springboot 2.0.3 源码分析(二)SpringApplication的run方法之prepareEnvironment
prepareEnvironment按字面意思就是准备环境,其源代码如下
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// Create and configure the environment获取或创建环境
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
//配置环境:配置PropertySources和activeProfiles
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
// listeners环境准备(就是广播ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件)。这个listeners就是上一章所讲的内容
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
//将环境绑定到SpringApplication
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
//如果是非web环境,将环境转换成StandardEnvironment,是否是web环境配置也在SpringApplicaiton的构造函数里讲过
if (this.webApplicationType == WebApplicationType.NONE) {
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader())
.convertToStandardEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment);
}
//配置PropertySources对它自己的递归依赖
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}从第一个方法看起,getOrCreateEnvironment,先上源码
private ConfigurableEnvironment getOrCreateEnvironment() {
if (this.environment != null) {
return this.environment;
}
// 根据webApplicationType创建对应的Environment
if (this.webApplicationType == WebApplicationType.SERVLET) {
//标准Servlet环境,也就是我们说的web环境
return new StandardServletEnvironment();
}
//标准环境,非web环境
return new StandardEnvironment();
}从字面上看,这个方法的作用就是获取或创建环境,应该就是存在就直接返回,不存在则创建一个并返回。
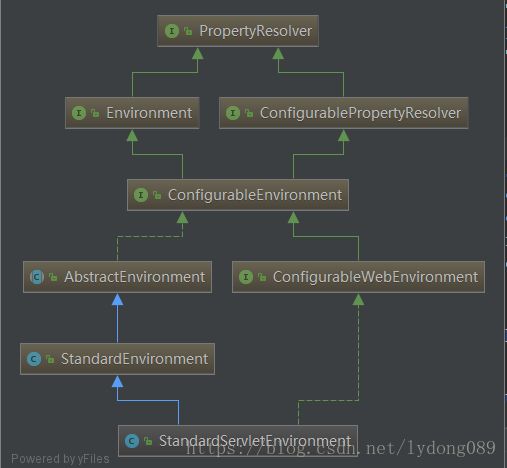
StandardServletEnvironment类图
StandardServletEnvironment继承自StandardEnvironment,也就是web环境是特殊的非web环境,有点类似正方形是特殊的长方形一样。AbstractEnvironment的构造方法调用了customizePropertySources方法,也就说StandardServletEnvironment在实例化的时候,他的customizePropertySources会被调用,customizePropertySources源代码如下
@Override
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
propertySources.addLast(new StubPropertySource(SERVLET_CONFIG_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME));
propertySources.addLast(new StubPropertySource(SERVLET_CONTEXT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME));
if (JndiLocatorDelegate.isDefaultJndiEnvironmentAvailable()) {
propertySources.addLast(new JndiPropertySource(JNDI_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME));
}
super.customizePropertySources(propertySources);
}从上图中可以看出StandardServletEnvironment的customizePropertySources方法只是往propertySources中添加了两个名字叫servletConfigInitParams、servletContextInitParams的StubPropertySource对象,没更多的操作;而StandardEnvironment的customizePropertySources方法则往propertySources中添加了两个包含java系统属性和操作系统环境变量的两个对象:MapPropertySource和SystemEnvironmentPropertySource。
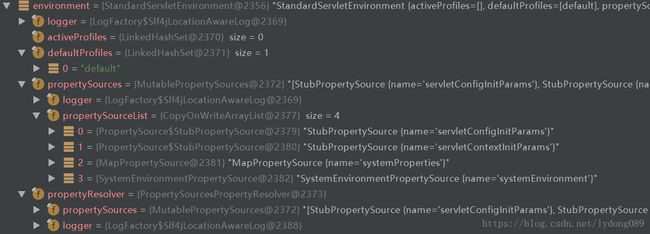
总结下,getOrCreateEnvironment方法创建并返回了一个环境:StandardServletEnvironment,该环境目前包含的内容如下
接着在看configureEnvironment
protected void configureEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment,
String[] args) {
// 配置PropertySources
configurePropertySources(environment, args);
// 配置Profiles
configureProfiles(environment, args);
}
从源码看,将配置任务按顺序委托给configurePropertySources和configureProfiles,那么我们来看看这两个方法
configurePropertySources
protected void configurePropertySources(ConfigurableEnvironment environment,
String[] args) {
MutablePropertySources sources = environment.getPropertySources();
// 此时defaultProperties还是null
if (this.defaultProperties != null && !this.defaultProperties.isEmpty()) {
// 存在的话将其放到最后位置
sources.addLast(
new MapPropertySource("defaultProperties", this.defaultProperties));
}
// 存在命令行参数,则解析它并封装进SimpleCommandLinePropertySource对象,同时将此对象放到sources的第一位置(优先级最高)
if (this.addCommandLineProperties && args.length > 0) {
String name = CommandLinePropertySource.COMMAND_LINE_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME;
if (sources.contains(name)) {
PropertySource source = sources.get(name);
CompositePropertySource composite = new CompositePropertySource(name);
composite.addPropertySource(new SimpleCommandLinePropertySource(
"springApplicationCommandLineArgs", args));
composite.addPropertySource(source);
sources.replace(name, composite);
}
else {
// 将其放到第一位置
sources.addFirst(new SimpleCommandLinePropertySource(args));
}
}
}注释说明是增加、移除或者重排序应用环境中的PropertySource。就目前而言,如果有命令行参数则新增封装命令行参数的PropertySource,并将它放到sources的第一位置。
configureProfiles
protected void configureProfiles(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) {
// 保证environment的activeProfiles属性被初始化了。从PropertySources中查找spring.profiles.active属性
// 存在则将其值添加activeProfiles集合中。我们可以通过命令行参数指定该参数,但我们没有指定
environment.getActiveProfiles(); // ensure they are initialized
// But these ones should go first (last wins in a property key clash)
// 如果存在其他的Profiles,则将这些Profiles放到第一的位置。此时没有,后面有没有后面再说
Set profiles = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.additionalProfiles);
profiles.addAll(Arrays.asList(environment.getActiveProfiles()));
environment.setActiveProfiles(StringUtils.toStringArray(profiles));
}
配置应用环境中的哪些配置文件处于激活状态(或默认激活)。可以通过spring.profiles.active属性在配置文件处理期间激活其他配置文件。说的简单点就是设置哪些Profiles是激活的。
这3个方法都是protected,也就说鼓励被重写。重写configureEnvironment可以完全控制自定义环境,或者重写configurePropertySources或configureProfiles,进行进行更细粒度控制。
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment)
public void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : this.listeners) {
listener.environmentPrepared(environment);
}
}
这个代码有没有很熟悉?参照listeners.starting()。上次广播的是ApplicationStartingEvent事件,而这次广播的是ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件。这里就不和大家一起跟源代码了,大家自行去跟哦。我在这总结下:
过滤出的与ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent相匹配的监听器列表如下,他们的onApplicationEvent会被调用,大致做了以下事情:
ConfigFileApplicationListener
1、加载EnvironmentPostProcessor列表,仍然是从META-INF/spring.factories中加载(在SpringApplication实例化的时候已经加载了,这次是从缓存中读取),然后实例化;
2、将自己也加入EnvironmentPostProcessor列表;ConfigFileApplicationListener实现了EnvironmentPostProcessor接口,可以看它的类图。
3、对EnvironmentPostProcessor列表进行排序;排序之后,EnvironmentPostProcessor列表图如下:
4、遍历EnvironmentPostProcessor列表,调用每个EnvironmentPostProcessor的postProcessEnvironment方法
SystemEnvironmentPropertySourceEnvironmentPostProcessor
将propertySourceList中名为systemEnvironment的SystemEnvironmentPropertySource对象替换成OriginAwareSystemEnvironmentPropertySource对象,source未变,还是SystemEnvironmentPropertySource对象的source;OriginAwareSystemEnvironmentPropertySource是SystemEnvironmentPropertySourceEnvironmentPostProcessor的静态内部类,且继承自SystemEnvironmentPropertySource。具体这么替换出于什么目的,便于原点查找?暂时还未知。
SpringApplicationJsonEnvironmentPostProcessor
spring.application.json(或SPRING_APPLICATION_JSON)是设置在系统属性或系统环境中;
如果spring.application.json(或SPRING_APPLICATION_JSON)有配置,那么给environment的propertySourceList增加JsonPropertySource,并将JsonPropertySource放到名叫systemProperties的PropertySource前;目前没有配置,那么此环境后处理器相当于什么也没做。
CloudFoundryVcapEnvironmentPostProcessor
云平台是否激活,激活了则给environment的propertySourceList增加名为vcap的PropertiesPropertySource对象,并将此对象放到命令行参数PropertySource(名叫commandLineArgs)后。很显然,我们没有激活云平台,那么此环境后处理器相当于什么也没做。
ConfigFileApplicationListener
添加名叫random的RandomValuePropertySource到名叫systemEnvironment的PropertySource后;
并初始化Profiles;初始化PropertiesPropertySourceLoader和YamlPropertySourceLoader这两个加载器从file:./config/,file:./,classpath:/config/,classpath:/路径下加载配置文件,PropertiesPropertySourceLoader加载配置文件application.xml和application.properties,YamlPropertySourceLoader加载配置文件application.yml和application.yaml。目前我们之后classpath:/路径下有个application.yml配置文件,将其属性配置封装进了一个名叫applicationConfig:[]的OriginTrackedMapPropertySource中,并将此对象放到了propertySourceList的最后。
AnsiOutputApplicationListener
设置ansi输出,将AnsiOutput的属性enabled设置成ALWAYS,即允许ANSI-colored输出
LoggingApplicationListener
初始化日志系统
ClasspathLoggingApplicationListener:没开启调试,所以什么也没做
BackgroundPreinitializer:此时什么也没做
DelegatingApplicationListener:此时什么也没做,因为环境中没有配置context.listener.classes属性
FileEncodingApplicationListener:此时什么也没做,环境中没有spring.mandatory-file-encoding属性
EnableEncryptablePropertiesBeanFactoryPostProcessor:此时什么也没有做
environmentPrepared方法会触发所有监听了ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件的监听器,这些监听器目前主要新增了两个PropertySource:RandomValuePropertySource和OriginTrackedMapPropertySource,这个OriginTrackedMapPropertySource一般就是我们应用的配置文件application.yml(application.properties)。
bindToSpringApplication(environment)
/**
* Bind the environment to the {@link SpringApplication}.
* @param environment the environment to bind
*/
protected void bindToSpringApplication(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
try {
Binder.get(environment).bind("spring.main", Bindable.ofInstance(this));
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot bind to SpringApplication", ex);
}
}代码比较简单,应该就是将environment绑定到SpringApplication,可我跟进去发现没有将environment绑定到SpringApplication,执行完bindToSpringApplication方法后,SpringApplication的属性environment仍是null,这我就有点懵圈了,那这个方法到底有什么用,有知道的朋友吗?
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment)
public static void attach(Environment environment) {
// 判断environment是否是ConfigurableEnvironment的实例
Assert.isInstanceOf(ConfigurableEnvironment.class, environment);
// 从environment获取PropertySources
MutablePropertySources sources = ((ConfigurableEnvironment) environment)
.getPropertySources();
PropertySource attached = sources.get(ATTACHED_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME);
if (attached != null && attached.getSource() != sources) {
sources.remove(ATTACHED_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME);
attached = null;
}
if (attached == null) {
// 将sources封装成ConfigurationPropertySourcesPropertySource对象,并把这个对象放到sources的第一位置
sources.addFirst(new ConfigurationPropertySourcesPropertySource(
ATTACHED_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME,
new SpringConfigurationPropertySources(sources)));
}
}将sources封装成了一个名叫configurationProperties的ConfigurationPropertySourcesPropertySource对象,并把这个对象放到了sources的第一个位置。SpringConfigurationPropertySources是一个将MutablePropertySources转换成ConfigurationPropertySources的适配器。这就相当于sources的第一个元素是它自己,形成了一个自己对自己的递归依赖,这么做的目的是什么,暂时还不得而知,也许后面会有所体现,这里先当做一个疑问留着。
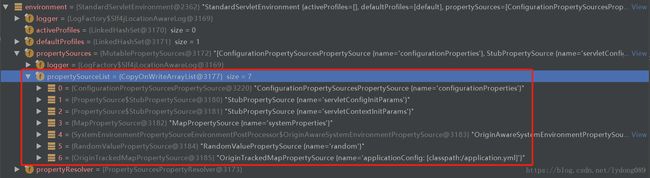
prepareEnvironment执行完后,此时environment中的内容如下:(重点看下propertySourceList)
总结
1、profile
直译的意思总感觉不对(其作用就是指定激活的配置文件,可以区分环境来加载不同的配置),所以文中没有对其进行翻译,直接采用的原单词。有更好理解的小伙伴可以在评论区提供翻译。
2、资源文件
加载外部化配置的资源到environment,Spring Boot设计了一个非常特别的PropertySource顺序,以允许对属性值进行合理的覆盖。具体有哪些外部化配置,以及他们的优先级情况可以参考《Spring Boot Reference Guide》的第24章节
3、prepareEnvironment方法到底做了什么
加载外部化配置资源到environment,包括命令行参数、servletConfigInitParams、servletContextInitParams、systemProperties、sytemEnvironment、random、application.yml(.yaml/.xml/.properties)等;
初始化日志系统。