Dubbo源码解析之:XML配置加载
如果阅读过前面文章的读者可以知道,我们使用的版本是2.5.4。GitHub链接https://github.com/apache/dubbo。选择tags的2.5.4下载。后面发现阿里将其重新开源并捐献给Apache后,做了一些改变,后面我们将使用tags2.6.5版本作为我们讲解版本。此文参考了https://juejin.im/post/5c1753b65188250850604ebe。
前言
在开始我们正式的讲解之前,这里先总览dubbo-demo中生产者的xml配置文件dubbo-demo-provider.xml,如果对xsd不了解的同学可以先看一下https://www.cnblogs.com/linjisong/p/3301096.html对xsd的介绍。
不难猜想以 dubbo 开头的 xml 标签应该和 dubbo 密切相关。那么这些标签的用途是什么?又是如何被识别的呢? 带着这个疑问我们继续往下面看。
1.Spring 自定义 XML 标签解析
事实上Dubbo 中的自定义 XML 标签实际上是依赖于 Spring 解析自定义标签的功能实现的,我们结合 Spring 自定义 xml 标签实现的相关内容来聊聊 Dubbo 是如何定义并加载这些自定义标签的,当然这里不会对Spring解析自定义XML标签做过多解读,仅介绍下实现相关功能需要的文件,有需要的可以自己搜索相关内容。
- 1.1定义 xsd 文件
XSD(XML Schemas Definition) 即 XML 结构定义。我们通过 XSD 文件不仅可以定义新的元素和属性,同时也使用它对我们的 XML 文件规范进行约束。 在 Dubbo 项目中可以找类似实现:dubbo.xsd。(dubbo捐献给Apache以后对之前版本做了兼容,所以这里会有两个xsd) - 1.2spring.schemas
该配置文件约定了自定义命名空间和 xsd 文件之间的映射关系,用于 spring 容器感知我们自定义的 xsd 文件位置。http\://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd=META-INF/dubbo.xsd http\://code.alibabatech.com/schema/dubbo/dubbo.xsd=META-INF/compat/dubbo.xsd注:这里同样是为了兼容之前版本的出现了两行。
- 1.3spring.handlers
该配置文件约定了自定义命名空间和 NamespaceHandler 类之间的映射关系。 NamespaceHandler 类用于注册自定义标签解析器。http\://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo=com.alibaba.dubbo.config.spring.schema.DubboNamespaceHandler http\://code.alibabatech.com/schema/dubbo=com.alibaba.dubbo.config.spring.schema.DubboNamespaceHandler注:这里同样是为了兼容之前版本的出现了两行。
- 1.4命名空间处理器
命名空间处理器主要用来注册 BeanDefinitionParser 解析器(dubbo中就对应上面 spring.handlers 文件中的 DubboNamespaceHandler)public class DubboNamespaceHandler extends NamespaceHandlerSupport { } - 1.5BeanDefinitionParser 解析器
实现 BeanDefinitionParser 接口中的 parse 方法,用于自定义标签的解析(Dubbo 中对应 DubboBeanDefinitionParser 类)public class DubboBeanDefinitionParser implements BeanDefinitionParser { private static BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext, Class beanClass, boolean required) { } }
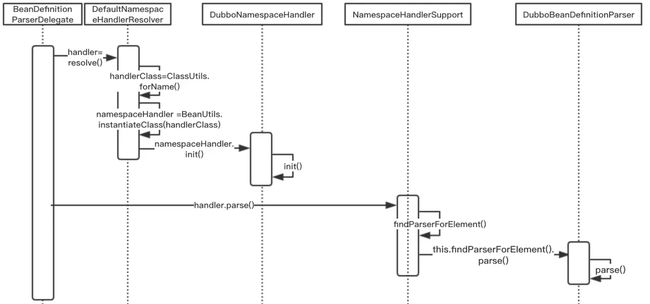
上图言尽于 handler.parse() 方法,如果你仔细看了上文,对 parse() 应该是有印象的。没错,1.5小节我们介绍了 DubboBeanDefinitionParser 类。该类有个方法就叫 parse()。那么这个 parse() 方法有什么用? Spring 是如何感知到我就要调用 DubboBeanDefinitionParser 类中的 parse() 方法的呢?我们带着这两个问题接着往下看。
2.Dubbo 解析自定义 XML 标签
上图最后一个类名为BeanDefinitionParserDelegate,那么我们从这里开始看起
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.java
public BeanDefinition parseCustomElement(Element ele, BeanDefinition containingBd) {
// 获取当前 element 的 namespaceURI
// 比如 dubbo.xsd 中的为 http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo
1、String namespaceUri = this.getNamespaceURI(ele);
// 根据 URI 获取对应的 NamespaceHandler
2、NamespaceHandler handler = this.readerContext.getNamespaceHandlerResolver().resolve(namespaceUri);
if (handler == null) {
this.error("Unable to locate Spring NamespaceHandler for XML schema namespace [" + namespaceUri + "]", ele);
return null;
} else {
3、return handler.parse(ele, new ParserContext(this.readerContext, this, containingBd));
}
}
这个方法干了三件事
- 获取 element 元素的 namespaceURI,并据此获取对应的 NamespaceHandler 对象。Dubbo 自定义标签(比如 Dubbo:provider) namespaceUri 的值为
http://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo; - 根据 step1 获取到的 namespaceUri ,获取对应的 NamespaceHandler 对象。这里会调用 DefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver 类的 resolve() 方法,我们下面会分析;
- 调用 handler 的 parse 方法,我们自定以的 handler 会继承 NamespaceHandlerSupport 类,所以这里调用的其实是 NamespaceHandlerSupport 类的 parse() 方法,后文分析;
我们下面着重分析每个方法干了什么事情。
上面parseCustomElement方法的第二步会调用resolve方法,我们来看看这个方法在哪里定义的
public interface NamespaceHandlerResolver {
/**
* Resolve the namespace URI and return the located {@link NamespaceHandler}
* implementation.
* @param namespaceUri the relevant namespace URI
* @return the located {@link NamespaceHandler} (may be {@code null})
*/
NamespaceHandler resolve(String namespaceUri);
}这是个接口,没有具体实现,可以找到其实现类
public class DefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver implements NamespaceHandlerResolver {}具体实现的方法如下:
DefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver.java
public NamespaceHandler resolve(String namespaceUri) {
Map handlerMappings = this.getHandlerMappings();//在下面专门讲解请先看下面
// 以 namespaceUri 为 Key 获取对应的 handlerOrClassName
Object handlerOrClassName = handlerMappings.get(namespaceUri);
if (handlerOrClassName == null) {
return null;
} else if (handlerOrClassName instanceof NamespaceHandler) {
return (NamespaceHandler)handlerOrClassName;
} else {
// 如果不为空且不为 NamespaceHandler 的实例,转换为 String 类型
// DubboNamespaceHandler 执行的便是这段逻辑
String className = (String)handlerOrClassName;
try {
Class handlerClass = ClassUtils.forName(className, this.classLoader);
// handlerClass 是否为 NamespaceHandler 的实现类,若不是则抛出异常
if (!NamespaceHandler.class.isAssignableFrom(handlerClass)) {
throw new FatalBeanException("Class [" + className + "] for namespace [" + namespaceUri + "] does not implement the [" + NamespaceHandler.class.getName() + "] interface");
} else {
// 初始化 handlerClass
NamespaceHandler namespaceHandler = (NamespaceHandler)BeanUtils.instantiateClass(handlerClass);
// 执行 handlerClass类的 init() 方法
namespaceHandler.init();
handlerMappings.put(namespaceUri, namespaceHandler);
return namespaceHandler;
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException var7) {
throw new FatalBeanException("NamespaceHandler class [" + className + "] for namespace [" + namespaceUri + "] not found", var7);
} catch (LinkageError var8) {
throw new FatalBeanException("Invalid NamespaceHandler class [" + className + "] for namespace [" + namespaceUri + "]: problem with handler class file or dependent class", var8);
}
}
}
我们先看这个方法中调用了getHandlerMappings方法,在这个类里可以找到这样一个方法
/**
* Load the specified NamespaceHandler mappings lazily.
*/
private Map getHandlerMappings() {
if (this.handlerMappings == null) {
//handlerMappings在这个类上方做了如下定义:private volatile Map handlerMappings;
synchronized (this) {
if (this.handlerMappings == null) {//用到了加锁二次检查
try {
//Properties 继承自Hashtable线程安全但是效率低
//定义如下public class Properties extends Hashtable
Properties mappings =PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadAllProperties(this.handlerMappingsLocation, this.classLoader);
//实际上这里的handlerMappingsLocation已经通过构造函数被赋值为META-INF/spring.handlers,具体见源码这样就会用loadAllProperties读取里面的内容,还记得spring.handlers里面是什么吗?返回去看看
//public static final String DEFAULT_HANDLER_MAPPINGS_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.handlers";
//private final String handlerMappingsLocation;
//public DefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver(ClassLoader classLoader, String
//handlerMappingsLocation) {//省去非核心逻辑
// this.handlerMappingsLocation = handlerMappingsLocation;
//}
。。。省略
Map handlerMappings = new ConcurrentHashMap(mappings.size());
CollectionUtils.mergePropertiesIntoMap(mappings, handlerMappings);
this.handlerMappings = handlerMappings;
省略。。。
} 通过这个方法就拿到了一个map,map的key是
http\://dubbo.apache.org/schema/dubbo
value是com.alibaba.dubbo.config.spring.schema.DubboNamespaceHandler
resolve() 方法用途是根据方法参数中的 namespaceUri 获取对应的 NamespaceHandler 对象。这里会先尝试以 namespaceUri 为 key 去 handlerMappings 集合中取对象。 如果 handlerOrClassName 不为 null 且不为 NamespaceHandler 的实例。那么尝试将 handlerOrClassName 作为 className 并调用 BeanUtils.instantiateClass() 方法初始化一个 NamespaceHandler 实例。初始化后,调用其 init() 方法。
public class DubboNamespaceHandler extends NamespaceHandlerSupport {
static {
Version.checkDuplicate(DubboNamespaceHandler.class);
}
@Override
public void init() {
registerBeanDefinitionParser("application", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ApplicationConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("module", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ModuleConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("registry", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(RegistryConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("monitor", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(MonitorConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("provider", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ProviderConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("consumer", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ConsumerConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("protocol", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ProtocolConfig.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("service", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ServiceBean.class, true));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("reference", new DubboBeanDefinitionParser(ReferenceBean.class, false));
registerBeanDefinitionParser("annotation", new AnnotationBeanDefinitionParser());
}
}
public abstract class NamespaceHandlerSupport implements NamespaceHandler {
/**
* Stores the {@link BeanDefinitionParser} implementations keyed by the
* local name of the {@link Element Elements} they handle.
*/
private final Map parsers =
new HashMap();
/**
* Subclasses can call this to register the supplied {@link BeanDefinitionParser} to
* handle the specified element. The element name is the local (non-namespace qualified)
* name.
*/
protected final void registerBeanDefinitionParser(String elementName, BeanDefinitionParser parser) {
this.parsers.put(elementName, parser);
}
}
DubboNamespaceHandler 类中的 init() 方法干的事情特别简单,就是新建 DubboBeanDefinitionParser 对象并将其放入 NamespaceHandlerSupport 类中创建的的 parsers 集合中。(细心的读者可以看到init后面的 RegistryConfig.class里的字段和xsd文件里的属性基本是一致的)
parseCustomElement方法的第三步会调用parse方法,具体会调用 NamespaceHandlerSupport 类的 parse() 方法
public BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) {
return this.findParserForElement(element, parserContext).parse(element, parserContext);
}
private BeanDefinitionParser findParserForElement(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) {
String localName = parserContext.getDelegate().getLocalName(element);
BeanDefinitionParser parser = (BeanDefinitionParser)this.parsers.get(localName);
if (parser == null) {
parserContext.getReaderContext().fatal("Cannot locate BeanDefinitionParser for element [" + localName + "]", element);
}
return parser;
}
看到这里大家有没有一丝豁然开朗的感觉?之前的 resolve() 方法实际上就是根据当前 element 的 namespaceURI 获取对应的 NamespaceHandler 对象(对于 Dubbo 来说是 DubboNamespaceHandler), 然后调用 DubboNamespaceHandler 中的 init() 方法新建 DubboBeanDefinitionParser 对象并注册到 NamespaceHandlerSupport 类的 parsers 集合中。 然后 parser 方法会根据当前 element 对象从 parsers 集合中获取合适的 BeanDefinitionParser 对象。对于 Dubbo 元素来说,实际上最后执行的是 DubboBeanDefinitionParser 的 parse() 方法。
private static BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext, Class beanClass, boolean required) {
RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition();
beanDefinition.setBeanClass(beanClass);
beanDefinition.setLazyInit(false);
String id = element.getAttribute("id");
// DubboBeanDefinitionParser 构造方法中有对 required 值进行初始化;
// DubboNamespaceHandler 类中的 init 方法会创建并注册 DubboBeanDefinitionParser 类
if ((id == null || id.length() == 0) && required) {
String generatedBeanName = element.getAttribute("name");
if (generatedBeanName == null || generatedBeanName.length() == 0) {
if (ProtocolConfig.class.equals(beanClass)) {
generatedBeanName = "dubbo";
} else {
// name 属性为空且不为 ProtocolConfig 类型,取 interface 值
generatedBeanName = element.getAttribute("interface");
}
}
if (generatedBeanName == null || generatedBeanName.length() == 0) {
// 获取 beanClass 的全限定类名
generatedBeanName = beanClass.getName();
}
id = generatedBeanName;
int counter = 2;
while (parserContext.getRegistry().containsBeanDefinition(id)) {
id = generatedBeanName + (counter++);
}
}
if (id != null && id.length() > 0) {
if (parserContext.getRegistry().containsBeanDefinition(id)) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Duplicate spring bean id " + id);
}
// 注册 beanDefinition
parserContext.getRegistry().registerBeanDefinition(id, beanDefinition);
// 为 beanDefinition 添加 id 属性
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue("id", id);
}
// 如果当前 beanClass 类型为 ProtocolConfig
// 遍历已经注册过的 bean 对象,如果 bean 对象含有 protocol 属性
// protocol 属性值为 ProtocolConfig 实例且 name 和当前 id 值一致,为当前 beanClass 对象添加 protocl 属性
if (ProtocolConfig.class.equals(beanClass)) {
for (String name : parserContext.getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
BeanDefinition definition = parserContext.getRegistry().getBeanDefinition(name);
PropertyValue property = definition.getPropertyValues().getPropertyValue("protocol");
if (property != null) {
Object value = property.getValue();
if (value instanceof ProtocolConfig && id.equals(((ProtocolConfig) value).getName())) {
definition.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue("protocol", new RuntimeBeanReference(id));
}
}
}
} else if (ServiceBean.class.equals(beanClass)) {
// 如果当前元素包含 class 属性,调用 ReflectUtils.forName() 方法加载类对象
// 调用 parseProperties 解析其他属性设置到 classDefinition 对象中
// 最后设置 beanDefinition 的 ref 属性为 BeanDefinitionHolder 包装类
String className = element.getAttribute("class");
if (className != null && className.length() > 0) {
RootBeanDefinition classDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition();
classDefinition.setBeanClass(ReflectUtils.forName(className));
classDefinition.setLazyInit(false);
parseProperties(element.getChildNodes(), classDefinition);
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue("ref", new BeanDefinitionHolder(classDefinition, id + "Impl"));
}
} else if (ProviderConfig.class.equals(beanClass)) {
parseNested(element, parserContext, ServiceBean.class, true, "service", "provider", id, beanDefinition);
} else if (ConsumerConfig.class.equals(beanClass)) {
parseNested(element, parserContext, ReferenceBean.class, false, "reference", "consumer", id, beanDefinition);
}
Set props = new HashSet();
ManagedMap parameters = null;
for (Method setter : beanClass.getMethods()) {
String name = setter.getName();
if (name.length() > 3 && name.startsWith("set")
&& Modifier.isPublic(setter.getModifiers())
&& setter.getParameterTypes().length == 1) {
Class type = setter.getParameterTypes()[0];
String propertyName = name.substring(3, 4).toLowerCase() + name.substring(4);
String property = StringUtils.camelToSplitName(propertyName, "-");
props.add(property);
Method getter = null;
try {
getter = beanClass.getMethod("get" + name.substring(3), new Class[0]);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
try {
getter = beanClass.getMethod("is" + name.substring(3), new Class[0]);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e2) {
}
}
if (getter == null
|| !Modifier.isPublic(getter.getModifiers())
|| !type.equals(getter.getReturnType())) {
continue;
}
if ("parameters".equals(property)) {
parameters = parseParameters(element.getChildNodes(), beanDefinition);
} else if ("methods".equals(property)) {
parseMethods(id, element.getChildNodes(), beanDefinition, parserContext);
} else if ("arguments".equals(property)) {
parseArguments(id, element.getChildNodes(), beanDefinition, parserContext);
} else {
String value = element.getAttribute(property);
if (value != null) {
value = value.trim();
if (value.length() > 0) {
// 如果属性为 registry,且 registry 属性的值为"N/A",标识不会注册到任何注册中心
// 新建 RegistryConfig 并将其设置为 beanDefinition 的 registry 属性
if ("registry".equals(property) && RegistryConfig.NO_AVAILABLE.equalsIgnoreCase(value)) {
RegistryConfig registryConfig = new RegistryConfig();
registryConfig.setAddress(RegistryConfig.NO_AVAILABLE);
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue(property, registryConfig);
} else if ("registry".equals(property) && value.indexOf(',') != -1) {
// 多注册中心解析
parseMultiRef("registries", value, beanDefinition, parserContext);
} else if ("provider".equals(property) && value.indexOf(',') != -1) {
parseMultiRef("providers", value, beanDefinition, parserContext);
} else if ("protocol".equals(property) && value.indexOf(',') != -1) {
// 多协议
parseMultiRef("protocols", value, beanDefinition, parserContext);
} else {
Object reference;
if (isPrimitive(type)) {
// type 为方法参数,type 类型是否为基本类型
if ("async".equals(property) && "false".equals(value)
|| "timeout".equals(property) && "0".equals(value)
|| "delay".equals(property) && "0".equals(value)
|| "version".equals(property) && "0.0.0".equals(value)
|| "stat".equals(property) && "-1".equals(value)
|| "reliable".equals(property) && "false".equals(value)) {
// 新老版本 xsd 兼容性处理
// backward compatibility for the default value in old version's xsd
value = null;
}
reference = value;
} else if ("protocol".equals(property)
&& ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Protocol.class).hasExtension(value)
&& (!parserContext.getRegistry().containsBeanDefinition(value)
|| !ProtocolConfig.class.getName().equals(parserContext.getRegistry().getBeanDefinition(value).getBeanClassName()))) {
// 如果 protocol 属性值有对应的扩展实现,而且没有被注册到 spring 注册表中
// 或者 spring 注册表中对应的 bean 的类型不为 ProtocolConfig.class
if ("dubbo:provider".equals(element.getTagName())) {
logger.warn("Recommended replace ");
}
}
reference = new RuntimeBeanReference(value);
}
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue(propertyName, reference);
}
}
}
}
}
}
NamedNodeMap attributes = element.getAttributes();
int len = attributes.getLength();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
Node node = attributes.item(i);
String name = node.getLocalName();
if (!props.contains(name)) {
if (parameters == null) {
parameters = new ManagedMap();
}
String value = node.getNodeValue();
parameters.put(name, new TypedStringValue(value, String.class));
}
}
if (parameters != null) {
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue("parameters", parameters);
}
return beanDefinition;
}
上面这一大段关于配置的解析的代码需要大家自己结合实际的代码进行调试才能更好的理解。确实不是很好理解,可以选择跳过,知道大致流程就行,最后放张Dubbo解析的时序图