Java面试宝典(一):JavaSE基础(4)——JavaSE常用API
1、Math.round(11.5)是多少?Math.round(-11.5)是多少
12,-11。四舍五入的原理是在参数上加0.5然后进行取整
2、switch是否能作用在byte上,能否能作用在long上,是否能作用在String上
Java5以前,switch(expr)中,expr只能是byte、short、char、int。从java5开始,java引入枚举类型,expr也可以是enum类型。
从java7开始,expr还可以是字符串(String),但是长整型(long)在目前所有版本都是不可以的。
3、数组 有没有length()方法?String 有没有length()方法
数组没有length()方法,而是有length属性。 String有length()方法。JavaScript中,获取字符串的长度是通过length属性得到的,容易混淆
4、String、StringBuild、StringBuffer的区别
Java平台提供了两种类型的字符串:String和StringBuffer/StringBuilder,它们 都可以储存和操作字符串,区别如下
(1) String是只读字符串,也就意味着String引用的字符串内容是不能改变的。
(2)StringBuffer/StringBuilder表示的字符串对象可以直接进行修改。
(3)StringBuilder是Java5引入的,它和StringBuffer的方法完全相同,区别在于它是在单线程环境下使用的,因为它的所有方法都没有被synchronized修饰,因此它的效率理论上也比StringBuffer要高。
5、什么情况下用“+”运算符进行字符串连接比调用StringBuffer/StringBuilder对的append方法连接字符串性能更好?
字符串是Java程序中最常用的数据结构之一。在Java中String类以及重载了“+”。也就是说,字符串可以直接使用“+”进行连接。
在Java中,无论使用何种方式进行字符串连接,实际上都使用的是StringBuilder。
从运行结果来解释,“+”和StringBuilder是完全 等效的,但从运行效率和资源消耗方面看,存在很大的区别。
在for循环语句中,如果使用“+”,这意味着每执行一次循环,就会创建一个StringBuilder对象,虽然Java有垃圾回收器,但这个回收器的工作时间是不定的。如果产生这样的垃圾仍会占用大量的资源。解决这个 问题的方法就是在 程序中直接使用 StringBuilder来连接字符串。
在使用StringBuilder时要注意,尽量不要“+”和StringBuilder混着用,否则 会创建更多的StringBuilder对象。
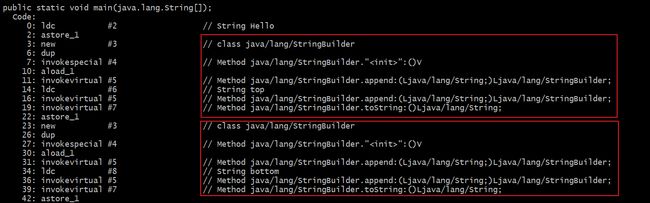
(1)字符串常量相加,jvm会进行优化,不会创建StringBuilder对象
String a = "Hello" + "world" + "!";(2)字符串变量加上常量,会创建StringBuilder对象,然后调用append方法
String a = "Hello";
a += "top";
a += "bottom";可以看到,两个加号,创建了两个 StringBuilder 对象
String a = "ab";
String b = "a" + "b";
System.out.println((a == b));//true,在JAVA代码进行编译时,JAVA编译器已经将String b="a"+"b";优化成String b="ab"; 然后,因为JVM中对字符串的操作是在栈中,所以在运行是,发现栈中已经有了"ab"所以就直接引用
String a = "ab";
String str = "b";
String b = "a" + str;
System.out.println((a == b)); //false,因为str是变量,所以String str = "b"; String b = "a" + str; 就不能优化成b="ab";会创建StringBuilder对象
String a = "ab";
final String str = "b";
String b = "a" + str;
System.out.println((a == b)); //true,tr声明成了final的, 又变成了常量
5、Java的日期和时间
(1)如果取得年月日、小时分钟秒?
public class DateTimeTest{
public static void main(String[] args){
Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance();
System.out.println(cal.get(Calendar.YEAR));
System.out.println(cal.get(Calendar.MONTH));//0-11
System.out.println(cal.get(Calendar.DATE));
System.out.println(cal.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY));
System.out.println(cal.get(Calendar.MINUTE));
System.out.println(cal.get(Calendar.SECOND));
//Java8
LocalDateTime dt = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println(dt.getYear());
System.out.println(dt.getMonthValue()); // 1-12
System.out.println(dt.getDayOfMonth());
System.out.println(dt.getHour());
System.out.println(dt.getMinute());
System.out.println(dt.getSecond());
}
}(2)取得从1970年1月1日0时0分0秒到现在的毫秒数
Calendar.getInstance().getTimeInMillis(); //第一种方式
System.currentTimeMillis(); //第二种方式
//Java8
Clock.systemDefaultZone().millis();(3)获取某月的最后一天
//获取当前月第一天
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
c.add(Calendar.MONTH, 0);
c.set(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH,1);//设置为 1 号 当前日期既为本月第一天
String first = format.format(c.getTime());
System.out.println("===============first:"+first);
//获取当前月最后一天
Calendar ca = Calendar.getInstance();
ca.set(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH, ca.getActualMaximum(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH));
String last = format.format(ca.getTime());
System.out.println("===============last:"+last);
//Java 8
LocalDate today = LocalDate.now();
//本月的第一天
LocalDate firstday = LocalDate.of(today.getYear(),today.getMonth(),1);
//本月最后一天
LocalDate lastDay =today.with(TemporalAdjusters.lastDayOfMonth());
System.out.println("本月的第一天"+firstday);
System.out.println("本月的最后一天"+lastDay);(4)如何格式化日期
Java.text.DataFormat 的子类(如 SimpleDateFormat 类)中的 format(Date) 方法可将日期格式化。
Java 8 中可以用 java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter 来格式化时间日期,代码如下所示
SimpleDateFormat oldFormatter = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM/dd");
Date date1 = new Date();
System.out.println(oldFormatter.format(date1));
//Java8
DateTimeFormatter newFormatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy/MM/dd");
LocalDate date2 = LocalDate.now();
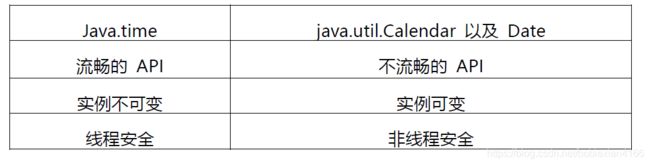
System.out.println(date2.format(newFormatter));Java 的时间日期 API 一直以来都是被诟病的东西,为了解决这一问题, Java 8 中引入了新的时间日期 API。其中包括 Local Date 、 LocalTime 、 LocalDateTime 、 Clock 、 Instant 等类,这些的类的设计都使用了不变模式,因此是线程安全的设计 。
(5)打印昨天当前时刻
class YesterdayCurrent{
public static void main(String[] args){
Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance();
cal.add(Calendar.DATE,-1);
System.out.println(cal.getTime());
}
}
//Java8
class YesterdayCurrent{
public static void main(String[] args){
LocalDateTime today = LocalDateTime.now();
LocalDateTime yesterday = today.minusDays(1);
System.out.println(yesterday);
}
}(7)Java 8 日期/时间特性
Java 8 日期/时间API 是JSR-310 的实现,它的实现目标是克服旧的日期时间实现中所有的缺陷,新的日期/时间
API的一些设计原则是:
- 不变性:新的日期/时间API中, 所有的类都是不可变的,这对多线程环境有好处。
- 关注点分离:新的API将人可读写的日期时间和机器时间(Unix timestamp)明确分离,它为日期(Date)、时间(Time)、日期时间(DateTime)、时间戳(Unix timestamp)以及时区定义了不同的类。
- 清晰:在所有的类中,方法都被明确定义用以完成相同的行为。举个例子,要拿到当前时间我们可以使用now() 方法,在所有的类中都定义力量format()和parse()方法,而不是像以前那样专门有个独立的类。为了更好的处理问题,所有的类都使用了工厂模式和策略模式,一旦你使用了其中某个类的方法,与其他类协同工作并不困难。
- 实用操作:所有新的日期/时间API类都实现了一系列方法用以完成通用的任务,如:加、减、格式化、解析、从日期/时间中提取单独部分等等
- 可扩展性:新的日期/时间API是工作在ISO-8610日历系统上的,但我们也可以将其应用在非IOS的日历上。
- java.time 包:这是新的 Java 日期 时间 API 的基础包,所有的主要基础类都是这个包的一部分,如: LocalDate,LocalTime, LocalDateTime, Instant, Pe riod, Duration 等等。所有这些类都是不可变的和线程安全的,在绝大多数情况下,这些类能够有效地处理一些公共的需求。
- java.time.chrono 包:这个包为非 ISO 的日历系统定义了一些泛化的 API ,我们可以扩展 AbstractChronology类来创建自己的日历系统。
- java.time.format 包:这个包包含能够格式化和解析日期时间对象的类,在绝大多数情况下,我们不应该直接使用它们,因为 java.time 包中相应的类已经提供了格式化和解析的方法。
- java.time.temporal 包 :这个包包含一些时态对象,我们可以用其找出关于日期 时间对象的某个特定日期或时间,比如说,可以找到某月的第一天或最后一天。你可以非常容易地认出这些方法,因为它们都具有 "withXXX" 的格式。
- java.time.zone 包:这个包包含支持不同时区以及相关规则的类。
(8)Java8日期/ 时间常用API
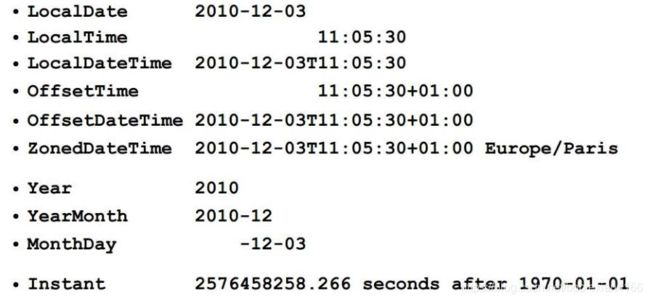
java.time.LocalDate
LocalDate是一个不可变的类,它表示默认格式 (yyyy MM dd) 的日期,我们可以使用 now() 方法得到当前时间,也可以提供输入年份、月份和日期的输入参数来 创建一个 LocalDate 实例。该类为 now() 方法提供了重载方法,我们可以传入 ZoneId 来获得指定时区的日期。该类提供与 java.sql.Date 相同的功能,对于如何使用该类,我们来看一个简单的例子。
//当前时间
LocalDate today = LocalDate.now();
System.out.println("Current Date="+today);//Current Date=2014-04-28
//根据条件创建时间
LocalDate firstDay_2014 = LocalDate.of(2014, Month.JANUARY, 1);
System.out.println("Specific Date="+firstDay_2014);//Specific Date=2014-01-01
LocalDate todayKolkata = LocalDate.now(ZoneId.of("Asia/Shanghai"));
System.out.println("Current Date in IST="+todayKolkata);//Current Date in IST=2014-04-29
//java.time.LocalDate.ofEpochDay(long epochDay)方法从纪元日计数中获取LocalDate的实例
LocalDate dateFromBase = LocalDate.ofEpochDay(365);
System.out.println("365th day from base date= "+dateFromBase);//365th day from base date= 1971-01-01
LocalDate hundredDay201 4 = LocalDate.ofYearDay(2014, 100);
System.out.println("100th day of 2014="+hundredDay2014);//100th day of 2014=2014-04-10java.time.LocalTime
LocalTime
是一个不可变的类,它的实例代表一个符合人类可读格式的时间,默认格式是 hh:mm:ss.zzz 。像LocalDate 一样,该类也提供了时区支持,同时也可以传入小时、分钟和秒等输入参数创建实例,我们来看一个简单的程序,演示该类的使用方法。
//当前时间
LocalTime time = LocalTime.now();
System.out.println("Current Time="+time);//Current Time=15:51:45.240
LocalTime specificTime = LocalTime.of(12,20,25,40);
System.out.println("Specific Time of Day="+specificTime);//Specific Time of Day=12:20:25.000000040
LocalTime timeKolkata = LocalTime.now(ZoneId.of("Asia/Shanghai"));
System.out.println("Current Time in IST="+timeKolkata);//Current Time in IST=04:21:45.276
LocalTime specificSecondTime = LocalTime.ofSecondOfDay(10000);
System.out.println("10000th second time= "+specificSecondTime);//10000th second time= 02:46:40java.time.LocalDateTime
LocalDateTime
是一个不可变的日期 时间对象,它表示一组日期 时间,默认格式是 yyyy MM dd HH mmss.zzz 。它提供了一个工厂方法,接收 LocalDate 和 LocalTime 输入参数,创建 LocalDateTime 实例。我们来看一个简单的例子。
LocalDateTime today = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println("Current DateTime="+today);//Current DateTime=2014 04 28T16:00:49.455
today = LocalDateTime.of(LocalDate.now(), LocalTime.now());
System.out.println("Current DateTime="+today);//Current DateTime =2014 04 28T16:00:49.493
LocalDateTime specificDate = LocalDateTime.of(2014, Month.JANUARY, 1, 10, 10, 30);
System.out.println("Specific Date="+specificDate);//Specific Date=2014 01 01T10:10:30
LocalDateTime todayKolkata = LocalDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("Asia/Kolkata"));
System.out.println("Current Date in IST="+todayKolkata);//Current Date in IST=2014 04 29T04:30:49.493
LocalDateTime dateFromBase = LocalDateTime.ofEpochSecond(10000, 0, ZoneOffset.UTC);
System.out.println("10000th second time from 01/01/1970= "+dateFromBase);//10000th second time from 01/01/1970= 1970 01 01T02:46:40在所有这三个例子中,我们已经看到如果我们提供了无效的参数去创建日期时间,那么系统会抛出java.time.DateTimeException ,这是一种运行时异常,我们并不需要显式地捕获它。
同时我们也看到,能够通过传入ZoneId 得到日期 时间数据,你可以从它的 Javadoc 中得到支持的 Zoneid 的列表,当运行以上类时,可以得到以 上 输出。
java.time.instant
Instant类是用在机器可读的时间格式上的,它以Unix时间戳的形式存储日期时间
Instant timestamp = Instant.now();
System.out.println("Current Timestamp = "+timestamp);//Timestamp = 2014-04-28T23:20:08.489Z
Instant specifi cTime = Instant.ofEpochMilli(timestamp.toEpochMilli());
System.out.println("Specific Time = "+specificTime);//Specific Time = 2014-04-28T23:20:08.489Z
Duration thirtyDay = Duration.ofDays(30);
System.out.println(thirtyDay);//PT720H日期API工具
我们早些时候提到过,大多数日期时间 API 类都实现了一系列工具方法,如:加 减天数、周数、月份数,等等。还有其他的工具方法能够使用 TemporalAdjuster 调整日期,并计算两个日期间的周期 。
LocalDate today = LocalDate.now();
System.out.println("Year "+today.getYear()+" is Leap Year? "+today.isLeapYear());//Year 2014 is Leap Year? false
System.out.println("Today is before 01/01/2015? "+today.isBefore(LocalDate.of(201 5,1,1)));//Today is before 01/01/2015? true
System.out.println("Current Time="+today.atTime(LocalTime.now()));//Current Time=2014-04-28T16:23:53.154
System.out.println("10 days after today will be "+today.plusDays(10));//10 days after today will be 2014-05-08
System.out.println("3 weeks after today will be "+today.plusWeeks(3));//3 weeks after today will be 2014-05-19
System.out.println("20 months after today will be "+today.plusMonths(20));//20 months after today will be 2015-12-28
System.out.println("10 days before today will be "+today.minusDays(10));
System.ou t.println("3 weeks before today will be "+today.minusWeeks(3));
System.out.println("20 months before today will be "+today.minusMonths(20));
System.out.println("First date of this month= "+today.with(TemporalAdjusters.firstDayOfMonth()));//First date of this month= 2014-04-01
LocalDate lastDayOfYear = today.with(TemporalAdjusters.lastDayOfYear());
System.out.println("Last date of this year= "+lastDayOfYear);//2014-12-31
Period period = today.until(lastDayOfYear);
System.out.println("Period Format= "+period);//Period Format= P8M3D
System.out.println("Months remaining in the year= "+period.getMonths());//Months remaining in the year= 8
解析和格式化
将一个日期格式转换为不同的格式,之后再解析一个字符串,得到日期时间对象,这些都是很常见的。
LocalDate date = LocalDate.now();
System.out.println("Default format of LocalDate="+date);//Default format of LocalDate=2014-04-28
System.out.println(date.format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("d::MMM::uuuu")));//28::Apr::2014
System.out.println(date.format(DateTimeFormatter.BASIC_ISO_DATE));//20140428
LocalDateTime dateTime = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println("Default format of LocalDateTime="+dateTime);//Default format of LocalDateTime=2014-04-28T16:25:49.341
System.out.println(dateTime.format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("d::MMM::uuuu HH::mm::ss")));//28::Apr::2014 16::25::49
System.out.println(dateTime.format(DateTimeFormatter.BASIC_ISO_DATE));//20140428
Instant timestamp = Instant.now();
Sy stem.out.println("Default format of Instant="+timestamp);//Default format of Instant=2014-04-28T23:25:49.342Z
LocalDateTime dt = LocalDateTime.parse("27::Apr::2014 21::39::48",
DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("d::MMM::uuuu HH::mm::ss"));
System.out.println("Default format after parsing = "+dt);//Default format after parsing = 2014-04-27T21:39:48旧的日期时间支持
旧的日期时间类已经在几乎所有的应用程序中使用,因此做到向下兼容是必须的。这也是为什么会有若干工具方法帮助我们将旧的类转换为新的类,反之亦然。我们来看一下简单的例子
Instant timestamp = new Date().toInstant();
LocalDateTime date = LocalDateTime.ofInstant(timestamp,ZoneId.of(ZoneId.SHORT_IDS.get("PST")));
System.out.println("Date = "+date);//Date = 2014-04-28T16:28:54.340
Instant time = Calendar.getInstance().toInstant();
System.out.println(time);//2014-04-28T23:28:54.395Z
ZoneId defaultZone = TimeZone.getDefault().toZoneId();
System.out.println(defaultZone);//America/Los_Angeles
ZonedDateTime gregorianCalendarDateTime = new GregorianCalendar().toZonedDateTime();
System.out.println(gregorianCalendarDateTime);//2014-04-28T16:28:54.404 07:00[America/Los_Angeles]
Date dt = Date.from(Instant.now());
System.out.println(dt);//Mo n Apr 28 16:28:54 PDT 2014
TimeZone tz = TimeZone.getTimeZone(defaultZone);
System.out.println(tz);
GregorianCalendar gc = GregorianCalendar.from(gregorianCalendarDateTime);
System.out.println(gc);