使用Linux命令cURL实现文件定时上传到ftp服务器的程序
前言
前段时间群里讨论,想实现某个文件定时上传到服务器要怎么来实现。我记得之前做过
一个项目:为高通的iot模组编写FOTA功能:实现模组可以远程下载升级镜像包,实现版本升级功能。并当时使用的一个超级强大的工具cURL。心血来潮,决定专门写一篇文章,送给需要的朋友。
文章分两部分
概念
cURL 是常用的命令行工具,用来请求 Web 服务器。它的名字就是客户端(client)的 URL 工具的意思。
cURL 的原作者是 Daniel Stenberg (目前是 cURL 的核心开发者),同时也是 IETF HTTPbis 工作组的资深成员。Daniel 在 1998 年创建了 curl 项目,他编写了最初的 curl 版本,并创建了 libcurl 库。到目前为止,代码仓库包括的 24000 次 commit 有超过一半是 Daniel 本人提交的,他依然是项目的核心开发者。Daniel 表示已将 curl 视为自己的孩子。
作为一款强力工具,支持的协议包括 (DICT, FILE, FTP, FTPS, GOPHER, HTTP, HTTPS, IMAP, IMAPS, LDAP, LDAPS, POP3, POP3S, RTMP, RTSP, SCP, SFTP, SMTP, SMTPS, TELNET and TFTP),还支持POST、cookies、认证、从指定偏移处下载部分文件等功能,具有用户代理字符串、限速、文件大小、进度条、cookie支持、用户认证、断点续传等特征。
一、命令的安装
sudo apt-get install curl
二、cURL命令语法:
curl [options] [URL...]
三、URL格式
URL的格式定义要参考 RFC 1808 。
地址:http://www.w3.org/Addressing/rfc1808.txt
《Relative Uniform Resource Locators 》
URL由三部分组成:资源类型、存放资源的主机域名、资源文件名。
也可认为由4部分组成:协议、主机、端口、路径
URL的一般语法格式为:
protocol :// hostname[:port] / path / [;parameters][?query]#fragment
(带方括号[]的为可选项)。
protocol(协议)
指定使用的传输协议,下表列出 protocol 属性的有效方案名称。 最常用的是HTTP协议,它也是WWW中应用最广的协议。
- file 资源是本地计算机上的文件。格式file:///,注意后边应是三个斜杠。
- ftp 通过 FTP访问资源。格式 FTP://
- gopher 通过 Gopher 协议访问该资源。
- http 通过 HTTP 访问该资源。 格式 HTTP://
- https 通过安全的 HTTPS 访问该资源。 格式 HTTPS://
- mailto 资源为电子邮件地址,通过 SMTP 访问。 格式 mailto:
- MMS 通过 支持MMS(流媒体)协议的播放该资源。(代表软件:Windows Media Player)格式 MMS://
- ed2k 通过 支持ed2k(专用下载链接)协议的P2P软件访问该资源。(代表软件:电驴) 格式 ed2k://
- Flashget 通过 支持Flashget:(专用下载链接)协议的P2P软件访问该资源。(代表软件:快车) 格式 Flashget://
- thunder 通过 支持thunder(专用下载链接)协议的P2P软件访问该资源。(代表软件:迅雷) 格式 thunder://
- news 通过 NNTP 访问该资源。
hostname(主机名)
是指存放资源的服务器的域名系统(DNS) 主机名或 IP 地址。有时,在主机名前也可以包含连接到服务器所需的用户名和密码(格式:username:password@hostname)。
port(端口号)
整数,可选,省略时使用方案的默认端口,各种传输协议都有默认的端口号,如http的默认端口为80。如果输入时省略,则使用默认端口号。有时候出于安全或其他考虑,可以在服务器上对端口进行重定义,即采用非标准端口号,此时,URL中就不能省略端口号这一项。
path(路径)
由零或多个“/”符号隔开的字符串,一般用来表示主机上的一个目录或文件地址。
parameters(参数)
这是用于指定特殊参数的可选项。
query(查询)
可选,用于给动态网页(如使用CGI、ISAPI、PHP/JSP/ASP/ASP.NET等技术制作的网页)传递参数,可有多个参数,用“&”符号隔开,每个参数的名和值用“=”符号隔开。
fragment(信息片断)
字符串,用于指定网络资源中的片断。例如一个网页中有多个名词解释,可使用fragment直接定位到某一名词解释。
四、curl命令参数详解:
由于linux curl功能十分强大,所以命令参数十分多,下表只筛选出来部分常用的参数,更多参数请运行“man curl”命令查看。
| 参数 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| -a/–append | 上传文件时,附加到目标文件 |
| -A/–user-agent | 设置用户代理发送给服务器 |
| -anyauth | 可以使用“任何”身份验证方法 |
| -b/–cookie |
cookie字符串或文件读取位置 |
| –basic | 使用HTTP基本验证 |
| -B/–use-ascii | 使用ASCII /文本传输 |
| -c/–cookie-jar | 操作结束后把cookie写入到这个文件中 |
| -C/–continue-at | 断点续转 |
| -d/–data | HTTP POST方式传送数据 |
| –data-ascii | 以ascii的方式post数据 |
| –data-binary | 以二进制的方式post数据 |
| –negotiate | 使用HTTP身份验证 |
| –digest | 使用数字身份验证 |
| –disable-eprt | 禁止使用EPRT或LPRT |
| –disable-epsv | 禁止使用EPSV |
| -D/–dump-header | 把header信息写入到该文件中 |
| –egd-file | 为随机数据(SSL)设置EGD socket路径 |
| –tcp-nodelay | 使用TCP_NODELAY选项 |
| -e/–referer | 来源网址 |
| -E/–cert |
客户端证书文件和密码 (SSL) |
| –cert-type | 证书文件类型 (DER/PEM/ENG) (SSL) |
| –key | 私钥文件名 (SSL) |
| –key-type | 私钥文件类型 (DER/PEM/ENG) (SSL) |
| –pass | 私钥密码 (SSL) |
| –engine | 加密引擎使用 (SSL). “–engine list” for list |
| –cacert | CA证书 (SSL) |
| –capath | CA目录 (made using c_rehash) to verify peer against (SSL) |
| –ciphers | SSL密码 |
| –compressed | 要求返回是压缩的形势 (using deflate or gzip) |
| –connect-timeout | 设置最大请求时间 |
| –create-dirs | 建立本地目录的目录层次结构 |
| –crlf | 上传是把LF转变成CRLF |
| -f/–fail | 连接失败时不显示http错误 |
| –ftp-create-dirs | 如果远程目录不存在,创建远程目录 |
| –ftp-method [multicwd/nocwd/singlecwd] | 控制CWD的使用 |
| –ftp-pasv | 使用 PASV/EPSV 代替端口 |
| –ftp-skip-pasv-ip | 使用PASV的时候,忽略该IP地址 |
| –ftp-ssl | 尝试用 SSL/TLS 来进行ftp数据传输 |
| –ftp-ssl-reqd | 要求用 SSL/TLS 来进行ftp数据传输 |
| -F/–form |
模拟http表单提交数据 |
| –form-string |
模拟http表单提交数据 |
| -g/–globoff | 禁用网址序列和范围使用{}和[] |
| -G/–get | 以get的方式来发送数据 |
| -H/–header | 自定义头信息传递给服务器 |
| –ignore-content-length | 忽略的HTTP头信息的长度 |
| -i/–include | 输出时包括protocol头信息 |
| -I/–head | 只显示请求头信息 |
| -j/–junk-session-cookies | 读取文件进忽略session cookie |
| –interface | 使用指定网络接口/地址 |
| –krb4 | 使用指定安全级别的krb4 |
| -k/–insecure | 允许不使用证书到SSL站点 |
| -K/–config | 指定的配置文件读取 |
| -l/–list-only | 列出ftp目录下的文件名称 |
| –limit-rate | 设置传输速度 |
| –local-port | 强制使用本地端口号 |
| -m/–max-time | 设置最大传输时间 |
| –max-redirs | 设置最大读取的目录数 |
| –max-filesize | 设置最大下载的文件总量 |
| -M/–manual | 显示全手动 |
| -n/–netrc | 从netrc文件中读取用户名和密码 |
| –netrc-optional | 使用 .netrc 或者 URL来覆盖-n |
| –ntlm | 使用 HTTP NTLM 身份验证 |
| -N/–no-buffer | 禁用缓冲输出 |
| -o/–output | 把输出写到该文件中 |
| -O/–remote-name | 把输出写到该文件中,保留远程文件的文件名 |
| -p/–proxytunnel | 使用HTTP代理 |
| –proxy-anyauth | 选择任一代理身份验证方法 |
| –proxy-basic | 在代理上使用基本身份验证 |
| –proxy-digest | 在代理上使用数字身份验证 |
| –proxy-ntlm | 在代理上使用ntlm身份验证 |
| -P/–ftp-port | 使用端口地址,而不是使用PASV |
| -q | 作为第一个参数,关闭 .curlrc |
| -Q/–quote | 文件传输前,发送命令到服务器 |
| -r/–range | 检索来自HTTP/1.1或FTP服务器字节范围 |
| –range-file | 读取(SSL)的随机文件 |
| -R/–remote-time | 在本地生成文件时,保留远程文件时间 |
| –retry | 传输出现问题时,重试的次数 |
| –retry-delay | 传输出现问题时,设置重试间隔时间 |
| –retry-max-time | 传输出现问题时,设置最大重试时间 |
| -s/–silent | 静默模式。不输出任何东西 |
| -S/–show-error | 显示错误 |
| –socks4 |
用socks4代理给定主机和端口 |
| –socks5 |
用socks5代理给定主机和端口 |
| –stderr | |
| -t/–telnet-option |
Telnet选项设置 |
| –trace | 对指定文件进行debug |
| –trace-ascii | Like --跟踪但没有hex输出 |
| –trace-time | 跟踪/详细输出时,添加时间戳 |
| -T/–upload-file | 上传文件 |
| –url | Spet URL to work with |
| -u/–user |
设置服务器的用户和密码 |
| -U/–proxy-user |
设置代理用户名和密码 |
| -w/–write-out [format] | 什么输出完成后 |
| -x/–proxy |
在给定的端口上使用HTTP代理 |
| -X/–request | 指定什么命令 |
| -y/–speed-time | 放弃限速所要的时间,默认为30 |
| -Y/–speed-limit | 停止传输速度的限制,速度时间 |
五、Linux curl命令退出码:
下面是linux curl命令的错误代码和她们的相应的错误消息,命令执行错误的时候可以通过错误码来查看出错原因,方便开发调试。
| 退 出 码 | 错误描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | Unsupported protocol. This build of curl has no support for this protocol. |
| 2 | Failed to initialize. |
| 3 | URL malformed. The syntax was not correct. |
| 5 | Couldn’t resolve proxy. The given proxy host could not be resolved. |
| 6 | Couldn’t resolve host. The given remote host was not resolved. |
| 7 | Failed to connect to host. |
| 8 | FTP weird server reply. The server sent data curl couldn’t parse. |
| 9 | FTP access denied. The server denied login or denied access to the particular resource or directory you wanted to reach. Most often you tried to change to a directory that doesn’t exist on the server. |
| 11 | FTP weird PASS reply. Curl couldn’t parse the reply sent to the PASS request. |
| 13 | FTP weird PASV reply, Curl couldn’t parse the reply sent to the PASV request. |
| 14 | FTP weird 227 format. Curl couldn’t parse the 227-line the server sent. |
| 15 | FTP can’t get host. Couldn’t resolve the host IP we got in the 227-line. |
| 17 | FTP couldn’t set binary. Couldn’t change transfer method to binary. |
| 18 | Partial file. Only a part of the file was transferred. |
| 19 | FTP couldn’t download/access the given file, the RETR (or similar) command failed. |
| 21 | FTP quote error. A quote command returned error from the server. |
| 22 | HTTP page not retrieved. The requested url was not found or returned another error with the HTTP error code being 400 or above. This return code only appears if -f/–fail is used. |
| 23 | Write error. Curl couldn’t write data to a local filesystem or similar. |
| 25 | FTP couldn’t STOR file. The server denied the STOR operation, used for FTP uploading. |
| 26 | Read error. Various reading problems. |
| 27 | Out of memory. A memory allocation request failed. |
| 28 | Operation timeout. The specified time-out period was reached according to the conditions. |
| 30 | FTP PORT failed. The PORT command failed. Not all FTP servers support the PORT command, try doing a transfer using PASV instead! |
| 31 | FTP couldn’t use REST. The REST command failed. This command is used for resumed FTP transfers. |
| 33 | HTTP range error. The range “command” didn’t work. |
| 34 | HTTP post error. Internal post-request generation error. |
| 35 | SSL connect error. The SSL handshaking failed. |
| 36 | FTP bad download resume. Couldn’t continue an earlier aborted download. |
| 37 | FILE couldn’t read file. Failed to open the file. Permissions? |
| 38 | LDAP cannot bind. LDAP bind operation failed. |
| 39 | LDAP search failed. |
| 41 | Function not found. A required LDAP function was not found. |
| 42 | Aborted by callback. An application told curl to abort the operation. |
| 43 | Internal error. A function was called with a bad parameter. |
| 45 | Interface error. A specified outgoing interface could not be used. |
| 47 | Too many redirects. When following redirects, curl hit the maximum amount. |
| 48 | Unknown TELNET option specified. |
| 49 | Malformed telnet option. |
| 51 | The peer’s SSL certificate or SSH MD5 fingerprint was not ok. |
| 52 | The server didn’t reply anything, which here is considered an error. |
| 53 | SSL crypto engine not found. |
| 54 | Cannot set SSL crypto engine as default. |
| 55 | Failed sending network data. |
| 56 | Failure in receiving network data. |
| 58 | Problem with the local certificate. |
| 59 | Couldn’t use specified SSL cipher. |
| 60 | Peer certificate cannot be authenticated with known CA certificates. |
| 61 | Unrecognized transfer encoding. |
| 62 | Invalid LDAP URL. |
| 63 | Maximum file size exceeded. |
| 64 | Requested FTP SSL level failed. |
| 65 | Sending the data requires a rewind that failed. |
| 66 | Failed to initialize SSL Engine. |
| 67 | The user name, password, or similar was not accepted and curl failed to log in. |
| 68 | File not found on TFTP server. |
| 69 | Permission problem on TFTP server. |
| 70 | Out of disk space on TFTP server. |
| 71 | Illegal TFTP operation. |
| 72 | Unknown TFTP transfer ID. |
| 73 | File already exists (TFTP). |
| 74 | No such user (TFTP). |
| 75 | Character conversion failed. |
| 76 | Character conversion functions required. |
| 77 | Problem with reading the SSL CA cert (path? access rights?). |
| 78 | The resource referenced in the URL does not exist. |
| 79 | An unspecified error occurred during the SSH session. |
| 80 | Failed to shut down the SSL connection. |
| 82 | Could not load CRL file, missing or wrong format (added in 7.19.0). |
| 83 | Issuer check failed (added in 7.19.0). |
| XX | More error codes will appear here in future releases. The existing ones are meant to never change. |
六、用法演示:
为节省篇幅,部分操作不再贴上执行结果。
1、查看网页源码
直接在curl命令后加上网址,就可以看到网页源码。我们以网址www.sina.com为例(选择该网址,主要因为它的网页代码较短):
root@ubuntu:/home/peng# curl www.sohu.com
<html>
<head><title>307 Temporary Redirect</title></head>
<body bgcolor="white">
<center><h1>307 Temporary Redirect</h1></center>
<hr><center>nginx</center>
</body>
</html>
执行结果显示 307 Temporary Redirect,说明该网址需要重定向。
如果要把这个网页保存下来,可以使用-o参数,这就相当于使用wget命令了。
curl -o [文件名] www.sohu.com
2、自动跳转
有的网址是自动跳转的。使用-L参数,curl就会跳转到新的网址。
curl -L www.sohu.com
键入上面的命令,结果就自动跳转为www.sohu.com.cn。
3、显示头信息
-i参数可以显示http response的头信息,连同网页代码一起。
root@ubuntu:/home/peng/driver/test# curl -i www.sohu.com
HTTP/1.1 307 Temporary Redirect
Content-Type: text/html
Content-Length: 180
Connection: keep-alive
Server: nginx
Date: Tue, 25 Aug 2020 10:10:54 GMT
Location: https://www.sohu.com/
FSS-Cache: from 9790436.18244590.10468709
FSS-Proxy: Powered by 2384755.3433341.3062915
<html>
<head><title>307 Temporary Redirect</title></head>
<body bgcolor="white">
<center><h1>307 Temporary Redirect</h1></center>
<hr><center>nginx</center>
</body>
</html>
-I参数则是只显示http response的头信息。
4、显示通信过程
-v参数可以显示一次http通信的整个过程,包括端口连接和http request头信息。
root@ubuntu:/home/peng/driver/test# curl -v www.sohu.com
* About to connect() to www.sohu.com port 80 (#0)
* Trying 240e:83:201:3700::5... connected
> GET / HTTP/1.1
> User-Agent: curl/7.22.0 (i686-pc-linux-gnu) libcurl/7.22.0 OpenSSL/1.0.1 zlib/1.2.3.4 libidn/1.23 librtmp/2.3
> Host: www.sohu.com
> Accept: */*
>
< HTTP/1.1 307 Temporary Redirect
< Content-Type: text/html
< Content-Length: 180
< Connection: keep-alive
< Server: nginx
< Date: Tue, 25 Aug 2020 10:11:49 GMT
< Location: https://www.sohu.com/
< FSS-Cache: from 9855973.18375663.10534247
< FSS-Proxy: Powered by 2450292.3564414.3128453
<
<html>
<head><title>307 Temporary Redirect</title></head>
<body bgcolor="white">
<center><h1>307 Temporary Redirect</h1></center>
<hr><center>nginx</center>
</body>
</html>
* Connection #0 to host www.sohu.com left intact
* Closing connection #0
如果你觉得上面的信息还不够,那么下面的命令可以查看更详细的通信过程。
curl --trace output.txt www.sohu.com
或者
curl --trace-ascii output.txt www.sohu.com
运行后,请打开output.txt文件查看。
5、发送表单信息
发送表单信息有GET和POST两种方法。GET方法相对简单,只要把数据附在网址后面就行。
curl example.com/form.cgi?data=xxx
POST方法必须把数据和网址分开,curl就要用到–data参数。
curl -X POST --data "data=xxx" example.com/form.cgi
如果你的数据没有经过表单编码,还可以让curl为你编码,参数是--data-urlencode。
curl -X POST--data-urlencode "date=April 1" example.com/form.cgi
6、HTTP动词
curl默认的HTTP动词是GET,使用-X参数可以支持其他动词。
curl -X POST www.example.com
curl -X DELETE www.example.com
7、文件上传
假定文件上传的表单是下面这样:
<form method="POST" enctype='multipart/form-data' action="upload.cgi">
<input type=file name=upload>
<input type=submit name=press value="OK">
</form>
你可以用curl这样上传文件:
curl --form upload=@localfilename --form press=OK [URL]
8、Referer字段
有时你需要在http request头信息中,提供一个referer字段,表示你是从哪里跳转过来的。
curl --referer http://www.example.com http://www.example.com
9、User Agent字段
这个字段是用来表示客户端的设备信息。服务器有时会根据这个字段,针对不同设备,返回不同格式的网页,比如手机版和桌面版。
iPhone4的User Agent是
Mozilla/5.0 (iPhone; U; CPU iPhone OS 4_0 like Mac OS X; en-us) AppleWebKit/532.9 (KHTML, like Gecko) Version/4.0.5 Mobile/8A293 Safari/6531.22.7
curl可以这样模拟:
curl --user-agent "[User Agent]" [URL]
10、cookie
使用--cookie参数,可以让curl发送cookie。
curl --cookie "name=xxx" www.example.com
至于具体的cookie的值,可以从http response头信息的Set-Cookie字段中得到。
-c cookie-file可以保存服务器返回的cookie到文件,-b cookie-file可以使用这个文件作为cookie信息,进行后续的请求。
curl -c cookies http://example.com
curl -b cookies http://example.com
11、增加头信息
有时需要在http request之中,自行增加一个头信息。--header参数就可以起到这个作用。
$ curl --header "Content-Type:application/json" http://example.com
12、认证
使用curl选项 -u 可以完成HTTP或者FTP的认证,可以指定密码,也可以不指定密码在后续操作中输入密码:
curl -u user:pwd http://man.linuxde.net
curl -u user http://man.linuxde.net
13、FTP
1)、列出ftp服务器上的目录列表
curl ftp://www.xxx.com/ --user name:passwd
curl ftp://www.xxx.com/ –u name:passwd #简洁写法
curl ftp://name:[email protected] #简洁写法2
例如:在IP地址192.168.43.117上搭建FTP服务器,并设置用户名为user,密码为123456
现在我们要显示服务器上根目录下的所有文件信息,命令如下:
curl -u user:123456 ftp://192.168.43.117
执行结果如下:
![]()
简洁写法:
curl ftp://user:[email protected]
执行结果如下:
![]()
2)、只列出目录,不显示进度条
curl ftp://www.xxx.com –u name:passwd -s
3)、下载一个文件:
格式
curl ftp://www.xxx.com/size.zip –u name:passwd -o size.zip
示例如下:
从服务器的根目录下下载文件test.c,保存到本地,本地文件名也为test.c。
【注意】如果没有-o选项,程序会吧数据流定向到stdout,即直接把文件内容显示到终端上。
curl ftp://user:[email protected]/test.c -o test.c
执行结果如下:
![]()
简洁模式
curl -u user:123456 ftp://192.168.43.117/list.h -o list.h
4)、上载一个文件:
curl –u name:passwd -T size.mp3 ftp://www.xxx.com/mp3/
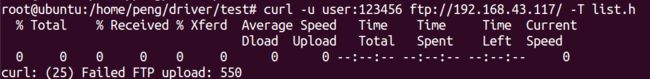
举例如下:
curl -u user:123456 ftp://192.168.43.117/ -T list.h
25 FTP couldn't STOR file. The server denied the STOR operation, used for FTP uploading.
可知,是因为服务器没有赋予存储的权限,所以设置服务器的write权限即可。
5)、从服务器上删除文件(使用curl传递ftp协议的DELE命令):
curl –u name:passwd ftp://www.xxx.com/ -X 'DELE mp3/size.mp3'
6)、另外curl不支持递归下载,不过可以用数组方式下载文件,比如我们要下载1-10.gif连续命名的文件:**
curl –u name:passwd ftp://www.xxx.com/img/[1-10].gif –O #O字母大写
7)、要连续下载多个文件:
curl –u name:passwd ftp://www.xxx.com/img/[one,two,three].jpg –O #O字母大写
六、实现日志文件定时上传
功能
- 程序运行时要记录当前日志文件的最后修改时间;
- 每个10秒钟就检查下log文件是否被修改,如果没有被修改就休眠10秒钟;
- 如果log文件被修改了,就将当前的日志文件拷贝成备份文件,备份文件名字加上当前时间;
- 通过curl发送给ftp服务器;
- 删除备份文件,重复步骤2。
程序流程图如下:
函数功能介绍
init()
首先记录当前log文件时间,并记录到全局变量last_mtime中。
check_file_change()
读取文件最后修改时间,并和last_mtime进行比较,如果相同就返回0,不同就返回1.
file_name_add_time()
将当前的日志文件拷贝成备份文件,备份文件名字加上当前时间。
stat()
得到对应文件的属性信息,存放到struct stat结构体变量中。
system()
执行参数中字符串对应的命令
代码如下:
/* Copyright (C) 公众号: yikoulinux */
#include 运行截图:
第二步:
手动输入字符串 yikoulinux 到日志文件 t.log中。
![]() 第三步:
第三步:
因为文件发生了改变,所以打印“file updated”,同时可以看到curl上传文件的log信息。
 以下是FTP服务器的根目录,可以看到,上传的日志文件:
以下是FTP服务器的根目录,可以看到,上传的日志文件:t-2020-7-26-1-19-45.log。

【补充】
- 配置信息,直接在代码中写死,通常应该从配置文件中读取,为方便读者阅读,本代码没有增加该功能;
- FTP服务器搭建,本文没有说明,相关文件比较多,大家可以自行搜索,一口君用的是File zilla;

- 通常这种需要长时间运行的程序,需要设置成守护进程,本文没有添加相应功能,读者可以自行搜索。如果强烈要求可以单开一篇详细介绍。
- 代码中time的管理函数,请读者自行搜索相关文章。
- curl也提供了相关的函数库curl.lib,如果要实现更灵活的功能可以使用对应的api。
- 之所以先把文件拷贝成备份文件,主要是考虑其他模块随时可能修改日志文件,起到一定保护作用。
想和博主交流,请关注公众号「一口Linux」