基于WSGI实现的mini-web框架
GitHub链接https://github.com/ChenJhua/WsgiMiniWeb
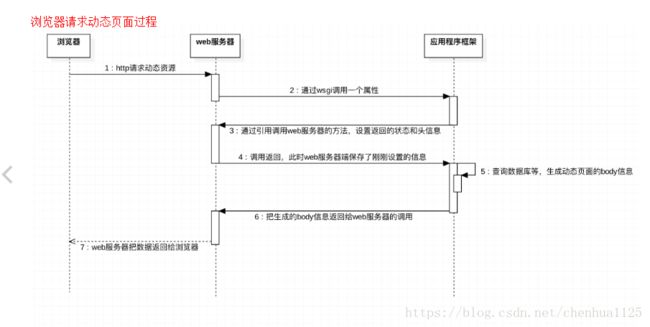
浏览器请求动态页面过程
为什么使用WSGI?
WSGI允许开发者将选择web框架和web服务器分开。可以混合匹配web服务器和web框架,选择一个适合的配对。
web服务器必须具备WSGI接口,所有的现代Python Web框架都已具备WSGI接口,它让你不对代码作修改就能使服务器和特点的web框架协同工作。
定义WSGI接口
WSGI接口定义非常简单,它只要求Web开发者实现一个函数,就可以响应HTTP请求。我们来看一个最简单的Web版本的“Hello World!”:
def application(environ, start_response):
start_response('200 OK', [('Content-Type', 'text/html')])
return 'Hello World!'application()函数就是符合WSGI标准的一个HTTP处理函数,它接收两个参数:
environ:一个包含所有HTTP请求信息的dict对象;
start_response:一个发送HTTP响应的函数。整个application()函数本身没有涉及到任何解析HTTP的部分,也就是说,把底层web服务器解析部分和应用程序逻辑部分进行了分离,这样开发者就可以专心做一个领域了
不过,等等,这个application()函数怎么调用?如果我们自己调用,两个参数environ和start_response我们没法提供,返回的str也没法发给浏览器。
所以application()函数必须由WSGI服务器来调用。有很多符合WSGI规范的服务器。而我们此时的web服务器项目的目的就是做一个既能解析静态网页还可以解析动态网页的服务器
my_web.py(实现具体路由匹配返回的页面内容)
import re
import urllib.parse
# 自动添加数据到字典
import pymysql
def route(my_date):
def func_out(func):
# 程序一运行就有参数
URL_FUNC_DICT[my_date] = func
def func_in():
# 这里使用的话需要调用index()才能添加
# URL_FUNC_DICT[my_date] = func
func()
return func_in
return func_out
# 函数列表
URL_FUNC_DICT = dict()
# 处理动态资源
@route("/index.html")
def index(ret):
with open("./templates/index.html") as f:
content = f.read()
# 创建数据库连接
db = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', port=3306, user='root', password='mysql', database='stock_db',
charset='utf8')
# 游标
cursor = db.cursor()
sql = "select * from info;"
cursor.execute(sql)
my_stock = cursor.fetchall()
html_template = """
%s
%s
%s
%s
%s
%s
%s
%s
"""
html = ""
for i in my_stock:
html += html_template % (i[0], i[1], i[2], i[3], i[4], i[5], i[6], i[7], i[1])
content = re.sub(r"\{%content%\}", html, content)
cursor.close()
db.close()
return content
@route("/center.html")
def center(ret):
with open("./templates/center.html") as f:
content = f.read()
# 创建数据库连接
db = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', port=3306, user='root', password='mysql', database='stock_db',
charset='utf8')
# 游标
cursor = db.cursor()
sql = "select i.code,i.short,i.chg,i.turnover,i.price,i.highs,f.note_info from info as i inner join focus as f on i.id = f.id;"
cursor.execute(sql)
my_stock = cursor.fetchall()
html_template = """
%s
%s
%s
%s
%s
%s
%s
修改
"""
html = ""
for i in my_stock:
html += html_template % (i[0], i[1], i[2], i[3], i[4], i[5], i[6], i[0], i[0])
content = re.sub(r"\{%content%\}", html, content)
return content
@route(r"/add/(\d+)\.html")
def add(ret):
stock_code = ret.group(1)
# 创建数据库连接
db = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', port=3306, user='root', password='mysql', database='stock_db',
charset='utf8')
# 游标
cursor = db.cursor()
# 1.检查股票是否存在
sql = "select * from info where code=%s"
cursor.execute(sql, [stock_code])
info_result = cursor.fetchall()
if not info_result:
cursor.close()
db.close()
return "没有这个股票"
# 2.股票是否关注了
sql = "select * from focus where id=(select id from info where code=%s)"
cursor.execute(sql, [stock_code])
focus_result = cursor.fetchall()
if focus_result:
cursor.close()
db.close()
return "股票已被关注"
# 3.添加数据
# sql = "select short from info where code=%s"
sql = "insert into focus(id) (select id from info where code=%s)"
cursor.execute(sql, [stock_code])
db.commit()
cursor.close()
db.close()
return "添加成功:%s" % stock_code
@route(r"/del/(\d+)\.html")
def my_delete(ret):
stock_code = ret.group(1)
# 创建数据库连接
db = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', port=3306, user='root', password='mysql', database='stock_db',
charset='utf8')
# 游标
cursor = db.cursor()
# 1.检查股票是否存在
sql = "select * from info where code=%s"
cursor.execute(sql, [stock_code])
info_result = cursor.fetchall()
if not info_result:
cursor.close()
db.close()
return "没有这个股票,无法删除"
# 2.股票是否关注了
sql = "select * from focus where id=(select id from info where code=%s)"
cursor.execute(sql, [stock_code])
focus_result = cursor.fetchall()
if not focus_result:
cursor.close()
db.close()
return "股票没有被关注,无法删除"
# 3.添加数据
# sql = "select short from info where code=%s"
sql = "delete from focus where id=(select id from info where code=%s)"
cursor.execute(sql, [stock_code])
db.commit()
cursor.close()
db.close()
return "删除成功:%s" % stock_code
@route(r"/update/(\d+)\.html")
def my_update(ret):
stock_code = ret.group(1)
with open("./templates/update.html") as f:
content = f.read()
# 创建数据库连接
db = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', port=3306, user='root', password='mysql', database='stock_db',
charset='utf8')
# 游标
cursor = db.cursor()
sql = "select note_info from focus where id=(select id from info where code=%s);"
cursor.execute(sql, [stock_code])
stock_info = cursor.fetchone()[0]
content = re.sub(r"\{%code%\}", stock_code, content)
content = re.sub(r"\{%note_info%\}", stock_info, content)
cursor.close()
db.close()
return content
@route(r"/update/(\d+)/(.*)\.html")
def my_change_info(ret):
stock_code = ret.group(1)
my_note_info = ret.group(2)
my_note_info = urllib.parse.unquote(my_note_info)
# 创建数据库连接
db = pymysql.connect(host='localhost', port=3306, user='root', password='mysql', database='stock_db',
charset='utf8')
# 游标
cursor = db.cursor()
sql = "update focus set note_info=%s where id=(select id from info where code=%s);"
cursor.execute(sql, [my_note_info, stock_code])
db.commit()
cursor.close()
db.close()
return "修改成功"
def application(environ, start_response):
file_name = environ["url"]
start_response('200 OK', [('Content-Type', 'text/html;charset=utf-8')])
try:
# key是键,value是值
for key, values in URL_FUNC_DICT.items():
ret = re.match(key, file_name)
if ret:
return values(ret)
# else:
# return values()
else:
return "%s 没有发现对应的函数 or 异常" % file_name
except:
return "异常"
web_server.py(服务器入口,启动服务器)
import socket
import re
import multiprocessing
import dynamic.my_web
class WebServer(object):
def __init__(self):
# 1. 创建套接字
self.tcp_server_socket = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
self.tcp_server_socket.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1)
# 2. 绑定
self.tcp_server_socket.bind(("", 7890))
# 3. 变为监听套接字
self.tcp_server_socket.listen(128)
def __del__(self):
# 6. 关闭监听套接字
self.tcp_server_socket.close()
def service_client(self, new_socket):
"""为客户端返回数据"""
# 1.接收浏览器发送过来的request请求(符合http协议的格式) ,即http请求
# GET /index.html HTTP/1.1
request = new_socket.recv(1024).decode("utf-8")
request_lines = request.splitlines()
print("")
print(">" * 20)
print(request_lines)
# 2.通过正则解析 GET /index.html HTTP/1.1 获取文件名 即 /index.html
file_name = ""
ret = re.match(r"[^/]+(/[^ ]*)", request_lines[0])
if ret:
file_name = ret.group(1)
if file_name == "/":
file_name = "/index.html"
if not file_name.endswith('.html'): # 静态资源
# 3. 通过文件名 /index.html 打开文件读取数据后 组织符合http格式的response
# 即应答报文 header + body 给浏览器
try:
f = open("./static" + file_name, "rb")
except:
response = "HTTP/1.1 404 NOT FOUND\r\n"
response += "\r\n"
response += "------file not found-----"
new_socket.send(response.encode("utf-8"))
else:
# 3.1 准备发送给浏览器的数据---response_header
response_header = "HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\n"
response_header += "\r\n"
# 3.2 准备发送给浏览器的数据---response_body
response_body = f.read()
f.close()
# 将response header发送给浏览器
new_socket.send(response_header.encode("utf-8"))
# 将response body发送给浏览器
new_socket.send(response_body)
else:
# 传参字典
env = dict()
env["url"] = file_name
# 调用接口
response_body = dynamic.my_web.application(env, self.set_respose_header)
# 需要函数调用后才有实例属性,设置应答头
response_header = "HTTP/1.1 %s\r\n" % self.statue
# response_header += "%s:%s\r\n" % (self.headers[0][0], self.headers[0][1])
for i in self.headers:
response_header += "%s:%s\r\n" % (i[0], i[1])
response_header += "\r\n"
# 设置应答体
response = response_header + response_body
new_socket.send(response.encode("utf-8"))
# 关闭套接
new_socket.close()
def set_respose_header(self, statue, headers):
self.statue = statue
self.headers = headers
def run_for_ever(self):
"""用来完成整体的控制"""
while True:
# 4. 等待新客户端的链接
new_socket, client_addr = self.tcp_server_socket.accept()
# 5. 为这个客户端服务
p = multiprocessing.Process(target=self.service_client, args=(new_socket,))
p.start()
new_socket.close()
def main():
"""业务流程"""
my_web_server = WebServer()
my_web_server.run_for_ever()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
你可能感兴趣的:(Python)