Hibernate中的CRUD基本操作以及三种对象状态
实现简单的增删改查
Save()方法
@Test
public void test() {
//读取核心配置文件
Configuration cfg=new Configuration().configure();
//构建核心SessionFactory
SessionFactory sessionFactory = cfg.buildSessionFactory();
//获取session
Session session = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
//开启事务
session.beginTransaction();
//添加对象
Student s1=new Student();
s1.setSname("李四");
s1.setScore(98.0);
s1.setAge(18);
session.save(s1);
//提交事务
session.getTransaction().commit();
}
Delete()方法
@Test
public void test001() {
//读取核心配置文件
Configuration cfg=new Configuration().configure();
//构建核心SessionFactory
SessionFactory sessionFactory = cfg.buildSessionFactory();
//获取session
Session session = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
//开启事务
session.beginTransaction();
//获取对象信息
Student stu = session.get(Student.class, 1);
//删除对象
session.delete(stu);
//提交事务
session.getTransaction().commit();
}
Update()方法
@Test
public void test002() {
//读取核心配置文件
Configuration cfg=new Configuration().configure();
//构建核心SessionFactory
SessionFactory sessionFactory = cfg.buildSessionFactory();
//获取session
Session session = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
//开启事务
session.beginTransaction();
//获取对象信息
Student stu = session.get(Student.class, 2);
//修改信息
stu.setSname("哈哈");
stu.setScore(100);
stu.setAge(22);
//修改对象
session.update(stu);
//提交事务
session.getTransaction().commit();
}
Get()方法:若对象不存在,则会返回null,但是不报错;
@Test
public void test003() {
//读取核心配置文件
Configuration cfg=new Configuration().configure();
//构建核心SessionFactory
SessionFactory sessionFactory = cfg.buildSessionFactory();
//获取session
Session session = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
//开启事务
session.beginTransaction();
//获取对象信息
Student stu1 = session.get(Student.class, 200);
System.out.println(stu1);
System.out.println("---get方法1----");
//提交事务
session.getTransaction().commit();
}
Load()方法:若对象不存在的情况下,会报异常;
@Test
public void test004() {
//读取核心配置文件
Configuration cfg=new Configuration().configure();
//构建核心SessionFactory
SessionFactory sessionFactory = cfg.buildSessionFactory();
//获取session
Session session = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
//开启事务
session.beginTransaction();
//获取对象信息
Student stu1 = session.load(Student.class, 200);
System.out.println(stu1);
System.out.println("---load方法1----");
//提交事务
session.getTransaction().commit();
}
Persister()方法:相当于save()
@Test
public void test005() {
//读取核心配置文件
Configuration cfg=new Configuration().configure();
//构建核心SessionFactory
SessionFactory sessionFactory = cfg.buildSessionFactory();
//获取session
Session session = sessionFactory.getCurrentSession();
//开启事务
session.beginTransaction();
//获取对象信息
Student stu=new Student();
stu.setAge(25);
stu.setScore(80);
stu.setSname("刘烨");
session.persist(stu);//持久化对象
//提交事务
session.getTransaction().commit();
}
一些方法的区别:
- get() VS load();
- load查询数据时若数据不存在,则报错;
- get数据时若数据不存在,则返回null;
- load懒加载,若缓存有,直接使用,get立即查询;
- load获取当前对象的代理
- saveOrUpdate()详解:
- 传入的实际参数若有id,则修改操作;
- 传入的对象若没有id,在自增的前提下,添加操作;
- evict VS delete区别:
- evict删除的是session中的对象,不需要发送sql语句;
- delete 删除的是数据库中的数据,故此要发送sql;
- getCurrentSession() vs OpenSession
- getCurrentSession 需要注册sesssion上下文
- getCurrentSession:
thread - session不需要关闭;
- getCurrentSession:
- OpenSession不需要注册session上下文;推荐手动关闭session
- getCurrentSession获取的式同一个session
- OpenSession 开启新的session对象
- getCurrentSession 需要注册sesssion上下文
工具类的封装;
SessionFactory 对象特点
重量级对象(系统开销大)、单例的、线程安全的。
按理说,单例对象一定是被共享的,是线程不安全的。但查看 SessionFactory 接口的实现类 SessionFactoryImpl 源码,可以看其大多数成员变量是 final 的,所以其是线程安全的。
public class HbnUtil {
// 线程安全,可以当做成员对象共享给各个成员;
public static SessionFactory sessionFactory;
/**
* 获取sessionFactory对象
* @return
*/
public static SessionFactory getSessionFactory() {
if (sessionFactory == null || sessionFactory.isClosed()) {
return new Configuration().configure().buildSessionFactory();
} else {
return sessionFactory;
}
}
/**
* 获取session *
* @return
*/
public Session getSession() {
// 调用方法
return getSessionFactory().getCurrentSession();
}
}
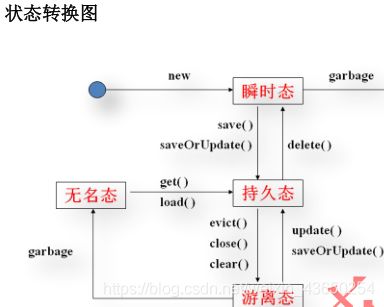
Hibernate三种对象状态:临时状态、持久化状态、游离化状态
Hibernate 的对象状态;
对象的状态一般是指对象的一组属性的值。而这里的状态是指对象处于什么存储介质中。
用于存放对象的存储介质有三个:普通内存(与 Hibernate 无关)、Session 缓存、数据库。
对象处于不同的介质,就将处于不同的状态
(1)瞬时态:transient 状态,对象在内存中存在,但 DB 中无记录,与 Session 无关,是个过渡状态。
(2)持久态:persistent 状态,在内存中存在,DB 中有记录,与 Session 相关,在 Session中有对象的副本。
(3)游离态:detached 状态,在内存中存在,在 DB 中有记录,与 Session 无关。
(4)无名态:在内存中不存在,但在 DB 中有记录,与 Session 无关
状态转换常用方法
| 方法 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| save( ) | 将瞬时态对象同步到 DB 中 |
| update( ) | 将游离态对象同步到 DB 中 |
| delete( ) | 将指定的对象从 session 中删除,同时也删除 DB 中的该数据 |
| close( ) | 关闭 Session 对象 |
| clear( ) | 清空 Session 的缓存 |
| saveOrUpdate( ) | 根据参数对象的 id 属性是否为 null 来判断是执行保存还是更新操作 |
| evict( ) | 将指定对象仅仅从 session 中删除,但不删除 DB 中的该数据 |
| load( )与 get( ) | 将无名态对象转换为持久态对象 |