iOS 分类category 源码解析
第一部分:有关分类的本质、原理
Q:分类的对象方法,类方法都存在哪里?
一个类的所有分类的 对象方法放在类对象中,所有分类的类方法存放在元类中
clang查看编译文件
xcrun -sdk iphoneos clang -arch arm64 -rewrite-objc NSObject+Test.m
编译文件NSObject+Test.cpp中有关分类内容
//声明结构体
struct _category_t {
const char *name; //类的名字(name)
struct _class_t *cls; //类(cls)
const struct _method_list_t *instance_methods;//category中所有给类添加的实例方法的列表(instanceMethods)
const struct _method_list_t *class_methods;//category中所有添加的类方法的列表(classMethods)
const struct _protocol_list_t *protocols; //category实现的所有协议的列表(protocols)
const struct _prop_list_t *properties; //category中添加的所有属性(instanceProperties)
};
//对结构体赋值
static struct _category_t _OBJC_$_CATEGORY_NSObject_$_Test __attribute__ ((used, section ("__DATA,__objc_const"))) =
{
"NSObject",
0, // &OBJC_CLASS_$_NSObject,
(const struct _method_list_t *)&_OBJC_$_CATEGORY_INSTANCE_METHODS_NSObject_$_Test,
(const struct _method_list_t *)&_OBJC_$_CATEGORY_CLASS_METHODS_NSObject_$_Test,
(const struct _protocol_list_t *)&_OBJC_CATEGORY_PROTOCOLS_$_NSObject_$_Test,
0,
};
Runtime中Category源码解读顺序
objc-os.mm
- _objc_init
- map_images
- map_images_nolock
objc-runtime-new.mm
- _read_images
- remethodizeClass
- attachCategories
- attachLists
- realloc、memmove、 memcpy
Runtime中Category的底层结构
struct category_t {
const char *name;
classref_t cls;
struct method_list_t *instanceMethods;
struct method_list_t *classMethods;
struct protocol_list_t *protocols;
struct property_list_t *instanceProperties;
// Fields below this point are not always present on disk.
struct property_list_t *_classProperties;
method_list_t *methodsForMeta(bool isMeta) {
if (isMeta) return classMethods;
else return instanceMethods;
}
property_list_t *propertiesForMeta(bool isMeta, struct header_info *hi);
};
objc-runtime-new.mm
// cls 类
// cats 分类列表
static void
attachCategories(Class cls, category_list *cats, bool flush_caches)
{
if (!cats) return;
if (PrintReplacedMethods) printReplacements(cls, cats);
bool isMeta = cls->isMetaClass();
// fixme rearrange to remove these intermediate allocations
/*方法数组
[
[method_t,method_t]
[method_t,method_t]
]
*/
method_list_t **mlists = (method_list_t **)
malloc(cats->count * sizeof(*mlists));
//属性数组
property_list_t **proplists = (property_list_t **)
malloc(cats->count * sizeof(*proplists));
//协议数组
protocol_list_t **protolists = (protocol_list_t **)
malloc(cats->count * sizeof(*protolists));
// Count backwards through cats to get newest categories first
int mcount = 0;
int propcount = 0;
int protocount = 0;
int i = cats->count;
bool fromBundle = NO;
while (i--) {
//取出分类
auto& entry = cats->list[i];
//取出分类对象方法
method_list_t *mlist = entry.cat->methodsForMeta(isMeta);
if (mlist) {
mlists[mcount++] = mlist;
fromBundle |= entry.hi->isBundle();
}
property_list_t *proplist =
entry.cat->propertiesForMeta(isMeta, entry.hi);
if (proplist) {
proplists[propcount++] = proplist;
}
protocol_list_t *protolist = entry.cat->protocols;
if (protolist) {
protolists[protocount++] = protolist;
}
}
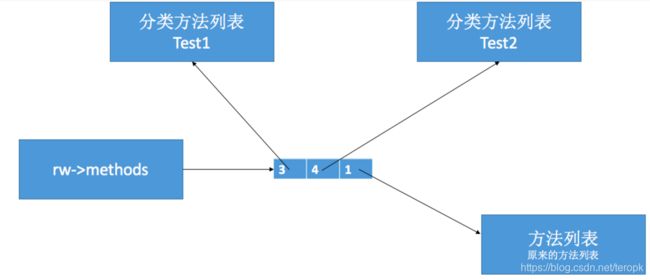
auto rw = cls->data();
prepareMethodLists(cls, mlists, mcount, NO, fromBundle);
rw->methods.attachLists(mlists, mcount);
free(mlists);
if (flush_caches && mcount > 0) flushCaches(cls);
rw->properties.attachLists(proplists, propcount);
free(proplists);
rw->protocols.attachLists(protolists, protocount);
free(protolists);
}
Q:分类的方法何时合并到类对象中?
通过runtime动态将分类的方法合并到类对象、元类对象中的
Q:分类的方法是如何添加到类对象方法列表中的?
runtime源码展示
void attachLists(List* const * addedLists, uint32_t addedCount) {
if (addedCount == 0) return;
if (hasArray()) {
// many lists -> many lists
uint32_t oldCount = array()->count;
uint32_t newCount = oldCount + addedCount;
setArray((array_t *)realloc(array(), array_t::byteSize(newCount)));
array()->count = newCount;
//array()->lists:原来类对象的方法列表
//内存移动
memmove(array()->lists + addedCount, array()->lists,
oldCount * sizeof(array()->lists[0]));
//addedLists:所有分类的方法列表
//内存拷贝
memcpy(array()->lists, addedLists,
addedCount * sizeof(array()->lists[0]));
}
else if (!list && addedCount == 1) {
// 0 lists -> 1 list
list = addedLists[0];
}
else {
// 1 list -> many lists
List* oldList = list;
uint32_t oldCount = oldList ? 1 : 0;
uint32_t newCount = oldCount + addedCount;
setArray((array_t *)malloc(array_t::byteSize(newCount)));
array()->count = newCount;
if (oldList) array()->lists[addedCount] = oldList;
memcpy(array()->lists, addedLists,
addedCount * sizeof(array()->lists[0]));
}
}
重要代码:
//array()->lists:原来类对象的方法列表
//内存移动
memmove(array()->lists + addedCount, array()->lists, oldCount * sizeof(array()->lists[0]));
//addedLists:所有分类的方法列表
//内存拷贝
memcpy(array()->lists, addedLists, addedCount * sizeof(array()->lists[0]));
大概流程
-
1.获取分类列表的count,然后原来的类方法列表内存移动count
-
2.分类列表内存拷贝到原来的类方法列表的前方
-
3.同样的方法,优先调用分类的方法
-
4.分类具有同样的方法,根据编译顺序决定,取最后编译分类的方法列表
Q:Category的加载处理过程?
- 1.通过Runtime加载某个类的所有Category数据
- 2.把所有Category的方法、属性、协议数据,合并到一个大数组中
- 3.后面参与编译的Category数据,会在数组的前面
- 4.将合并后的分类数据(方法、属性、协议),插入到类原来数据的前面
Q:Category的实现原理
- Category编译之后的底层结构是struct category_t,里面存储着分类的对象方法、类方法、属性、协议信息
- 在程序运行的时候,runtime会将Category的数据,合并到类信息中(类对象、元类对象中)
Q:memmove和memcpy的区别?
memmove会根据内存大小,移动方向,数量来移动内存;memcpy是按照一定规则一个地址一个地址拷贝。memmove能保证原数据完整性,内部移动最好不要使用memcpy,外部内存移动可以使用。
第二部分:+load 和 +initialize方法
Q: +load方法调用原理?
objc4源码解读过程:
objc-os.mm
_objc_init
load_images
prepare_load_methods
schedule_class_load
add_class_to_loadable_list
add_category_to_loadable_list
call_load_methods
call_class_loads
call_category_loads
(*load_method)(cls, SEL_load)
objc-loadmethod.mm
struct loadable_class {
Class cls; // may be nil
IMP method; // +load
};
struct loadable_category {
Category cat; // may be nil
IMP method; // 分类的+load
};
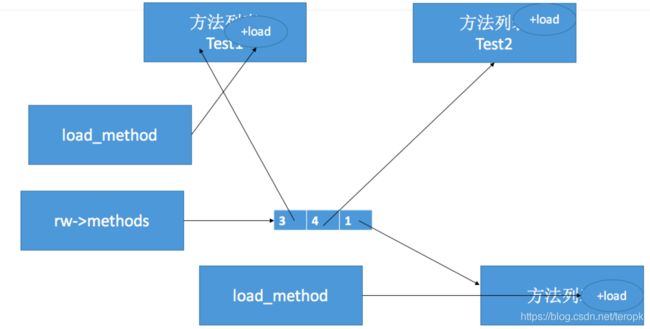
Q:+load方法调用顺序?
- 先调用类的+load方法
- 1.1按照编译先后顺序调用(先编译,先调用)
- 1.2先调用父类的+load再调用子类的+load
- 再调用分类的+load方法
- 2.1按照编译先后顺序调用(先编译,先调用)
// 1. Repeatedly call class +loads until there aren't any more
while (loadable_classes_used > 0) {
call_class_loads();
}
// 2. Call category +loads ONCE
more_categories = call_category_loads();
- 每个类、分类的+load,在程序运行过程中只调用一次,只有在加载类时候调用一次
- 不存在分类的+load方法覆盖类的+load方法
Q:+load方法为什么和其他的类方法调用方式不同?
其他分类类方法是通过消息转发机制调用的,isa和superclass来寻找的;而+load是通过函数指针指向函数,拿到函数地址,分开来直接调用的,直接通过内存地址查找调用的。
Q:Category中有load方法吗?load方法是什么时候调用的?load 方法能继承吗?
- 有load方法
- load方法在runtime加载类、分类的时候调用
- load方法可以继承,但是一般情况下不会主动去调用load方法,都是让系统自动调用
Q:+initialize方法是怎么调用的?
+initialize方法会在类第一次接收到消息时调用,消息转发机制调用的(objc_send)
Q:+initialize方法调用顺序?
先调用父类的+initialize,再调用子类的+initialize;(先初始化父类,再初始化子类,每个类只会初始化1次),子类内部+initialize会主动调用父类的+initialize
runtime探索objc_msgSend内部调用initialize
objc4源码解读过程
objc-msg-arm64.s
objc_msgSend
objc-runtime-new.mm
class_getInstanceMethod
lookUpImpOrNil
lookUpImpOrForward
_class_initialize
callInitialize
objc_msgSend(cls, SEL_initialize)
部分源码展示:
IMP lookUpImpOrForward(Class cls, SEL sel, id inst,
bool initialize, bool cache, bool resolver)
{
//.......中间省略一部分源码
//下面代码展示如果initialize需要初始化 && 类未被初始化过就执行以下函数
if (initialize && !cls->isInitialized()) {
runtimeLock.unlockRead();
_class_initialize (_class_getNonMetaClass(cls, inst));
runtimeLock.read();
// If sel == initialize, _class_initialize will send +initialize and
// then the messenger will send +initialize again after this
// procedure finishes. Of course, if this is not being called
// from the messenger then it won't happen. 2778172
}
}
Q:+initialize和+load的很大区别是?
- +initialize是通过objc_msgSend进行调用的
- 如果子类没有实现+initialize,会调用父类的+initialize(所以父类的+initialize可能会被调用多次)
- 如果分类实现了+initialize,就覆盖类本身的+initialize调用
- +load是通过函数指针指向函数,拿到函数地址,分开来直接调用的,直接通过内存地址查找调用的。
Q:load、initialize方法的区别什么?
-
1.调用方式
1> load是根据函数地址直接调用
2> initialize是通过objc_msgSend调用 -
2.调用时刻
1> load是runtime加载类、分类的时候调用(只会调用1次)
2> initialize是类第一次接收到消息的时候调用,每一个类只会initialize一次(父类的initialize方法可能会被调用多次)
Q:load、initialize的调用顺序?
1.load
-
1> 先调用类的load
a) 先编译的类,优先调用load
b) 调用子类的load之前,会先调用父类的load -
2> 再调用分类的load
a) 先编译的分类,优先调用load
2.initialize
1> 先初始化父类
2> 再初始化子类(可能最终调用的是父类的initialize方法)
第三部分:关联对象
Q:分类声明属性,系统都做了什么?
分类声明属性,系统只生成setter和getter方法的声明,但是成员变量、setter和getter方法的实现均没有。
Q:为什么不能用字典为分类增加实例变量
字典为分类增加实例变量存在全局变量中,内存泄漏
多线程访问会存在同时访问变量的情况,还得加锁处理
每增加一个变量,字典、setter、getter方法就得重新编写
Q:Category能否添加成员变量?如果可以,如何给Category添加成员变量?
不能直接给Category添加成员变量,但是可以间接实现Category有成员变量的效果
默认情况下,因为分类底层结构的限制,不能添加成员变量到分类中。但可以通过关联对象来间接实现
Q:如何给分类关联对象?
添加关联对象
// object:当前对象
// key:标记key
//value :关联属性值
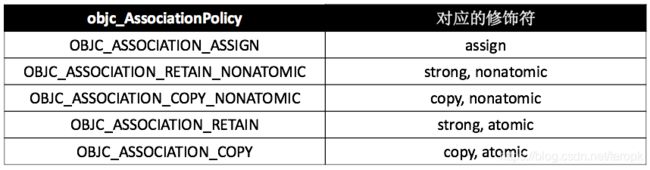
//objc_AssociationPolicy:关联对象策略
void objc_setAssociatedObject(id object, const void * key,
id value, objc_AssociationPolicy policy)
-
获得关联对象
id objc_getAssociatedObject(id object, const void * key) -
移除所有的关联对象
void objc_removeAssociatedObjects(id object)
关联对象代码示例:
#import "Person.h"
@interface Person (Test1)
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *name;
@end
#import "Person+Test1.h"
#import
@implementation Person (Test1)
//保证nameKey唯一即可
static void * nameKey = &nameKey;
- (void)setName:(NSString *)name{
objc_setAssociatedObject(self, nameKey, name, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_COPY_NONATOMIC);
}
- (NSString *)name{
return objc_getAssociatedObject(self, nameKey);
}
@end
保证关联对象key唯一的其他方法
static void *MyKey = &MyKey;
objc_setAssociatedObject(obj, MyKey, value, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN_NONATOMIC)
objc_getAssociatedObject(obj, MyKey)
//static char MyKey;
objc_setAssociatedObject(obj, &MyKey, value, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN_NONATOMIC)
objc_getAssociatedObject(obj, &MyKey)
//使用属性名作为key
//直接使用的@"name"类似的变量是存在常量区的,所以地址会相同
objc_setAssociatedObject(obj, @"property", value, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN_NONATOMIC);
objc_getAssociatedObject(obj, @"property");
//使用get方法的@selecor作为key
objc_setAssociatedObject(obj, @selector(getter), value, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN_NONATOMIC)
objc_getAssociatedObject(obj, @selector(getter))
objc_getAssociatedObject(self, _cmd);
//_cmd:表示当前方法的selector方法
Q:关联对象的原理
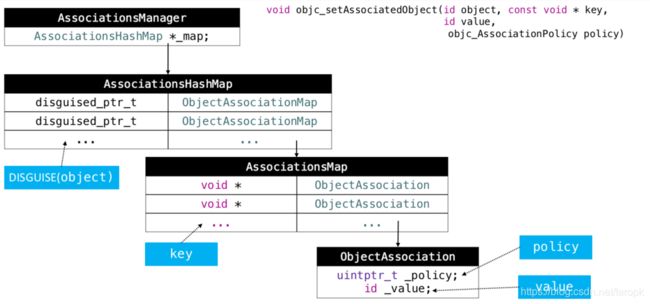
实现关联对象技术的核心对象有
- AssociationsManager
- AssociationsHashMap
- ObjectAssociationMap
- ObjcAssociation
objc4源码解读:objc-references.mm
void _object_set_associative_reference(id object, void *key, id value, uintptr_t policy) {
// retain the new value (if any) outside the lock.
ObjcAssociation old_association(0, nil);
id new_value = value ? acquireValue(value, policy) : nil;
{
AssociationsManager manager;
AssociationsHashMap &associations(manager.associations());
disguised_ptr_t disguised_object = DISGUISE(object);
if (new_value) {
// break any existing association.
AssociationsHashMap::iterator i = associations.find(disguised_object);
if (i != associations.end()) {
// secondary table exists
ObjectAssociationMap *refs = i->second;
ObjectAssociationMap::iterator j = refs->find(key);
if (j != refs->end()) {
old_association = j->second;
j->second = ObjcAssociation(policy, new_value);
} else {
(*refs)[key] = ObjcAssociation(policy, new_value);
}
} else {
// create the new association (first time).
ObjectAssociationMap *refs = new ObjectAssociationMap;
associations[disguised_object] = refs;
(*refs)[key] = ObjcAssociation(policy, new_value);
object->setHasAssociatedObjects();
}
} else {
// setting the association to nil breaks the association.
AssociationsHashMap::iterator i = associations.find(disguised_object);
if (i != associations.end()) {
ObjectAssociationMap *refs = i->second;
ObjectAssociationMap::iterator j = refs->find(key);
if (j != refs->end()) {
old_association = j->second;
refs->erase(j);
}
}
}
}
// release the old value (outside of the lock).
if (old_association.hasValue()) ReleaseValue()(old_association);
}
核心对象内部:
//AssociationsManager内包含AssociationsHashMap
class AssociationsManager {
static AssociationsHashMap *_map;
}
//AssociationsHashMap内包含ObjectAssociationMap
class AssociationsHashMap : public unordered_map
//ObjectAssociationMap内包含ObjcAssociation
class ObjectAssociationMap : public std::map
//ObjcAssociation 内包含策略和属性值
class ObjcAssociation {
uintptr_t _policy;
id _value;
}
Q:关联对象是否储存在类对象内存中?
答案:不是的
- 关联对象并不是存储在被关联对象本身内存中
- 关联对象存储在全局的统一的一个AssociationsManager,AssociationsHashMap中
Q:设置关联对象为nil,会发生什么?
相当于是移除关联对象,内部会有一个erase操作
Q:如何移除所有关联对象?
移除所有的关联对象
void objc_removeAssociatedObjects(id object)
Q:如果类对象销毁,分类的关联对象会移除么?
会的