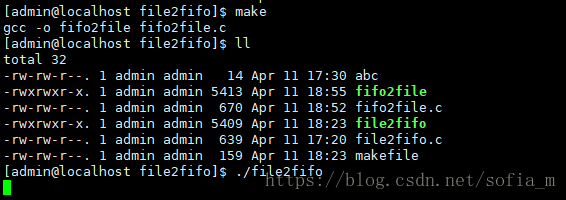
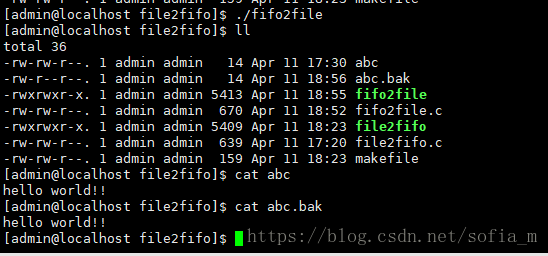
- MacOS上安装Homebrew的详细教程
MacOS上安装Homebrew的详细教程一、引言Homebrew(通常简称为brew)是一款专门为MacOS操作系统设计的开源包管理器,它提供了一种简单、高效的方式来安装、管理和升级命令行工具、编程语言环境以及各种应用程序。其核心概念和作用如下:简化安装流程:在MacOS中,用户无需手动下载软件源码并配置编译环境,只需通过Homebrew提供的命令即可一键安装软件。Homebrew会自动处理软件
- Mac上安装Claude Code的步骤
以下是基于现有信息的简明安装指南,适用于macOS系统。请按照以下步骤操作:前提条件操作系统:macOS10.15或更高版本。Node.js和npm:ClaudeCode基于Node.js,需安装Node.js18+和npm。请检查是否已安装:打开终端,运行node--version和npm--version。如果未安装,访问Node.js官方网站下载并安装最新LTS版本,或使用Homebrew:
- 在Mac上安装Homebrew
XbpObjectivec
macos操作系统
Homebrew是一个流行的软件包管理器,可以在Mac操作系统上轻松安装、更新和管理各种开源软件。下面是在Mac上安装Homebrew的详细步骤。步骤一:打开终端在Mac上,你可以通过启动应用程序文件夹中的"终端"应用程序来打开终端。步骤二:安装Homebrew在终端中,执行以下命令来安装Homebrew:/bin/bash-c"$(curl-fsSLhttps://raw.githubuserc
- 大学专业科普 | 计算智能、信息学与大数据
鸭鸭鸭进京赶烤
大数据
一、专业背景随着信息技术的飞速发展,数据的产生速度呈爆炸式增长,传统数据处理技术已经无法满足如此庞大的数据量和复杂的数据类型,大数据专业应运而生,旨在培养能够应对大数据挑战的专业人才。二、主要课程内容数学基础课程高等数学、概率论与数理统计、线性代数是大数据分析的核心数学基础,为数据处理、算法优化和模型构建提供必要的理论支持。计算机基础课程数据结构与算法、计算机网络、操作系统是大数据技术的重要支撑,
- 大学专业科普 | 人工智能、物联网和云计算技术
鸭鸭鸭进京赶烤
人工智能物联网云计算5G信号处理信息与通信网络
一、专业概述人工智能专业是一门融合计算机科学、数学、信息学等多学科知识的交叉学科。它旨在培养学生掌握人工智能领域的基本理论、方法和技能,以应对人工智能在各个领域的应用需求和发展挑战。二、主要课程基础课程:包括高等数学、线性代数、概率论与数理统计、离散数学等数学基础课程,为人工智能算法提供理论支撑;以及数据结构、算法设计与分析、计算机组成原理、操作系统、计算机网络等计算机科学基础课程,帮助学生理解人
- Reids
子柒s
redis数据库
标题目录Redis概述Redis数据库特点Redis应用场景Redis安装RockyLinux操作系统Windows操作系统Mac操作系统Redis服务启动失败解决方案配置文件详解常见数据类型全局命令String类型字符串数值应用场景列表List基本命令应用场景Hash散列特性基本命令应用场景Set类型基本命令应用场景SortedSet类型有序集合示例基本命令应用场景数据持久化RDB数据持久化SA
- 进程线程,并发并行的基本概念以及线程的初步使用
还得是乖乖
java服务器jvm
今天分享一个关于线程的编写以及制作一个简单的小动态。首先了解并区分一下进程/线程并发/并行这几个概念:进程:在操作系统中,进程是程序的一次动态执行过程。它不仅仅是一个静态的程序代码,还包括程序在执行时所涉及的数据和资源。更精确地说,进程是一个具有独立功能的程序在一个数据集合上运行的过程,它是系统进行资源分配和调度的独立单位。线程:线程是操作系统中程序执行的基本单位,是进程内部的独立执行路径。每个进
- 直接内存溢出
p&f°
JVMjvm
一、什么是直接内存直接捏成是一块由操作系统直接管理的内存,也叫堆外内存可以使用Unsafe或ByteBuffer分配直接内存可用-XX:MaxDirectMemorySize控制,默认是0,表示不限制二、为什么使用直接内存直接内存vs堆内存io效率高推荐参考:Java直接内存与非直接内存性能测试-阿里云开发者社区三、什么场景使用直接内存1有很大的数据需要存储,它的生命周期又很长2适合频繁的IO操作
- 人类文明演进三元辩证模型构建
人类文明演进三元辩证模型构建——基于技术-人文-生态的动态平衡研究------摘要本文提出"技术-人文-生态"三元辩证模型(Technology-Humanity-EcologyDialecticalModel,THE-Model),突破传统线性发展观,通过构建动态平衡方程与多宇宙对照实验框架,揭示文明演进中技术熵减、人文熵增与生态混沌的量子纠缠关系。基于中国"文明操作系统2.0"实践案例与多学科
- Selenium 处理表单、弹窗与文件上传:从基础到实战
二向箔reverse
selenium爬虫自动化
在Web自动化领域,表单交互、弹窗处理和文件上传是最常见也最容易踩坑的场景。想象一下:你编写的脚本明明定位到了输入框,却无法输入文字;点击按钮后弹出的对话框让脚本瞬间“卡壳”;好不容易找到文件上传按钮,却发现Selenium无法直接操作系统文件选择框……这些问题往往让新手头疼不已。本文将系统讲解Selenium在这三类场景中的解决方案,结合实战案例帮你突破瓶颈。一、表单处理:搞定输入、选择与提交网
- 操作系统系统面试常问(进程、线程、协程相关知识)
程序猿莫悔
面试linux职场和发展
进程、线程和协程的区别和联系进程定义资源分配和调度的基本单位线程定义程序执行的基本单位协程定义用户态的轻量级线程,线程内部调度的基本单位进程切换情况进程切换时,操作系统会保存当前进程的CPU状态(如寄存器、页表等),并加载新进程的保存状态到CPU线程切换情况保存和设置程序计数器、少量寄存器和栈的内容协程切换情况先将寄存器上下文和栈保存,等切换回来的时候再进行恢复线程拥有资源CPU资源、内存资源、文
- 从宿主机到虚拟机,云环境下主机端IO路径的变化
数据存储张
存储技术从入门到精通php开发语言
前文我们对云计算的整体架构进行了介绍,并且了解到云计算的核心是虚拟化技术。这里的虚拟化技术包括计算虚拟化、网络虚拟化和存储虚拟化等技术。以基于Linux操作系统的虚拟化为例,通常在物理机上安装Linux操作系统和虚拟化软件,然后基于虚拟化软件创建虚拟机,并在虚拟机中按照操作系统。简而言之,虚拟化可以认为是通过软件虚拟出CPU、内存和硬盘等硬件,并在其上运行操作系统,具体如下图所示。添加图片注释,不
- Dev-C++——winAPI贪吃蛇小游戏
雾狩
c++开发语言
欢迎互三:雾狩关注博主,后期持续更新系列文章如果有错误感谢请大家批评指出,及时修改感谢大家点赞收藏⭐评论✍今天水一篇吧……老样子,先上效果一、概述本文将对“登录+贪吃蛇”游戏的代码进行详细剖析。该游戏实现了用户登录和注册功能,同时包含经典的贪吃蛇游戏玩法,还支持游戏存档和加载功能。代码使用了C++语言,并结合了Windows操作系统的API函数,以实现窗口化的游戏界面和多媒体功能。二、代码结构与功
- 深入解析Linux命令:创建目录mkdir的全面指南
梦幻南瓜
linuxlinux服务器运维
在Linux操作系统中,mkdir命令是创建目录的基础工具。无论是系统管理员还是普通用户,掌握mkdir的使用方法都是必不可少的。本文将详细解读mkdir命令的用法、选项及其在实际操作中的应用场景。1.mkdir命令的基本用法mkdir是“makedirectory”的缩写,用于在指定路径下创建新目录。其基本语法如下:mkdir[选项]目录名1.1创建单个目录最简单的用法是创建一个目录。例如,要在
- 从“一人干多活”到“团队协作”:RTOS多任务调度,居然藏着这么多小聪明!
从“一人干多活”到“团队协作”:RTOS多任务调度,居然藏着这么多小聪明!你有没有过这种经历:一边炖着汤,一边炒着菜,还得时不时跑去看一眼烤箱里的面包,结果手忙脚乱打翻了盐罐?嵌入式系统处理任务时,也曾面临同样的“窘境”——裸机系统就像一个人包揽所有活,只能按顺序挨个做;而RTOS(实时操作系统)则像雇了个“智能调度员”,能让多个任务“轮流上岗”,甚至“紧急任务插队”,效率直接翻倍!今天咱们就从裸
- 从零开始:搭建你的人工智能开发环境
人工智能教程
人工智能YOLO机器学习transformer线性回归动态规划排序算法
前言在人工智能和机器学习的旅程中,一个稳定且高效的开发环境是成功的关键第一步。无论是初学者还是经验丰富的开发者,一个配置良好的开发环境都能大大提高工作效率,减少遇到的问题。本文将从零开始,逐步指导你如何搭建一个完整的人工智能开发环境,包括操作系统选择、Python安装、常用库的配置以及开发工具的选择。一、选择合适的操作系统(一)主流操作系统介绍在搭建人工智能开发环境时,首先需要选择一个合适的操作系
- Prometheus搭建 和 Node_Exporter搭建
强_子
prometheus
1.Prometheus和Node_Exporter的关系●Prometheus:是一个开源的监控和告警工具,能够从各种数据源(如NodeExporter)拉取指标,并存储这些指标。它提供了一个强大的查询语言(PromQL),可以用来分析和可视化监控数据。●Node_Exporter:是Prometheus的一个官方插件,用于收集主机系统的硬件和操作系统级别的指标(如CPU使用率、内存使用情况、磁
- Linux部署Milvus数据库及Attu UI工具完全指南
一、准备工作1.1环境要求操作系统:Ubuntu20.04/Debian11/CentOS7+硬件配置:至少8GB内存,4核CPU,50GB磁盘空间网络要求:可访问互联网(用于拉取Docker镜像)1.2安装Docker和DockerCompose1.2.1安装Dockersudoapt-getupdatesudoapt-getinstall-ydocker.iosudosystemctlstar
- Linux 交叉编译分享
Mr_-G
编程入门Linux底层软件开发linux运维服务器交叉编译嵌入式底层软件
一、交叉编译的基本概念与应用场景1.1交叉编译的定义交叉编译是指在一个操作系统平台上编译出能在另一个不同架构或操作系统平台上运行的程序的过程。通俗地说,就是"在A机器上编译出能在B机器上运行的程序",其中A和B的硬件架构、操作系统可能完全不同。在传统的本地编译中,编译环境与运行环境是一致的,例如在x86_64的Linux系统上编译并运行程序。而交叉编译的核心特点在于编译环境与目标运行环境的分离,这
- Linux 0.01源码深入解析
羊迪
本文还有配套的精品资源,点击获取简介:Linux0.01源码代表了Linux操作系统的起点,揭示了其基本架构和内核设计原理。通过源码分析,开发者可以了解早期的进程管理、内存管理、文件系统、设备驱动、中断处理、系统调用等关键概念。此外,源码还展现了如何进行编译和构建,为想要深入理解操作系统和开源精神的开发者提供了一份宝贵的学习资源。1.Linux0.01源码概述Linux操作系统的核心是其内核,而L
- Jetson平台编译Tengine
space01
AIoTJetson人工智能深度学习计算机视觉
1.Tengine简介Tengine于2017年在GitHub(https://github.com/OAID/Tengine)开源,是OPENAILAB(开放智能)推出的自主知识产权的边缘AI计算框架,致力于解决AIoT产业链碎片化问题,加速AI产业化落地。Tengine兼容多种操作系统和深度学习算法框架,简化和加速面向场景的AI算法在嵌入式边缘设备上快速迁移,以及实际应用部署落地,可以十倍提升
- 14 款命令行常用工具的替代品!
杰哥的IT之旅
作者:JackTian文章首发于公众号:【杰哥的IT之旅】大家好,我是杰哥。在Linux操作系统下,ls(list)可以说是我们日常使用率较高的命令了,它主要用来显示目标列表,输出信息可以进行彩色加亮显示,以分区不同类型的文件。关于ls[^1]的语法、选项、实例、扩展知识,这里就不详细介绍了。一、lsdlsd[^2]是一个基于Rust语言编写的ls命令替代品,增加了颜色、图标、树视图、更多格式选项
- Shell 脚本编程全面学习指南
前言Shell脚本编程是Linux和Unix系统管理、自动化任务的核心工具之一。通过Shell脚本,你可以自动化重复性操作、简化复杂流程、提高系统管理效率,甚至构建完整的自动化运维工具。本文将带你从基础到进阶,全面学习Shell脚本编程,涵盖语法、结构、调试、最佳实践等内容。一、Shell简介与环境搭建1.1什么是Shell?Shell是命令行解释器,是用户与操作系统内核之间的桥梁。它接收用户输入
- MYOJ_8515:CSP初赛题单4:计算机软件
Jayfeather松鸦羽_sch
CSP初赛题目算法c++
更多初赛题单请参见题目整理CSP初赛题目整理题单,谢谢。题目描述1.[J-2015-3]操作系统的作用是()。A.把源程序译成目标程序B.便于进行数据管理C.控制和管理系统资源D.实现硬件之间的连接答案:C解析:操作系统(OperatingSystem,简称OS)是管理计算机硬件与软件资源的系统软件,其主要功能包括:处理器管理(CPU调度)内存管理(分配和回收内存)设备管理(管理输入/输出设备)文
- MySQL(147)如何进行跨平台迁移?
辞暮尔尔-烟火年年
mysqladb数据库
跨平台迁移涉及将数据库从一个操作系统或平台迁移到另一个,例如从Windows迁移到Linux,或从不同架构的硬件之间进行迁移。这个过程比同平台迁移更加复杂,需要特别注意数据库的兼容性、数据编码、文件路径等问题。以下是一步一步的指导,详细介绍如何进行跨平台数据库迁移。一、准备工作1.确认源与目标平台源平台:当前运行数据库的操作系统和硬件平台。目标平台:新的操作系统和硬件平台。2.安装数据库软件在目标
- 从零开始学 Linux:循序渐进的学习指南
我爱学嵌入式
Linux基础linux服务器
Linux作为一款开源、稳定且安全的操作系统,在服务器领域、嵌入式开发、云计算等场景中占据着举足轻重的地位。对于程序员、运维工程师或IT爱好者而言,掌握Linux技能已成为一项核心竞争力。但面对命令行界面和复杂的系统架构,很多初学者往往感到无从下手。本文将为你梳理一条清晰的Linux学习路径,助你从入门到精通。一、明确学习目标:为什么学Linux?学习Linux前需明确目标,不同目标对应不同的学习
- 基于 MySQL 8.0.40 MGR 与 ProxySQL 的高可用集群部署实践
derek2026
部署实践mysql数据库
构建高可用MySQL8.0.40集群:MGR+ProxySQL实战指南一、部署架构图流量路径:应用→ProxySQL(DNS解析ProxySQLIP)→MySQLMGR集群二、环境准备1.系统要求**操作系统:**CentOS7.x服务器配置3台节点(建议最小配置:4核CPU/8GB内存/100GB磁盘)网络互通(关闭防火墙或开放端口:3306,33081,6032,6033节点规划节点1:192
- JVM对synchronized的锁优化
ycllycll
一、Synchronized实现Synchronized是通过对象内部的一个叫做监视器锁(monitor)来实现的,监视器锁本质又是依赖于底层的操作系统的MutexLock(互斥锁)来实现的。而操作系统实现线程之间的切换需要从用户态转换到核心态,这个成本非常高,状态之间的转换需要相对比较长的时间,这就是为什么Synchronized效率低的原因。因此,这种依赖于操作系统MutexLock所实现的锁
- 47、确保文件属性设置的安全性
vv45678
C语言安全编码指南解析文件属性安全性只读
确保文件属性设置的安全性1.文件属性概述文件属性是操作系统用于管理和控制文件访问权限的重要机制。常见的文件属性包括只读、隐藏、系统文件、存档等。这些属性不仅影响文件的可见性和可访问性,还对文件的读写操作、备份行为等产生重要影响。因此,正确设置文件属性对于保护文件的安全至关重要。文件属性的作用只读:防止文件内容被修改。隐藏:使文件在默认情况下不显示,增加隐私性。系统文件:标记为操作系统的一部分,通常
- Windows环境下批量重命名文件的三种高效方法
数据冰山
本文还有配套的精品资源,点击获取简介:在Windows系统中,批量修改文件夹内文件名称能极大提高工作效率。本文介绍了三种方法:利用Windows自带的批量重命名功能、使用批处理脚本和借助第三方工具“批量改变文件名称.exe”。每种方法都提供了操作步骤,并强调了数据备份的重要性,以防止文件误改或丢失。1.Windows自带批量重命名功能的使用方法在本章中,我们将从零开始,探索Windows操作系统内
- 戴尔笔记本win8系统改装win7系统
sophia天雪
win7戴尔改装系统win8
戴尔win8 系统改装win7 系统详述
第一步:使用U盘制作虚拟光驱:
1)下载安装UltraISO:注册码可以在网上搜索。
2)启动UltraISO,点击“文件”—》“打开”按钮,打开已经准备好的ISO镜像文
- BeanUtils.copyProperties使用笔记
bylijinnan
java
BeanUtils.copyProperties VS PropertyUtils.copyProperties
两者最大的区别是:
BeanUtils.copyProperties会进行类型转换,而PropertyUtils.copyProperties不会。
既然进行了类型转换,那BeanUtils.copyProperties的速度比不上PropertyUtils.copyProp
- MyEclipse中文乱码问题
0624chenhong
MyEclipse
一、设置新建常见文件的默认编码格式,也就是文件保存的格式。
在不对MyEclipse进行设置的时候,默认保存文件的编码,一般跟简体中文操作系统(如windows2000,windowsXP)的编码一致,即GBK。
在简体中文系统下,ANSI 编码代表 GBK编码;在日文操作系统下,ANSI 编码代表 JIS 编码。
Window-->Preferences-->General -
- 发送邮件
不懂事的小屁孩
send email
import org.apache.commons.mail.EmailAttachment;
import org.apache.commons.mail.EmailException;
import org.apache.commons.mail.HtmlEmail;
import org.apache.commons.mail.MultiPartEmail;
- 动画合集
换个号韩国红果果
htmlcss
动画 指一种样式变为另一种样式 keyframes应当始终定义0 100 过程
1 transition 制作鼠标滑过图片时的放大效果
css
.wrap{
width: 340px;height: 340px;
position: absolute;
top: 30%;
left: 20%;
overflow: hidden;
bor
- 网络最常见的攻击方式竟然是SQL注入
蓝儿唯美
sql注入
NTT研究表明,尽管SQL注入(SQLi)型攻击记录详尽且为人熟知,但目前网络应用程序仍然是SQLi攻击的重灾区。
信息安全和风险管理公司NTTCom Security发布的《2015全球智能威胁风险报告》表明,目前黑客攻击网络应用程序方式中最流行的,要数SQLi攻击。报告对去年发生的60亿攻击 行为进行分析,指出SQLi攻击是最常见的网络应用程序攻击方式。全球网络应用程序攻击中,SQLi攻击占
- java笔记2
a-john
java
类的封装:
1,java中,对象就是一个封装体。封装是把对象的属性和服务结合成一个独立的的单位。并尽可能隐藏对象的内部细节(尤其是私有数据)
2,目的:使对象以外的部分不能随意存取对象的内部数据(如属性),从而使软件错误能够局部化,减少差错和排错的难度。
3,简单来说,“隐藏属性、方法或实现细节的过程”称为——封装。
4,封装的特性:
4.1设置
- [Andengine]Error:can't creat bitmap form path “gfx/xxx.xxx”
aijuans
学习Android遇到的错误
最开始遇到这个错误是很早以前了,以前也没注意,只当是一个不理解的bug,因为所有的texture,textureregion都没有问题,但是就是提示错误。
昨天和美工要图片,本来是要背景透明的png格式,可是她却给了我一个jpg的。说明了之后她说没法改,因为没有png这个保存选项。
我就看了一下,和她要了psd的文件,还好我有一点
- 自己写的一个繁体到简体的转换程序
asialee
java转换繁体filter简体
今天调研一个任务,基于java的filter实现繁体到简体的转换,于是写了一个demo,给各位博友奉上,欢迎批评指正。
实现的思路是重载request的调取参数的几个方法,然后做下转换。
- android意图和意图监听器技术
百合不是茶
android显示意图隐式意图意图监听器
Intent是在activity之间传递数据;Intent的传递分为显示传递和隐式传递
显式意图:调用Intent.setComponent() 或 Intent.setClassName() 或 Intent.setClass()方法明确指定了组件名的Intent为显式意图,显式意图明确指定了Intent应该传递给哪个组件。
隐式意图;不指明调用的名称,根据设
- spring3中新增的@value注解
bijian1013
javaspring@Value
在spring 3.0中,可以通过使用@value,对一些如xxx.properties文件中的文件,进行键值对的注入,例子如下:
1.首先在applicationContext.xml中加入:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.
- Jboss启用CXF日志
sunjing
logjbossCXF
1. 在standalone.xml配置文件中添加system-properties:
<system-properties> <property name="org.apache.cxf.logging.enabled" value=&
- 【Hadoop三】Centos7_x86_64部署Hadoop集群之编译Hadoop源代码
bit1129
centos
编译必需的软件
Firebugs3.0.0
Maven3.2.3
Ant
JDK1.7.0_67
protobuf-2.5.0
Hadoop 2.5.2源码包
Firebugs3.0.0
http://sourceforge.jp/projects/sfnet_findbug
- struts2验证框架的使用和扩展
白糖_
框架xmlbeanstruts正则表达式
struts2能够对前台提交的表单数据进行输入有效性校验,通常有两种方式:
1、在Action类中通过validatexx方法验证,这种方式很简单,在此不再赘述;
2、通过编写xx-validation.xml文件执行表单验证,当用户提交表单请求后,struts会优先执行xml文件,如果校验不通过是不会让请求访问指定action的。
本文介绍一下struts2通过xml文件进行校验的方法并说
- 记录-感悟
braveCS
感悟
再翻翻以前写的感悟,有时会发现自己很幼稚,也会让自己找回初心。
2015-1-11 1. 能在工作之余学习感兴趣的东西已经很幸福了;
2. 要改变自己,不能这样一直在原来区域,要突破安全区舒适区,才能提高自己,往好的方面发展;
3. 多反省多思考;要会用工具,而不是变成工具的奴隶;
4. 一天内集中一个定长时间段看最新资讯和偏流式博
- 编程之美-数组中最长递增子序列
bylijinnan
编程之美
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;
public class LongestAccendingSubSequence {
/**
* 编程之美 数组中最长递增子序列
* 书上的解法容易理解
* 另一方法书上没有提到的是,可以将数组排序(由小到大)得到新的数组,
* 然后求排序后的数组与原数
- 读书笔记5
chengxuyuancsdn
重复提交struts2的token验证
1、重复提交
2、struts2的token验证
3、用response返回xml时的注意
1、重复提交
(1)应用场景
(1-1)点击提交按钮两次。
(1-2)使用浏览器后退按钮重复之前的操作,导致重复提交表单。
(1-3)刷新页面
(1-4)使用浏览器历史记录重复提交表单。
(1-5)浏览器重复的 HTTP 请求。
(2)解决方法
(2-1)禁掉提交按钮
(2-2)
- [时空与探索]全球联合进行第二次费城实验的可能性
comsci
二次世界大战前后,由爱因斯坦参加的一次在海军舰艇上进行的物理学实验 -费城实验
至今给我们大家留下很多迷团.....
关于费城实验的详细过程,大家可以在网络上搜索一下,我这里就不详细描述了
在这里,我的意思是,现在
- easy connect 之 ORA-12154: TNS: 无法解析指定的连接标识符
daizj
oracleORA-12154
用easy connect连接出现“tns无法解析指定的连接标示符”的错误,如下:
C:\Users\Administrator>sqlplus username/
[email protected]:1521/orcl
SQL*Plus: Release 10.2.0.1.0 – Production on 星期一 5月 21 18:16:20 2012
Copyright (c) 198
- 简单排序:归并排序
dieslrae
归并排序
public void mergeSort(int[] array){
int temp = array.length/2;
if(temp == 0){
return;
}
int[] a = new int[temp];
int
- C语言中字符串的\0和空格
dcj3sjt126com
c
\0 为字符串结束符,比如说:
abcd (空格)cdefg;
存入数组时,空格作为一个字符占有一个字节的空间,我们
- 解决Composer国内速度慢的办法
dcj3sjt126com
Composer
用法:
有两种方式启用本镜像服务:
1 将以下配置信息添加到 Composer 的配置文件 config.json 中(系统全局配置)。见“例1”
2 将以下配置信息添加到你的项目的 composer.json 文件中(针对单个项目配置)。见“例2”
为了避免安装包的时候都要执行两次查询,切记要添加禁用 packagist 的设置,如下 1 2 3 4 5
- 高效可伸缩的结果缓存
shuizhaosi888
高效可伸缩的结果缓存
/**
* 要执行的算法,返回结果v
*/
public interface Computable<A, V> {
public V comput(final A arg);
}
/**
* 用于缓存数据
*/
public class Memoizer<A, V> implements Computable<A,
- 三点定位的算法
haoningabc
c算法
三点定位,
已知a,b,c三个顶点的x,y坐标
和三个点都z坐标的距离,la,lb,lc
求z点的坐标
原理就是围绕a,b,c 三个点画圆,三个圆焦点的部分就是所求
但是,由于三个点的距离可能不准,不一定会有结果,
所以是三个圆环的焦点,环的宽度开始为0,没有取到则加1
运行
gcc -lm test.c
test.c代码如下
#include "stdi
- epoll使用详解
jimmee
clinux服务端编程epoll
epoll - I/O event notification facility在linux的网络编程中,很长的时间都在使用select来做事件触发。在linux新的内核中,有了一种替换它的机制,就是epoll。相比于select,epoll最大的好处在于它不会随着监听fd数目的增长而降低效率。因为在内核中的select实现中,它是采用轮询来处理的,轮询的fd数目越多,自然耗时越多。并且,在linu
- Hibernate对Enum的映射的基本使用方法
linzx0212
enumHibernate
枚举
/**
* 性别枚举
*/
public enum Gender {
MALE(0), FEMALE(1), OTHER(2);
private Gender(int i) {
this.i = i;
}
private int i;
public int getI
- 第10章 高级事件(下)
onestopweb
事件
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/
- 孙子兵法
roadrunners
孙子兵法
始计第一
孙子曰:
兵者,国之大事,死生之地,存亡之道,不可不察也。
故经之以五事,校之以计,而索其情:一曰道,二曰天,三曰地,四曰将,五
曰法。道者,令民于上同意,可与之死,可与之生,而不危也;天者,阴阳、寒暑
、时制也;地者,远近、险易、广狭、死生也;将者,智、信、仁、勇、严也;法
者,曲制、官道、主用也。凡此五者,将莫不闻,知之者胜,不知之者不胜。故校
之以计,而索其情,曰
- MySQL双向复制
tomcat_oracle
mysql
本文包括:
主机配置
从机配置
建立主-从复制
建立双向复制
背景
按照以下简单的步骤:
参考一下:
在机器A配置主机(192.168.1.30)
在机器B配置从机(192.168.1.29)
我们可以使用下面的步骤来实现这一点
步骤1:机器A设置主机
在主机中打开配置文件 ,
- zoj 3822 Domination(dp)
阿尔萨斯
Mina
题目链接:zoj 3822 Domination
题目大意:给定一个N∗M的棋盘,每次任选一个位置放置一枚棋子,直到每行每列上都至少有一枚棋子,问放置棋子个数的期望。
解题思路:大白书上概率那一张有一道类似的题目,但是因为时间比较久了,还是稍微想了一下。dp[i][j][k]表示i行j列上均有至少一枚棋子,并且消耗k步的概率(k≤i∗j),因为放置在i+1~n上等价与放在i+1行上,同理