okhttp之RealCall.execute()流程介绍
转载请以链接形式标明出处:
本文出自:103style的博客
base on 3.12.0
目录
- 前言
- OkHttpClient.newCall(Request)
- RealCall.execute()
- RealInterceptorChain.proceed(request)
- 小结
前言
前面我们对 OkHttpClient 和 Request 做了相关的介绍。
此时我们已经构建了 http客户端 和 http请求,接下来就好通过 http客户端 来执行http请求。即先通过OkHttpClient.newCall(Request)构建RealCall,然后通过 RealCall.execute() 来执行请求。
OkHttpClient.newCall(Request)
通过下面的源码我们知道 OkHttpClient 的 newCall 方法即通过 RealCall.newRealCall()构建了一个RealCall实例,将 OkHttpClient 和 Request 赋值给实例的成员变量. 以及初始化了拦截器 RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor.
//OkHttpClient
public Call newCall(Request request) {
return RealCall.newRealCall(this, request, false );
}
//RealCall
private RealCall(OkHttpClient client, Request originalRequest, boolean forWebSocket) {
this.client = client;
this.originalRequest = originalRequest;
this.forWebSocket = forWebSocket;
this.retryAndFollowUpInterceptor = new RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor(client, forWebSocket);
this.timeout = new AsyncTimeout() {
@Override protected void timedOut() {
cancel();
}
};
this.timeout.timeout(client.callTimeoutMillis(), MILLISECONDS);
}
static RealCall newRealCall(OkHttpClient client, Request originalRequest, boolean forWebSocket) {
// Safely publish the Call instance to the EventListener.
RealCall call = new RealCall(client, originalRequest, forWebSocket);
call.eventListener = client.eventListenerFactory().create(call);
return call;
}
RealCall.execute()
public Response execute() throws IOException {
...
try {
client.dispatcher().executed(this);
Response result = getResponseWithInterceptorChain();
...
} catch (IOException e) {
...
} finally {
client.dispatcher().finished(this);
}
}
通过上面的代码我们知道是通过getResponseWithInterceptorChain();获取到请求的结果。
Response getResponseWithInterceptorChain() throws IOException {
// Build a full stack of interceptors.
List interceptors = new ArrayList<>();
interceptors.addAll(client.interceptors());
interceptors.add(retryAndFollowUpInterceptor);
interceptors.add(new BridgeInterceptor(client.cookieJar()));
interceptors.add(new CacheInterceptor(client.internalCache()));
interceptors.add(new ConnectInterceptor(client));
if (!forWebSocket) {
interceptors.addAll(client.networkInterceptors());
}
interceptors.add(new CallServerInterceptor(forWebSocket));
Interceptor.Chain chain = new RealInterceptorChain(interceptors, null, null, null, 0,
originalRequest, this, eventListener, client.connectTimeoutMillis(),
client.readTimeoutMillis(), client.writeTimeoutMillis());
return chain.proceed(originalRequest);
}
getResponseWithInterceptorChain中依次添加了以下的拦截器,后面会具体介绍:
client.interceptors():我们通过OkhttpClient添加的自定义拦截器retryAndFollowUpInterceptor:重试及重定向拦截器BridgeInterceptor:桥接拦截器CacheInterceptor:缓存拦截器ConnectInterceptor:连接拦截器client.networkInterceptors():网络请求的拦截器CallServerInterceptor:读写拦截器
然后将 request请求 和 interceptors这个拦截器集合构建了一个 RealInterceptorChain.
然后通过RealInterceptorChain.proceed(originalRequest);返回请求结果。
RealInterceptorChain.proceed(request)
public Response proceed(...) throws IOException {
if (index >= interceptors.size()) throw new AssertionError();
calls++;
...
RealInterceptorChain next = new RealInterceptorChain(interceptors, streamAllocation, httpCodec,
connection, index + 1, request, call, eventListener, connectTimeout, readTimeout,
writeTimeout);
Interceptor interceptor = interceptors.get(index);
Response response = interceptor.intercept(next);
...
return response;
}
我们可以看到这里通过interceptor.intercept(next);获取的请求结果。
我们先以RetryAndFollowUpInterceptor来介绍下。
public Response intercept(Chain chain) throws IOException {
RealInterceptorChain realChain = (RealInterceptorChain) chain;
...
response = realChain.proceed(request, streamAllocation, null, null);
...
}
看到上面代码中的realChain.proceed(...);方法,是不是又回到了上面的RealInterceptorChain.proceed(request).
所以由此可知RealInterceptorChain.proceed(request)会 “依次” 去调用拦截器列表每个interceptors中的interceptor.intercept(next),如下图:
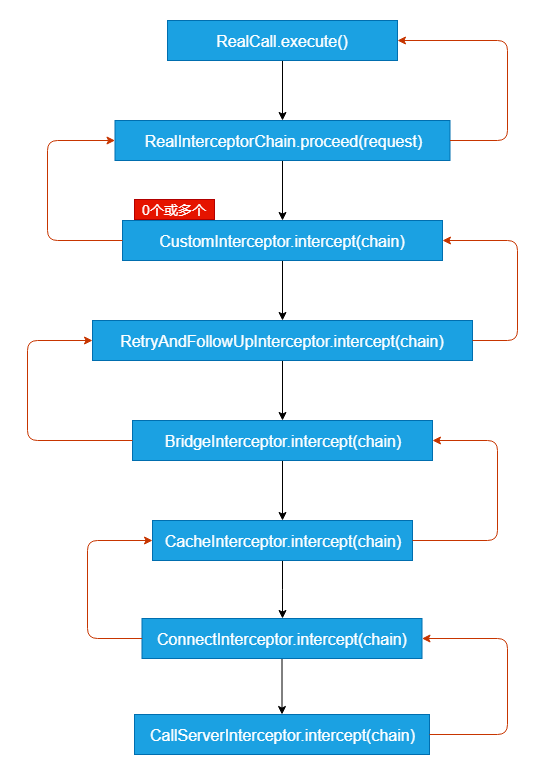
拦截器具体做了什么操作呢?请听下回分解。见 okhttp之五个拦截器的介绍
小结
通过上面的介绍,我们知道了:
OkHttpClient.newCall(Request)构建了一个RealCall实例。RealCall.execute()通过添加一系列拦截器,然后依次执行拦截器的intercept(chain)方法,然后把响应结果再一层一层回传到给RealCall。
以上