_module(请求限制)
HTTP请求建立在一次TCP连接基础上,一次TCP连接至少产生一次HTTP请求。
默认支持这几个模块。
./configure –help | grep limit
–without-http_limit_conn_module disable ngx_http_limit_conn_module
–without-http_limit_req_module disable ngx_http_limit_req_module
–without-stream_limit_conn_module disable ngx_stream_limit_conn_module
limit_conn_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=conn_zone:1m;
limit_req_zone $binary_remote_addr zone=req_zone:1m rate=1r/s;
server {
listen 80;
server_name m3.com;
location /test1.html{
root html;
index default4.html;
limit_conn conn_zone 1;
}
location /test2.html{
root html;
index default4.html;
#limit_req zone=req_zone burst=3 nodelay;
limit_req zone=req_zone;
}
}conn参考:https://blog.csdn.net/wanglei_storage/article/details/51076561
req参考:https://blog.csdn.net/keketrtr/article/details/75315330
6.4 ngx_http_access_module、ngx_http_auth_basic_module(访问控制)
location /test1.html{
root html;
index default4.html;
allow 127.0.0.1;
deny all;
}Nginx基于access_module有局限性
原理:基于客户端的IP,但是对于Nginx来说,它不会管你哪个是真正的客户端,如果我们的访问不是客户端与服务端直接连接,而是通过了一层代理,比如它的代理可以负载均衡、CDN的这种代理实现,也就是我们的访问不是客户端直接访问的服务端,而是通过其他的中间件访问服务端,这时候会出现一个问题,因为Nginx的access_module它是基于remote_addr这个变量来识别客户端的IP的,那么如果一个ip通过中间件访问服务端,那么Nginx认为访问的ip就是中间件的IP,那么我们在基于IP做限制的时候,那么其实是没有作用的。所以这样的话,准确性是不高的,所以就是利用nginx的access_module有局限性
解决方法:
①:采用别的http头信息访问控制,如HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR。
![]()
为防止XFF欺骗,第一层代理,用$remote_addr来设置 X-Forwarded-For即可
proxy_set_header Host $proxy_host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $remote_addr;②:通过HTTP自定义变量传递
nginx用户认证配置
htpasswd -bc auth_htpwd admin admin –创建用户密码
htpasswd -b auth_htpwd admin2 admin –增加用户
htpasswd -D auth_htpwd admin3 –删除用户
location /test2.html{
root html;
auth_basic "nginx basic http test !";
auth_basic_user_file /app/nginx-1.15.2/conf/auth_htpwd;
index default4.html;
}6.5 ngx_http_gzip_module、ngx_http_headers_module、ngx_http_referer_module(静态服务)
压缩和http缓存
server {
listen 80;
server_name m5.com;
sendfile on;
location ~ ^.*\.(html|htm|gif|jpg|jpeg|png|ico|txt|js|css)$ {
root html;
gzip on;
gzip_http_version 1.1;
gzip_comp_level 2;
gzip_disable "MSIE [1-6]."
gzip_types text/plain application/javascript application/x-javascript text/css application/xml text/javascript application/x-httpd-php image/jpeg image/gif image/png;
expires 1d;
}
}压缩参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/zhang-shijie/p/5451919.html
HTTP缓存原理:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000010690320
防盗链
server_name m5.com;
...
location ~ /tp.bb {
valid_referers none blocked m5.com;
if ($invalid_referer) {
return 403;
}
rewrite ^/ http://m5.com/tp.jpg;
}// 点击 正常
http://m5.com/test3.html
// 点击 503
http://m1.com/test3.html
跨域
location ~ /test1.html {
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Origin *;
add_header Access-Control-Allow-Methods GET,POST,PUT,DELETE,OPTIONS;
root html;
}其它站点的跨域,可以通过反向代理解决。
6.6 ngx_http_proxy_module,ngx_http_upstream_module,ngx_http_upstream_check_module(代理服务)
正向代理
// 代理的是客户端
listen 80;
server_name localhost ;
resolver 8.8.8.8;
location ~ / {
proxy_pass http://$http_host$request_uri;
}正向代理和反向代理区别:
从用途 上来讲:
正向代理的典型用途是为在防火墙内的局域网客户端提供访问Internet的途径。正向代理还可以使用缓冲特性减少网络使用率。反向代理的典型用途是将 防火墙后面的服务器提供给Internet用户访问。反向代理还可以为后端的多台服务器提供负载平衡,或为后端较慢的服务器提供缓冲服务。
另外,反向代理还可以启用高级URL策略和管理技术,从而使处于不同web服务器系统的web页面同时存在于同一个URL空间下。
从安全性 来讲:
正向代理允许客户端通过它访问任意网站并且隐藏客户端自身,因此你必须采取安全措施以确保仅为经过授权的客户端提供服务。
反向代理对外都是透明的,访问者并不知道自己访问的是一个代理。
参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/Anker/p/6056540.html
反向代理
// 代理的是内网的服务
server {
listen 80;
server_name m6.com;
location ~ / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8080;
proxy_connect_timeout :10;跟后端服务器连接的超时时间,发起握手等候响应超时时间
proxy_read_timeout:60;连接成功后_等候后端服务器响应时间_其实已经进入后端的排队之中等候处理(也可以说是后端服务器处理请求的时间)
proxy_send_timeout :60;设置代理服务器转发请求的超时时间,同样指完成两次握手后的时间,如果超过这个时间代理服务器没有数据转发到后端服务器,nginx将关闭连接
}
}反向代理-负载均衡
upstream backend {
server localhost:8080;
server localhost:8081;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name m6.com;
location ~ ^/index.jsp$ {
proxy_pass http://backend;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_connect_timeout 30;
proxy_send_timeout 60;
proxy_read_timeout 60;
proxy_buffer_size 32k;
proxy_buffering on;
proxy_buffers 4 128k;
proxy_busy_buffers_size 256k;
proxy_max_temp_file_size 256k;
}
}Nginx proxy_set_header中 $proxy_host host http_host的区别
https://blog.csdn.net/a19860903/article/details/49914131
nginx 的 upstream目前支持 4 种方式的分配
1)、轮询 rr(默认)
每个请求按时间顺序逐一分配到不同的后端服务器,如果后端服务器down掉,能自动剔除。
2)、weight
指定轮询几率,weight和访问比率成正比,用于后端服务器性能不均的情况。
upstream backend {
server A max_fails=3 fail_timeout=30s weight=9;
server B max_fails=3 fail_timeout=30s weight=9;
server C backup;
server D backup;
}max_fails=3 fail_timeout=30s代表在30秒内请求某一应用失败3次,认为该应用宕机,后等待30秒,这期间内不会再把新请求发送到宕机应用,而是直接发到正常的那一台,时间到后再有请求进来继续尝试连接宕机应用且仅尝试1次,如果还是失败,则继续等待30秒…以此循环,直到恢复。
2)、ip_hash
每个请求按访问ip的hash结果分配,这样每个访客固定访问一个后端服务器,可以解决session的问题。
upstream backend {
server A;
server B;
ip_hash;
}3)、fair(第三方)
按后端服务器的响应时间来分配请求,响应时间短的优先分配。
4)、url_hash(第三方)
按访问url的hash结果来分配请求,使每个url定向到同一个后端服务器,后端服务器为缓存时比较有效。
后端负载健康检查-ngx_http_upstream_check_module
参考配置:http://tengine.taobao.org/document_cn/http_upstream_check_cn.html
upstream cluster {
server localhost:8081;
server localhost:8080;
#添加了nginx_upstream_check_module模块之后,该项生效
#用于检测后方realserver的健康状态,如果后端服务器不可用,则请求不转发到这台服务器。
#interval:每隔3s检测一次
#rise:检测次数,如果连续检测2次都成功,那就证明该后端服务器好使
#fall:检测次数,如果连续检测5次都失败,那就证明该后端服务器不好使
#timeout:超时时间为1s
check interval=3000 rise=2 fall=5 timeout=1000;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name m6.com;
location ~ ^/index2.jsp {
proxy_pass http://cluster;
}
location ~ /status {
check_status;
access_log off;
}
}有个小问题,访问status,报500错误,可能是nginx版本过高和下载的插件不匹配
2018/08/15 17:45:41 [error] 54468#0: *213 http upstream check module can not find any check server, make sure you’ve added the check servers, client: 192.168.79.1, server: m6.com, request: “GET /status HTTP/1.1”, host: “m6.com”
6.7 ngx_http_rewrite_module(重定向)
http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_rewrite_module.html#set
参考1:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000008102599
参考2:https://blog.csdn.net/fantexi1984/article/details/70307261
注意:regex正则表达是的匹配对象是上文的$uri变量,即不带host和参数的。
root html;
location /test1 {
default_type application/json;
return 200 '{"status":"success"}';
}
location /test2 {
#chrome
if ( $http_user_agent ~ Chrome ){
rewrite ^/test2/(.*)$ /msie/$1 break;
}
rewrite ^/test2/(.*)$ /msie/ie.html break;
}
#把/test3 重写向到 /test1 ,找不到直接break;
location /test3 {
rewrite ^/test3 /test1 break;
}
#把/test4 重写向到 /test1 ,url地址不变化
location /test4 {
rewrite ^/test4 /test1 last;
}
#把/test5 重写向到 /test1 ,url地址变化
location /test5 {
rewrite ^/test5 /test1 redirect;
}
#删除URL结尾的斜杠
location /test6/ {
rewrite ^/(.*) $1 redirect;
}
#把/test7?a=a&b=b 重写向到 /test0?a=b
location /test7/ {
rewrite ^/(.*) /$1?a=$arg_b? redirect;
}
#/test8/post-21.html?a=1&b=2 重定向到 /test0?page=21&a=1&b=1
location /test8 {
rewrite /test8/post-(\d+).html /test0?page=$1 permanent;
}
6.8 ngx_http_ssl_module(https)
1.https简介
HTTPS其实是有两部分组成:HTTP + SSL / TLS,也就是在HTTP上又加了一层处理加密信息的模块。服务端和客户端的信息传输都会通过TLS进行加密,所以传输的数据都是加密后的数据
2.https协议原理
首先,客户端与服务器建立连接,各自生成私钥和公钥,是不同的。服务器返给客户端一个公钥,然后客户端拿着这个公钥把要搜索的东西加密,称之为密文,并连并自己的公钥一起返回给服务器,服务器拿着自己的私钥解密密文,然后把响应到的数据用客户端的公钥加密,返回给客户端,客户端拿着自己的私钥解密密文,把数据呈现出来
证书和私钥的生成:
1.创建服务器证书密钥文件 server.key:
openssl genrsa -des3 -out server.key 1024
输入密码,确认密码,自己随便定义,但是要记住,后面会用到。
2.创建服务器证书的申请文件 server.csr
openssl req -new -key server.key -out server.csr
输出内容为:
Enter pass phrase for root.key: ← 输入前面创建的密码
Country Name (2 letter code) [AU]:CN ← 国家代号,中国输入CN
State or Province Name (full name) [Some-State]:BeiJing ← 省的全名,拼音
Locality Name (eg, city) []:BeiJing ← 市的全名,拼音
Organization Name (eg, company) [Internet Widgits Pty Ltd]:MyCompany Corp. ← 公司英文名
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []: ← 可以不输入
Common Name (eg, YOUR name) []: ← 此时不输入
Email Address []:admin@mycompany.com ← 电子邮箱,可随意填
Please enter the following ‘extra’ attributes
to be sent with your certificate request
A challenge password []: ← 可以不输入
An optional company name []: ← 可以不输入
4.备份一份服务器密钥文件
cp server.key server.key.org
5.去除文件口令
openssl rsa -in server.key.org -out server.key
6.生成证书文件server.crt
openssl x509 -req -days 365 -in server.csr -signkey server.key -out server.crt配置文件
server {
listen 443 ssl;
#证书(公钥.发送到客户端的)
ssl_certificate vhost/ssl/server.crt;
#私钥
ssl_certificate_key vhost/ssl/server.key;
#设置缓存
ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
ssl_session_timeout 5m;
server_name m8.com;
location / {
proxy_pass https://www.taobao.com/;
}
}http和https共存
server {
listen 80;
listen 443 ssl;
server_name xx.com;
root /var/www/html;
#ssl on; //这行必须要注释掉
ssl_certificate vhost/ssl/server.crt;
ssl_certificate_key vhost/ssl/server.key;
}
nginx强制使用https访问(http跳转到https)
server {
listen 80;
server_name test.com;
rewrite ^(.*)$ https://$host$1 permanent;
}6.9 nginx-rtmp-module
1.安装nginx-rtmp-module。
2.安装ffmpeg
由于CentOS没有官方FFmpeg rpm软件包。但是,我们可以使用第三方YUM源(Nux Dextop)完成此工作。
rpm -Uvh http://li.nux.ro/download/nux/dextop/el6/x86_64/nux-dextop-release-0-2.el6.nux.noarch.rpm
yum install ffmpeg ffmpeg-devel -y
3.配置nginx
放到nginx main域
rtmp {
server {
listen 1935;
application myapp {
live on;
}
application hls {
live on;
hls on;
hls_path /tmp/hls;
}
}
}vlc播放器 打开 rtmp://192.168.79.128:1935/myapp/test1
// 开始推流
ffmpeg -re -i /app/cc.mp4 -c copy -f flv rtmp://192.168.79.128:1935/myapp/test1
或
ffmpeg -re -i rtsp://184.72.239.149/vod/mp4://BigBuckBunny_175k.mov -c copy -f flv rtmp://192.168.79.128:1935/myapp/test1hls播放
ffmpeg -re -i rtsp://184.72.239.149/vod/mp4://BigBuckBunny_175k.mov -c copy -f flv rtmp://192.168.79.128:1935/hls/test2视频地址:http://m9.com/hls/test2.m3u8
播放:http://m9.com/ckplayer/ccc.html
6.10 ngx_http_autoindex_module(目录索引)
ngx_http_autoindex_module只在 ngx_http_index_module模块未找到索引文件时发出请求
server {
listen 80;
server_name m10.com;
location / {
autoindex on;
autoindex_localtime on;
autoindex_exact_size on;
}
}6.11 ngx_http_map_module
ngx_http_map_module模块可以创建变量,这些变量的值与另外的变量值相关联。允许分类或者同时映射多个值到多个不同值并储存到一个变量中,map指令用来创建变量,但是仅在变量被接受的时候执行视图映射操作,对于处理没有引用变量的请求时,这个模块并没有性能上的缺失。
map $http_user_agent $agent {
~Trident ie;
~Chrome chrome;
}
map $arg_a $stream {
default "c";
"1" "a";
"2" "b";
}
upstream a{
server localhost:8081;
}
upstream b{
server localhost:8080;
}
upstream c{
server hf.ahnw.gov.cn;
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name map.com;
location /useragent {
default_type text/plain;
set $agent2 $agent;
echo useragent:$agent2;
}
location / {
proxy_pass http://$stream;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header Host $proxy_host;
}
} 6.12 ngx_http_geo_module、ngx_http_geoip_module
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/heshan307/article/details/54232114
ngx_http_geo_module
1 geo $arg_ip $str {
2 default xxx;
3 127.0.0.1 localhost;
4 127.0.0.2 222;
5
6 include /app/nginx-1.15.2/conf/ips.conf;
7 }
8 server {
9 listen 80;
10 server_name m12.com;
11
12 location /hello {
13 default_type text/plain;
14 echo str:$str;
15 }
16
17 error_page 404 /404.html;
18 error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
19 location = /50x.html {
20 root html;
21 }
22 }访问:http://m12.com/hello?ip=127.0.0.2
http://m12.com/hello?ip=8.8.8.8
ngx_http_geoip_module 使用
安装: Centos 6.x:(rpm -Uvh:升级一个包)
rpm -Uvh http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/x86_64/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
yum install GeoIP GeoIP-data GeoIP-devel
./configure --group=nginx --user=nginx --prefix=/app/nginx-1.15.2 --error-log-path=/app/nginx-1.15.2/log/error.log --http-log-path=/app/nginx-1.15.2/log/access.log --pid-path=/app/nginx-1.15.2/nginx.pid --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-http_sub_module --with-http_geoip_module --with-http_secure_link_module --with-stream --with-stream_ssl_module --with-http_realip_module --with-pcre --add-module=/app/software/echo-nginx-module-master --add-module=/app/software/nginx_upstream_check_module-mastergeoip_country /app/nginx-1.15.2/conf/GeoIP.dat;
geoip_city /app/nginx-1.15.2/conf/GeoLiteCity.dat;
...省略...
location /bb {
if ($geoip_country_code != CN) {
return 403;
}
default_type text/plain;
return 200 "$remote_addr $geoip_country_name $geoip_country_code $geoip_city";
}6.13 ngx_http_secure_link_module
参考:http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_secure_link_module.html#secure_link_md5
http://www.iigrowing.cn/nginx-ngx-http-secure-link-module-mo-kuai-ji-ben-zhi-ling-zheng-li.html
location / {
secure_link $arg_md5,$arg_expires;
secure_link_md5 "$secure_link_expires$uri bbb";
if ( $secure_link = "" ) {
return 403;
}
if ( $secure_link = "0" ) {
return 410;
}
}访问:http://m13.com/tp.jpg?md5=jBospNIehv3PZx5QgeCsSg&expires=1609344000
6.14 ngx_stream_core_module(待实践)
nginx在版本1.9.0以后支持tcp的负载均衡,低版本可以使用在编译时增加tcp代理模块支持,即nginx_tcp_proxy_module
stream{
upstream mysql{
server 192.168.1.106:3306 weight=1;
server 192.168.1.108:3306 weight=1;
}
server{
listen 3306;
proxy_pass mysql;
}
}6.15 ngx_http_mirror_module 流量拷贝(待实践)
http://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_mirror_module.html
参考:https://www.centos.bz/2017/08/nginx-request-copy-ngx_http_mirror_module/
# original配置
location / {
mirror /mirror;
mirror_request_body off;
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:9502;
}
# mirror配置
location /mirror {
#internal指令指定某个location只能被“内部的”请求调用,外部的调用请求会返回”Not found” (404)
internal;
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8081$request_uri;
proxy_set_header X-Original-URI $request_uri;
}7.扩展
7.1 location语法
格式:location [=|~|~*|^~|@] pattern { … }
匹配优先级:
1. =
2. (None) 如果 pattern 完全匹配 URI(不是只匹配 URI 的头部)
3. ^~
4. ~ 或 ~*
5. (None) pattern 匹配 URI 的头部
server {
listen 80;
server_name location.com;
location = / {
default_type text/plain;
echo 'A';
}
location = /login {
default_type text/plain;
echo 'B';
}
location ^~ /static/ {
default_type text/plain;
echo 'C';
}
location ~ \.(gif|jpg|png|js|css)$ {
default_type text/plain;
echo 'D';
}
location ~* \.css$ {
default_type text/plain;
echo 'E';
}
location / {
default_type text/plain;
echo 'F';
}
}http://location.com/ 将匹配规则A
http://location.com/login 将匹配规则B
http://location.com/register 则匹配规则F
http://location.com/static/a.html 将匹配规则C
http://location.com/a.css 将匹配规则D和规则E,但是规则D顺序优先,规则E不起作用
http://location.com/static/c.css 则优先匹配到 规则C
http://location.com/a.CSS 则匹配规则E, 而不会匹配规则D,因为规则E不区分大小写。
@ 用于定义一个 Location 块,且该块不能被外部 Client 所访问,只能被 Nginx 内部配置指令所访问,比如 try_files or error_page
location /404 {
error_page 404 = @my404;
}
location @my404 {
rewrite ^(.)*$ http://demo.cssmoban.com/cssthemes2/ftpm_42/index.html;
}访问:http://location.com/404
7.2 root 、alias的区别
location /bbb/ {
if ( $arg_p = '1' ) {
root html/test;
break;
}
alias html/test;
}root的用法
访问 http://test2.com/bbb/root.html?p=1
这样配置的结果就是当客户端请求 /bbb/root.html 的时候,
Nginx把请求映射为html/test/bbb/root.html
alias的用法
访问 http://test2.com/bbb/root.html?p=2
这样配置的结果就是当客户端请求 /bbb/root.html 的时候,
Nginx把请求映射为html/test/root.html
注意 alias uri结尾的/ 和 alias的/
7.3 try_files的用法
Syntax: try_files file … uri;
location /ccc {
index test.html;
try_files $uri $uri/ @backend;
}
location @backend {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8080;
}访问:http://test2.com/ccc/index.html?p=11
访问: http://test2.com/ccc 如果文件不存在,目录存在且索引不到的时候,403
7.4 nginx日志切割
定时任务nginx_log_cut.sh
#!/bin/bash
year=`date +%Y`
month=`date +%m`
day=`date +%d`
logs_backup_path="/app/dailylog" #日志存储路径
logs_path="/app/nginx-1.15.2/log/" #要切割的日志
logs_error="error"
logs_access="access"
pid_path="/app/nginx-1.15.2/nginx.pid"
[ -d $logs_backup_path ]||mkdir -p $logs_backup_path
rq=`date +%Y%m%d`
mv ${logs_path}${logs_access}.log ${logs_backup_path}/${logs_access}_${rq}.log
mv ${logs_path}${logs_error}.log ${logs_backup_path}/${logs_error}_${rq}.log
kill -USR1 $(cat $pid_path)定时任务:
crontab –e 每天0点
0 0 * * * bash /app/dailylog/ngnix_log_cut.sh
7.5 nginx + php-fpm + php (ngx_http_fastcgi_module)
参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/jecyhw/p/5504855.html
nginx本身不能处理PHP,它只是个web服务器,当接收到请求后,如果是php请求,则发给php解释器处理,并把结果返回给客户端。
nginx一般是把请求发fastcgi管理进程处理,fascgi管理进程选择cgi子进程处理结果并返回被nginx
PHP-FPM是一个PHP FastCGI管理器,是只用于PHP的,可以在 http://php-fpm.org/download下载得到.
PHP-FPM其实是PHP源代码的一个补丁,旨在将FastCGI进程管理整合进PHP包中。必须将它patch到你的PHP源代码中,在编译安装PHP后才可以使用。
新版PHP已经集成php-fpm了,不再是第三方的包了,推荐使用。PHP-FPM提供了更好的PHP进程管理方式,可以有效控制内存和进程、可以平滑重载PHP配置,比spawn-fcgi具有更多优点,所以被PHP官方收录了。在./configure的时候带 –enable-fpm参数即可开启PHP-FPM,其它参数都是配置php的,具体选项含义可以查看这里。
# 添加 epel 源
# rpm -Uvh http://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/x86_64/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm
# yum install
gcc bison bison-devel zlib-devel libmcrypt-devel mcrypt mhash-devel openssl-devel libxml2-devel libcurl-devel bzip2-devel readline-devel libedit-devel sqlite-devel
#编译安装php7
#配置php-fpm
#启动php-fpm
#配置nginx
fastcgi_connect_timeout 300;
fastcgi_send_timeout 300;
fastcgi_read_timeout 300;
fastcgi_buffer_size 64k;
fastcgi_buffers 4 64k;
fastcgi_busy_buffers_size 128k;
fastcgi_temp_file_write_size 128k;
server {
listen 80;
server_name php.com;
location ~ \.php$ {
root html;
fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;#php-fpm的默认端口是9000
fastcgi_index index.php;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
include fastcgi_params;
}
error_page 404 /404.html;
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}访问:http://php.com/index.php
7.5 nginx + keepalive 高可用
参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/youzhibing/p/7327342.html
关闭防火区:
chkconfig --level 2345 iptables off
sed -i 's/SELINUX=enforcing/SELINUX=disabled/g' /etc/selinux/config
service iptables stop
setenforce 0keepalived配置
master配置:
global_defs {
notification_email {
350938930@qq.com
}
notification_email_from 350938930@qq.com
smtp_server 127.0.0.1
smtp_connect_timeout 30
router_id LVS_DEVEL
vrrp_skip_check_adv_addr
#vrrp_strict #不关闭 启动keep自动加一个drop 虚拟ip的防火墙限制
vrrp_garp_interval 0
vrrp_gna_interval 0
}
vrrp_script chk_http_port {
script "/app/keepalived/check_nginx_pid.sh"
interval 1 #(检测脚本执行的间隔)
weight 2
}
vrrp_instance VI_1 {
state MASTER
interface eth0
virtual_router_id 51
priority 100
advert_int 1
authentication {
auth_type PASS
auth_pass 1111
}
track_script {
chk_http_port #(调用检测脚本)
}
virtual_ipaddress {
192.168.79.110
}
}check_nginx_pid.sh
#!/bin/bash
A=`ps -C nginx --no-header |wc -l`
if [ $A -eq 0 ];then
# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx #重启nginx
if [ `ps -C nginx --no-header |wc -l` -eq 0 ];then #nginx重启失败,则停掉keepalived服务,进行VIP转移
killall keepalived
fi
fibackup配置:
state BACKUP
priority 101
#其他一样/app/keepalived/keepalived -f /app/keepalived/keepalived.conf
killall keepalived
ip addr show 查看vip是否开启
访问:http://192.168.79.110/123.html
7.6 nginx+upsync+consul 构建动态nginx配置系统
参考:https://github.com/weibocom/nginx-upsync-module
参考:http://blog.51cto.com/lee90/2056182
使用1.8的nginx + upsync1.8
consul安装
# wget https://releases.hashicorp.com/consul/0.8.1/consul_0.8.1_linux_amd64.zip
# unzip consul_0.8.1_linux_amd64.zip && mv consul /usr/local/bin
# nohup consul agent -server -bootstrap-expect=1 -data-dir=/tmp/consul -node=consul1 -bind=192.168.79.131 -dc=dc1 -client 0.0.0.0 -ui &
# nohup consul agent -server -data-dir=/tmp/consul -node=consul2 -bind=192.168.79.128 -dc=dc1 -client 0.0.0.0 -ui -join 192.168.79.131 &
# nohup consul agent -server -data-dir=/tmp/consul -node=consul3 -bind=192.168.79.129 -dc=dc1 -client 0.0.0.0 -ui -join 192.168.79.131 &
查看节点
# consul members
也可以这样加入
# consul join 192.168.79.129 192.168.79.128访问ui:http://192.168.79.131:8500/ui/#/dc1/services
添加节点信息:
curl -X PUT -d '{"weight":10, "max_fails":2, "fail_timeout":10, "down":0}' http://192.168.79.131:8500/v1/kv/upstreams/test/192.168.79.128:8080
curl -X PUT -d '{"weight":10, "max_fails":2, "fail_timeout":10, "down":0}' http://192.168.79.131:8500/v1/kv/upstreams/test/192.168.79.129:8080配置nginx
#consul-test 不能用 _ 不然报400错误
upstream consul-test {
server 192.168.79.129:8081 down;#必须节点,要不语法不能检测通过
upsync 127.0.0.1:8500/v1/kv/upstreams/test upsync_timeout=6m upsync_interval=500ms upsync_type=consul strong_dependency=off;
upsync_dump_path /usr/local/nginx/conf/servers_test.conf;
}
...
location / {
proxy_pass http://consul-test;
}测试:Tomcat shutdown看效果正常。
7.7 nginx + docker
构建dockfile
FROM centos
MAINTAINER 2018-08-19 javacheng javacheng@qq.com
RUN yum -y install gcc* wget git make pcre-devel zlib-devel openssl-devel \
&& mkdir -p /app/nginx \
&& cd /app \
&& git clone https://github.com/yaoweibin/nginx_upstream_check_module.git && wget http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.14.0.tar.gz \
&& tar -zxvf /app/nginx-1.14.0.tar.gz -C /app/
RUN useradd -s /sbin/nologin -M nginx
WORKDIR /app/nginx-1.14.0
RUN ./configure --prefix=/app/nginx --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-http_stub_status_module --add-module=../nginx_upstream_check_module && make && make install
RUN ln -s /app/nginx/sbin/* /usr/local/sbin/
EXPOSE 80 443
WORKDIR /app/nginx/sbin
CMD ["nginx", "-g", "daemon off;"]docker命令
# docker build -t nginx:test .
# docker run -p 8899:80 -d 8ebc27ac899f nginx配置
upstream test {
server 192.168.79.131:8080;
}
。。。
location / {
proxy_pass http://test;
#root html;
#index index.html index.htm;
}访问:http://192.168.79.131:8899/
7.8 nginx + lua
安装
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/dexter_wang/article/details/71454467
安装lua环境,安装LuaJIT 2.0,下载解压ngx_devel_kit,下载解压lua-nginx-module
./configure --group=nginx --user=nginx --prefix=/app/nginx-1.15.2 --error-log-path=/app/nginx-1.15.2/log/error.log --http-log-path=/app/nginx-1.15.2/log/access.log --pid-path=/app/nginx-1.15.2/nginx.pid --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-http_sub_module --with-http_geoip_module --with-http_secure_link_module --with-stream --with-stream_ssl_module --with-http_realip_module --with-pcre --add-module=/app/software/echo-nginx-module-master --add-module=/app/software/nginx_upstream_check_module-master --add-module=/app/nginx-1.15.2/nginx-rtmp-module-master --add-module=/app/ngx_devel_kit-0.2.19 --add-module=/app/lua-nginx-module-master如果编译出现如下错误:
./configure: error: ngx_http_lua_module requires the Lua library
export LUAJIT_LIB=/usr/local/luajit/lib
export LUAJIT_INC=/usr/local/luajit/include/luajit-2.0
nginx: error while loading shared libraries: libluajit-5.1.so.2: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
ln -s /usr/local/luajit/lib/libluajit-5.1.so.2 /lib64/libluajit-5.1.so.2(本例是安装在 /usr/local/luajit下)
案例:
https://github.com/openresty/lua-nginx-module#content_by_lua
http://outofmemory.cn/code-snippet/14396/nginx-and-lua
输出:
server_name testlua.com;
location / {
default_type text/plain;
content_by_lua '
local p = ngx.var.arg_p
ngx.say("hello lua!!!!," , p)';
}访问限制
location /hello.html {
access_by_lua '
if ngx.var.remote_addr == "192.168.79.129" then
ngx.exit(ngx.HTTP_FORBIDDEN)
end
if ngx.var.remote_addr == "192.168.79.131" then
ngx.exec("@client")
end
';
root html;
}
location @client{
proxy_pass http://192.168.79.131:8080;
}根据ip控制转发
location /index2.jsp {
default_type "text/html";
content_by_lua_file /app/nginx-1.15.2/conf/vhost/ppppp.lua;
}
location @aaa {
proxy_pass http://localhost:8080;
}
location @bbb {
proxy_pass http://192.168.79.131:8080;
}clientIP = ngx.req.get_headers()["X-Real-IP"]
if clientIP == nil then
clientIP = ngx.req.get_headers()["x_forwarded_for"]
end
if clientIP == nil then
clientIP = ngx.var.remote_addr
end
local memcached = require "resty.memcached"
local memc, err = memcached:new()
if not memc then
ngx.say("failed to instantiate memc: ", err)
return
end
local ok, err = memc:connect("127.0.0.1", 11211)
if not ok then
ngx.say("failed to connect: ", err)
return
end
local res, flags, err = memc:get(clientIP)
ngx.say("value key: ",res,clientIP)
if err then
ngx.say("failed to get clientIP ", err)
return
end
if res == "1" then
ngx.say("/hello.html")
return
end
ngx.exec("@bbb")openresty
我们可以使用OpenResty来搭建开发环境,OpenResty将Nginx核心、LuaJIT、许多有用的Lua库和Nginx第三方模块打包在一起;这样开发人员只需要安装OpenResty,不需要了解Nginx核心和写复杂的C/C++模块就可以,只需要使用Lua语言进行Web应用开发了。
★★http://openresty.org/cn/download.html
★★http://blog.51cto.com/xsunday/2049650
https://blog.csdn.net/forezp/article/details/78616856
https://www.cnblogs.com/xd502djj/p/6097773.html
安装:
wget https://openresty.org/download/openresty-1.13.6.2.tar.gz
./configure –with-http_stub_status_module –with-http_v2_module –with-http_ssl_module
gmake && gmake install
默认install创建链接:ln -sf /usr/local/openresty/nginx/sbin/nginx /usr/local/openresty/bin/openresty
启动:
/usr/local/openresty/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /app/nginx_aaa/nginx.conf
8.nginx优化
worker_rlimit_nofile
设置毎个进程的最大文件打开数。如果不设的话上限就是系统的ulimit –n的数字,一般为65535。
worker_cpu_affinity
默认情况下,Nginx的多个进程有可能跑在某一个CPU或CPU的某一核上,导致Nginx进程使用硬件的资源不均,因此绑定Nginx进程到不同的CPU上是为了充分利用硬件的多CPU多核资源的目的。
worker_cpu_affinity用来为每个进程分配CPU的工作内核,参数有多个二进制值表示,每一组代表一个进程,每组中的每一位代表该进程使用CPU的情况,1代表使用,0代表不使用。所以我们使用worker_cpu_affinity 0001 0010 0100 1000;来让进程分别绑定不同的核上。
worker_processes 4;
worker_cpu_affinity 0001 0010 0100 1000;
# 1.9之后可以用auto实现
worker_cpu_affinity auto;查看绑定情况:
ps -eo pid,args,psr |grep nginx
worker_processes
为cpu核数 =cpu个数*核数
查看物理CPU个数
cat /proc/cpuinfo| grep “physical id”| sort| uniq| wc -l
查看每个物理CPU中core的个数(即核数)
cat /proc/cpuinfo| grep “cpu cores”| sort| uniq| wc -l
查看逻辑CPU的个数
cat /proc/cpuinfo| grep “processor”| sort| uniq| wc -l
或者
显示cpu的相关信息
lscpu
use epoll
设置事件驱动模型使用epoll。事件驱动模型有select、poll、poll等。
- select先创建事件的描述符集合,对于一个描述符,可以关注其上面的Read事件、Write事件以及Exception事件,所以要创建三类事件描述符集合,分别用来处理Read事件的描述符、Write事件的描述符、Exception事件的描述符,然后调用底层的select()函数,等待事件发生,轮询所有事件描述符集合的每一个事件描述符,检查是否有事件发生,有的话就处理。select效率低,主要是轮询效率低,而且还要分别轮询三个事件描述符的集合。
- poll方法与select类似,都是先创建一个关注事件的描述符集合,再去等待这些事件发生,然后再轮询描述符集合,检查有无事件发生,如果有,就去处理。不同点是poll为Read事件、Write事件以及Exception事件只创建一个集合,在每个描述符对应的结构上分别设置Read事件、Write事件以及Exception事件。最后轮询的时候,可以同时检察权这三个事件是否发生。可以说,poll库是select库的优化实现。
- epoll是Nginx支持的高性能事件驱动库之一。是公认的非常优秀的事件驱动模型。和poll库跟select库有很大的不同,最大区别在于效率。我们知道poll库跟select库都是创建一个待处理的事件列表,然后把这个列表发给内核,返回的时候,再去轮询检查这个列表,以判断事件是否发生。这样在描述符多的应用中,效率就显得比较低下了。一种比较好的方式是把列表的管理交由内核负责,一旦某种事件发生,内核就把发生事件的描述符列表通知给进程,这样就避免了轮询整个描述符列表。首先,epoll库通过相关调用同志内核创建一个有N个描述符的事件列表,然后给这些描述符设置所关注的事件,并把它添加到内核的事件列表中去。完成设置以后,epoll库就开始等待内核通知事件发生了,某一事件发生后,内核讲发生事件的描述符列表上报给epoll库,得到事件列表的epoll库,就可以进行事件处理了。epoll库在linux平台是高效的,它支持一个进程打开大数目的事件描述符,上限是系统可以打开文件的最大数目;同时,epoll库的IO效率不随描述符数量的增加而线性下降,因为它只会对内核上报的活跃的描述符进行操作。
worker_connections
设置一个进程理论允许的最大连接数,理论上越大越好,但不可以超过worker_rlimit_nofile的值。
accept_mutex
1.11.3版本之前默认开
当一个新连接到达时,如果激活了accept_mutex,那么多个Worker将以串行方式来处理,其中有一个Worker会被唤醒,其他的Worker继续保持休眠状态;如果没有激活accept_mutex,那么所有的Worker都会被唤醒,不过只有一个Worker能获取新连接,其它的Worker会重新进入休眠状态,这就是「惊群问题」
events {
accept_mutex off;
} multi_accept on;
Nginx服务器的每个工作进程可以同时接受多个新的网络连接,但是需要在配置文件中配置,此指令默认为关闭,即默认为一个工作进程只能一次接受一个新的网络连接,打开后几个同时接受多个
server_tokens off;
隐藏ngxin版本号
sendfile
设置为on表示启动高效传输文件的模式。sendfile可以让Nginx在传输文件时直接在磁盘和tcp socket之间传输数据。从Linux内核中的一个文件描述符(FD)拷贝数据到另一个文件描述符比read() + write()更有效率。如果这个参数不开启,会先在用户空间(Nginx进程空间)申请一个buffer,用read函数把数据从磁盘读到cache,再从cache读取到用户空间的buffer,再用write函数把数据从用户空间的buffer写入到内核的buffer,最后到tcp socket。开启这个参数后可以让数据不用经过用户buffer。
tcp_nopush
sendfile为on时这里也应该设为on,数据包会累积一下再一起传输,可以提高一些传输效率。建议做静态文件服务器使用。
tcp_nodelay
小的数据包不等待直接传输。默认为on。
看上去是和tcp_nopush相反的功能,但是两边都为on时nginx也可以平衡这两个功能的使用。
设置为on非常适合于实时频繁发送小数据.(比如图片,pdf,ppt文件之类不是小数据的,应该设置为off)
gzip on
启用gzip,对响应数据进行在线实时压缩,减少数据传输量。
gzip on;
gzip_min_length 1k;
gzip_buffers 4 32k;
gzip_http_version 1.1;
gzip_comp_level 9;
gzip_disable "msie6";
gzip_types text/css text/xml application/javascript;
gzip_vary on;9.结束
推荐pdf书
| 书名 | 地址 |
|---|---|
| Nginx高性能Web服务器详解.pdf | right-aligned |
| 精通nginx.pdf | centered |
| 深入理解Nginx模块开发与架构解析第2版LinuxUnix技术丛书.pdf | are neat |