Python网络爬虫之Re(正则表达式)库入门 学习笔记手札及代码实战
Re(正则表达式)库入门
- 学习笔记手札及单元小结
- Re库的基本使用
-
- re.search(pattern,string,flags=0)
- re.match(pattern,string,flags=0)
- re.findall(pattern,string,flags=0)
- re.split(pattern,string,maxsplit=0,flags=0)
- re.finditer(pattern,string,flags=0)
- re.sub(pattern,repl,string,count=0,flags=0)
- Re库的另一种等价用法
-
- regex = re.compile(pattern,flags=0)
- Re库的Match对象
-
- Match对象介绍
- Match对象实例
- Re库的贪婪匹配和最小匹配
-
- 贪婪匹配
- 最小匹配
学习笔记手札及单元小结
Re库的基本使用
import re
re.search(pattern,string,flags=0)
在一个字符串中搜索匹配正则表达式的第一个位置,返回match对象
>>> import re
>>> match = re.search(r'[1-9]\d{5}','BIT 100081')
>>> if match:
print(match.group(0))
100081
re.match(pattern,string,flags=0)
从一个字符串的开始位置起匹配正则表达式,返回match对象
>>> import re
>>> match = re.match(r'[1-9]\d{5}','BIT 100081')
>>> if match:
match.group(0)
>>> match.group(0)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "" , line 1, in <module>
match.group(0)
AttributeError: 'NoneType' object has no attribute 'group'
>>> match = re.match(r'[1-9]\d{5}','100081 BIT')
>>> if match:
match.group(0)
'100081'
re.findall(pattern,string,flags=0)
搜索字符串,以列表类型返回全部能匹配的子串
>>> import re
>>> ls = re.findall(r'[1-9]\d{5}','BIT100081 TSU100084')
>>> ls
['100081', '100084']
re.split(pattern,string,maxsplit=0,flags=0)
将一个字符串按照正则表达式匹配结果进行分割,返回列表类型
>>> import re
>>> ls = re.findall(r'[1-9]\d{5}','BIT100081 TSU100084')
>>> ls
['100081', '100084']
>>> import re
>>> re.split(r'[1-9]\d{5}','BIT100081 TSU100084')
['BIT', ' TSU', '']
>>> re.split(r'[1-9]\d{5}','BIT100081 TSU100084',maxsplit=1)
['BIT', ' TSU100084']
re.finditer(pattern,string,flags=0)
搜索字符串,返回一个匹配结果的迭代类型,每个迭代元素是match对象
>>> import re
>>> for m in re.finditer(r'[1-9]\d{5}','BIT100081 TSU100084'):
if m:
print(m.group(0))
100081
100084
re.sub(pattern,repl,string,count=0,flags=0)
在一个字符串中替换所有匹配正则表达式的子串,返回替换后的字符串
>>> import re
>>> re.sub(r'[1-9]\d{5}',':zipcode','BIT100081 TSU100084')
'BIT:zipcode TSU:zipcode'
Re库的另一种等价用法
函数式用法:一次性操作
>>> rst = re.search(r'[1-9]\d{5}','BIT 100081')
面向对象用法:编译后的多次操作
>>> import re
>>> pat = re.compile(r'[1-9]\d{5}')
>>> rest = pat.search('BIT 100081')
>>> pat
re.compile('[1-9]\\d{5}')
>>> rest
<re.Match object; span=(4, 10), match='100081'>
>>>
regex = re.compile(pattern,flags=0)
将正则表达式的字符串形式编译成正则表达式对象
>>> regex = re.compile(r'[1-9]\d{5}')
Re库的Match对象
Match对象介绍
Match对象是一次匹配的结果,包含匹配的很多信息
>>> import re
>>> regex = re.compile(r'[1-9]\d{5}')
>>>
>>> import re
>>> match = re.search(r'[1-9]\d{5}','BIT 100081')
>>> if match:
print(match.group(0))
100081
>>> type(match)
Match对象实例
>>> import re
>>> m = re.search(r'[1-9]\d{5}',"BIT100081 TSU100084")
>>> m.re
re.compile('[1-9]\\d{5}')
>>> m.pos
0
>>> m.endpos
20
>>> m.group(0)
'100081'
>>> m.start()
3
>>> m.end()
9
>>> m.span()
(3, 9)
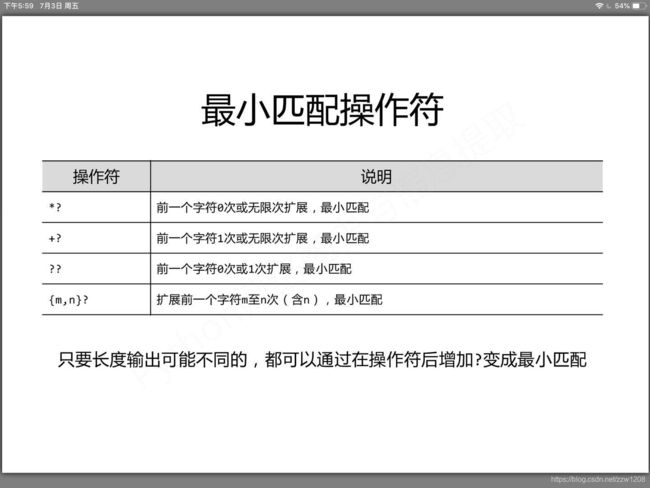
Re库的贪婪匹配和最小匹配
贪婪匹配
Re库默认采用贪婪匹配,即输出匹配最长的子串
>>> match = re.search(r'PY.*N','PYANBNCNDN')
>>> match.group(0)
'PYANBNCNDN'