队列同步器AbstractQueueSynchronizer
目录
什么是队列同步器
队列同步器的实现
同步队列
独占式同步状态获取与释放
共享式同步状态获取与释放
等待队列
队列同步器使用
什么是队列同步器
队列同步器是用来构建锁或者其他同步组件的基础框架,它使用了一个int成员变量表示同步状态,通过内置的FIFO队列来完成资源获取线程的排队工作。
同步器的主要使用方式是继承,子类通过继承同步器并实现它的抽象方法来管理同步状态,在抽象方法的实现过程种免不了要对同步状态进行更改,这时就需要使用同步器提供的三个抽象方法(getState()、setState(int newState)和compareAndSet(int expect,int update))来进行操作,因为它们能够保证状态的改变是安全的,子类推荐被定义为自定义同步组件的静态内部类。
同步器的实现锁(也可以是任意同步组件)的关键,在锁的实现种聚合同步器,利用同步器实现锁的语义。可以这样理解二者之间的关系:
- 锁是面向使用者的,它定义了使用者与锁的交互的接口,隐藏了实现细节;
- 同步器面向的是锁的实现者,它简化了锁的实现方式,屏蔽了同步状态管理、线程的排队、等待与唤醒等底层操作。锁和同步器很好的隔离了使用者和实现者所需关注的领域。
队列同步器的实现
同步队列
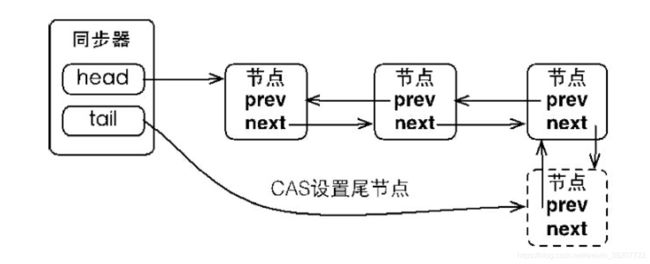
同步器依赖内部的同步队列(一个FIFO双向队列)来完成同步状态的管理,当前线程获取同步状态失败时,同步器会将当前线程以及等待状态等信息构造成为一个节点(Node)并将其加入同步队列,同时会阻塞当前线程。当同步状态释放时,会把首节点中的线程唤醒,使其再次尝试获取同步状态。
同步队列中的节点(Node)用来保存获取同步状态失败的线程引用、等待状态以及前驱和后继节点、等待队列的后继节点。
static final class Node {
/**
* 等待状态
* 1.CANCELLED,值为1,由于在同步队列中等待的线程超时或被中断,需要从同步队列中取消等待,节点进入该状态将不会变化。
* 2.SIGNAL,值为-1,后继节点的线程处于等待状态,而当前节点的线程如果释放了同步状态或者被取消,将会通知后继节点,使后继节点的线程得以运行。
* 3.CONDITION,值为-2,节点在等待队列中,节点线程等待在Condition上,当其他线程对Condition调用了signal方法后,该节点将会从等待队列中转移到同步队列中,加入到对同步状态的获取中。
* 4.PROPAGATE,值为-3,表示下一次共享式同步状态获取将会无条件被传播下去。
* 5.INITIAL,值为0,初始状态。int初始化为0。
*/
volatile int waitStatus;
//前驱节点
volatile AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.Node prev;
//后继节点
volatile AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.Node next;
//获取同步状态的线程
volatile Thread thread;
//等待队列中的后继节点。
//如果当前节点是共享的,那么这个字段将是一个SHARED常量,
//如果当前节点是独占的,那么字段将是一个EXCLUSIVE常量,
//也就是说节点类型(独占和共享)和等待队列中的后继节点共用同一个字段。
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.Node nextWaiter;
static final AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.Node SHARED = new AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.Node();
static final AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.Node EXCLUSIVE = null;
}同步器包含了两个节点类型的引用,一个指向头节点(head),而另一个指向尾节点(tail)。
public abstract class AbstractQueuedSynchronizer extends AbstractOwnableSynchronizer {
//首节点引用
private transient volatile AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.Node head;
//尾节点引用
private transient volatile AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.Node tail;
}没有成功获取同步状态的线程将会称为节点加入该队列的尾部。
同步队列遵循FIFO,首节点是获取同步状态成功的节点,首节点的线程在释放同步状态时,将会唤醒后继节点,而后继节点将会在获取同步状态成功时,将自己设置为首节点。由于只有一个线程能够成功获取到同步状态,因此设置头节点不需要CAS来保证。
独占式同步状态获取与释放
在获取同步状态时,同步器维护一个同步队列,获取状态失败的线程都会加入到队列中并在队列中进行自旋;移除队列(或停止自选)的条件是前驱节点为头节点且当前节点成功获取了同步状态。在释放同步状态时,同步器调用tryRelease(int arg)方法释放同步状态,然后唤醒头节点的后继节点。
独占式同步状态获取流程
public final void acquire(int arg) {
//先调用自定义同步器实现的tryAcquire,获取成功,执行结束。若获取失败!this.tryAcquire为true,构造节点加入同步队列
if (!this.tryAcquire(arg) && this.acquireQueued(this.addWaiter(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg)) {
selfInterrupt();
}
}
private AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.Node addWaiter(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.Node mode) {
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.Node node = new AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.Node(mode);
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.Node oldTail;
//循环CAS,将node设置为尾节点
do {
while(true) {
oldTail = this.tail;
if (oldTail != null) {
//将node的perv指向oldTail
node.setPrevRelaxed(oldTail);
break;
}
this.initializeSyncQueue();
}
} while(!this.compareAndSetTail(oldTail, node));
//将oldTail的next指向node,上链
oldTail.next = node;
return node;
}独占式同步状态释放流程
public final boolean release(int arg) {
//调用自定义同步器实现的tryRelease(arg)
if (this.tryRelease(arg)) {
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.Node h = this.head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0) {
//唤醒处于等待状态的线程
this.unparkSuccessor(h);
}
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}共享式同步状态获取与释放
共享式同步状态获取在同一时刻有多个线程能够同时获取到同步状态。
public final void acquireShared(int arg) {
//先调用自定义同步器实现的tryAcquireShared,大于等于0,表示获取到了同步状态,执行结束。
if (this.tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0) {
this.doAcquireShared(arg);
}
}
private void doAcquireShared(int arg) {
//加入同步队列中
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.Node node = this.addWaiter(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.Node.SHARED);
boolean interrupted = false;
try {
//循环,直到前节点是头节点,尝试获取同步状态
while(true) {
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == this.head) {
int r = this.tryAcquireShared(arg);
if (r >= 0) {
this.setHeadAndPropagate(node, r);
p.next = null;
return;
}
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node)) {
interrupted |= this.parkAndCheckInterrupt();
}
}
} catch (Throwable var9) {
this.cancelAcquire(node);
throw var9;
} finally {
if (interrupted) {
selfInterrupt();
}
}
}共享式同步状态释放流程。
public final boolean releaseShared(int arg) {
if (this.tryReleaseShared(arg)) {
this.doReleaseShared();
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
private void doReleaseShared() {
//循环CAS将waitStatus由-1设置为0
while(true) {
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.Node h = this.head;
if (h != null && h != this.tail) {
int ws = h.waitStatus;
if (ws == -1) {
if (!h.compareAndSetWaitStatus(-1, 0)) {
continue;
}
//唤醒等待线程
this.unparkSuccessor(h);
} else if (ws == 0 && !h.compareAndSetWaitStatus(0, -3)) {
continue;
}
}
if (h == this.head) {
return;
}
}
}等待队列
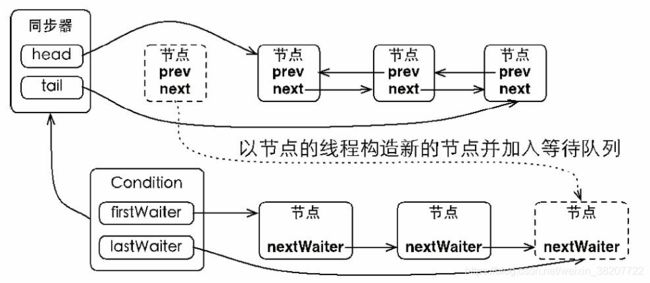
锁可以创建多个Condition与之关联,所以一个同步器有一个同步队列和多个等待队列。
ConditionObject是同步器AbstractQueueSynchronizer的内部类,每一个ConditionObject有一个等待队列,ConditionObject包含了首节点(firstWaiter)和尾节点(lastWaiter)的引用。等待队列节点复用了AbstractQueueSynchronizer.Node,下一节点为Node的nextWaiter。
public class ConditionObject implements Condition, Serializable {
private transient AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.Node firstWaiter;
private transient AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.Node lastWaiter;
}等待,调用Condition.await()方法,会使当前线程进入等待队列并释放锁,同时线程状态更新为等待状态(-2)。以当前线程构造节点,将节点从尾部加入等待队列。新增尾节点只需要将原有的尾节点nextWaiter指向它,并更新尾节点。没有用CAS保证,因为调用await()的线程必定是获取了Condition相关联锁的线程,由锁保证线程安全。
public final void await() throws InterruptedException {
//响应中断
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
throw new InterruptedException();
} else {
//加入等待队列
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.Node node = this.addConditionWaiter();
//释放锁
int savedState = AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.this.fullyRelease(node);
int interruptMode = 0;
//自旋,直到signal唤醒,也就是节点在同步队列中
while(!AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.this.isOnSyncQueue(node)) {
//阻塞该线程
LockSupport.park(this);
//检查中断
if ((interruptMode = this.checkInterruptWhileWaiting(node)) != 0) {
break;
}
}
//竞争同步状态
if (AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.this.acquireQueued(node, savedState) && interruptMode != -1) {
interruptMode = 1;
}
if (node.nextWaiter != null) {
this.unlinkCancelledWaiters();
}
if (interruptMode != 0) {
this.reportInterruptAfterWait(interruptMode);
}
}
}通知,调用Condition.signal()方法,将会唤醒在等待队列中等待时间最长的节点(首节点),在唤醒节点前,会将节点移动到同步队列中。
public final void signal() {
//是否持有锁
if (!AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.this.isHeldExclusively()) {
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
} else {
//将等待队列的第一个加入到同步队列中
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.Node first = this.firstWaiter;
if (first != null) {
this.doSignal(first);
}
}
}队列同步器使用
同步器可重写的方法
//独占式获取同步状态,实现该方法需要查询当前状态并同步判断同步状态是否符合预期,然后再进行CAS设置同步状态。
protected boolean tryAcquire(int arg) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
//独占式释放同步状态,等待获取同步状态的线程将有机会获取同步状态。
protected boolean tryRelease(int arg) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
//共享式获取同步状态,返回大于等于0的值,表示获取成功,反之,获取失败。
protected int tryAcquireShared(int arg) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
//共享式释放同步状态
protected boolean tryReleaseShared(int arg) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
//当前同步状态是否在独占模式下被线程占用,一般该方法表示是否被当前线程所占。
protected boolean isHeldExclusively() {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}同步器提供了众多模板方法,大概分为3类:
-
独占式获取或释放同步状态。
-
共享式获取与释放同步状态。
-
查询同步队列种的等待线程情况。
//调用重写的tryAcquire(int arg)方法,独占式获取同步状态
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!this.tryAcquire(arg) && this.acquireQueued(this.addWaiter(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg)) {
selfInterrupt();
}
}
//与tryAcquire(int arg)相同,该方法响应中断
public final void acquireInterruptibly(int arg) throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
throw new InterruptedException();
} else {
if (!this.tryAcquire(arg)) {
this.doAcquireInterruptibly(arg);
}
}
}
//在acquireInterruptibly(int arg)基础上加上超时限制,在限制时间内未获取到返回false
public final boolean tryAcquireNanos(int arg, long nanosTimeout) throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
throw new InterruptedException();
} else {
return this.tryAcquire(arg) || this.doAcquireNanos(arg, nanosTimeout);
}
}
//独占式释放同步状态
public final boolean release(int arg) {
if (this.tryRelease(arg)) {
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.Node h = this.head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0) {
this.unparkSuccessor(h);
}
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
//共享式获取同步状态
public final void acquireShared(int arg) {
if (this.tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0) {
this.doAcquireShared(arg);
}
}
//与acquiredShared(int arg)相同,该方法响应中断
public final void acquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg) throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
throw new InterruptedException();
} else {
if (this.tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0) {
this.doAcquireSharedInterruptibly(arg);
}
}
}
//在acquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)基础上加上超时限制,在限制时间内未获取到返回false
public final boolean tryAcquireSharedNanos(int arg, long nanosTimeout) throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
throw new InterruptedException();
} else {
return this.tryAcquireShared(arg) >= 0 || this.doAcquireSharedNanos(arg, nanosTimeout);
}
}
//共享式释放同步状态
public final boolean releaseShared(int arg) {
if (this.tryReleaseShared(arg)) {
this.doReleaseShared();
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
//同步队列中是否有其他线程等待获取同步状态
public final boolean hasQueuedThreads() {
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.Node p = this.tail;
for(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.Node h = this.head; p != h && p != null; p = p.prev) {
if (p.waitStatus <= 0) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//是否存在争抢
public final boolean hasContended() {
return this.head != null;
}
//获得队列第一个线程(等待时间最长)
public final Thread getFirstQueuedThread() {
return this.head == this.tail ? null : this.fullGetFirstQueuedThread();
}
//getFirstQueuedThread()调用,判断两次是防止在判断过程中其他线程并发执行了setHead
private Thread fullGetFirstQueuedThread() {
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.Node h;
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.Node s;
Thread st;
if (((h = this.head) == null || (s = h.next) == null || s.prev != this.head || (st = s.thread) == null) && ((h = this.head) == null || (s = h.next) == null || s.prev != this.head || (st = s.thread) == null)) {
Thread firstThread = null;
for(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.Node p = this.tail; p != null && p != this.head; p = p.prev) {
Thread t = p.thread;
if (t != null) {
firstThread = t;
}
}
return firstThread;
} else {
return st;
}
}
//如果给定线程的当前已加入队列,则返回 true。
public final boolean isQueued(Thread thread) {
if (thread == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
} else {
for(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.Node p = this.tail; p != null; p = p.prev) {
if (p.thread == thread) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
//同步队列第一个线程是独占式的
final boolean apparentlyFirstQueuedIsExclusive() {
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.Node h;
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.Node s;
return (h = this.head) != null && (s = h.next) != null && !s.isShared() && s.thread != null;
}
//是否有前置线程
public final boolean hasQueuedPredecessors() {
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.Node h;
if ((h = this.head) != null) {
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.Node s;
if ((s = h.next) == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {
s = null;
for(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.Node p = this.tail; p != h && p != null; p = p.prev) {
if (p.waitStatus <= 0) {
s = p;
}
}
}
if (s != null && s.thread != Thread.currentThread()) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//获得队列长度
public final int getQueueLength() {
int n = 0;
for(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.Node p = this.tail; p != null; p = p.prev) {
if (p.thread != null) {
++n;
}
}
return n;
}
//获得队列全部线程
public final Collection getQueuedThreads() {
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
for(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.Node p = this.tail; p != null; p = p.prev) {
Thread t = p.thread;
if (t != null) {
list.add(t);
}
}
return list;
}
//获取独占式的线程
public final Collection getExclusiveQueuedThreads() {
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
for(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.Node p = this.tail; p != null; p = p.prev) {
if (!p.isShared()) {
Thread t = p.thread;
if (t != null) {
list.add(t);
}
}
}
return list;
}
//获取共享式线程
public final Collection getSharedQueuedThreads() {
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
for(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.Node p = this.tail; p != null; p = p.prev) {
if (p.isShared()) {
Thread t = p.thread;
if (t != null) {
list.add(t);
}
}
}
return list;
}
创建一个独占锁,创建静态内部类Sync来继承AbstractQueueSynchronizer,主类实现Lock接口,调用静态内部类的方法。
public class Mutex implements Lock {
private final Sync sync = new Sync();
//静态内部类,继承队列同步器
private static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
//是否处于占用状态
@Override
protected boolean isHeldExclusively() {
return getState() == 1;
}
//获取锁,state用CAS操作置为1
@Override
protected boolean tryAcquire(int arg) {
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
return true;
}
return false;
}
//释放锁,state置为0
@Override
protected boolean tryRelease(int arg) {
if (getState() == 0) {
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
}
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
setState(0);
return true;
}
Condition newCondition() {
return new ConditionObject();
}
}
//仅需要将操作代理到Sync上
@Override
public void lock() {
sync.tryAcquire(1);
}
@Override
public void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException {
}
@Override
public boolean tryLock() {
return sync.tryAcquire(1);
}
@Override
public boolean tryLock(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
return false;
}
@Override
public void unlock() {
sync.release(1);
}
@Override
public Condition newCondition() {
return sync.newCondition();
}
public boolean isLocked() { return sync.isHeldExclusively(); }
}